Class 9 Geography Chapter 3 Extra Question Answers - Drainage
1) Give one example each of lagoon, and inland saline lake in India.
Ans: Lagoon – Chilika/Pulicat; Inland saline – Sambhar.
2) Which is the largest natural inland lake in India?
Ans: The Wular lake in Jammu and Kashmir, with a maximum area of 260 sq km, is the largest natural inland lake in India.
3) The Satluj is a tributary of which river?
Ans: The river Satluj is a tributary of the Indus and joins it in Pakistan.
4) What are other names given to the Brahmaputra river?
Ans: Tsangpo is the name of the Brahmaputra in Tibet (China) and Dihang is its name in Arunachal Pradesh.
5) What is the Sunderban famous for?
Ans: Sunderban is famous for being the home of the Royal Bengal tiger.
 Royal Bengal Tiger
Royal Bengal Tiger
6) Through which states in India does the river Satluj flow?
Ans: The river Satluj flows through the states of the Himachal Pradesh and the Punjab in India.
7) What is the major objective of the National River Conservation Plan (NRCP)?
Ans: The major objective of NRCP is to improve water quality of rivers by preventing pollution from sewage and industrial effluents.
8) Identify the rivers of which the following are tributaries: the Gandak, the Dibang, the Ganga and the Tungabhadra.
Ans: The Gandak is a tributary of the Ganga, the Dibang is a tributary of the Brahmaputra, the Ganga joins the Brahmaputra in Bangladesh to form the Meghna, and the Tungabhadra is a tributary of the Krishna.
9) Which of the three rivers, the Chenab, the Ravi and the Beas, flows in India only through the state of Jammu and Kashmir?
Ans: The Chenab flows only through the state of Jammu and Kashmir in India. The Ravi and the Beas rivers flow through the Punjab and the Himachal Pradesh in India.
10) List three salient features of inland salt lakes.
Ans: The three features are
(i) They are found in arid or semi-arid regions of the country.
(iii) They dry up during summers.
(iii) They are fed by short and intermittent streams.
11) Is it true that the water in a delta is salty, as it is close to the sea?
Ans: Since, the sea is at a lower level than the river in a delta, normally the delta will not be salty.
12) Which river in South India receives water both in summer and winter?
Ans: The river Kaveri rises in the Western Ghats and thus receives water from the summer monsoon. Since, it flows through Tamil Nadu into the Arabian sea, it receives rainfall from the winter monsoon also.
13) Which of the rivers Beas, Ghaghara, Indus and Yamuna rises from a glacier in Uttarakhand?
Ans: The Yamuna rises from the Yamunotri glacier in Uttarakhand. The Beas rises in Himachal Pradesh, the Indus in China (Tibet) and the Ghaghara in Nepal.
14) Which is the highest waterfall in India?
Ans: The Kunchikal falls on the river Varahi in Karnataka have a drop of 455 m.  Kunchikal falls
Kunchikal falls
15) Which river flows for the longest length in India?
Ans: The Ganga river flows for 2525 km in India. Although other rivers like the Brahmaputra and Indus may be longer in their total length, their length of flow in India is much less than that of the Ganga.
16) Make a list of natural and artificial lakes with the help of the atlas.
Ans: Natural Lakes: Wular lake, Dal lake, Nainital lake, Bhimtal lake, Loktak lake, Barapani lake, Chilika lake, Sambhar lake, Pulicat lake, Kolleru lake, Vembanad lake.
Artificial Lakes: Guru Gobind sagar, Rana Pratap sagar, Nizam sagar, Nagarjuna sagar, Hirakud.
17) Why has industrial development flourished along rivers?
Ans: The reason for industries being near rivers is because of the free availability of fresh water required for industrial processes.
18) Out of the tributaries Ghaghara, Son, Kosi and Yamuna, which ones join the Ganga from the South and which from the North?
Ans: The Yamuna and Son rivers join the river Ganga from the South, while the Ghaghara and Kosi Join it from the North.
19) What is the meaning of the word 'doab'?
Ans: In the Persian language, 'do' means 'two' and 'ab' mean 'water'. So 'doab' means a tract of land lying between two confluent rivers
20) The Kaveri basin covers parts of which Indian states?
Ans: The Kaveri basin covers parts of Karnataka, Tamil Nadu and Kerala.
21) Which is the longest river of peninsular India?
Ans: The river Godavari, with a length of 1465 km, is the longest river of peninsular India.
22) What do you understand by the term "Drainage Basin"?
Ans: The area drained by a single river system is called "Drainage Basin".
23) Name the place where the Ganga emerges from the mountains on to the plains.
Ans: At Haridwar, the Ganga emerges from the mountains on to the plains.
24) Name the Indian state where river Brahmaputra enters in India.
Ans: At the Indian state of Arunachal Pradesh river Brahmaputra enters in India.
25) Which river is known as "Dakshin Ganga"?
Ans: The Godavari, because of its length and area it cover is known as 'Dakshin Ganga'.
26) Name the saline water lake located in Rajasthan.
Ans: The saline water lake located in Rajasthan is the Sambhar lake.
27) At which place do the Satluj, the Beas, the Ravi, the Chenab and the Jhelum rivers join together to enter the river Indus?
