Issue and Redemption of Debentures Chapter Notes | Accountancy Class 12 - Commerce PDF Download
Introduction
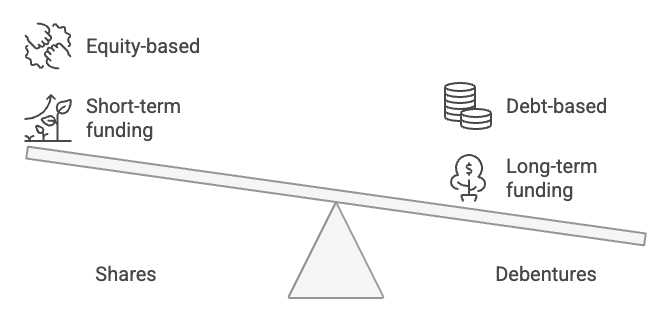
- Companies often raise capital by issuing shares, but the funds from shares are usually not enough to meet their long-term financial needs.
- To address this shortfall, many companies also raise long-term funds through debentures, which can be issued via private placement or offered to the public.
- Money raised through debentures is considered long-term debt.
- This chapter focuses on the accounting treatment of issuing and redeeming debentures, along with other related aspects.
Debenture: Meaning and Distinction from Shares
Meaning of Debentures:
- Debenture is derived from the Latin word 'debere,' meaning to borrow.
- A debenture is a written document that acknowledges a debt under the common seal of a company.
- It includes a contract for the repayment of principal either after a specified period, at intervals, or at the company's option, along with a fixed interest rate payable usually half-yearly or yearly.
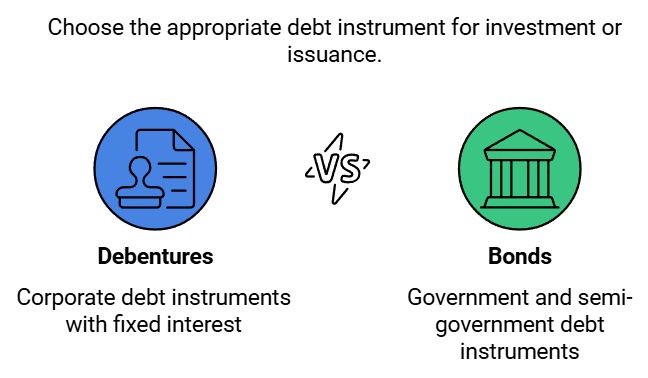
- According to The Companies Act, 2013, debentures encompass debenture inventory, bonds, and other securities of a company, regardless of whether they constitute a charge on the company's assets.
Bonds are also instruments of debt acknowledgement. While traditionally issued by the Government, they are now issued by semi-government and non-governmental organizations as well. The terms 'debentures' and 'bonds' are often used interchangeably.
Distinction between Shares and Debentures:
- Ownership: A share represents ownership in the company, while a debenture is merely an acknowledgement of debt. Shares are part of owned capital, whereas debentures are part of borrowed capital.
- Return: The return on shares is called a dividend, which can vary yearly based on the company's profits. In contrast, the return on debentures is fixed interest. A dividend payment is an appropriation of profits, while an interest payment is a charge on profits and must be paid even if there are no profits.
- Repayment: Generally, the amount of shares is not returned during the company's life, while debentures are issued for a specified period and are repayable at the end of that period.
- Voting Rights: Shareholders have voting rights, whereas debenture holders typically do not.
- Security: Shares are not secured by any charge, while debentures are usually secured and may carry a fixed or floating charge over the company's assets.
- Convertibility: Shares cannot be converted into debentures, but debentures can be converted into shares if the terms of issue allow it. In such cases, they are known as convertible debentures.
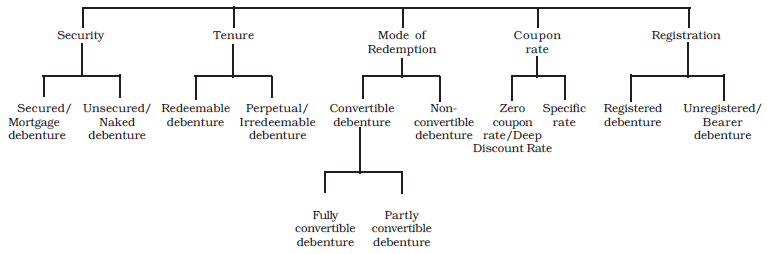
Types of Debentures
A company may issue different kinds of debentures which can be classified as under:
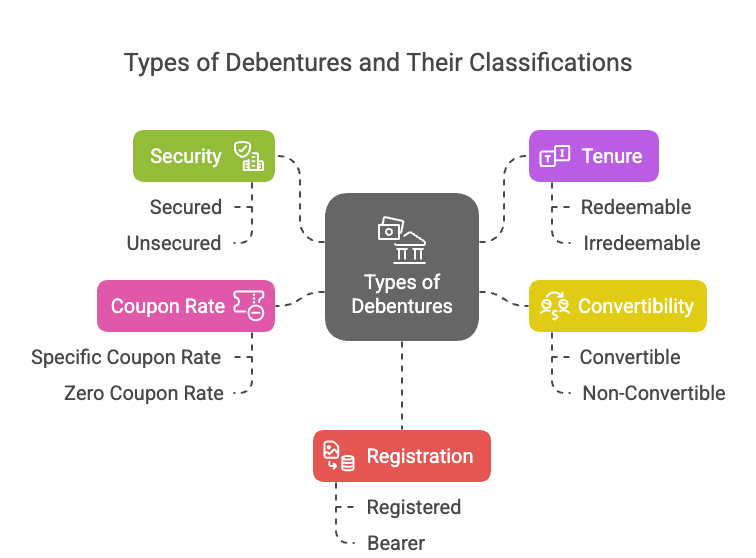
From the Point of View of Security:
(a) Secured Debentures: Secured debentures involve a charge on the company's assets to ensure payment in case of default. This charge can be either fixed or floating:
- Fixed Charge: Applies to specific assets, typically those used in operations and not intended for sale.
- Floating Charge: Covers general assets of the company, excluding those assigned to secured creditors.
(b) Unsecured Debentures: Unsecured debentures lack a specific charge on the company's assets. While a floating charge may be created in case of default, these debentures are generally not issued.
