Solutions of Metals and Non-metals (Page No - 192) - Chemistry Lakhmir Singh, Class 10 | Extra Documents, Videos & Tests for Class 10 PDF Download
Question 31:
How is manganese extracted from manganese dioxide, MnO2 ? Explain with the help of an equation.
Solution :
Manganese metal is extracted by the reduction of its oxide with aluminium powder as the reducing agent. Thus, when manganese dioxide is heated with aluminium powder, then manganese metal is formed.
Question 32:
What is a thermite reaction ? Explain with the help of an equation. State one use of this reaction.
Solution :
The reduction of a metal oxide to form metal by using aluminium powder as a reducing agent is called a thermite reaction.
This property of reduction by aluminium is made use of in thermite welding for joining the broken pieces of heavy iron objects like girders etc.
A mixture of Iron (III) oxide and aluminium powder is ignited with a burning magnesium ribbon. Aluminium reduces iron oxide to produce iron metal with the evolution of a lot of heat. Due to this heat, iron metal is produced in the molten state. This molten iron is then poured between the broken iron pieces to weld them (to join them).![]()
Question 33:
Which one of the methods given in column I is applied for the extraction of each of the metals given in column II :
Column I | Column II |
Electrolytic Reduction | Aluminium |
Reduction with carbon | Zinc |
Reduction with Aluminium | Sodium |
Iron | |
Manganese | |
Tin |
Solution :
Electrolytic reduction: Aluminium and Sodium;
Reduction with carbon : Zinc, Iron and Tin;
Reduction with aluminium: Manganese
Question 34:
(a) Give reason why copper is used to make hot water tanks but steel (an alloy of iron) is not.
(b) Explain why, the surface of some metals acquires a dull appearance when exposed to air for a long time.
Solution :
(a) Copper does not corrode easily in the presence of water but steel rusts in the presence of water.
(b) The surface of some metals acquires a dull appearance when exposed to air b ecause of the formation of an oxide layer on the surface of the metal.
Question 35:
(a) Why does aluminium not corrode right through ?
(b) What is meant by ‘anodising’ ? Why is it done ?
Solution :
(a) Aluminium does not corrode right through because aluminium is more reactive than iron and it forms a layer of aluminium oxide as soon as it comes in contact with moist air. This aluminium oxide layer is very tough and prevents the aluminium underneath from corroding.
(b) The process of thickening of aluminium oxide layer on the surface of aluminium objects by electrolysis is called anodizing. It is done to provide more protection to the aluminium object from corrosion.
Question 36:
(a) Why is an iron grill painted frequently ?
(b) Explain why, though aluminium is more reactive than iron, yet there is less corrosion of aluminium when both are exposed to air.
Solution :
(a) An iron grill is painted frequently to prevent its rusting .
(b)There is less corrosion of aluminium than iron when both are exposed to air because aluminium forms a layer of aluminium oxide on its surface as soon as it comes in contact with moist air. This aluminium oxide is very tough and prevents it from corroding right through.
Question 37:
(a) Name the method by which aluminium metal is extracted.
(b) Give the name and chemical formula of one ore of copper.
(c) How is zinc extracted from its carbonate ore (calamine) ? Explain with equations.
Solution :
(a) Electrolytic reduction .
(b)Copper glance (Cu2 S)
(c) When calamine ore is heated strongly in the absence of air i.e. calcined, it decomposes to form zinc oxide and carbon dioxide.
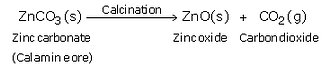
Then, zinc oxide is heated with carbon and zinc metal is produced.
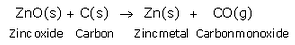
Question 38:
(a) Name two metals which occur in nature in free state as well as in combined state.
(b) Name one ore of manganese. Which compound of manganese is present in this ore ? Also write its chemical formula.
(c) A zinc ore on heating in air forms sulphur dioxide. Describe briefly any two stages involved in the conversion of this concentrated ore into zinc metal.
Solution :
(a) Copper and Silver occur in nature in free state as well as in combined state.
(b) Pyrolusite; Manganese dioxide; MnO2
(c) (i) Roasting: When zinc sulphide (zinc blende ore) is strongly heated in air (roasted), it forms zinc oxide and sulphur dioxide.
(ii) Reduction: Zinc oxide obtained is heated with carbon to form zinc metal.
Question 39:
How does the method used for extracting a metal from its ore depend on the metal’s position in the reactivity series ? Explain with examples.
Solution :
Different methods are used for extracting metals belonging to category of highly reactive metals, moderately reactive metals and less reactive metals. This is because the extraction of a metal from its concentrated ore is essentially a process of reduction of the metal compound present in the ore. For example: Manganese metal is obtained by the reduction of its oxide with aluminium powder and not carbon. This is because carbon is less reactive than manganese. Carbon, which is a non-metal, is more reactive than zinc and it can be placed just above Zn in the reactivity series. Hence, carbon can reduce the oxides of zinc and all other metals below zinc to form metals
Question 40:
Explain giving one example, how highly reactive metals (which are high up in the reactivity series) are extracted.
Solution :
The highly reactive metals are extracted by the electrolytic reduction of their molten chlorides or oxides.
Example: Sodium metal is extracted by the electrolytic reduction of molten sodium chloride. When electric current is passed through molten sodium chloride, it decomposes to form sodium metal and chlorine gas.![]()
Question 41:
Describe with one example, how moderately reactive metals (which are in the middle of reactivity series) are extracted.
Solution :
The moderately reactive metals are extracted by the reduction of their oxides with carbon, aluminium, sodium or calcium.
Example: When zinc sulphide (zinc blende ore) is strongly heated in air (roasted), it forms zinc oxide and sulphur dioxide. This process is called roasting. Then, zinc oxide is heated with carbon to form zinc metal. This process is termed as reduction.
Question 42:
How are the less reactive metals (which are quite low in the reactivity series) extracted ? Explain with the help of an example.
Solution :
The less reactive metals are extracted by the reduction of their oxides by heat alone.
Example: Mercury (II) sulphide ore is roasted in air when mercury (II) oxide is formed. When this mercury (II) oxide is heated to about 300oC, it decomposes to form mercury metal.
Question 43:
What is meant by refining of a metal ? Name the most widely used method for the refining of impure metals obtained by various reduction processes. Describe this method with the help of a labelled diagram by taking the example of any metal.
Solution :
The process of purifying impure metals is called refining of metals.
Electrolytic refining is the most widely used method for the refining of impure metals obtained by various reduction processes.
In an electrolytic tank, acidified copper sulphate (CuSO4+ dilute H2O4) solution forms the electrolyte. A block of impure copper is made into an anode by connecting the positive terminal of a power supply (battery). A thin strip of highly pure copper metal is the cathode of the cell. The negative terminal of the power supply is connected to it.
A small electric curr ent is passed through the cell. Atoms from the anode enter the electrolyte. The copper from the anode gets converted into copper sulphide. An equal number of copper atoms from the solution get deposited on the cathode. This is to keep the concentration of the solution constant. Impurities from the anode block either remain in solution or collect below the anode, as they are unable to displace copper from the sulphate solution. The insoluble impurities remain in the electrolyte and are called anode mud.
Copper sulphate solution contains ions of Cu++ and SO4— . The following reactions take place at the anode and cathode when an electric current is passed.

