Class 9 NCERT - Solved Question Answers Documents
Q1. Refer to Find Out, Textbook page 17.
Which river has the largest basin in India?
Ans. River Ganga has the largest basin in India.
Q2. Refer to Find Out, Textbook page 22.
The name of the biggest waterfall in India.
Ans. Jog Falls.
Q3. Refer to Find Out, Textbook page 22.
Lakes of large extent are called the seas, like the Caspian, the Dead and the Aral Seas.
Ans. For Learning purpose.
NCERT textbook questions solved
Q1. Choose the right answer from the four alternatives given below:
(i) Which one of the following describes the drainage patterns resembling the branches of a tree?
(a) Radial
(b) Dendritic
(c) Centrifugal
(d) Trellis
(ii) In which of the following states is the Wular lake located?
(a) Rajasthan
(b) Uttar Pradesh
(c) Punjab
(d) Jammu and Kashmir
(iii) The river Narmada has its source at
(a) Satpura
(b) Brahmagiri
(c) Amarkantak
(d) Slopes of the Western Ghats
(iv) Which one of the following lakes is a salt water lake?
(a) Sambhar
(b) Dal
(c) Wular
(d) Gobind Sagar
(v) Which one of the following is the longest river of the Peninsular India?
(a) Narmada
(b) Krishna
(c) Godavari
(d) Mahanadi
(vi) Which one amongst the following rivers flows through a rift valley?
(a) Mahanadi
(b) Tungabhadra
(c) Krishna
(d) Tapi
Ans. (i)—(b) (ii)—(d) (iii)—(c) (iv)—(a) (v)—(c) (vi)—(d)
Q2. Answer the following questions briefly:
(i) What is meant by a water divide? Give an example.
(ii) Which is the largest river basin in India?
(iii) Where do the rivers Indus and Ganga have their origin?
(iv) Name the two headstreams of the Ganga. Where do they meet to form the Ganga?
(v) Why does the Brahmaputra in its Tibetan part have less silt, despite a longer course?
(vi) Which two peninsular rivers flow through trough?
(vii) State some economic benefits of rivers and lakes.
Ans. (i) An elevated area, such as a mountain or an upland, that separates two drainage basins is known as water divide. Example – The water divide between the Indus and the Ganga river system. Ambala is situated on this water divide.
(ii) The Ganga river basin is the largest one in India. The length of this river basin is over 2500 km.
(iii) The river Indus has its origin in Tibet, near Lake Mansarovar. The river Ganga originates at the Gangotri glacier on the southern slopes of the Himalayas.
(iv) The two headstreams of the Ganga – Bhagirathi and Alaknanda. They meet to form the Ganga at Devprayag in Uttarakhand.
(v) The Brahmaputra in its Tibetan part carries a szmaller volume of water and less silt as it is a cold and a dry area.
(vi) Narmada and Tapi are the two peninsular rivers that flow through trough.
(vii) Economic benefits of rivers:
• They provide water which is a basic natural resource essential for various human activities.
• They are used for irrigation, navigation and hydro power generation.
• They moderate the climate of the surroundings and maintain the aquatic ecosystem.
Economic benefits of lakes:
• They help to regulate the flow of a river.
• During heavy rainfall, they prevent flooding and during the dry season, they help to maintain an even flow of water.
• They also moderate the climate of the surroundings and maintain the aquatic ecosystem.
• They help develop tourism. They enhance natural beauty and provide recreation.
• Lakes can also be used for developing hydel power.
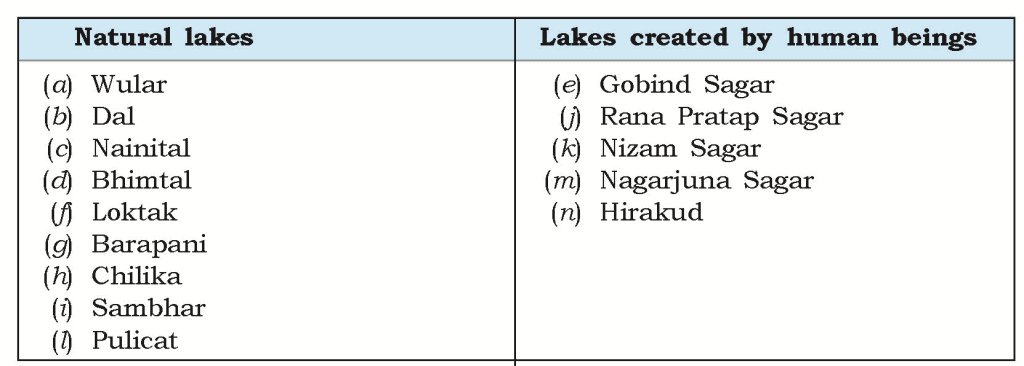
Q3. Below are given names of a few lakes of India. Group them under two categories — natural and created by human beings.