From the Point of View of Tenure:
(a) Redeemable Debentures: Redeemable debentures are payable after a specific period, either in a lump sum or in installments during the company's lifetime. They can be redeemed at par or at a premium.
(b) Irredeemable Debentures: Also known as Perpetual Debentures, irredeemable debentures do not have a repayment commitment from the company. They are repayable upon the winding-up of the company or after a long period.
From the Point of View of Convertibility:
(a) Convertible Debentures: These debentures can be converted into equity shares or other securities at the option of either the company or the debenture holders. They can be fully convertible or partly convertible.
(b) Non-Convertible Debentures: Non-convertible debentures cannot be transformed into shares or other securities. Most debentures issued by companies fall into this category.
From the Point of View of Coupon Rate:
(a) Specific Coupon Rate Debentures: These debentures are issued with a specified interest rate, known as the coupon rate, which can be either fixed or floating. Floating rates are often linked to the bank rate.
(b) Zero Coupon Rate Debentures: Zero coupon rate debentures do not have a specific interest rate. They are issued at a substantial discount, and the difference between the nominal value and the issue price is considered the interest for the duration of the debentures.
From the Point of View of Registration:
(a) Registered Debentures: Registered debentures are recorded in a register maintained by the company, detailing the names, addresses, and holdings of debenture holders. These debentures can only be transferred through a regular transfer deed.
(b) Bearer Debentures: Bearer debentures can be transferred by delivery, and the company does not maintain a record of these debentures. Interest on bearer debentures is paid to the person who presents the attached interest coupon.
 Types of Debenture/Bond
Types of Debenture/Bond
Issue of Debentures
The process of issuing debentures is similar to that of issuing shares. Investors apply for debentures based on the prospectus provided by the company. The company may require the full amount to be paid upfront or in instalments at various stages such as application, allotment, and calls. Debentures can be issued at par, at a premium, or at a discount. They can also be issued for non-cash considerations or as collateral security.
Issue of Debentures for Cash
- When debentures are issued at par, it means the issue price is equal to the face value. The journal entries for such an issue are recorded accordingly.

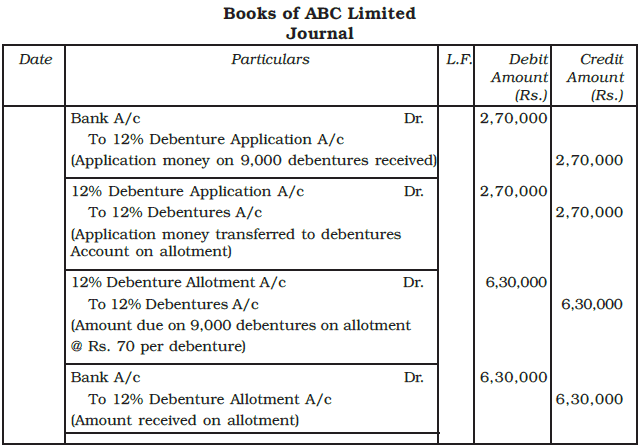
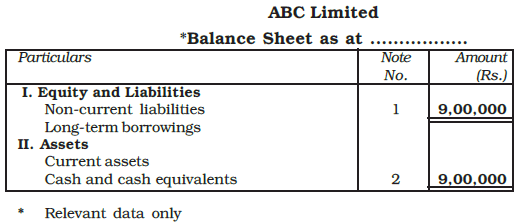
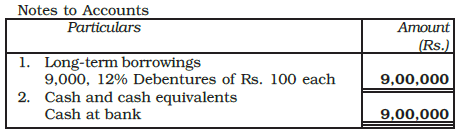
Example: ABC Lmited issued 10,000, 12% debentures of Rs. 100 each payable Rs. 30 on application and remaining amount on allotment. The public applied for 9,000 debentures which were fully allotted, and all the relevant allotment money was duly received. Give journal entries in the books of ABC Ltd., and exhibit the relevent information in the balance sheet.
Ans:
Issue of Debentures at a Discount:
- Definition: When a debenture is sold for less than its nominal value, it is considered to be issued at a discount. For instance, Rs. 100 debentures sold at Rs. 95 implies a discount of Rs. 5.
- Writing off Discount: The discount on debenture issuance can be written off by debiting it to the Securities Premium Reserve, if available, during the debentures' lifetime.
- Current and Non-Current Assets: Discount to be written off within 12 months is classified under ‘Other Current Assets’. The portion to be written off after 12 months is categorized under ‘Other Non-Current Assets’.
- Regulatory Aspect: The Companies Act, 2013 does not restrict the issuance of debentures at a discount.
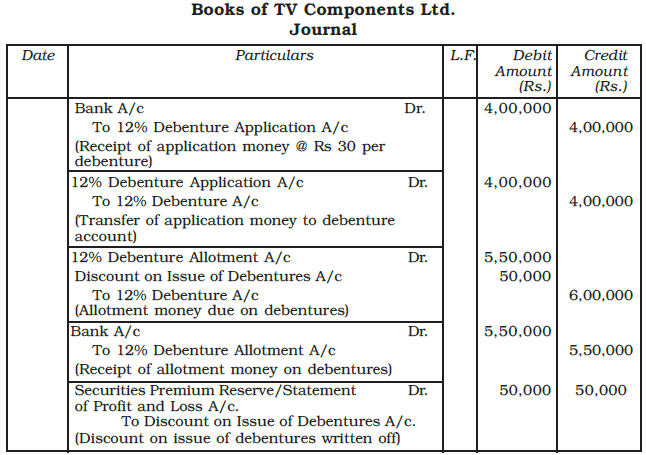
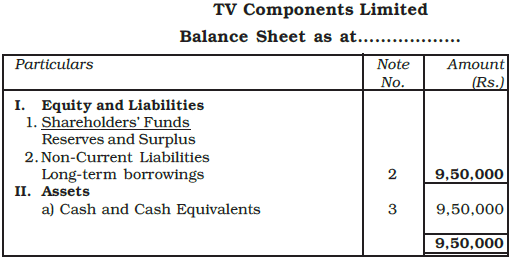
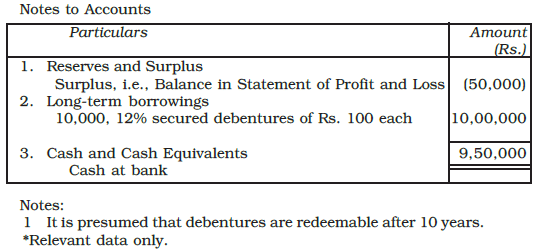
Example: TV Components Ltd., issued 10,000, 12% debentures of Rs. 100 each at a discount of 5% payable as follows:
On application - Rs. 40
On allotment - Rs. 55
Show the journal entries including those for cash, assuming that all the instalments were duly collected. Also show the relevant portion of the balance sheet.
