Syllabus of Computer Applications Class 10 | Computer Application: Class 10 PDF Download
The CBSE Class 10 Computer Applications syllabus for the academic session 2025-2026 is designed to equip students with essential skills in digital literacy and web development. The syllabus covers both theoretical and practical aspects of CA, with a strong focus on networking, HTML, and cyber ethics. With the aim of preparing students for the digital age, the syllabus also emphasizes the importance of internet usage, mobile technologies, and web design, along with awareness of security threats and preventive measures.
For the session, the Board exam for Class 10 CA will consist of 55 marks for the theory paper and 60 marks for practical work, reflecting the increased focus on hands-on learning and project-based activities.
Learning Outcomes
After the completion of the course, the student will be able to:
- Understand the components of Computer Networking including web servers and network protocols.
- Explore the functionality and applications of the services available on the Internet.
- Create simple web pages using various HTML elements.
- Implement links and forms to create user-friendly web pages that facilitate navigation and data collection.
- Apply basic styling techniques using CSS to improve the visual appearance and layout of web content.
- Understand the importance of netiquettes, intellectual property rights, and responsible online behaviour.
Distribution of Marks and Periods
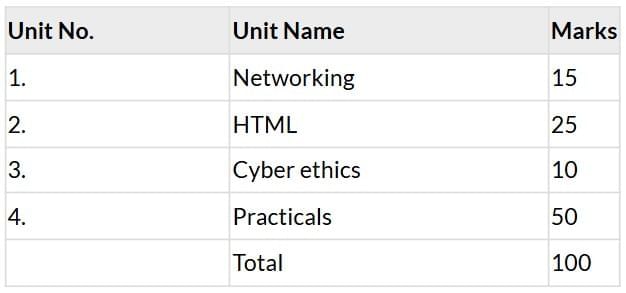
Unit 1: Networking
- Internet: World Wide Web, web servers, web clients, web sites, web pages, web browsers, blogs, news groups, HTML, web address, e-mail address, downloading and uploading files from a remote site.
- Internet protocols: TCP/IP, SMTP, POP3, HTTP, HTTPS. Remote login and file transfer protocols: SSH, SFTP, FTP, SCP, TELNET, SMTP, TCP/IP.
- Services available on the internet: information retrieval, locating sites using search engines and finding people on the net;
- Web services: chat, email, video conferencing, e-Learning, e-Banking, e-Shopping, e-Reservation, e-Governance, e-Groups, social networking.
- Mobile technologies: SMS, MMS, 3G, 4G, 5G.
Unit 2: HTML
- Introduction to web page designing using HTML: create and save an HTML document, access a web page using a web browser.
- HTML tags: html, head, title, body, (attributes: text, background, bgcolor, link, vlink, alink), br (break), hr (horizontal rule), inserting comments, h1..h6 (heading), p (paragraph), b (bold), i (italics), u (underline), ul (unordered list), ol (ordered list), and li (list item). Description lists: dl, dt and dd. Attributes of ol (start, type), ul (type).
- Font tags (attributes: face, size, color).
- Insert images: img (attributes: src, width, height, alt), sup (super script), sub (subscript).
- HTML Forms: Textbox, radio buttons, checkbox, password, list, combobox.
- Embed audio and video in a HTML page.
- Create a table using the tags: table, tr, th, td, rowspan, colspan.
- Links: significance of linking, anchor element (attributes: href, mailto), targets.
- Cascading style sheets: colour, background-colour, border-style, margin, height, width, outline, font (family, style, size), align, float.
Unit 3: Cyber ethics
- Netiquettes.
- Software licenses and the open source software movement.
- Intellectual property rights, plagiarism and digital property rights.
- Freedom of information and the digital divide.
- E-commerce: Privacy, fraud, secure data transmission.
Unit 4: Lab Exercises
- Create static web pages.
- Use style sheets to enforce a format in an HTML page (CSS).
- Embed pictures, audio and videos in an HTML page.
- Add tables and frames in an HTML page.
- Decorate web pages using graphical elements.
- Create a website using several web pages. Students may use any open source or proprietary tool.
- Work with HTML forms: text box, radio buttons, checkbox, password, list, combo box.
- Write a blog using HTML pages discussing viruses, malware, spam and antiviruses.
- Create a web page discussing plagiarism. List some reported cases of plagiarism and the consequent punishment meted out. Explain the nature of the punishment in different countries as per their IP laws.
Breakup of Marks for the Practicals

|
10 videos|97 docs|18 tests
|
FAQs on Syllabus of Computer Applications Class 10 - Computer Application: Class 10
| 1. What is the main objective of the Computer Applications syllabus for Class 10? |  |
| 2. What are the key topics covered in the Class 10 Computer Applications syllabus? |  |
| 3. How is the assessment for Computer Applications in Class 10 structured? |  |
| 4. What skills can students expect to gain from the Computer Applications course in Class 10? |  |
| 5. How can students prepare effectively for the Computer Applications exam in Class 10? |  |






