(a) Wular (b) Dal (c) Nainital (d) Bhimtal (e) Gobind Sagar (f) Loktak (g) Barapani (h) Chilika
(i) Sambhar (j) Rana Pratap Sagar (k) Nizam Sagar (l) Pulicat (m) Nagarjuna Sagar (n) Hirakud
Ans.
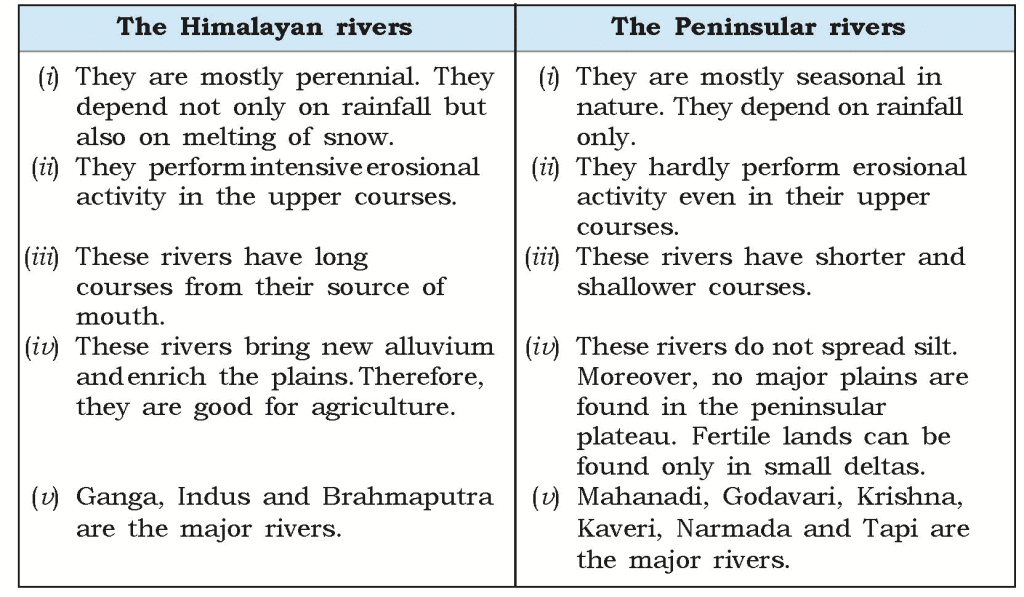
Q4. Discuss the significant differences between the Himalayan and the Peninsular rivers.
Ans.
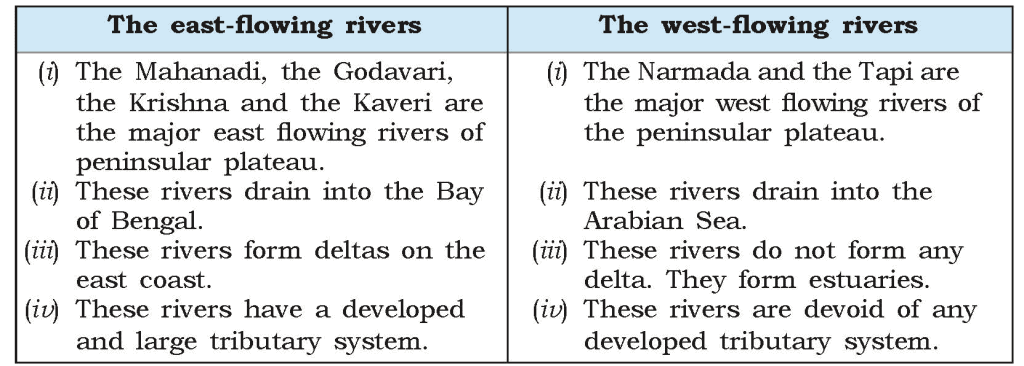
Q5. Compare the east-flowing and the west-flowing rivers of the peninsular plateau.