Ans:
Debentures Issued at a Premium
- A debenture is considered to be issued at a premium when it is sold for more than its nominal value. For instance, if Rs. 100 debentures are issued for Rs. 110, the premium is Rs. 10.
- The premium amount is credited to the Securities Premium Reserve account, which is displayed on the liabilities side of the balance sheet under the section "Reserves and Surpluses."
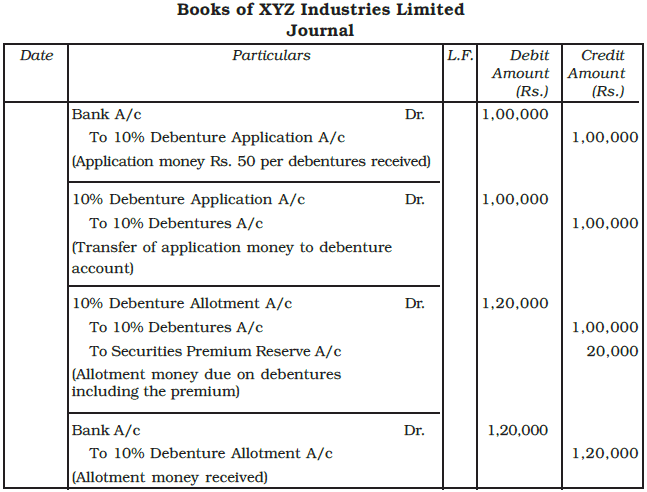
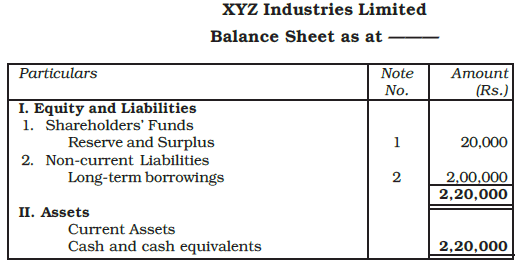
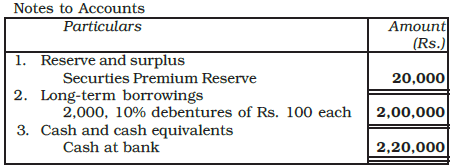
Example: XYZ Industries Ltd., issued 2,000, 10% debentures of Rs. 100 each, at a premium of Rs. 10 per debenture payable as follows:
On application - Rs. 50
On allotment - Rs. 60
The debentures were fully subscribed and all money was duly received. Record the journal entries in the books of a company. Show how the amounts will appear in the balance sheet.
Ans:
Over Subscription:
- When more debentures are applied for than are available, the issue is considered over-subscribed.
- A company cannot allot more debentures than it has offered for subscription.
- The excess money received from oversubscription can be kept for adjusting against allotment and future calls.
- However, any money received from applicants who do not receive debentures will be refunded.
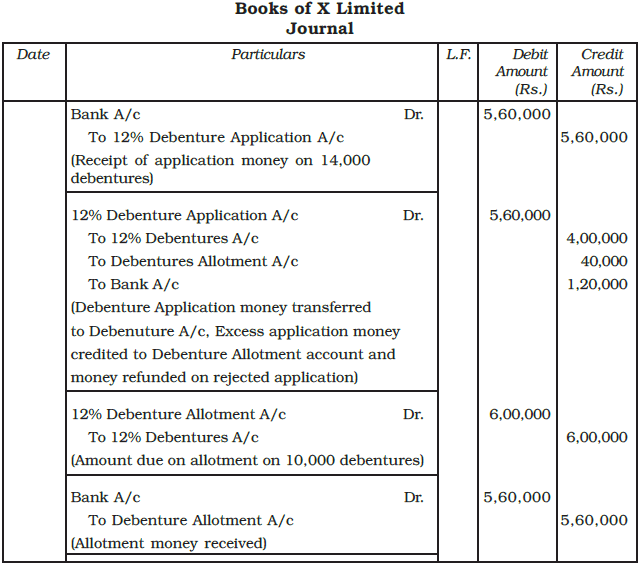
Example: X Limited Issued 10,000, 12% debentures of Rs. 100 each payable Rs. 40 on application and Rs. 60 on allotment. The public applied for 14,000 debentures. Applications for 9,000 debentures were accepted in full; applications for 2,000 debentures were allotted 1,000 debentures and the remaining applications, were rejected. All money was duly received. Journalise the transactions.
Ans:
Issue of Debentures for Consideration other than Cash:
Sometimes, a company acquires assets from vendors and instead of making payment in cash, it issues debentures as consideration. This practice is known as issuing debentures for consideration other than cash. Similar to shares issued for consideration other than cash, debentures can be issued at par, at a premium, or at a discount. The entries made in such cases are akin to those of shares issued for consideration other than cash.

Purchase of Business with Assets and Liabilities:
- When a company buys another business, it may acquire both the assets and the liabilities of that business.
- This usually occurs when purchasing the entire business.
- In such cases, the purchase consideration is determined by the value of net assets, which is calculated as:
Net Assets = Assets - Liabilities. - If the entire consideration is paid through the issuance of debentures, the journal entry for the purchase of the business would reflect this transaction.
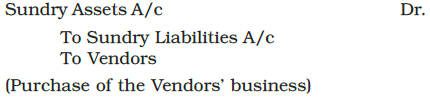
Example: Romi Ltd. acquired assets of Rs. 20 lakh and took over creditors of Rs. 2 lakh from Kapil Enterprises. Romi Ltd., issued 8% debentures of Rs 100 each at par as purchase consideration. Record necessary journal entries in the books of Romi Ltd.
