NEET Previous Year Questions (2016-2025): Locomotion & Movement | Biology Class 11 PDF Download
2024
Q1: Three types of muscles are given as a, b and c. Identify the correct matching pair along with their location in human body: (NEET 2024)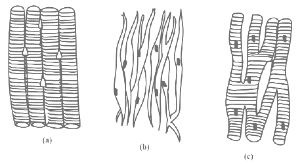 Name of muscle/location
Name of muscle/location(a) (a) Smooth - Toes (b) Skeletal - Legs (c) Cardiac - Heart
(b) (a) Skeletal - Triceps (b) Smooth - Stomach (c) Cardiac - Heart
(c) (a) Skeletal - Biceps (b) Involuntary - Intestine (c) Smooth - Heart
(d) (a) Involuntary - Nose tip (b) Skeletal - Bone (c) Cardiac - Heart
Ans: (b)
The correct answer is option (b) because:
- Skeletal muscles are attached to bones, such as the triceps, and have a striped appearance.
- Smooth muscles are found in the walls of internal organs like the stomach and intestines, and they do not have stripes.
- Cardiac muscles are unique to the heart, are striated, and work involuntarily.
Q2: Match List I with List II : (NEET 2024)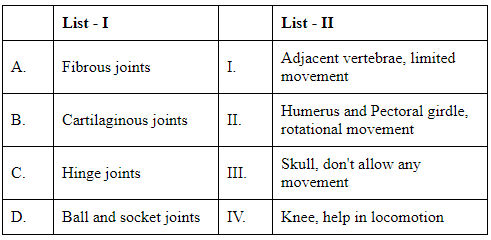
Choose the correct answer from the options given below :
(a) A-IV, B-II, C-III, D-I
(b) A-I, B-III, C-II, D-IV
(c) A-II, B-III, C-I, D-IV
(d) A-III, B-I, C-IV, D-II
Ans: (d)
To match List I (Types of Joints) with List II (Descriptions/Functions), let us consider each type:
Fibrous Joints (A): These joints are found where bones are closely fitted together, allowing very little or no movement, such as in the sutures of the skull. So, Fibrous joints correspond to: III. Skull, don't allow any movement
Cartilaginous Joints (B): These joints occur where the connection between the articulating bones is made up of cartilage, such as between vertebrae in the spine. These allow for limited movement. So, Cartilaginous joints correspond to: I. Adjacent vertebrae, limited movement
Hinge Joints (C): These include joints like the elbow and knee, where movement is primarily in one axis (like opening and closing a door). So, Hinge joints correspond to: IV. Knee, help in locomotion
Ball and Socket Joints (D): These joints, such as the hip and shoulder joints, allow for a wide range of movement including rotational. So, Ball and socket joints correspond to: II. Humerus and Pectoral girdle, rotational movement
The correct matching based on the descriptions and joint types is: A-III, B-I, C-IV, D-II
Q3: Match List-I with List-II (NEET 2024)
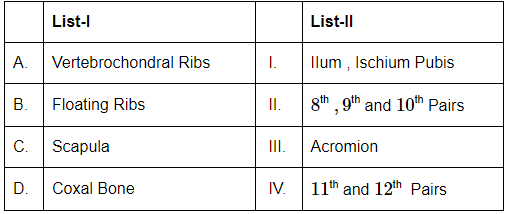 Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A-I, B-III, C-II, D-IV
(b) A-III, B-IV, C-II, D-I
(c) A-II, B-IV, C-III, D-I
(d) A-I, B-IV, C-II, D-III
Ans: (c)
- Vertebrochondral ribs (A): These are the 8th, 9th, and 10th pairs of ribs that are indirectly connected to the sternum through cartilage. This corresponds to (II) in List II.
- Floating ribs (B): These are the 11th and 12th pairs of ribs, which do not have any anterior attachment to the sternum or cartilage, making them "floating." This corresponds to (IV) in List II.
- Scapula (C): The acromion is a bony process on the scapula that forms the highest point of the shoulder. This corresponds to (III) in List II.
- Coxal Bone (D): The coxal bone (also called the pelvic bone) consists of three parts: the ilium, ischium, and pubis. This corresponds to (I) in List II.
Thus, the correct match is:
- A-II: Vertebrochondral ribs are the 8th, 9th, and 10th pairs.
- B-IV: Floating ribs are the 11th and 12th pairs.
- C-III: The acromion is part of the scapula.
- D-I: The coxal bone consists of the ilium, ischium, and pubis.