Ans.
Q6. Why are rivers important for the country’s economy?
Ans. Rivers are important for the country’s economy in the following ways:
(i) Rivers provide water which is a basic natural resource and is essential for various human activities.
(ii) The river banks have attracted settlers from ancient times. These settlements have now become big cities.
(iii) River water is used in irrigation, navigation and hydro-power generation.
(iv) Agriculture, which is the backbone of the country, is possible only because of the rivers.
(v) Rivers moderate the climate of the surroundings and maintain the aquatic ecosystem.
(vi) They prevent flood during heavy downpour.
Map Skills
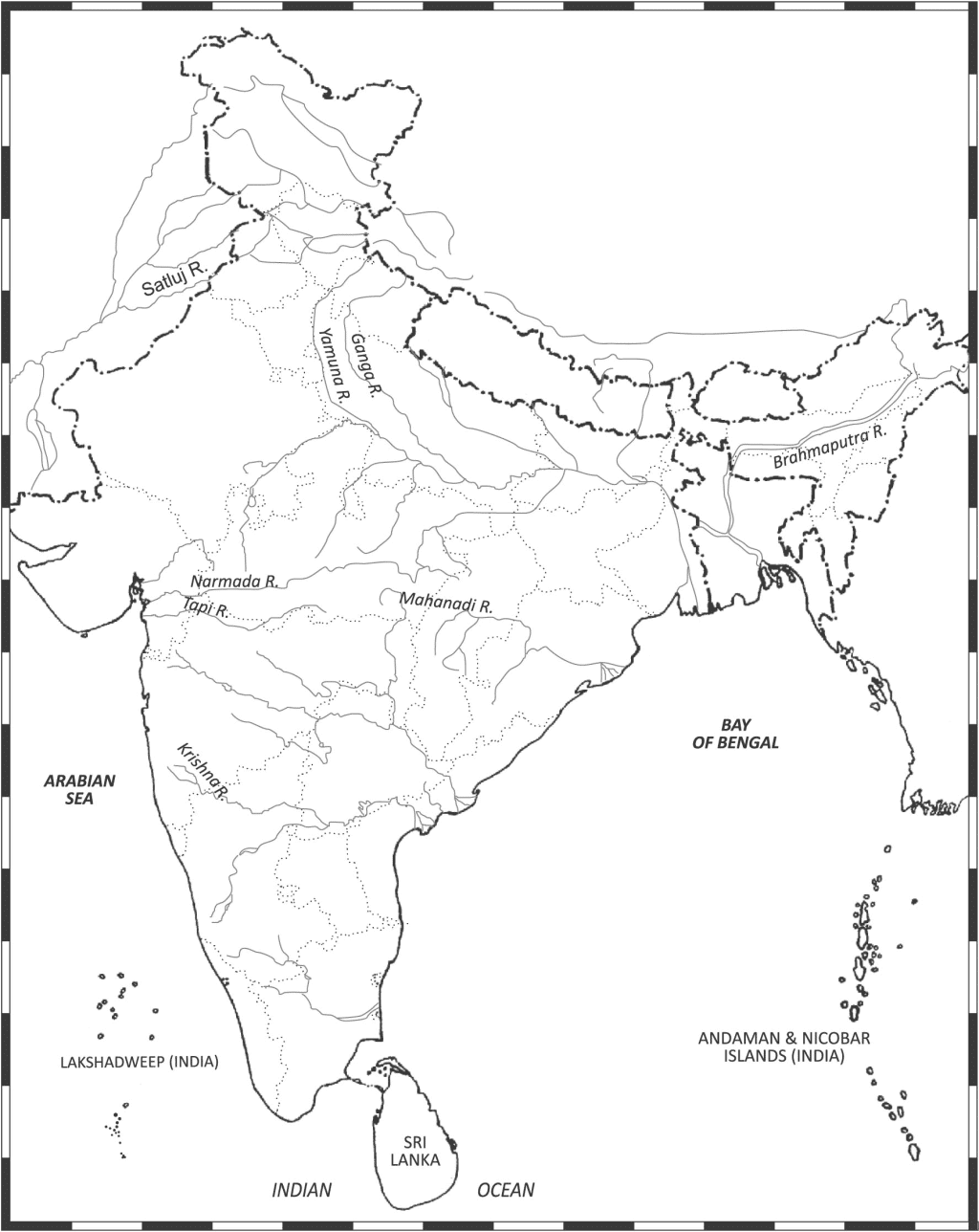
(i) On an outline map of India, mark and label the following rivers:
Ganga, Satluj, Yamuna, Krishna, Narmada, Tapi, Mahanadi, and Brahmaputra
Ans.
