NEET Previous Year Questions (2016-2025): Body Fluids & Circulation | Biology Class 11 PDF Download
2025
Q1: Cardiac activities of the heart are regulated by: (NEET 2025)
A. Nodal tissue
B. A special neural centre in the medulla oblongata
C. Adrenal medullary hormones
D. Adrenal cortical hormones
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A, C and D only
(b) A, B and D only
(c) A, B and C only
(d) A, B C and D
Ans: (c)
- A. Nodal tissue: The heart has specialized nodal tissues, such as the sinoatrial (SA) node and atrioventricular (AV) node, which generate and conduct electrical impulses. The SA node is known as the natural pacemaker of the heart, initiating rhythmic contractions. This is a critical intrinsic mechanism for regulating heart activity.
- B. A special neural center in the medulla oblongata: The medulla oblongata in the brainstem contains the cardiovascular center that regulates heart rate and blood pressure. This center has two components: the cardiac accelerator center (sympathetic stimulation increases heart rate) and the cardiac inhibitory center (parasympathetic stimulation decreases heart rate). This represents the extrinsic neural regulation of the heart.
- C. Adrenal medullary hormones: Hormones such as adrenaline and noradrenaline secreted by the adrenal medulla play a vital role in increasing heart rate and the force of cardiac contractions during stress or emergencies, part of the "fight or flight" response.
Other options:
- D. Adrenal cortical hormones: These hormones, such as cortisol and aldosterone, are involved in long-term stress responses and electrolyte balance, but they do not play a direct role in the immediate regulation of cardiac activities. Therefore, this option is incorrect.
2024
Q1: Following are the stages of pathway for conduction of an action potential through the heart (NEET 2024)A. AV bundle
B. Purkinje fibres
C. AV node
D. Bundle branches
E. SA node
Choose the correct sequence of pathway from the options given below
(a) E-C-A-D-B
(b) A-E-C-B-D
(c) B-D-E-C-A
(d) E-A-D-B-C
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a)
The electrical pathway for the conduction of an action potential through the heart is a precisely coordinated process, essential for maintaining the heart's rhythmic beating. To understand this conduction pathway, it’s important to know the roles of the specific components involved:
SA node (Sinoatrial node): Often referred to as the pacemaker of the heart. It initiates the electrical impulse, causing the atria to contract.
AV node (Atrioventricular node): Receives the impulse from the SA node and provides a slight delay, allowing the ventricles time to fill with blood before they contract.
AV bundle (Bundle of His): Transfers the electrical impulse from the AV node to the bundle branches.
Bundle branches: Conducts the impulses through the interventricular septum.
Purkinje fibers: Distribute the electrical impulse throughout the ventricles, stimulating them to contract uniformly and powerfully.
The correct sequence for the pathway of an action potential through the heart follows a route designed to efficiently coordinate the heartbeat starting from the initiation of the action potential to the consequential contraction of the heart muscles. The sequence is:
SA node (E): The pacemaker where the electrical activity originates.
AV node (C): Where the impulse is delayed slightly.
AV bundle (A): Conducts the impulse from the AV node to the bundle branches.
Bundle branches (D): Leads the impulse to the Purkinje fibers.
Purkinje fibers (B): Distributes the impulse throughout the ventricles.
Q2: Match List I with List II (NEET 2024)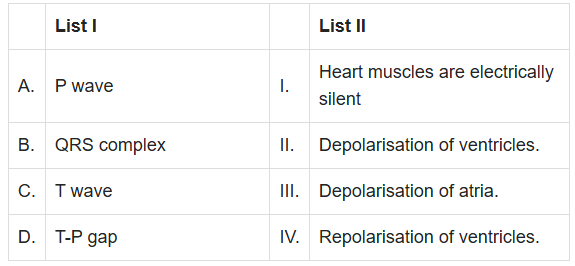
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A-III, B-II, C-IV, D-I
(b) A-II, B-III, C-I, D-IV
(c) A-IV, B-II, C-I, D-III
(d) A-I, B-III, C-IV, D-II
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a)
P wave represents depolarisation of atria.
QRS complex represents depolarisation of ventricles.
T wave represents repolarisation of ventricles.
T-P gap represents the time when heart muscles are electrically silent.
Q3: In standard ECG diagram, the P-wave represents: (NEET 2024)
(a) Depolarisation of the atria
(b) Repolarisation of the ventricle
(c) Depolarisation of the ventricle
(d) End of systole
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a)
The P-wave in the ECG represents the electrical activity associated with depolarisation of the atria.