Q4: Match List-I with List-II: (NEET 2024)
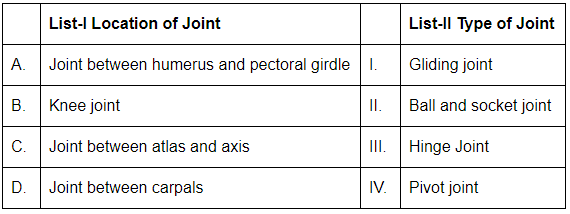
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A-II,B-III,C-IV,D-I
(b) A-III,B-II,C-I,D-IV
(c) A-I,B-IV,C-III,D-II
(d) A-II,B-I,C-III,D-IV
Ans: (a)
- A. Joint between humerus and pectoral girdle: This is a Ball and socket joint (II), which allows rotational movement. It is the shoulder joint.
- B. Knee joint: The knee is a Hinge joint (III), allowing movement in one plane (flexion and extension).
- C. Joint between atlas and axis: This is a Pivot joint (IV), which allows rotation, such as the rotation of the head.
- D. Joint between carpals: The joints between the carpal bones in the wrist are Gliding joints (I), which allow limited sliding movements.
Thus, the correct matches are:
- A-II: Ball and socket joint for the humerus and pectoral girdle.
- B-III: Hinge joint for the knee.
- C-IV: Pivot joint for the atlas and axis.
- D-I: Gliding joint for the carpals.
Q5: Select the correct statements regarding mechanism of muscle contraction. (NEET 2024)
A. It is initiated by a signal sent by CNS via sensory neuron.
B. Neurotransmitter generates action potential in the sarcolemma.
C. Increased Ca++ level leads to the binding of calcium with troponin actin filaments.
D. Masking of active site for actin is activated.
E. Utilising the energy from ATP hydrolysis to form cross bridge.
Choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below:
(a) B, C and E only
(b) C, D and E only
(c) A and D only
(d) B, D and E only
Ans: (a)
- A. It is initiated by a signal sent by CNS via sensory neuron: This statement is incorrect because the signal for muscle contraction is sent from the motor neuron (not sensory neuron) to the muscle.
- B. Neurotransmitter generates action potential in the sarcolemma: This is correct. The neurotransmitter (acetylcholine) released at the neuromuscular junction generates an action potential in the sarcolemma (muscle cell membrane), which triggers muscle contraction.
- C. Increased Ca++ level leads to the binding of calcium with troponin actin filaments: This is correct. When calcium ions (Ca++) are released from the sarcoplasmic reticulum, they bind to troponin, causing a conformational change that allows actin and myosin filaments to interact.
- D. Masking of active site for actin is activated: This statement is incorrect. The active sites on actin are masked by tropomyosin under resting conditions, and unmasked (exposed) when calcium binds to troponin.
- E. Utilizing the energy from ATP hydrolysis to form cross bridge: This is correct. ATP is hydrolyzed to provide energy for the formation of the cross-bridge between actin and myosin, which is essential for muscle contraction.
Thus, the correct statements are B, C, and E. Therefore, the answer is (a).
2023
Q1: Match List I with List II. (NEET 2023)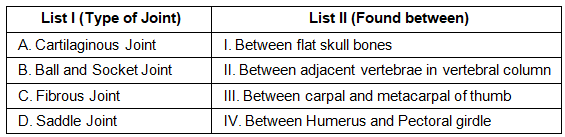
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A-III, B-I, C-II, D-IV
(b) A-II, B-IV, C-I, D-III
(c) A-I, B-IV, C-III, D-II
(d) A-II, B-IV, C-III, D-I
Ans: (b)
(A) Cartilaginous Joint : These joints are connected by cartilage and allow limited movement. They are found between adjacent vertebrae in the vertebral column.
(B) Ball and Socket Joint : These joints consist of a ball-like structure fitting into a socket, allowing for a wide range of movement. They are found between the humerus and the pectoral girdle.
(C) Fibrous Joint : These joints are connected by fibrous connective tissue and allow little or no movement. They are found between flat skull bones.
(D) Saddle Joint : These joints have two bones with concave and convex surfaces that fit together, allowing movement in two planes. They are found between the carpal and metacarpal of the thumb.
