Verb - 2 | English Grammar Basic - Class 10 PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Person And Number |

|
| Participle |

|
| Gerund |

|
| Past Tense and Past Participle |

|
Person And Number
Person
Person refers to the relationship that an author has with the text that he or she writes, and with the reader of that text. English has three persons (first, second, and third).
- The First Person
- The Second Person
- The Third Person
As,
(a) I read.
(b) You read.
(c) He reads.
- In the first sentence, I read, the subject is of the First Person, therefore, the verb is also of the First Person.
- In the second sentence, You read, the subject is of the Second Person, therefore the verb is also of the Second Person.
- In the third sentence, He reads, the subject is of the Third Person, therefore, the verb is also of the Third Person.
Thus, we see that the verb takes the same Person and its subject or, that the verb agrees with its subject is Person.
Number
There are two numbers: singular and plural. The table below separates pronouns according to number. You may notice that the second person is the same for both singular and plural: you.
As,
(a) He listens
(b) They listen
This is because of the difference in Number of the subjects.
Therefore,
- In the first sentence He listens, we find the Subject is singular and so, the verb is also singular.
- In the next sentence They listen, we find the subject is plural and so, the verb is also plural.
Thus, we see that the verb takes the same Number as its subject or, that the verb agrees with its subject in Number.
Participle
A participle is that form of the verb which partakes of the nature both of a verb and of an adjective.
As,
- Hearing the song, the girl woke up. Here, hearing qualifies the noun girl as an adjective does.
- Therefore, learning partakes of the nature of both a verb and an adjective and is called participle.
There are the two kinds of participle:
1. Present Participles are those which ends in–ing and represents an action as going on or incomplete or imperfect.
As,
- We met a girl carrying a bunch of flowers.
- The blind man, thinking all was safe, attempted to cross the road.
- Loudly knocking at the door, he demanded admission.
Past Participles are those forms of verbs which represents a completed action or state of the thing spoken of.
As,
- Deceived by his girl, he lost all hope.
- Time misspent is time lost.
- We saw a few trees, ladden with fruit.
- Driven by hunder, he stole a piece of cake.
Note: The past participle usually ends in -ed,-d,-t, -en, -n etc.
The participles are used as simple qualifying adjectives in front of a noun and are thus called Participial Adjectives.
As,
- A rolling stone gathers no moss.
- He played a losing game.
- A burnt child dreads the fire.
- He wears a worried look.
- Education is the most pressing need of our country.
- A lying witness ought to be punished.
Thus, we recall that:
- A participle is a verbal adjective.
- A participle may govern a noun or pronoun, like a verb.
- A participle may be modified by an adverb, like a verb.
- A participle may qualify a noun or pronoun, like an adjective.
- A participle may be compared, like an adjective.
Gerund
A Gerund is that form of the verb which ends in -ing and has the force of a Noun and a Verb.
As,
- Hunting deer is a favourite sport in India.
- I like writing poetry.
In these sentences, the gerund, like a noun, is the subject of a verb, but like a verb, it also takes an object, thus, showing it has also the force of a verb.
Again,
- He is fond of collecting stamps. In this sentence, the gerund like a noun as governed by a preposition, but like a verb, it also takes an object.
- Both the gerund and the infinitive have the force of a noun and a verb and also their usages are same. Thus, in many sentences, either of them may be used without any special difference in meaning
As,
- To see is to believe.
- Seeing is believing.
- To give is better than to receive.
- Giving is better than receiving.
Uses of Gerund
The Gerund has the force of a noun and a verb. It is thus a Verbal-Noun and may be used as:
1. Subject of a verb
As,
- Seeing in believing
- Hunting deer is a favourite sport in India.
2. Object of a transitive verb
As,
- Stop talking.
- Children love making noise.
- I like writing poetry.
3. Object of a preposition
As,
- I am tired of waiting.
- He is fond of fishing.
- He was punished for telling a lie.
4. Complement of a verb
As,
- Writing is learning.
- What I most dislike is smoking.
5. Absolutely
As,
- Playing cards being his aversion, we did not play bridge.
- Moreover, the Present Participle has the force of an adjective and a verb. It is called a Verbal Adjective.
As,
- Walking along the road, he noticed a big elephant.
- Seeing, he believed.
Past Tense and Past Participle
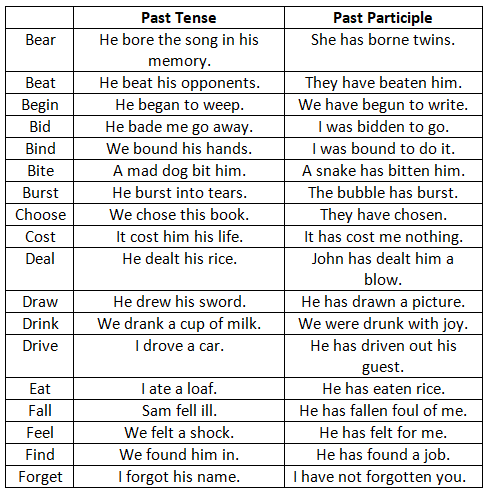
Past Participle forms like - bounden, clove, drunken, gotten, graven, hewn, hidden, molten, shorn, shrunken, stricken and sunken etc., are used as Adjectives only.
As,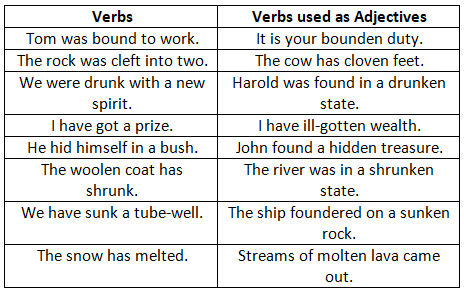
|
20 videos|143 docs|18 tests
|
FAQs on Verb - 2 - English Grammar Basic - Class 10
| 1. What is the difference between a gerund and a participle? |  |
| 2. How do you form the past tense of regular verbs? |  |
| 3. What are the examples of past participles for irregular verbs? |  |
| 4. Can gerunds and participles be used in the same sentence? |  |
| 5. How do I identify the subject of a gerund? |  |















