Class 10 English Grammar - Noun its Classifications Part 2
Noun: Case
Cases in nouns tell about the position and role of a noun in a sentence.
There are four kinds of cases:
- Nominative
- Accusative
- Possessive
- Dative

Let us discuss these cases in detail. Each noun case is made bold.
Nominative Case
If a noun or a pronoun is used as the subject, it is called nominative use.
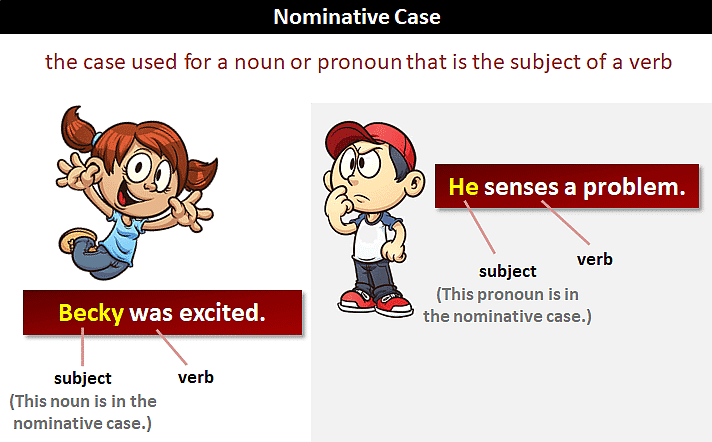
For example,
She is reading.
↓
Nominative
Mohan is walking
↓
Nominative
Accusative Case
If a noun or pronoun is used as the object, called accusative use.
For example,
I like her.
↓
Accusative
That is Anjali.
↓
Accusative
Possessive Case
A possessive case shows the possession, ownership, or authority of a noun. That case shows a relationship between two nouns or between a noun and a pronoun.
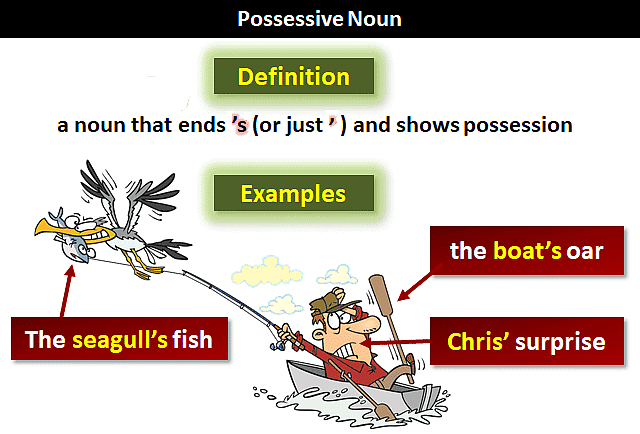
For example,
Rahul's book.
↓
possession
Sharukh's brother.
↓
relation
Rules to write possessive cases:
- At the end of a singular noun we put —'s for possessive case :
- For example,
Rajiv's book, Meena's mother, President's bodyguard.
- For example,
- —s ending plural nouns take only (’):
- For example
Boys' hostel, Girls' school
But,
Women's college, Men's competition, Children's park
- For example

- In compound nouns, we use possessive with the last term:
- For example,
Commander-in-chief's order
Mother-in-law's house
Father-in-law's problem
Engineer-in-chiefs' office
Brother-in-law's wife.
- For example,
- If possessive is used before than, it should be used after than:
- For example,
Ravi's sister is more beautiful than Karan. —wrong
Ravi's sister is more beautiful than Karan's. —correct.
Kareena's husband is more handsome than Karishma. — wrong
Kareena's husband is more handsome than Karishma's. — correct
Rohan's brother is more intelligent than Mohan. —wrong
Rohan's brother is more intelligent than Mohan's. —correct
- For example,
Dative Case
A noun is said to be in a dative case if it is the Indirect object of the verb. (Indirect object of the verb is the noun for whom or for which the action of the verb is carried out). There should not be a preposition before the indirect object because in that case, it will be the object of that preposition. For example,
Get him a pen
↓
Dative
The postman brought me a letter.
↓
Dative
Noun: Gender
What is gender?
In grammar, there is a classification of a noun or pronoun as masculine or feminine. Therefore, gender is the sexual classification in grammar. Gender comes from Latin genus, meaning kind or sort.
- We know that living beings are of either the male or the female sex.
 The words in the first column under A are the names of all male animals.
The words in the first column under A are the names of all male animals. - And, the words in the second column under B are the names of all female animals.
- A noun that denotes a male animal is said to be of the Masculine Gender.
- A noun that denotes a female animal is said to be of the Feminine Gender.
- Besides, Masculine Gender and Feminine Gender, there is a gender which is said to be the Common Gender. In this, a noun that denotes either a male or a female is included.
- As,
- Parent, child, pupil, servant, friend, thief, relation, enemy, cousin, orphan, student, person, baby, guardian, monarch, infant, neighbour, tutor etc.
- A noun that denotes a thing that is neither male nor female is said to be of Neuter Gender.
[Neuter means neither, i.e., neither male nor female.]
- As,
- Book, pen, table, chair, room, wall, tree, paper, ball, sword, radio, telephone, bag, cloth, cigarette, music, key, bus, auto, motor, song etc.
- Masculine Gender is often applied to objects remarkable for strength, violence, sublimity and superiority.
- As,
- Death, time, winter, summer, the sun, fear, love etc.
- Feminine Gender is often applied to objects remarkable for beauty, gentleness, gracefulness, fertility, softness, sweetness and weakness etc.
- As,
- The moon, the earth, spring, liberty, autumn, nature, charity, church, hope, justice, mercy, peace, religion, spring, truth, virtue, names of countries, locomotive engines, cars, ships and of arts and sciences.
Note:
- Some Masculine nouns are used in the Common Gender.
As, Actor, Advocate, Author, Chairman, Doctor, Hound, Lawyer, Man, Painter, Poet, Teacher, Tutor, Hunter - Some Feminine nouns are used in the Common Gender.
As, Cow, Duck, Bee - Some Feminine nouns have no corresponding Masculine forms.
As,- House-wife (mistress of the house)
- Virgin (an unmarried woman)
- Flirt (woman pretending to make love) Virago (a turbulent woman)
- Dowager (widow with late husband's property)
- Siren (an enticing woman)
- Brunette (a dark-complexioned woman)
- Prude (a woman of a affected modestry)

- Some Masculines have no corresponding Feminines.
As,- Captain, Judge, Knight, Squire, Parson
|
20 videos|110 docs|18 tests
|
FAQs on Class 10 English Grammar - Noun its Classifications Part 2
| 1. What is the definition of 'case' in English grammar? |  |
| 2. What are the different types of noun cases? |  |
| 3. How does gender classification in nouns work? |  |
| 4. Why is understanding noun cases and gender important in English grammar? |  |
| 5. Can you provide examples of nouns in different cases and genders? |  |

|
Explore Courses for Class 10 exam
|

|
 The words in the first column under A are the names of all male animals.
The words in the first column under A are the names of all male animals.

