Q2: Which of the following statements are correct regarding skeletal muscle? (NEET 2023)
A. Muscle bundles are held together by collagenous connective tissue layer called fascicle.
B. Sarcoplasmic reticulum of muscle fibre is a store house of calcium ions.
C. Striated appearance of skeletal muscle fibre is due to distribution pattern of actin and myosin proteins.
D. M line is considered as functional unit of contraction called sarcomere.
Choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below:
(a) A, B and C only
(b) B and C only
(c) A, C and D only
(d) C and D only
Ans: (b)
Option (B) is the correct answer because statements B and C are only correct statements while A and D are incorrect statements.
Muscle bundles are held together by collagenous connective tissue layer called fascia. Muscle bundles are called fascicles. The portion of the myofibril between two successive ‘Z’ lines is considered as functional unit of contraction called sarcomere.
Q3: Match List - I with List - II (NEET 2023)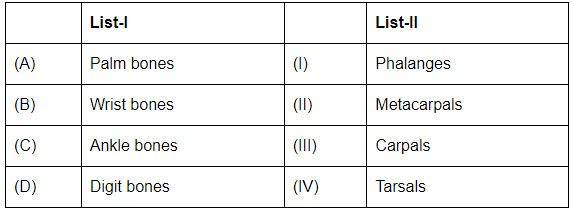 Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) (A)-II (B)-III (C)-I (D)-IV
(b) (A)-IV (B)-I (C)-II (D)-III
(c) (A)-III (B)-IV (C)-I (D)-II
(d) (A)-II (B)-III (C)-IV (D)-I
Ans: (d)
- (A) Palm bones: These are the Metacarpals (II). The metacarpals are the bones in the palm of the hand.
- (B) Wrist bones: These are the Carpals (III). The carpals are the eight bones that form the wrist.
- (C) Ankle bones: These are the Tarsals (IV). The tarsals are the bones in the ankle.
- (D) Digit bones: These are the Phalanges (I). The phalanges are the bones in the fingers and toes.
Thus, the correct match is:
- (A) II: Palm bones are the metacarpals.
- (B) III: Wrist bones are the carpals.
- (C) IV: Ankle bones are the tarsals.
- (D) I: Digit bones are the phalanges.
2022
Q1: Choose the correct statement about a muscular tissue (NEET 2022 Phase 2)
(a) Smooth muscles are multinucleated and involuntary.
(b) Skeletal muscle fibres are uninucleated and found in parallel bundles.
(c) Intercalated discs allow the cardiac muscle cells to contract as a unit.
(d) The walls of blood vessels are made up of columnar epithelium.
Ans: (c)
Option (c) is the correct answer because cardiac muscle fibres have special connections called intercalated discs. These discs enable the muscle cells to work together as a unit. When one cell receives a signal to contract, its neighbouring cells are also stimulated to contract.
Q2: According to the sliding filament theory: (NEET 2022 Phase 2)
(a) The actin filaments slide away from A-band resulting in shortening of sarcomere.
(b) Actin and myosin filaments slide over each other to increase the length of the sarcomere.
(c) Length of A-band does not change
(d) I-band increases in length.
Ans: (c)
- Option (c) is the correct answer because length of A band remains unchanged during muscle contraction.
- Option (a) is incorrect because actin filaments slide towards A-band.
- Option (b) is incorrect because length of sarcomere decreases during muscle contraction.
- Option (d) is incorrect because length of I-band decreases during muscle contraction.
Q3: Gout is a type of disorder which leads to: (NEET 2022 Phase 2)
(a) Weakening of bones due to low calcium level
(b) Inflammation of joints due to accumulation of uric acid crystals
(c) Weakening of bones due to decreased bone mass
(d) Inflammation of joints due to cartilage degeneration
Ans: (b)
- Option (b) is the correct answer as inflammation of joints due to accumulation of uric acid crystals is known as gout.
- Options (a) and (c) are incorrect because weakening of bones due to decreased bones mass, calcium deficiency, decreased levels of estrogen, etc., is termed as osteoporosis.
- Option (d) is incorrect because inflammation of joints due to cartilage degeneration is known as osteoarthritis.
Q4: Given below are two statements : one is labelled as Assertion (A) and the other is labelled as Reason (R).
Assertion (A) : Osteoporosis is characterised by decreased bone mass and increased chance of fractures.
Reason (R) : Common cause of osteoporosis is increased levels of estrogen.
In the light of the above statements, choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below:
(a) Both (A) and (R) are correct and (R) is the correct explanation of (A)
(b) Both (A) and (R) are correct but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A)
(c) (A) is correct but (R) is not correct
(d) (A) is not correct but (R) is correct (NEET 2022 Phase 1)
Ans: (c)
Option (c) is the correct answer as osteoporosis is due to decreased levels of estrogen. Osteoporosis is an age-related disorder characterised by decreased bone mass hence, the chances of fractures increase.
