Tissues - NEET PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| What are Tissues? |

|
| Two Types of Plant Tissues |

|
| 1. Meristematic Tissues |

|
| 2. Permanent Tissues |

|
| Two Important Theories Explaining Growth of the Plant at Shoot (Apex) & Root Tip |

|
What are Tissues?
In simple terms, tissue can be defined as a group of cells with similar shape and function are termed as tissues. They form a cellular organizational level, intermediate between the cells and organ system. Organs are then created by combining the functional groups of tissues.
- Organs such as stem, roots in plants and stomach, heart and lungs in animals are made up of different kinds of tissues.
- A tissue is a group of cells with a common origin, structure, and function. Their common origin means they are derived from the same layer (details in lesson No. 20) of cells in the embryo.
- Being of a common origin, they are similar in structure and hence perform the same function. Many kinds of tissues organize to form an organ.
Example: Blood, bone, cartilage are some examples of animal tissues, whereas parenchyma, collenchyma, xylem, and phloem are different tissues in plants.
- Hence, to summarize: A group of cells with similar origin, structure, and function is called tissue.
Example: Bone, muscle in animals, and meristem in tips of root and shoot in plants. - And the study of tissues is called histology.
Two Types of Plant Tissues
- Meristematic Tissues (Gk. Meristos: Dividing)
- Permanent Tissues (Non-Dividing)
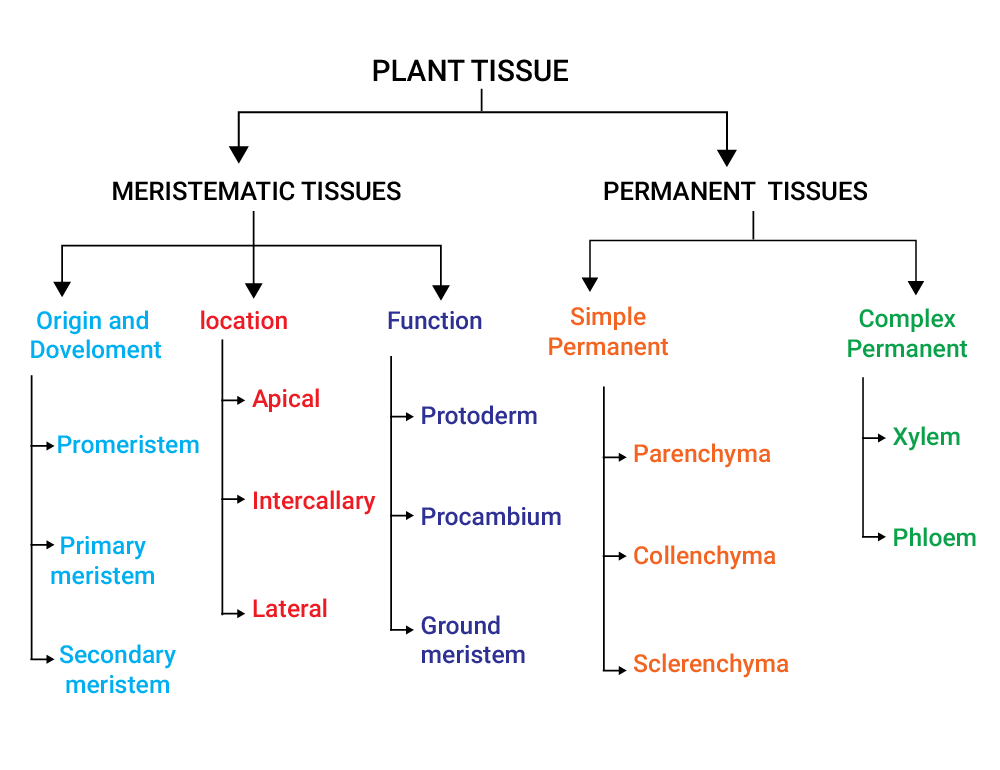
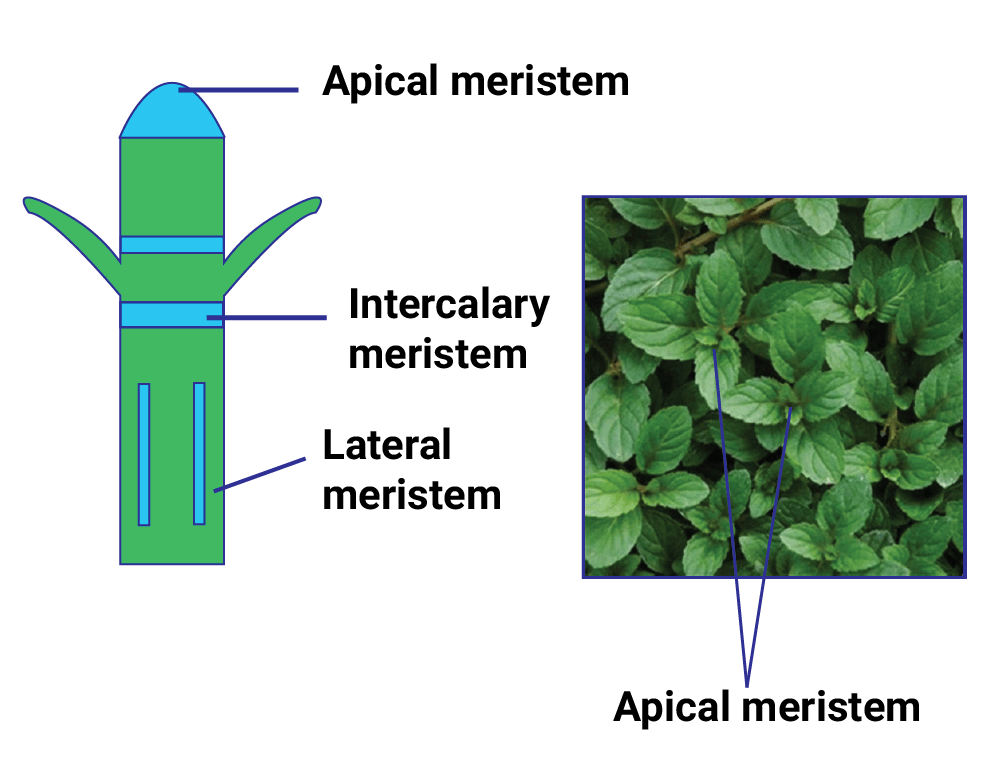
1. Meristematic Tissues
- Composed of immature or undifferentiated cells without intercellular spaces.
- The cells may be rounded, oval or polygonal; always living and thin walled.
 Different Types of Meristematic Tissue
Different Types of Meristematic Tissue
- Each cell has abundant cytoplasm and prominent nuclei in it.
- Vacuoles may be small or absent.
Table: Types of Meristematic Tissue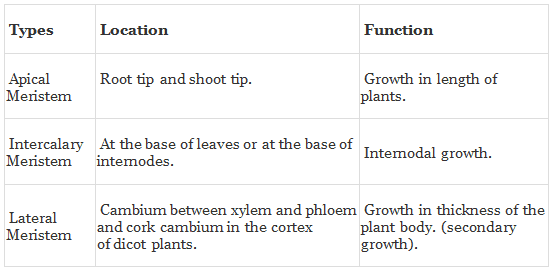
2. Permanent Tissues
- Permanent tissues are those in which growth has stopped either completely or for the time being.
- Cells of these tissues may be living or dead; and thin walled or thick walled.
- Thin walled permanent tissues are generally living, whereas the thick walled tissues may be living or dead.
Types of Permanent Tissues
- Simple Tissues
Simple tissue is made up of only one type of cells. Common simple tissues are parenchyma, collenchyma and sclerenchyma. - Complex Tissues
Complex tissue is made up of more than one type of cells working together as a unit. Common examples are xylem and phloem.