Q4: Match List-I with List-II (NEET 2024)
| List I | List II |
|---|---|
| A. Tricuspid valves | I. Guards the opening between the right atrium and the right ventricle |
| B. Sino-atrial node | II. Guards the opening between the left atrium and the left ventricle |
| C. Mitral valves | III. Guards the opening of right and left ventricles into pulmonary artery and aorta, respectively |
| D. Semilunar valves | IV. Cardiac musculature in the right upper corner of right atrium |
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A-III, B-IV, C-II, D-I
(b) A-II, B-I, C-IV, D-III
(c) A-III, B-IV, C-I, D-II
(d) A-I, B-IV, C-II, D-III
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (d)
Tricuspid valves guard the opening between right atrium and right ventricle.
Sino-atrial node is the cardiac musculature in the right upper corner of the right atrium.
Mitral valves guard the opening between the left atrium and left ventricle.
Semilunar valves guard the opening of the ventricles into the pulmonary artery and aorta.
Q5: 'Lub' sound of heart is caused by the ___________ (NEET 2024)
(a) Closure of the semilunar valves
(b) Opening of tricuspid and bicuspid valves
(c) Opening of the semilunar valves
(d) Closure of the tricuspid and bicuspid valves
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (d)
The 'Lub' sound occurs due to the closure of the tricuspid and bicuspid (mitral) valves during the start of systole, preventing backflow of blood into the atria.
2023
Q1: Match List I with List II. (NEET 2023)
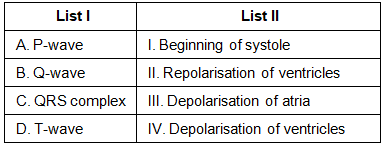
Choose the correct answer from the options given below :
(a) A-III, B-I, C-IV, D-II
(b) A-IV, B-III, C-II, D-I
(c)(d) A-II, B-IV, C-I, D-III
(d) A-I, B-II, C-III, D-IV
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a)
- P-wave: Depolarisation of atria
- Q-wave: Beginning of systole
- QRS complex: Depolarisation of ventricles
- T-wave: Repolarisation of ventricles
Q2: Which of the following are correct? (NEET 2023)
A. Basophils are the most abundant cells of the total WBCs
B. Basophils secrete histamine, serotonin and heparin
C. Basophils are involved in inflammatory response
D. Basophils have kidney shaped nucleus
E. Basophils are agranulocytes
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) D and E only
(b) C and E only
(c) B and C only
(d) A and B only
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (c)
The correct answer is Option C : B and C only.
- Statement A is incorrect. Basophils are actually the least abundant cells of the total white blood cells (WBCs), not the most abundant.
- Statement B is correct. Basophils do secrete histamine, serotonin, and heparin. Histamine and serotonin are involved in inflammatory response, while heparin is an anticoagulant.
- Statement C is also correct. Basophils are involved in the inflammatory response. They release chemicals such as histamine and serotonin that dilate blood vessels and attract other white blood cells to the site of inflammation.
- Statement D is incorrect. Basophils do not have a kidney-shaped nucleus. That description is more appropriate for monocytes, another type of white blood cell.
- Statement E is incorrect. Basophils are not agranulocytes. They are granulocytes, a category of white blood cells characterized by the presence of granules in their cytoplasm. Agranulocytes, which lack visible cytoplasmic granules, include lymphocytes and monocytes.
Q3: Match List-I with List-II
| List-I | List-II |
|---|---|
| (A) Eosinophils | (I) 6-8% |
| (B) Lymphocytes | (II) 2-3% |
| (C) Neutrophils | (III) 20-25% |
| (D) Monocytes | (IV) 60-65% |
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A-IV, B-I,C- II, D-III
(b) A-IV, B-I, C-III, D-II
(c) A-II, B-III, C-IV, D-I
(d) A-II, B-III, C-I, D- IV
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (c)
Neutrophils are the most abundant, around 60-65%.
Monocytes make up about 6-8%.
Lymphocytes make up about 20-25%.
Eosinophils make up about 2-3%.
2022
Q1: Given below are two statements: (NEET 2022 Phase 1)
Statement I: The coagulum is formed of network of threads called thrombins.
Statement II: Spleen is the graveyard of erythrocytes.