Q5: Which of the following is a correct match for disease and its symptoms? (NEET 2022 Phase 1)
(a) Arthritis - Inflammed joints
(b) Tetany - High Ca2+ level causing rapid spasms
(c) Myasthenia gravis - Genetic disorder resulting in weakening and paralysis of skeletal muscle
(d) Muscular dystrophy - An auto immune disorder causing progressive degeneration of skeletal muscle
Ans: (a)
- Option (a) is the correct answer because Arthritis is inflammation of joints.
- Option (c) is incorrect because myasthenia gravis is an immune disorder affecting neuro-muscular junction leading to fatigue, weakening and paralysis of skeletal muscle.
- Option (d) is incorrect because muscular dystrophy is progressive degeneration of skeletal muscle mostly due to genetic disorder.
- Option (b) is incorrect because tetany is rapid spasms in muscle due to low Ca++ in body fluid.
2021
Q1: Chronic auto immune disorder affecting neuro muscular junction leading to fatigue, weakening and paralysis of skeletal muscle is called as: (NEET 2021)
(a) Gout Muscular dystrophy
(b) Arthritis
(c) Muscular dystrophy
(d) Myasthenia gravis
Ans: (d)
- Option (d) is correct because myasthenia gravis is a chronic auto immune disorder affecting neuromuscular junction leading to fatigue, weakening and paralysis of skeletal muscle.
- Gout is caused due to deposition of uric acid crystals in joints leading to its inflammation.
- Arthritis is the swelling and tenderness of one or more number of joints. It is caused by injury, abnormal metabolism, and genetic makeup.
- Muscular dystrophy is a disease characterised by progressive degeneration of muscle fibres without the involvement of nervous system.
Q2: Match List-I with List-II (NEET 2021)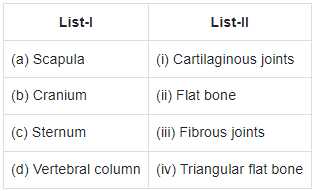
Choose the correct answer from the options given below.
Ans: (b)
- Sternum is a flat bone on the ventral midline of thorax.
- Scapula is a large triangular flat bone situated in the dorsal part of the thorax between the second and the seventh ribs.
- Fibrous joints do not allow any movement.
- This type of joint is shown by the flat skull bones which fuse end-to-end with the help of dense fibrous connective tissues in the form of sutures, to form the cranium.
- In cartilaginous joints, the bones involved are joined together with the help of cartilages.
- The joint between the adjacent vertebrae in the vertebral column is of this pattern and it permits limited movements.
Q3: During muscular contraction which of the following events occur? (NEET 2021)
(a) 'H' zone disappears
(b) 'A' band widens
(c) 'I' band reduces in width
(d) Myosine hydrolyzes ATP, releasing the ADP and Pi
(e) Z-lines attached to actins are pulled inwards
Choose the correct answer from the options given below.
(a) (b), (c), (d), (e) only
(b) (b), (d), (e), (a) only
(c) (a), (c), (d), (e) only
(d) (a), (b), (c), (d) only
Ans: (c)
The correct option is (c) because the length of A-band is retained. During muscle contraction, the following events occur:
(1) The globular head of myosin acts as ATPase and hydrolysis ATP molecule and eventually leads to the formation of cross bridge.
(2) This pulls the actin filament towards the centre of 'A-band'.
(3) The Z-line attached to these actins are also pulled inwards thereby causing a shortening of the sarcomere.
(4) The thin myofilaments move past the thick myofilaments due to which the H-zone narrows. This reduces the length of I-band but retains the length of A-band.
(5) The myosin then releases ADP + Pi, and goes back to its relaxed state.
2020
Q7. Match the following columns and select the correct option (NEET 2020)
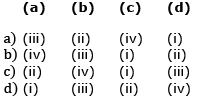
Ans: (b)
- The 11th and 12th pairs of ribs are known as floating ribs because they are not connected to the sternum at the front.
- The acromion is a flat, expanded part of the spine of the scapula.
- The clavicle's lateral end connects with the acromion.
- The scapula is a flat, triangular bone located in the back of the thorax, situated between the 2nd and 7th ribs.
- The glenoid cavity of the scapula connects with the head of the humerus, forming the shoulder joint.