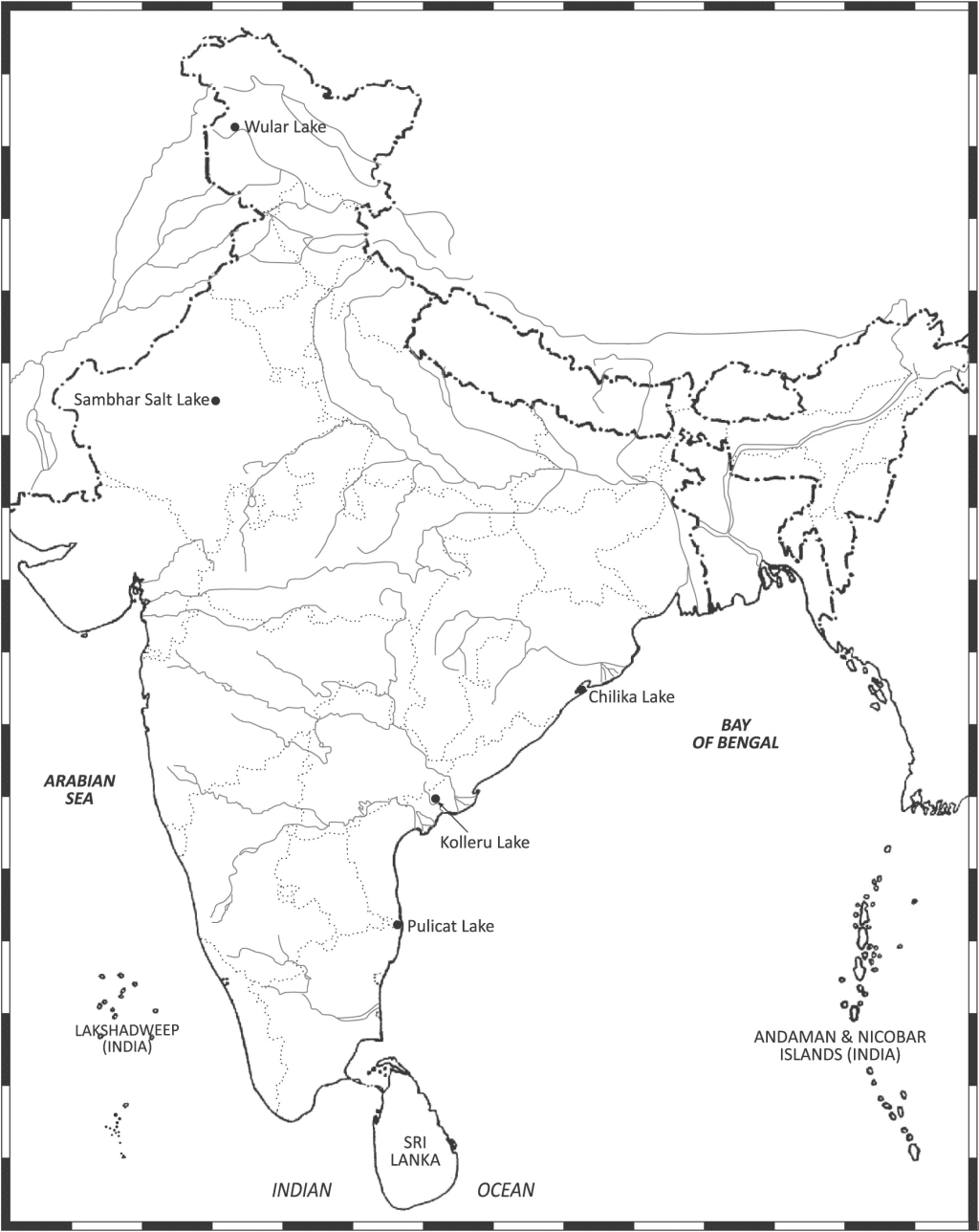
(ii) On an outline map of India, mark and label the following lakes:
Chilika, Sambhar, Wular, Pulicat and Kolleru
Ans.