a) Simple Plant Tissues
There are three types of simple plant tissues:
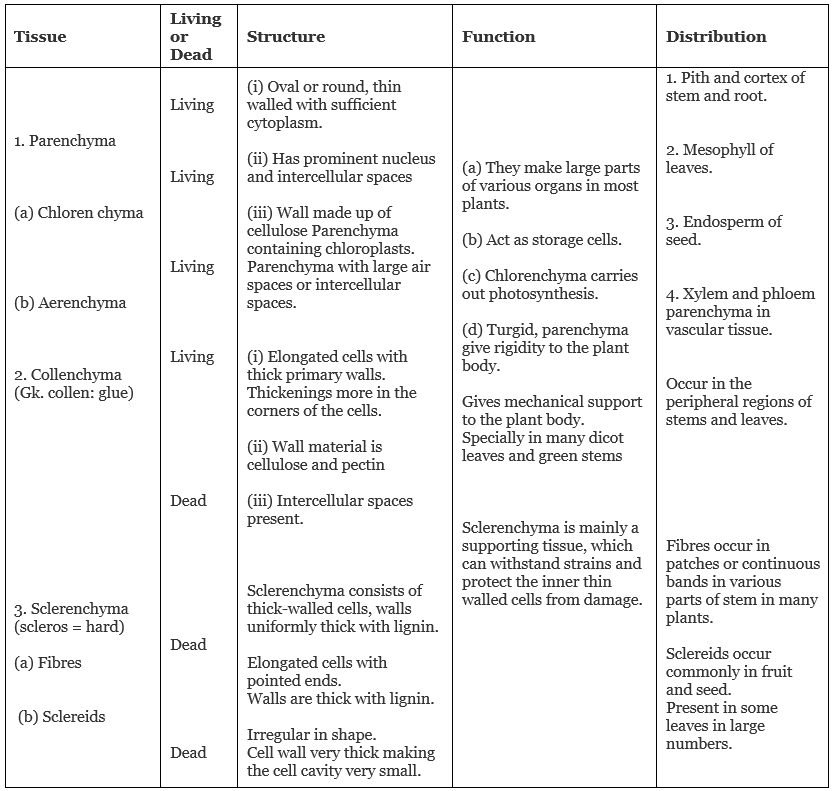
- Parenchyma (Chlorenchyma and Aerenchyma)
- Collenchyma
- Sclerenchyma
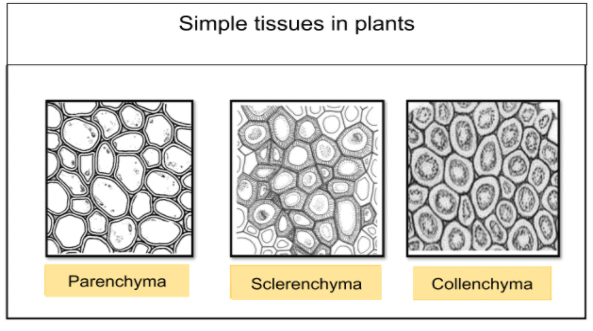
Table: Structure, Function and Distribution of simple tissues
b) Complex Plant Tissues
Complex tissues are mainly of two types:
(i) Xylem
(ii) Phloem
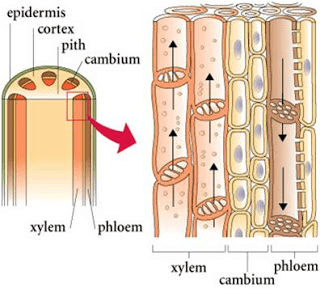
- Xylem and phloem form a continuous system inside the plants, that is from the roots through the stem and leaves.
- They are known as vascular tissues and form vascular bundles in roots and stems. Xylem (Greek xylo = wood)
1. Xylem
- Xylem is a conducting tissue which conducts water and salts upward from roots to leaves.
- Xylem is composed of
(a) Tracheids
(b) Vessels
(c) Fibres
(d) Xylem Parenchyma
 Complex Tissue
Complex Tissue
2. Phloem
- Phloem is a conducting tissue that conducts food synthesised in the leaves to different parts of the plant.
- Phloem is composed of:
(a) Sieve Tubes
(b) Companion Cells
(c) Phloem Fibre
(d) Phloem Parenchyma - The structure, function of the complex plant tissues is given in the table below.