Ans: 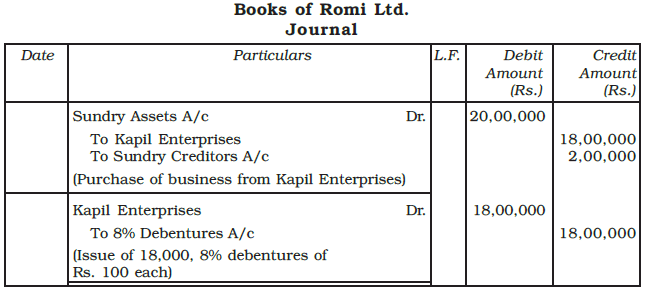
- When a whole business is taken over and the total amount of debentures issued exceeds the value of the net assets being acquired, the excess amount will be considered as the value of goodwill. - This excess goodwill will be debited in the journal entry when recording the purchase of the vendor's business.
Issue of Debentures as a Collateral Security
- When a company takes a loan or overdraft from a bank or financial institution, it usually provides primary security, like pledging or mortgaging assets. However, lenders may require additional security, known as collateral security, to ensure the loan can be fully recovered.
- Collateral security acts as extra protection for the lender. If the primary security doesn't cover the entire loan amount upon sale, the lender can rely on the collateral security to recover the remaining amount.
- To provide this collateral security, a company may issue its own debentures in addition to other pledged assets. This practice is referred to as 'Debentures issued as Collateral Security.'
- If the company defaults on the loan and fails to repay the principal and interest, the lender has the right to sell the primary security. If the sale of the primary security doesn't cover the full loan amount, the lender can redeem the debentures or sell them in the open market to recover the remaining debt.
- There are two methods for handling debentures issued as collateral security in the company's books:
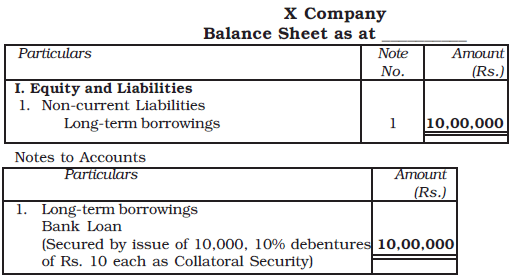
First Method: No entry is made in the accounts because no liability is created by the issuance of debentures. Instead, a note is added on the liability side of the balance sheet, below the loan item, indicating that the loan is secured by debentures issued as collateral security.
- For example, if X Company issues 9%, 10,000 debentures of Rs.100 each for a loan of Rs.10,00,000 from a bank, the balance sheet will reflect this note without creating an additional liability.
This fact may be shown in the balance sheet as under:
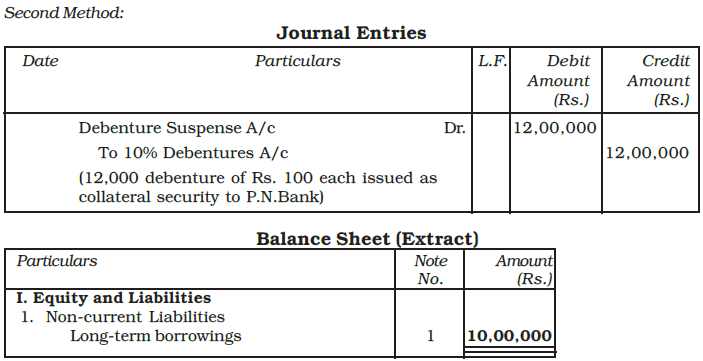
Second Method: The issue of debentures as a collateral security may be recorded by means of journal entry as follows:
i) Issue of 10,000, 9% debentures of Rs. 100 each as collateral security for bank loan of Rs. 10,00,000.
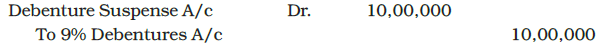
ii) For cancellation of 9% debentures as collateral security on repayment of bank loan.
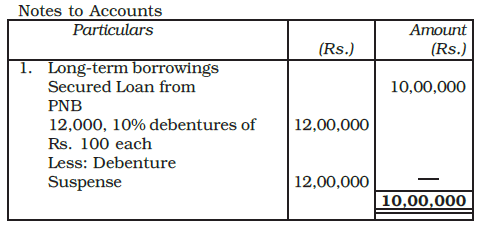
- When a company issues debentures, a Debenture Suspense Account may be created to hold the funds temporarily.
- This account appears as a detailed deduction from the total debentures in the notes to accounts under long-term borrowings.
- When the loan is repaid, the entry in the Debenture Suspense Account is reversed to cancel it out.

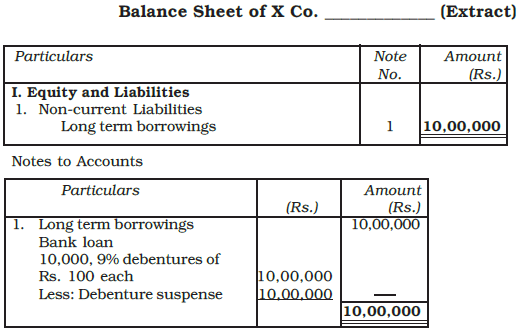
Example: A company took a loan of Rs. 10,00,000 from Punjab National Bank and issued 10% debentures of Rs. 12,00,000 of Rs. 100 each as a collateral security. Explain how you will deal with the issue of debentures in the books of the company.