Pure copper is scraped or removed from the cathode. Anode becomes thinner as the electrolysis process proceeds. Some important metals like gold and silver are present in the anode mud. These can be recovered separately.
Question 44:
(a) Define the terms (i) mineral (ii) ore, and (iii) gangue.
(b) What is meant by the ‘concentration of ore’ ?
(c) Name one ore of copper (other than cuprite). Which compound of copper is present in this ore ? Also, write its chemical formula.
Solution :
(a) (i) Minerals – The natural materials in which the metals or their compounds are found in earth are called minerals.
(ii) Ores – Those minerals from which the metals can be extracted conveniently and profitably are called ores.
(iii) Gangue – The unwanted impurities like sand, rocky material, earthy particles etc., present in an ore are called gangue.
(b) Before extracting metal from an ore, it is necessary to remove these impurities (gangue) from it. By removing the gangue, we get a concentrated ore containing a much higher percentage of metal. This is called concentration of ore; also known as enrichment of ore.
(c) Ore: Copper glance; Copper (I) sulphide, Cu2S.
|
5 videos|292 docs|59 tests
|
FAQs on Solutions of Metals and Non-metals (Page No - 192) - Chemistry Lakhmir Singh, Class 10 - Extra Documents, Videos & Tests for Class 10
| 1. What are metals and non-metals? |  |
| 2. What are some examples of metals and non-metals? |  |
| 3. How do metals and non-metals differ in their physical properties? |  |
| 4. What is the reactivity of metals and non-metals? |  |
| 5. How are metals and non-metals used in everyday life? |  |
|
5 videos|292 docs|59 tests
|

|
Explore Courses for Class 10 exam
|

|

