In the light of the above statements, choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below:
(a) Both statement I and statement II are incorrect
(b) Statement I is correct but statement II is incorrect
(c) Statement I is incorrect but statement II is correct
(d) Both statement I and statement II are correct
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (c)
- Option (c) is the correct answer because coagulum or clot is formed mainly of a network of threads called fibrins. Hence, Statement I is incorrect.
- RBCs are destroyed in the spleen so spleen is known as the graveyard of erythrocytes. Hence, Statement II is correct.
Q2: Which one of the following statements is correct? (NEET 2022 Phase 1)
(a) The tricuspid and the bicuspid valves open due to the pressure exerted by the simultaneous contraction of the atria
(b) Blood moves freely from atrium to the ventricle during joint diastole
(c) Increased ventricular pressure causes closing of the semilunar valves
(d) The atrio-ventricular node (AVN) generates an action potential to stimulate atrial contraction
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (b)
- Option (a) is incorrect because bicuspid and tricuspid valves open due to pressure exerted by blood present in atria and decrease in pressure in ventricles during ventricular diastole.
- Option (b) is the correct answer because during joint diastole, blood moves freely from atrium to ventricle as atrioventricular valve remain open during joint diastole.
- Option (c) is incorrect because decrease in ventricular pressure, during ventricular diastole closes semilunar valves to produce 'dub' heart sound.
- Option (d) is incorrect because SA node generates action potential to stimulate atrial contraction.
Q3: A unique vascular connection between the digestive tract and liver is called______. (NEET 2022 Phase 2)
(a) Hepato-cystic system
(b) Hepato-pancreatic system
(c) Hepatic portal system
(d) Renal portal system
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (c)
- Option (c) is the correct answer because hepatic portal system is a unique vascular connection between digestive tract and liver.
- Option (a) is not correct because hepato-cystic system is part of biliary pathway where common hepatic duct joins cystic duct of gall bladder.
- Option (b) is incorrect because hepato-pancreatic system is a part of biliary pathway where common bile duct fuses with pancreatic duct.
- Option (d) is incorrect because renal portal system is a unique vascular connection between lower parts of the body and kidney.
Q4: Arrange the following formed elements in the decreasing order of their abundance in blood in humans:
(a) Platelets
(b) Neutrophils
(c) Erythrocytes
(d) Eosinophils
(e) Monocytes
Choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below:
(a) (a), (c), (b), (d), (e)
(b) (c), (a), (b), (e), (d)
(c) (c), (b), (a), (e), (d)
(d) (d), (e), (b), (a), (c) (NEET 2022 Phase 2)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (b)
Option (b) is the correct answer as a healthy adult man has, on an average, 5 millions to 5.5 millions of RBCs (erythrocytes) mm–3 of blood.
Blood normally contains 1,50,000 – 3,50,000 platelets mm–3.
Neutrophils form 60-65 percent of the total WBCs, monocytes form 6-8 percent of the total WBCs and eosinophils form 2-3 percent of the total WBCs. The total WBCs are approximately 6000-8000 mm–3 of blood.
Thus, the formed elements in the decreasing order of their abundance in blood in humans: -
Erythrocytes – Platelets – Neutrophils – Monocytes – Eosinophils
2021
Q1: Persons with 'AB' blood group are called as "Universal recipients". This is due to: (NEET 2021)
(a) Presence of antibodies, anti-A and anti-B, on RBCs
(b) Absence of antibodies, anti-A and anti-B, in plasma
(c) Absence of antigens A and B on the surface of RBCs
(d) Absence of antigens A and B in plasma
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (b)
Individuals with the AB blood group have both A and B antigens on the surface of their red blood cells (RBCs). Since they do not have anti-A and anti-B antibodies in their plasma, they can receive blood from any blood group (A, B, AB, or O) without experiencing an immune reaction. Hence, they are referred to as "universal recipients.
Q2: Which enzyme is responsible for the conversion of inactive fibrinogens to fibrins? (NEET 2021)
(a) Epinephrine
(b) Thrombokinase
(c) Thrombin
(d) Renin
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (c)
- During coagulation of blood, an enzyme complex thrombokinase helps in the conversion of prothrombin (present in plasma) into thrombin.
- Thrombin further helps in the conversion of inactive fibrinogens into fibrins which form network of threads.
- Renin is secreted by JG cells in response to fall in glomerular blood flow, which converts angiotensinogen in blood to angiotensin-I
- Epinephrine or adrenaline is secreted by adrenal medulla in response to stress of any kind and during emergency.