Ans:
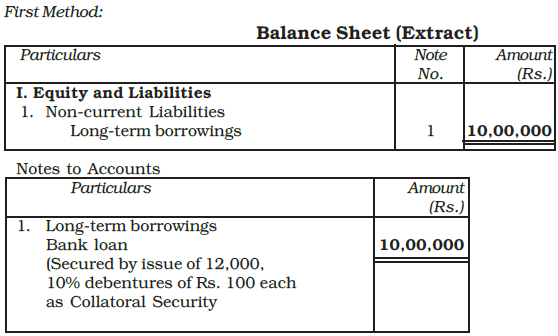
Terms of Issue of Debentures
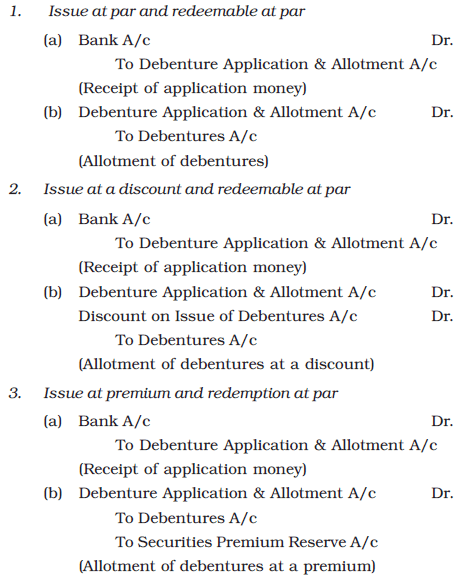
When a company issues debentures, it specifies the terms for their redemption at maturity. Redemption refers to the repayment made to debenture holders, discharging the liability associated with the debentures. Debentures can be redeemed either at par (face value) or at a premium (above face value). The following six common scenarios illustrate the terms and conditions of debenture issuance and redemption:
- Issued at par and redeemable at par: Debentures are issued at their face value and redeemed at the same value.
- Issued at a discount and redeemable at par: Debentures are issued at a lower price than their face value but redeemed at par.
- Issued at a premium and redeemable at par: Debentures are issued at a higher price than their face value but redeemed at par.
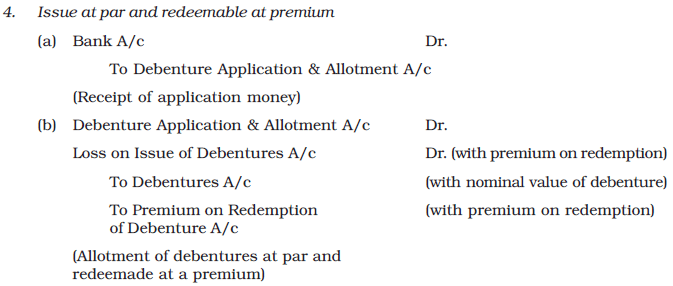
- Issued at par and redeemable at a premium: Debentures are issued at par and redeemed at a higher price than their face value.
- Issued at a discount and redeemable at a premium: Debentures are issued at a lower price than their face value and redeemed at a higher price.
- Issued at a premium and redeemable at a premium: Debentures are issued and redeemed at prices above their face value.
In all the above six cases, the following journal entries will be passed:

Interest on Debentures
- Obligation to Pay Interest: When a company issues debentures, it is required to pay interest at a fixed percentage (usually semi-annually) until the debentures are repaid. This percentage is often indicated in the name of the debentures, such as 8% debentures or 10% debentures. The interest is calculated based on the nominal value of the debentures.
- Charge Against Profit: Interest on debentures is considered a charge against the company's profit and must be paid regardless of whether the company has made a profit or not.
- Tax Deducted at Source (TDS): According to the Income Tax Act of 1961, if the interest payable on debentures exceeds a certain limit, the company must deduct income tax at a prescribed rate from the interest. This is known as Tax Deducted at Source (TDS), and the deducted amount must be deposited with the tax authorities. Debenture holders can adjust this deducted amount against their own tax liabilities.
Accounting Treatment:
The following journal entries are recorded in the books of a company in connection with the interest on debentures:

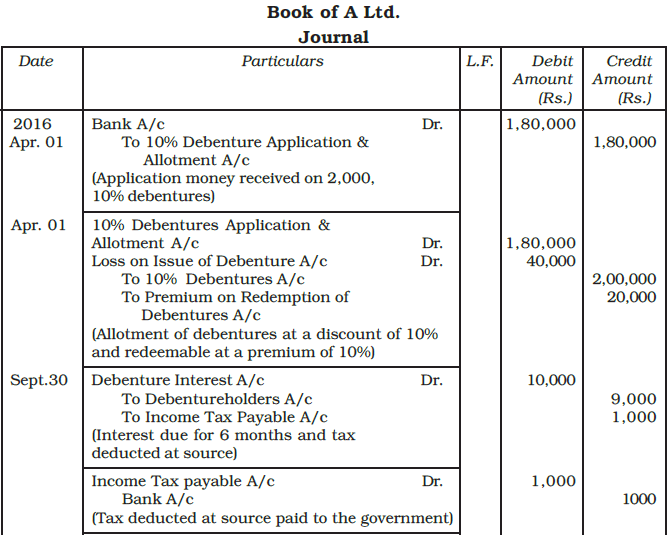
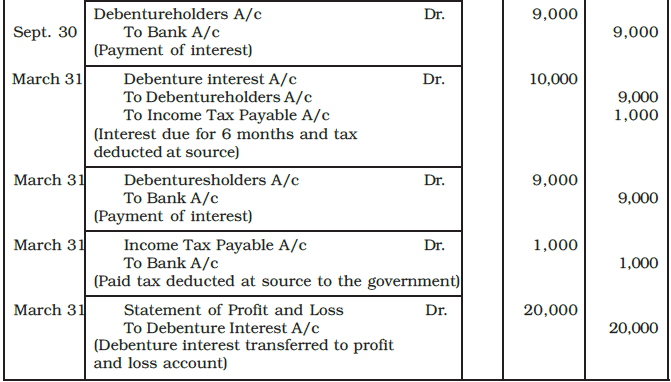
Example: A Ltd., issued 2,000, 10% debentures of Rs. 100 each on April 01, 2016 at a discount of 10% redeemable at a premium of 10%.
Give journal entries relating to the issue of debentures and debenture interest for the period ending March 31, 2017 assuming that interest was paid half yearly on September 30 and March 31 and tax deducted at source is 10%.
Ans:
Writing Off Discount/Loss on Issue of Debentures
- Discount or Loss on the issue of debentures is considered a capital loss and is written off in the year when the debentures are issued.
- This loss can be written off from the Securities Premium Reserve as per section 52(2).
- If there are no capital profits or if they are insufficient, the amount should be written off against the revenue profits of the year.
