Tense - 2 | English Grammar Basic - Class 10 PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| The Past Tense |

|
| The Future Tense |

|
| Conjugation of Verb ‘To be’ |

|
| Modal |

|
| Uses of Modals |

|

The Past Tense
1. Past Indefinite Tense
- The Past Indefinite, also known as the Simple Past Tense, is used to describe actions that were completed in the past. For example:
- The boy left school an hour ago.
- I did this work a week ago.
- The ship sailed last week.
- It is also used to indicate past habits. For instance:
- He practiced many hours every day.
- She always sang a romantic song.
2. Past Continuous Tense
- The Past Continuous Tense is employed to signify an action that was ongoing at a particular time in the past. For instance:
- The light went out while I was reading.
- We were watching television all evening.
- It is also used with words like always and continuallyto describe persistent habits in the past. For example:
- He was always refusing.
- She was continually neglecting her duty.
3. Past Perfect Tense
- The Past Perfect Tense is utilized to depict an action that was completed before a specific moment in the past. For example:
- I met him in 1995.
- I had seen him five years before.
- I called him at 5 am.
- I found him at 7 am.
- When two actions occurred in the past, it is sometimes necessary to indicate which action happened earlier. For instance:
- By the time I reached the station, the train had already started.
- I had completed my work before the officer came.
- I had done my work when Seema came to see me.
4. Past Perfect Continuous Tense
- The Past Perfect Continuous Tense is used for an action that started before a certain point in the past and continued up to that time. For example:
- He had been serving the institution for the last year.
- At that time, he had been writing a short story for three months.
The Future Tense
1. Future Indefinite Tense
The Future Indefinite or Simple Future Tense is used for an action that has still to take place.
As,
- I shall meet him tomorrow.
- Day after tomorrow will be Friday.
2. Future Continuous Tense
(i) The Future Continuous Tense represents an action as going on at some time in Future time.
As,
- I shall be writing the letter then.
- When I go into the class, the teacher will be teaching.
(ii) The Future Continuous Tense is also used for representing future events that are planned.
As,
- I shall be waiting for you till 4 pm.
- She will be meeting me next week.
3. Future Perfect Tense
The Future Perfect Tense is used to indicate the completion of an action by a certain future time.
As,
- I shall have done my homework by that time.
- Before you go to meet him, he will have left the office.
4. Future Perfect Continuous Tense
The Future Perfect Continuous Tense indicates an action represented as being in progress over a period of time that will end in the future.
As,
- By next January, we shall have been living in Delhi for three years.
- When he completes his school, he will have been studying at NIIT.
Conjugation of Verb ‘To be’
1. Present Indefinite Tense
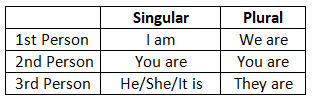
2. Present Continuous Tense
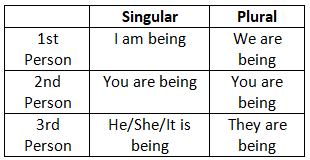
3. Present Perfect Tense
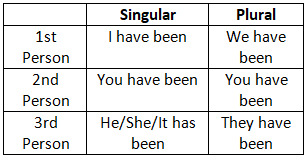
4. Present Perfect Continuous Tense
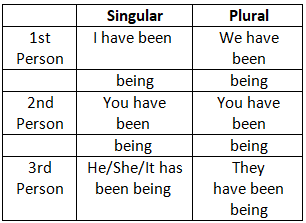
5. Past/Indefinite Tense
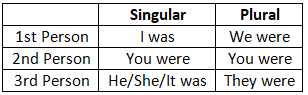
6. Past Continuous Tense
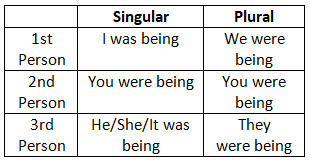
7. Past Perfect Tense
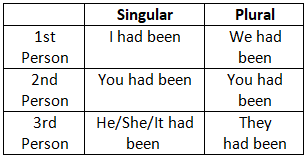
8. Past Perfect Continuous Tense
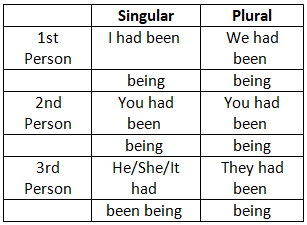
9. Future Indefinite Tense
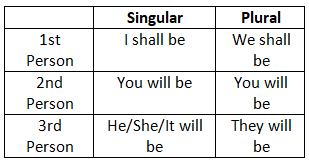
10. Future Continuous Tense
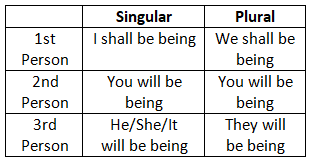
11. Future Perfect Tense
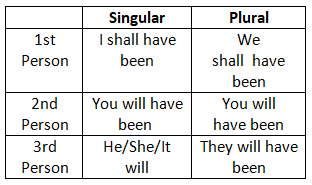
12. Future Perfect Continuous Tense
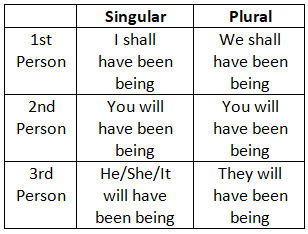
Modal