Table: Structure and function of the components of xylem and phloem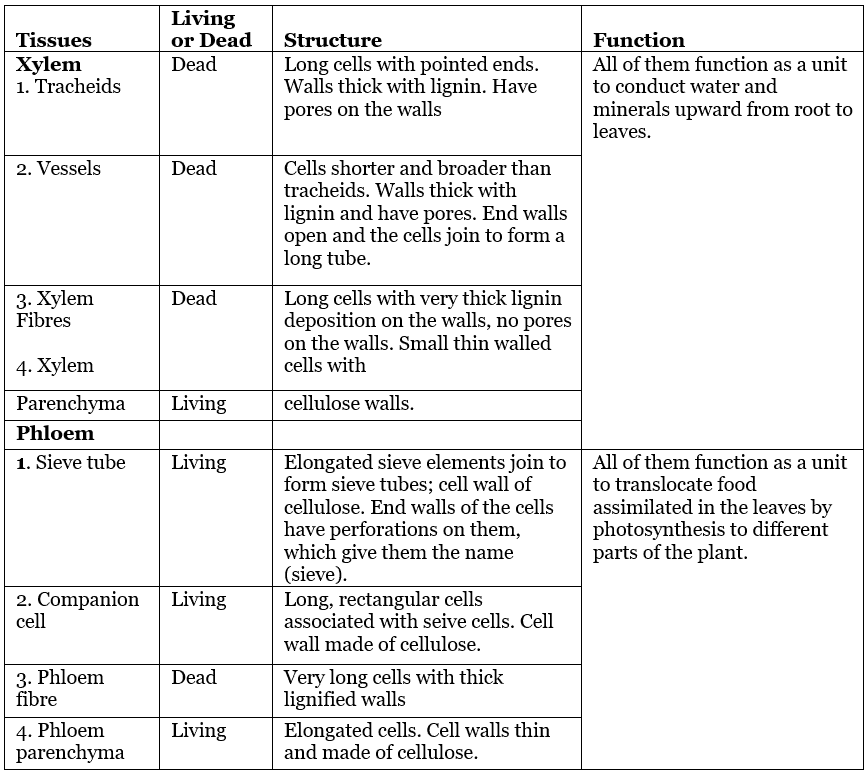
Two Important Theories Explaining Growth of the Plant at Shoot (Apex) & Root Tip
1. Tunica Corpus Theory
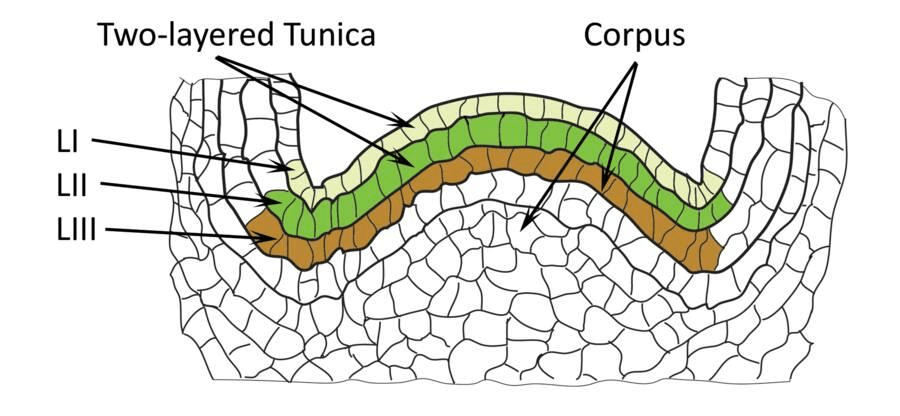
- Tunica corpus theory was developed for vegetative shoot apex.
- According to this theory, there are two zones of tissues in the apical meristems the tunica (Tunic = cover) consisting of one or more layers of peripheral layers of cells, and the corpus (corpus = body) a mass of cells enclosed by the tunica.
- According to the theory, different rates and methods of growth in the apex set apart two regions.
- The layers of tunica show anticlinal (perpendicular to periphery) divisions and bring about surface growth.
- In the corpus, cell division is irregular and at various planes resulting in growth in the volume of the mass.
- Tunica gives rise to the epidermis and cortex. Corpus gives rise to endodermis, pericycle, pith, and vascular tissue.
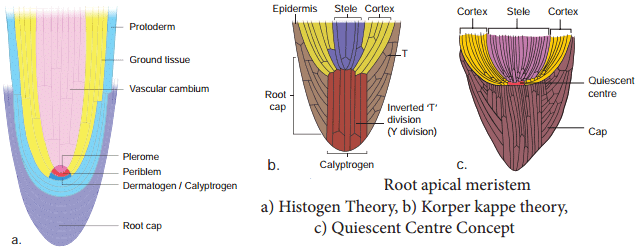
2. Histogen Theory
- According to this theory, apical meristem of stem and root are composed of small mass of cells which are all alike and divide fast (meristematic).
- These meristematic cells form promeristem, which differentiate into three zones dermatogen, periblem and plerome.
- Every zone consists of a group of initials called a histogen (tissue builder).
(i) Dermatogen gives rise to epidermis of stems and epiblema of roots.
(ii) Periblem (middle layer) gives rise to cortex of stems and roots.
(iii) Plerome gives rise to central meristematic region– pericycle, pith and vascular tissue.
FAQs on Tissues - NEET
| 1. What are the different types of plant tissues? |  |
| 2. What are meristematic tissues? |  |
| 3. What are permanent tissues in plants? |  |
| 4. What are the two important theories explaining the growth of plant tissues at the shoot and root tip? |  |
| 5. What is the role of meristematic tissues in plant growth? |  |