The journal entry passed is—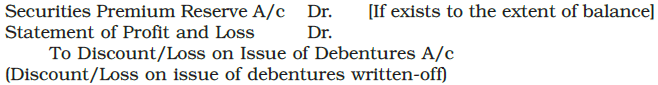
For example, on July 01, 2019 a company issued 15,000, 9% debentures of Rs. 100 each at 10% discount. It has a balance of Rs. 1, 00,000 in a securities premium reserve account. The discount on issue of debentures of Rs. 1,50,000 will be written-off in the year ending March 31, 2020 as follows:

Redemption of Debentures
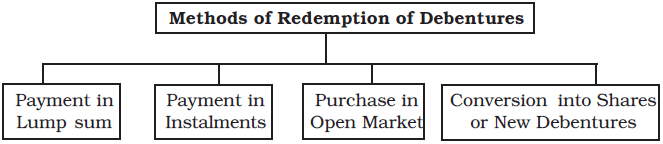
Redemption of debentures involves settling the liability associated with debentures as per the terms of their issuance. In simpler terms, it means the company repaying the amount owed on the debentures. There are four methods by which debentures can be redeemed:
- Payment in lump sum: Repaying the entire amount of debentures at once.
- Payment in instalments: Repaying the amount in multiple smaller payments over time.
- Purchase in the open market: Buying back the debentures from the open market.
- By conversion into shares or new debentures: Converting the debentures into equity shares or new debentures.
- Payment in Lump Sum: The company redeems the debentures by paying the amount in a lump sum to the debenture holders at maturity, according to the terms of the issue.
- Payment in Installments: Under this method, the redemption of debentures is typically made in instalments on specified dates during the debentures' tenure. The total debenture liability is divided by the number of years. The actual debentures to be redeemed are determined by drawing lots from the outstanding debentures.
- Purchase in Open Market: When a company buys back its own debentures for cancellation, this act of purchasing and cancelling the debentures constitutes redemption by purchase in the open market.
- Conversion into Shares or New Debentures: A company can redeem its debentures by converting them into shares or a new class of debentures. If debenture holders find the offer beneficial, they can choose to convert their debentures. The new shares or debentures can be issued at par, at a discount, or at a premium. It's important to note that only the actual proceeds from the debentures are considered when determining the number of shares to be issued in exchange for the converted debentures. If debentures were issued at a discount, the actual amount realized at the time of issue is used to compute the number of shares. This method is applicable only to convertible debentures.
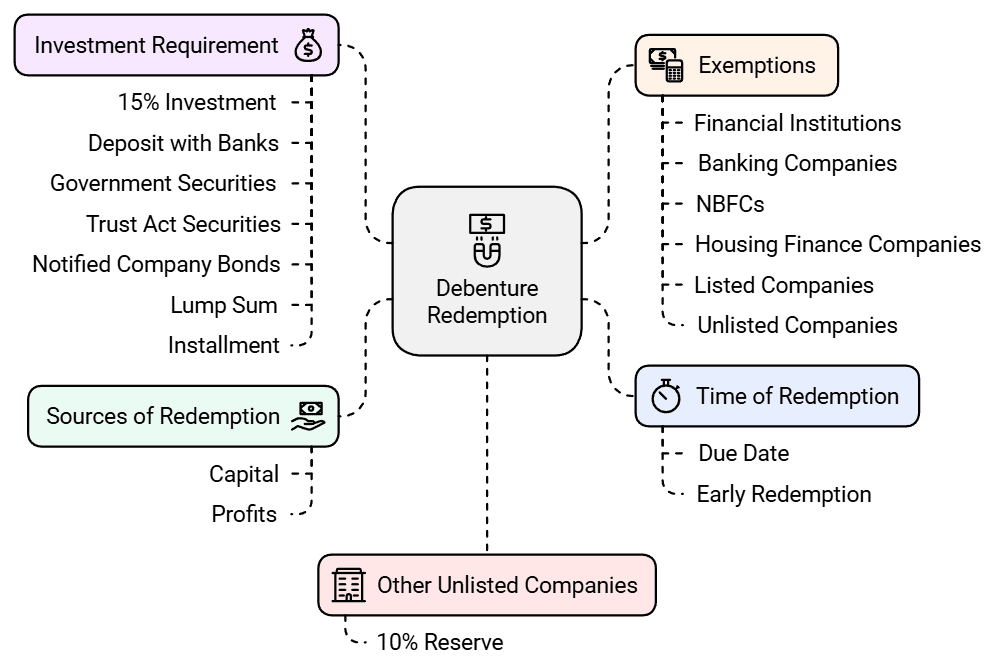
Factors to Consider for Debenture Redemption
Time of Redemption: Debentures are typically redeemed on their due date. However, a company can redeem them before the maturity date if its articles of association allow for such early redemption.
Sources of Redemption: A company can redeem debentures using either capital or profits. The Companies Act specifies different rules for various types of companies.
Exemptions: Certain entities, such as all-India financial institutions, banking companies, NBFCs, housing finance companies, listed companies, and unlisted companies, are exempt from creating a Debenture Redemption Reserve and can redeem debentures out of capital.
Other Unlisted Companies: For these companies, the Debenture Redemption Reserve must be 10% of the value of outstanding debentures.
Investment Requirement: Companies must invest or deposit at least 15% of the debentures maturing during the year by April 30 in specified methods, such as:
1. Deposit with a scheduled bank
2. Central or State Government securities
3. Securities under the Indian Trusts Act, 1982
4. Bonds from notified companies under the Indian Trusts Act, 1982Lump Sum vs. Installment Redemption: If debentures are redeemed in a lump sum, 15% of the value must be invested. For instalment redemption, the investment requirement is carried forward to meet future redemptions, with at least 15% of the next year's debentures to be redeemed.
 For example, Kays Ltd. has 10,000, 60% debentures to be redeemed as follows:
For example, Kays Ltd. has 10,000, 60% debentures to be redeemed as follows:
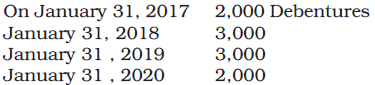
- Kays Ltd. will invest a total of Rs. 30,000 by April 30, 2016, for the redemption of 2,000 debentures on January 31, 2017.
- Additionally, Kays Ltd. will invest Rs. 15,000 by April 30, 2017, to ensure a total investment of Rs. 45,000 by that date. This amount represents 15% of the debentures to be redeemed on January 31, 2018.
- As of April 20, 2018, the investment in debenture redemption will reach Rs. 45,000, meeting the requirement of 15% of the debentures (Rs. 3,00,000) to be redeemed that year.