2020
Q1: The QRS complex in a standard ECG represents : (NEET 2020)
(a) Depolarisation of ventricles
(b) Repolarisation of ventricles
(c) Repolarisation of auricles
(d) Depolarisation of auricles
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a)
The QRS complex represents the depolarisation of the ventricles, which initiates the ventricular contraction. The contraction starts shortly after Q and marks the beginning of the systole.
Q2: Match the following columns and select the correct option. (NEET 2020)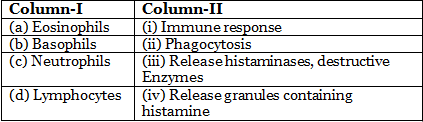
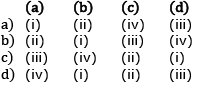
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (c)
Eosinophils are associated with allergic reactions and release histaminase, Basophils secrete histamine, serotonin, heparin etc. and are involved in inflammatory reactions, Neutrophils are phagocytic cells; Both B and T lymphocytes are responsible for immune responses of the body.
2019
Q1: Match the Column - I with Column - II. (NEET 2019)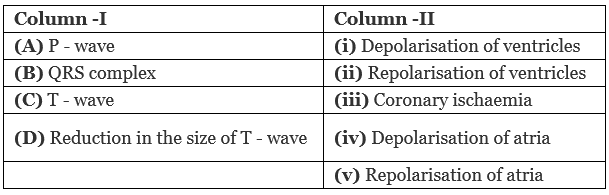
Select the correct option.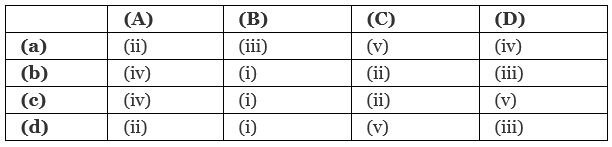
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (b)
P wave represent atrial depolarization.
QRS complex '' ventricular ''.
T - wave '' repolarisation of ventricles.
Reduction in the size of T-wave indicates coronary ischemia.
Q2: What would be the heart rate of a person if the cardiac output is 5 L, blood volume in the ventricles at the end of diastole is 100 mL and at the end of the ventricular systole is 50 mL? (NEET 2019)
(a) 125 beats per minute
(b) 50 beats per minute
(c) 75 beats per minute
(d) 100 beats per minute
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (d)
Cardiac output = Stroke volume × Heart rate
Where stroke volume = End diastolic volume – End systolic volume
= 100 ml – 50 ml
= 50 ml
∴ 5000 mL = 50 mL × Heart rate
⇒ Heart rate = 5000 / 50 = 100 beats per minute.
2018
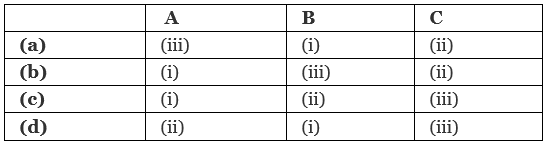
Q1: Match the items given in Column I with those in column II and select the correct option given below. (NEET 2018)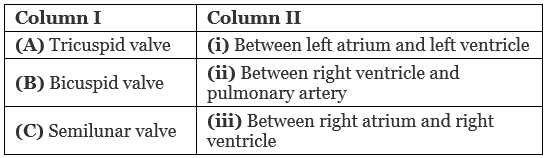
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a)
The opening between the right atrium and the right ventricle is guarded by a valve formed of three muscular flaps or cusps, the tricuspid valve, whereas a bicuspid or mitral valve guards the opening between the left atrium and the left ventricle.
Q2: Match the items given in column I with (hose in column II and select the correct option given below. (NEET 2018)
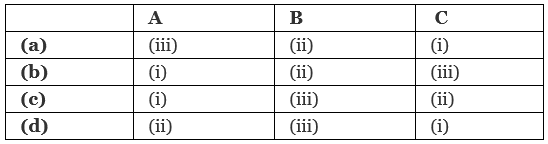
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans. (d)
- Fibrinogen is a protein present in the plasma of the blood. It plays an essential role in blood clotting.
- Antibodies are derived from γ-Globulin fraction of plasma proteins which means globulins are involved in defence mechanisms.
- Albumin is a plasma protein mainly responsible for Blood Colloidal Osmotic Pressure (BCOP).
2017
Q1: Adult human RBCs are enucleated. Which of the following statement(s) is/are most appropriate explanation for this feature? (NEET 2017)
(1) They do not need to reproduce.