Modal verbs are a type of auxiliary verb that express various attitudes such as permission, possibility, and necessity. They are used to convey different shades of meaning in a sentence. Here are some examples:
- Modal Auxiliaries: These include verbs like Can, Could, May, Might, Shall, and Should.
- Other Modals: This category includes verbs like Will, Would, Must, Ought, Need, and Dare.
Modal verbs are also referred to as Modal Auxiliaries.
Uses of Modals
1. Can, Could
Can is a Principal verb followed by an Infinitive with its to omitted. Its Past Tense is could but, it has no Past Participle. It means ability or capacity.
As,
- I can help you.
↓
am able - I can swim across the river.
↓
have capacity
2. May, Might
May is used in expressing doubt or in asking or giving permission.
As,
- He may catch the train (doubt).
- May I go out? (asking permission).
- You may sleep now (permission).
- May is used to express possibility in affirmative sentences.
As,
- It may rain tomorrow.
- He may be at home.
- May is also used to express a wish.
As,
- May you live long!
- May success attend you!
- Might is the past tense of may and is used to express a degree of dissatisfaction or reapproach.
As,
- He cried aloud so that his friends might hear him.
- You might see me tomorrow.
- You might pay a little more attention to your appearance.
- Might is also used in polite request.
As,
- Might I have your umbrella for a day?
3. Shall, Should
Shall is used in the first person to express pure future.
As,
- I shall do this work.
- When shall we visit the zoo?
- Shall I do it for you?
- Tomorrow we shall meet our uncle.
- Shall is used to express command, desire, promise or threat etc., in second and third person.
As,
- Shall you go tomorrow? (desire).
- He shall not enter my house (command).
- You shall have a surprise tomorrow (promise).
- You shall be punished for unfair means in examination (threat).
4. Will, Would
Will is used in the second and third persons to express pure future.
As,
- Tomorrow will be Sunday.
- You will see that I am correct.
- Will is used to express volition.
As,
- I will (= am willing) to carry your luggage.
- I will (= promise to) try to do better the next time.
- Will is used to express characteristic habit.
As,
- He will talk about nothing but politics.
- She will sit for hours watching the television.
- Will is used to express assumption or probability.
5. Must, Ought
- Must is used to express:
- (i) Necessity or Obligation:
- We must obey our parents.
- One must do his duty.
- (ii) Fixed determination:
- I must have my way in this matter.
- He must be fifty now.
Ought
- Ought is followed by an infinitive and expresses:
- (i) Moral obligation, duty or desirability:
- You ought to have come in time.
- We ought to love our parents.
6. Need not, Dare not
Need is commonly used in negatives, which denote necessity or obligation.
As,
- He need not go there. (It was not necessary for him to go.)
- I need not have bought it. (It was not necessary for me to buy it, but I bought it.)
- Dare is generally used in negative sentences, meaning be brave enough to.
As,
- He dare not take such a step?
- He dared not to do it.
7. Understanding "Do," "Does," "Did," and "Used To"
- Objective: Do, Does, Did are auxiliary verbs used to form negatives, questions, and emphatic statements in the present and past simple tenses.
- They also replace a previous ordinary verb.
- Used to indicates a past habit or state that no longer exists.
(i) Forming Negatives and Questions
- Present Simple: Do and Does are used to create negatives and questions.
- Past Simple: Did is used for negatives and questions.
Examples:
- Negative: He doesn't talk.
- Question: Does she talk?
(ii) Avoiding Repetition
Use do, does, or did to avoid repeating a verb.
Examples:
- Do you know her? Yes, I do.
- She sings well. Yes, she does.
- You called him, didn't you?
- He eats apples and so do you.
(iii) Emphasizing Positivity
- Do can stress the positive nature of a statement.
Examples:
- You do go there.
- I told him not to do it, but he did.
(iv) Understanding "Used To"
- Used is followed by the infinitive to.
- Used to signifies a habit or situation that has ceased.
Examples:
- I used to live there during the 1980s.
- There used to be a house in the garden.
Used to functions as a semi-modal verb.
|
20 videos|143 docs|18 tests
|
FAQs on Tense - 2 - English Grammar Basic - Class 10
| 1. What are the different tenses discussed in the article? |  |
| 2. Can you provide an example of the conjugation of the verb 'to be'? |  |
| 3. What is a modal verb and how is it used in the English language? |  |
| 4. How can modals be used in sentences to express different meanings? |  |
| 5. How can understanding tenses and modals improve English language skills? |  |





