- During the redemption of debentures on January 31, 2019, Kays Ltd. will realize debenture redemption investments of Rs. 15,000. After this realization, the remaining investments will total Rs. 30,000, which is equal to 15% of Rs. 2,00,000.
- When redeeming the 2,000 debentures on January 31, 2020, all investments will be realized.
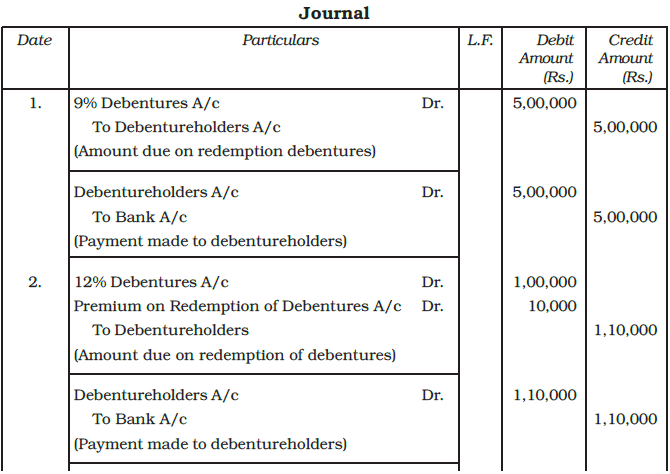
Redemption by Payment in Lump Sum
When the company pays the whole amount in a lump sum, the following journal entries are recorded in the books of the company:


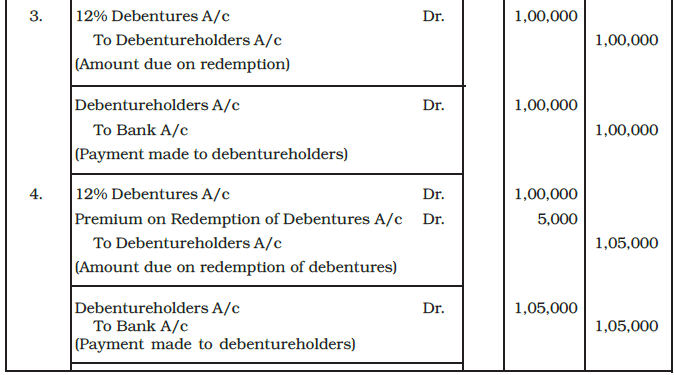
Example: Give the necessary journal entries at the time of redemption of debentures in each of the following cases.
1. X Ltd. issued 5,000, 9% debentures of Rs. 100 each at par and redeemable at par at the end of 5 years out of capital.
2. X Ltd. issued 1,000, 12% debentures of Rs. 100 each at par. These debentures are redeemable at 10% premium at the end of 4 years.
3. X Ltd. issued 12% debentures of the total face value of Rs. 1,00,000 at premium of 5% to be redeemed at par at the end of 4 years.
4. X Ltd. issued Rs. 1,00,000, 12% debentures at a discount of 5% but redeemable at a premium of 5% at the end of 5 years.
Ans:
Redemption by Payment in Instalments
- When debentures are set to be redeemed in instalments starting from a specific year, the debentures to be redeemed are typically chosen through a draw of lots.
- At the time of redemption, specific journal entries are recorded to reflect the transaction.

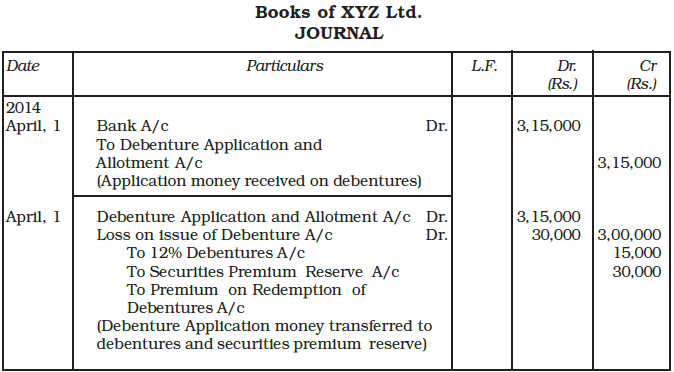
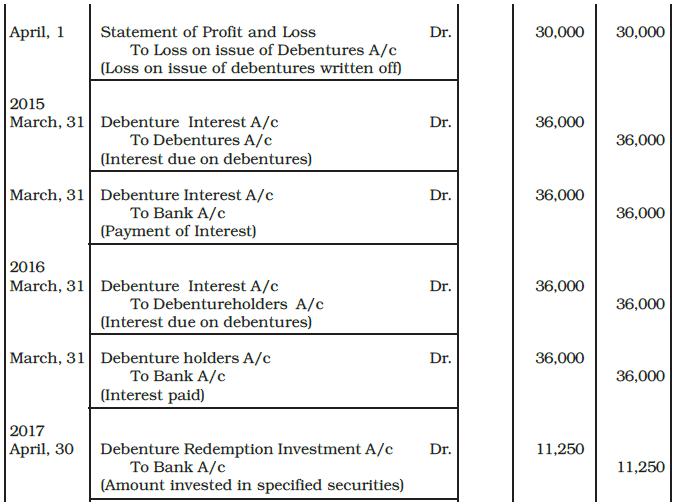
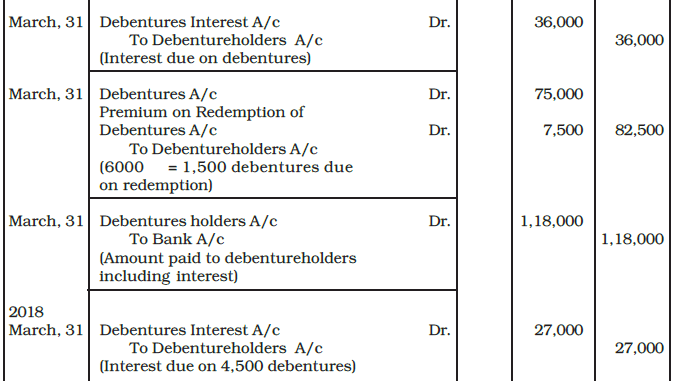
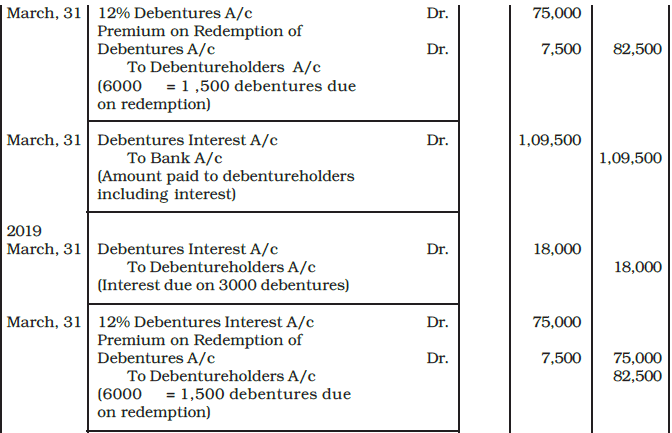
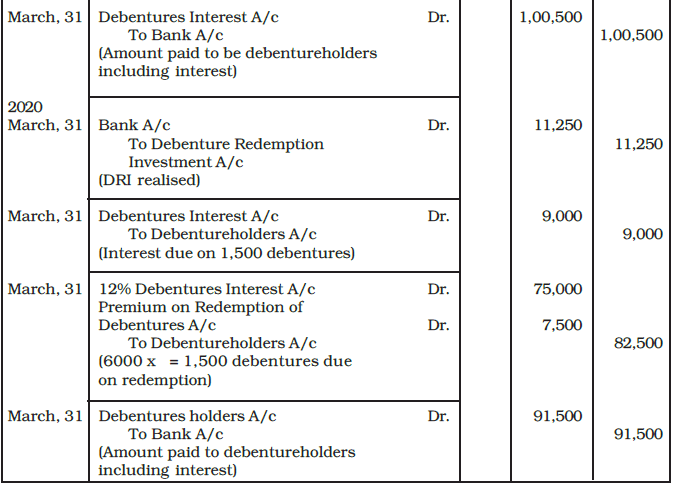
Example: XYZ Ltd. a listed company issued 6,000, 12% Debentures of Rs. 50 each at a premium of 5% on April 1, 2014. Interest on these debenture is payable annually on 31st March each year. The debentures are redeemable in four equal installments at the end of third, fourth, fifth and sixth year at a premium of 10%. The company invested in specified securities as investment for the redemption of debentures.
You are required to pass journal entries at the time of issue and redemption of debentures in the books of the company.
Ans:
Redemption by Purchase in Open Market
- When a company buys back its own debentures from the open market to cancel them immediately, this process is called redemption by purchase in the open market.
- Advantages:
1. Convenience: The company can redeem debentures at its convenience whenever it has surplus funds.
2. Cost Savings: The company can buy back debentures when they are available in the market at a discount.
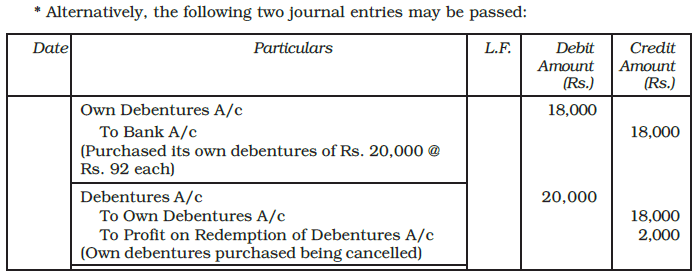
When the debentures are purchased from the market at a discount and cancelled, the journal entries are recorded as follows :

- If debentures are bought from the market for a price higher than their face value, the extra amount paid will be recorded as a loss on redemption of debentures. The journal entry in that case will be

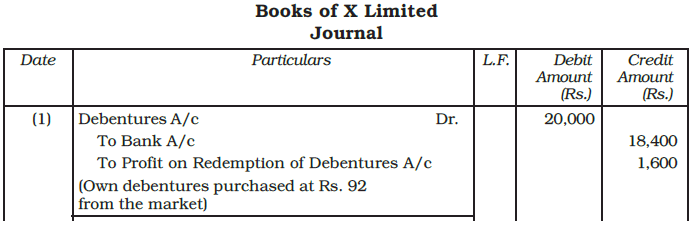
Example: X Ltd. purchased its own debentures of Rs. 100 each of the face value of Rs. 20,000 from the open market for cancellation at Rs. 92. Record necessary journal entries.
Ans:

Redemption by Conversion
- Debentures can be redeemed by converting them into shares or new debentures.
- If debenture holders find the offer beneficial, they may choose to convert.
- The new shares or debentures can be issued at par, discount, or premium.
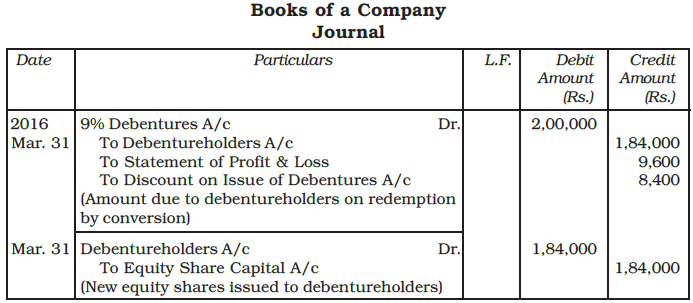
Example: On April 01, 2013, a company made an issue of 10,000, 9% Debentures of Rs. 100 each at Rs. 92 per debenture. The terms of issue provided for the redemption of 2,000 debentures every year starting from the March 31, 2016 either by conversion in to equity shares of Rs. 20 each or by draw of lot at per at the company’s option. On March 31, 2016, company redemption, 2,000, 9% debentures by converting them into Equity shares of Rs. 20 each. Give the necessary Journal entries.
Ans:
|
51 videos|270 docs|51 tests
|
FAQs on Issue and Redemption of Debentures Chapter Notes - Accountancy Class 12 - Commerce
| 1. What is the difference between debentures and shares? |  |
| 2. How are debentures issued? |  |
| 3. What does it mean for debentures to be issued as collateral security? |  |
| 4. What are the common terms associated with the issue of debentures? |  |
| 5. How is interest on debentures calculated and paid? |  |






