(2) They are somatic cells.
(3) They do not metabolise.
(4) All their internal space is available for oxygen transport.
(a) Only (1)
(b) (1), (3) and (4)
(c) (2) and (3)
(d) Only (4)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (d)
Red blood cells of adult humans do not have cell organelles including nucleus, Golgi bodies, mitochondria, ribosomes, etc. It increases the surface area of RBCs and enables them to contain more haemoglobin (the oxygen carrying pigment).
Q2: The hepatic portal vein drains blood to liver from (NEET 2017)
(a) Stomach
(b) Kidneys
(c) Intestine
(d) Heart.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (c)
In hepatic portal system, hepatic portal vein drains blood to liver from intestine.
2016
Q1: Name the blood cells, whose reduction in number can cause clotting disorder, leading to excessive loss of blood from the body. (NEET 2016 Phase 2)
(a) Erythrocytes
(b) Leucocytes
(c) Neutrophils
(d) Thrombocytes
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (d)
Thrombocytes are called blood platelets. They are minute disc-shaped cell fragments in mammalian blood. They are formed as fragments of larger cells found in red bone marrow; they have no nucleus. They play an important role in blood clotting and release thromboxane A2 , serotonin and other chemicals, which cause a chain of events leading to the formation of a plug at the site of the damage, thus preventing further blood loss. A reduction in their number can lead to clotting factors which will lead to excessive loss of blood from the body.
Q2: Serum differs from blood in (NEET 2016 Phase 2)
(a) Lacking globulins
(b) Lacking albumins
(c) Lacking clotting factors
(d) Lacking antibodies.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (c)
Serum is the fluid that separates from blood plasma on centrifugation. Serum is essentially similar in composition to plasma but lacks fibrinogen and other substances that are used in the coagulation process.
Q3: In mammals, which blood vessel would normally carry largest amount of urea? (NEET 2016 Phase 1)
(a) Hepatic Vein
(b) Hepatic Portal Vein
(c) Renal Vein
(d) Dorsal Aorta
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a)
Hepatic Vein, because the liver produces urea and other waste materials and then it pours it all in the right ventricle of the heart for oxygenation. The heart distributes the blood to various parts of the body from here. So the impure blood brought by the Hepatic Vein and other blood vessels get distributed through the aorta. This will automatically imply that the Renal Artery will contain lesser impure blood than the Hepatic Vein.
Q4. Blood pressure in the pulmonary artery is (NEET 2016 Phase1)
(a) Same as that in the aorta.
(b) More than that in the carotid.
(c) More than that in the pulmonary vein.
(d) Less than that in the venae cavae
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (c)
Arteries have higher blood pressure than vein because blood is forced inside them from heart and also their lumen is narrow.
Q5. Which one of the following is correct? (2015)
(a) Serum = Blood + Fibrinogen
(b) Lymph = Plasma + RBC + WBC
(c) Blood = Plasma + RBC + WBC
(d) Plasma = Blood – Lymphocytes
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (c)
- Blood is a connective tissue that is composed of plasma, red blood cells (erythrocytes), white blood cells (leukocytes), and platelets (thrombocytes). Plasma is the liquid component of blood that makes up about 55% of the total blood volume. It is composed of water, proteins, salts, hormones, and other substances. Red blood cells carry oxygen to the tissues and remove carbon dioxide, while white blood cells are responsible for immune responses and fighting infections.
- Serum is the liquid component of blood that remains after the blood has clotted and the clotting factors (including fibrinogen) have been removed. Hence, option (a) is incorrect.
- Lymph is a fluid that is similar in composition to plasma but contains a lower concentration of proteins. It is formed from the interstitial fluid that bathes the body tissues and returns to the bloodstream through lymphatic vessels. Hence, option (b) is incorrect.
- Option (d) is also incorrect as plasma cannot be obtained from the subtraction of lymphocytes from blood.
|
169 videos|525 docs|136 tests
|
FAQs on NEET Previous Year Questions (2016-2025): Body Fluids & Circulation - Biology Class 11
| 1. What is the composition of human blood and its significance in the body? |  |
| 2. How does the circulatory system function in maintaining homeostasis? |  |
| 3. What are the differences between arterial and venous blood? |  |
| 4. What role do platelets play in blood clotting? |  |
| 5. How do the components of blood interact during an immune response? |  |

