Ans: The Satluj, the Beas, the Ravi, the Chenab and the Jhelum rivers join together to enter river Indus at Mithankot in Pakistan.
28) What is the origin of the River Krishna?
Ans: River Krishna rises from a spring near Mahabaleshwar (Maharashtra).
29) Which drainage pattern does the river Ganga forms?
Ans: River Ganga forms dendritic drainage pattern.
30) Where does river Narmada has its source?
Ans: The Narmada rises in the Amarkantak hills in Madhya Pradesh.
31) Which is the largest brackish water lake in India? Where it is located?
Ans: The Chilika lake is the largest brackish water lake in India. It lies in the state of Odisha to the South of Mahanadi delta.
32) Make a comparison in tabular form between the East flowing and West flowing rivers of the Peninsular plateau.
Or
Differentiate between East flowing and West flowing rivers of Peninsular plateau. Mention their name also.
Or
Differentiate between the salient features of East flowing and West flowing rivers of Peninsular India.
Ans: Comparison between the East/lowing and West flowing rivers of the Peninsular plateau.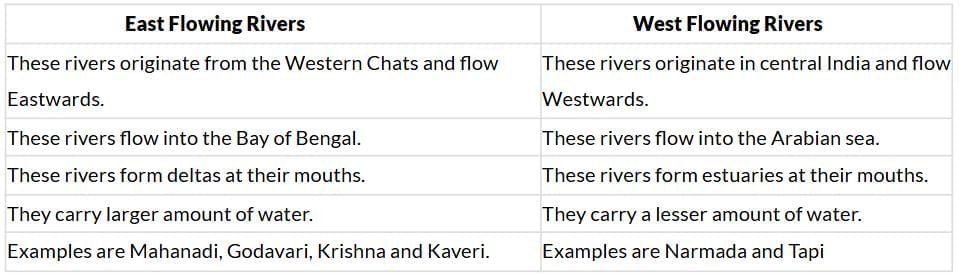
33) Explain what life would be like if freshwater is not available.
Ans: For survival, man depends on water. It circulates and goes through our bodies, replenishing nutrients and carrying away waste materials. Without freshwater, no activities of human beings and life would be possible. Seawater is salty and it cannot substitute for freshwater. Life as we know it, will not be there. No, trees will be able to grow and no land based animals can survive. Even birds will not exist.
34) Describe inland drainage, giving its main features.
Ans: When rivers do not reach a sea or ocean, but empty their water in an inland sea or lake, this is known as inland drainage. Its main features are:
(i) The streams joining lakes or inland seas are fed by rainwater.
(ii) During the rainy season, we may have flash floods and during other seasons they may dry up.
(iii) In some cases they may form salt water lakes, like the Sambhar lake in Rajasthan.
35) Make a comparison in tabular form between a delta and an estuary.
Ans: Comparison between a delta and an estuary. 36) List the differences between glaciers and rivers.
36) List the differences between glaciers and rivers.
Ans: Differences between glaciers and rivers. 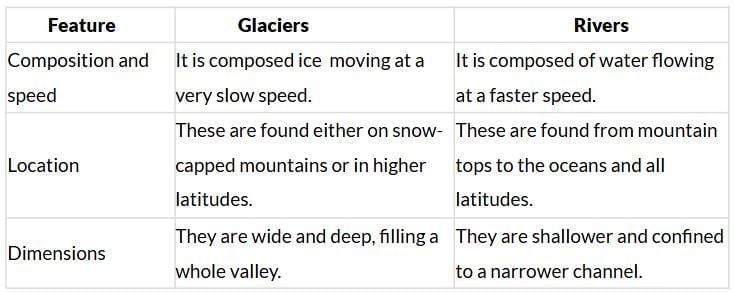
37) Distinguish between a tributary and a distributary.
Ans: A tributary is a stream which flows into a main stream (or parent) river. A tributary does not flow directly into a sea, ocean or lake. Tributaries and the main stream river drain the surrounding drainage basin of its surface water and groundwater. The reverse to a tributary is a distributary, a river that branches off and flows away from the main stream. The Yamuna is a tributary of the Ganga, whereas the Hugli is a distributary of the Ganga.
38) Why are rivers important for the country's economy?
Ans: Rivers are important for the country's economy because water from the rivers is a basic natural resource is essential for various human activities. The importance of the rivers for the country's economy are
(i) The rivers provide water for irrigation.
(ii) They provide fertility to the soil.
(iii) They are useful for navigation.
(iv) They help to generate hydroelectricity.
(v) They help to develop tourism.
(vi) They provide water for various domestic uses.
(vii) They provide livelihood to fishermen.
(viii) They help to moderate the climate and environment of nearby areas.
|
55 videos|637 docs|79 tests
|
FAQs on Class 9 Geography Chapter 3 Extra Question Answers - Drainage
| 1. What is drainage and why is it important? |  |
| 2. What are the different types of drainage systems? |  |
| 3. How does surface drainage work? |  |
| 4. What are the benefits of subsurface drainage? |  |
| 5. How can I improve the drainage in my garden? |  |

