Project/Activity
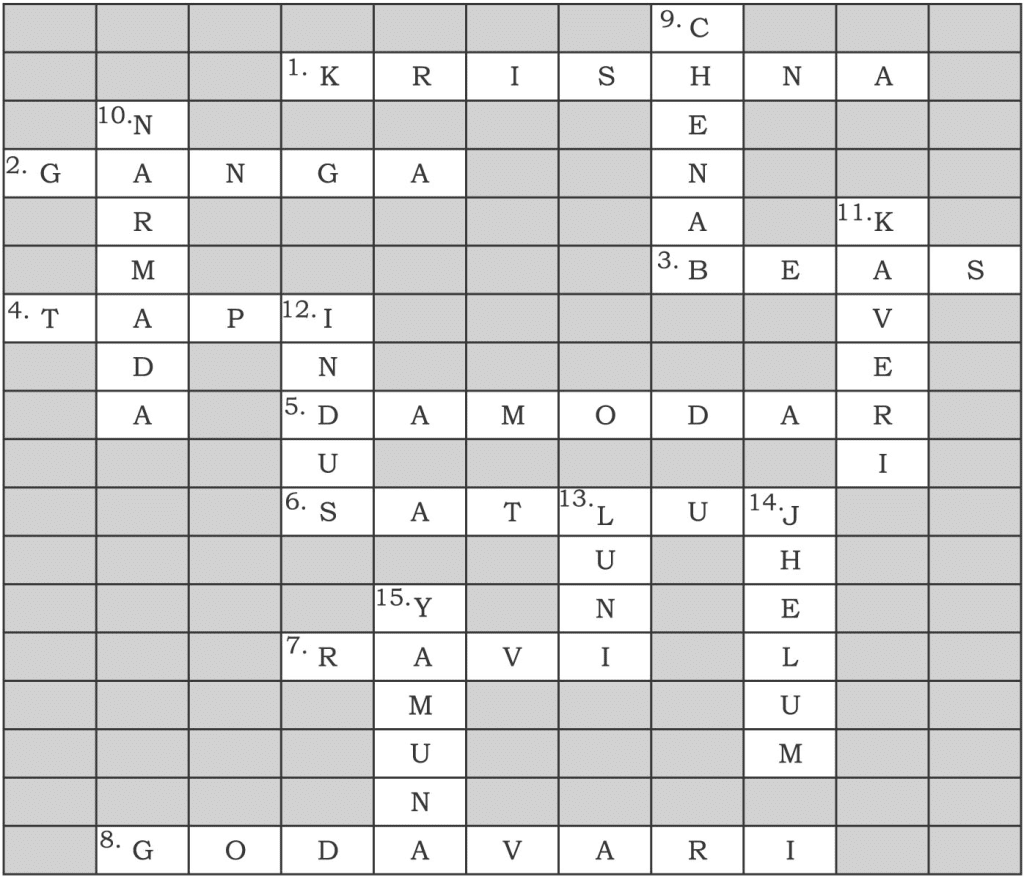
Q. Solve this crossword puzzle with the help of given clues.
Across:
- Nagarjuna Sagar is a river valley project. Name the river.
- The longest river of India.
- The river which originates from a place known as Beas Kund.
- The river which rises in the Betul district of MP and flows westwards.
- The river which was known as the ‘Sorrow of West Bengal’.
- The river on which the reservoir for Indira Gandhi canal has been built.
- The river whose source lies near Rohtang Pass.
- The longest river of Peninsular India.
Down: - A tributary of Indus originating from Himachal Pradesh.
- The river flowing through fault, drains into the Arabian Sea.
- A river of South India, which receives rain water both in summer and winter.
- A river which flows through Ladakh, Gilgit and Pakistan.
- An important river of the Indian desert.
- The river which joins Chenab in Pakistan.
- A river which rises at Yamunotri glacier.
Ans.
|
1 videos|228 docs|21 tests
|
FAQs on Class 9 NCERT - Solved Question Answers Documents
| 1. What are NCERT questions? |  |
| 2. How can I access NCERT questions? |  |
| 3. Are NCERT questions important for exams? |  |
| 4. Can I rely solely on NCERT questions for exam preparation? |  |
| 5. How should I approach solving NCERT questions? |  |

|
Explore Courses for Class 9 exam
|

|


