2019
Q1: Select the correct option. (NEET 2019)
(a) There are seven pairs of vertebrosternal, three pairs of vertebrochondral and two pairs of vertebral ribs.
(b) 8th, 9th and 10th pairs of ribs articulate directly with the sternum.
(c) 11th and 12th pairs of ribs are connected to the sternum with the help of hyaline cartilage.
(d) Each rib is a flat thin bone and all the ribs are connected dorsally to the thoracic vertebrae and ventrally to the sternum.
Ans: (a)
Seven pairs of Ribs are vertebrosternal while 8th, 9th and 10th pair of ribs are vertebrochondral and the last 11th, 12th pair are vertebral ribs.
Q2: Which of the following muscular disorders is inherited? (NEET 2019)
(a) Botulism
(b) Tetany
(c) Muscular dystrophy
(d) Myasthenia gravis
Ans: (c)
- Myasthenia gravis is a chronic auto immune disorder. It affects neuromuscular junction leading to fatigue, weakening and paralysis of skeletal muscles.
- Botulism is rare and dangerous type of food poisoning caused by bacterium Clostridium botulinum.
- Tetany is a rapid spasm in muscle due to low Ca2+ in body fluid.
- Muscular dystrophy is a genetic disorder. It is characterized by progressive degeneration of skeletal muscles, which are the muscles that control movement.
2018
Q1: Calcium is important in skeletal muscle contraction because it (NEET 2018)
(a) Binds to troponin to remove the masking of active sites on actin for myosin
(b) Activates the myosin ATPase by binding to it
(c) Detaches the myosin head from the actin filament
(d) Prevents the formation of bonds between the myosin cross bridges and the actin filament.
Ans: (a)
The sarcoplasmic reticulum to release calcium ions into the muscle interior where they bind to troponin, thus causing tropomyosin to shift from the face of the actin filament to which myosin heads need to bind to produce contraction.
2017
Q1: The pivot joint between atlas and axis is a type of (NEET 2017)
(a) Cartilaginous joint
(b) Synovial joint
(c) Saddle joint
(d) Fibrous joint.
Ans: (b)
Pivot joint is a type of synovial joint which provide freely movement between atlas and axis vertebrae of vertebral column.
Q2: Out of ‘X ’ pairs of ribs in humans only ‘Y' pairs are true ribs. Select the option that correctly represents values of X and Y and provides their explanation. (NEET 2017)
| (a) X = 12, T = 5 | True ribs are attached dorsally to vertebral column and sternum on the two ends |
| (b) X = 24 ,Y = 7 | True ribs are dorsally attached to vertebral column but are free on ventral side |
| (c) X = 24, Y = 12 | True ribs are dorsally attached to vertebral column but are free on ventral side |
| (d) X = 12, Y = 7 | True ribs are attached dorsally to vertebral column and ventrally to the sternum |
Ans: (d)
In humans, there are 12 pairs of ribs. Out of these:
- 7 pairs (1st to 7th) are known as true ribs.
- These true ribs are attached:
- Dorsally to the vertebral column
- Ventrally to the sternum
The remaining ribs include:
- 3 pairs of false ribs (8th to 10th) that connect to the 7th rib via cartilage.
- 2 pairs of floating ribs (11th and 12th) that are not attached to the sternum.
This structure forms the rib cage, which protects vital organs in the thoracic cavity.
2016
Q1: Name the ion responsible for unmasking of active sites for myosin for cross-bridge activity during muscle contraction.
(a) Calcium
(b) Magnesium
(c) Sodium
(d) Potassium (NEET 2016 Phase 2)
Ans: (a)
Calcium ion plays an important role in muscle contraction. Calcium ions bind to troponin causing a change in its shape and position. Thus, in turn alters shape and position of tropomyosin to which troponin binds. This shift exposes the active sites on F-actin molecules. Myosin cross-bridge are then able to bind to these active sites.
Q2: Osteoporosis, an age-related disease of skeletal system, may occur due to (NEET 2016 Phase 2)
(a) Immune disorder affecting neuromuscular junction leading to fatigue
(b) High concentration of Ca++ and Na+
(c) Decreased level of estrogen
(d) Accumulation of uric acid leading to inflammation of joints.
Ans: (c)
Osteoporosis is reduction in bone mineral density, resulting in bones that are brittle and liable to fracture. Infection, injury and synovitis can cause localised osteoporosis of adjacent bone. Generalised osteoporosis is common in the elderly and in women after menopause. After menopause the estrogen levels in blood plasma are much reduced. Estrogen helps to regulate bone cells called osteoclasts which are responsible for building new bone. When estrogen levels drop fewer osteoclasts are produced resulting in osteoporosis.
Q16. Lack of relaxation between successive stimuli in sustained muscle contraction is known as (NEET 2016 Phase 1)
(a) Spasm
(b) Fatigue
(c) Tetanus
(d) Tonus
Ans: (c)
- The condition where there is a lack of relaxation between successive stimuli in muscle contraction is known as muscle tetanus.
- This occurs when muscles are stimulated repeatedly without rest.
- As a result, the muscle remains in a state of continuous contraction.
2015
Q1: Which of the following is not a function of the skeletal system? (NEET 2015 / AIPMT 2015)
(a) Storage of minerals
(b) Production of body heat
(c) Locomotion
(d) Production of erythrocytes
Ans: (b)
Production of body heat is caused by the process of metabolism (respiration).
Q2: Which of the following joints would allow no movement? (NEET 2015 / AIPMT 2015)
(a) Cartilaginoius joint
(b) Synovial joint
(c) Ball and Socket joint
(d) Fibrous joint
Ans: (d)
Fibrous joint is an attachment between bones, being held together by fibrous connective tissue. For example- suture between skull bones.
Q3: Sliding filament theory can be best explained as: (NEET / AIPMT 2015 Cancelled Paper)
(a) Actin and Myosin filaments shorten and slide pass each other
(b) Actin and Myosin filaments do not shorten but rather slide pass each other
(c) When myofilaments slide pass each other, Myosin filaments shorten while Actin filaments do not shorten
(d) When myofilaments slide pass each other Actin filaments shorten while Myosin filament do not shorten
Ans: (b)
Sliding filament theory was given by Huxley and Huxley (1954). It states that Actin and Myosin filaments do not become short but rather slide pass each other. Because of sliding of actin filaments over myosin the length of I-band will change.
Q4: Glenoid cavity articulates: (NEET AIPMT 2015 Cancelled Paper)
(a) Scapula with acromion
(b) Clavicle with scapula
(c) Humerus with scapula
(d) Clavicle with acromion
Ans: (c)
- The glenoid cavity connects the humerus to the scapula.
- This joint is crucial for the shoulder movement.
- It allows a wide range of motion in the arm.
2014
Q1: Select the correct matching of the type of the joint with the example in human skeletal system: (NEET 2014 / AIPMT 2014)
Type of joint Example
(a) Cartilaginous joint between frontal and pariental
(b) Pivot joint between third and fourth cervical vertebrae
(c) Hinge joint between humerus and pectoral girdle
(d) Gliding joint between carpals
Ans: (d)
A gliding joint is a common type of synovial joint formed between bones that meet at flat or nearly flat articular surfaces. Gliding joints allow the bones to glide past one another in any direction along the plane of the joint - up and down, left and right, and diagonally. Many gliding joints are formed in the appendicular skeleton between the carpal bones of the wrist; between the carpals and the metacarpals of the palm; between the tarsal bones of the ankle; and between the tarsals and the metatarsals of the foot.
Q2: Stimulation of a muscle fiber by a motor neuron occurs at (NEET 2014 / AIPMT 2014)
(a) the neuromuscular junction
(b) the transverse tubules
(c) the myofibril
(d) the sacroplasmic reticulum.
Ans: (a)
- A motor neuron sends signals to muscle tissue.
- A motor unit consists of one motor neuron and the muscle fibres it controls.
- The area where the motor neuron connects with the muscle fibre is called the neuromuscular junction or motor end plate.
- When a signal reaches this junction, it releases a neurotransmitter, which generates an action potential in the muscle fibre.
- This action potential triggers the release of calcium ions from the sarcoplasmic reticulum.
- The increase in calcium levels allows myosin to bind to actin, leading to muscle contraction.
|
150 videos|399 docs|136 tests
|
FAQs on NEET Previous Year Questions (2016-2025): Locomotion & Movement - Biology Class 11
| 1. What is the difference between osteoblasts and osteoclasts in bone remodeling? |  |
| 2. How do muscles work together to produce movement in the human body? |  |
| 3. What role do ligaments play in locomotion and movement? |  |
| 4. How does the structure of a joint impact its range of motion? |  |
| 5. What are some common injuries associated with locomotion and movement? |  |

















