Introduction to Pericyclic Reactions | Organic Chemistry PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Pericyclic Reactions |

|
| Electrocyclic Reactions |

|
| Cycloaddition Reactions |

|
| Cheletropic Reactions |

|
| Sigmatropic Rearrangements |

|
| Group Transfer Reactions |

|
Pericyclic Reactions
All types of pericyclic reactions are concerted and involve a cyclic transition state without any intermediate formed during the reaction.
- A pericyclic reaction is characterized as a change in bonding relationships that takes place as a continuous, concerted reorganization of electrons.
- The term "concerted" specifies that there is one single transition state and therefore no intermediates are involved in the process. To maintain continuous electron flow, pericyclic reactions occur through cyclic transition states.
- More precisely: The cyclic transition state must correspond to an arrangement of the participating orbitals which has to maintain a bonding interaction between the reaction components throughout the course of the reaction
The Five Major Classes of Pericyclic Reactions
Electrocyclic Reactions
Electrocyclic reactions are intramolecular pericyclic reactions that involve the rearrangement of π-electrons in an open conjugated system leading to the formation of a cyclic product with a new σ bond at the expense of a π-bond.

- Electrocyclic ring closure is the creation of a new sigma bond at the expense of the terminal π orbitals of a conjugated π system.
- There is a corresponding reorganization of the conjugated pi system. We classify the reaction according to the number of electrons involved.

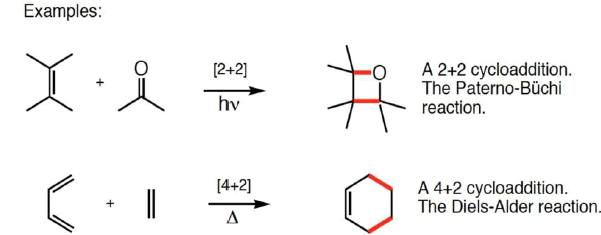
Cycloaddition Reactions
Cycloaddition reactions involve the formation of a cyclic product due to the addition of two different π bond-containing components, which are joined by newly formed two σ bonds at their ends at the expense of two π bonds.
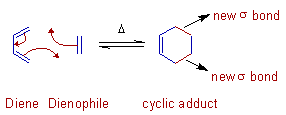
- Involves the union of two smaller, independent π systems.
- Sigma bonds are created at the expense of π bonds.
- Referred to as [m + n] additions when a system of m conjugated atoms combines with a system of n conjugated atoms.
- A cycloreversion is simply the reverse of a cycloaddition.
Cheletropic Reactions
Cheletropic reactions are a special class of cycloadditions or retro-cycloadditions in which the two σ-bonds are either made or broken to the same atom.

- A special group of cycloaddition/cycloreversion reactions.
- Two bonds are formed or broken at a single atom.
- The nomenclature for cheletropic reactions is the same as for cycloadditions.



Sigmatropic Rearrangements
Involves migration of a sigma bond from one position in a conjugated system to another position in the system, accompanied by reorganization of the connecting π bonds.

- The number of π and sigma bonds remains constant.
- The rearrangement is an [m, n] shift when the sigma bond migrates across m atoms of one system and n atoms of the second system.

Group Transfer Reactions
The concerted transfer of a group from one molecule to another due to concomitant movement of a σ-bond (from one molecule to another) and formation of a new σ-bond (between two molecules) at the expense of a π-bond is generally referred to as group transfer pericyclic reaction
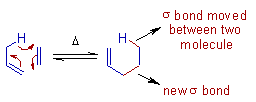
- For E.g. The Ene reaction between propene and ethene to give 1-pentene is a classic example of group transfer reaction.


|
35 videos|92 docs|46 tests
|
FAQs on Introduction to Pericyclic Reactions - Organic Chemistry
| 1. What are pericyclic reactions in chemistry? |  |
| 2. What are some examples of pericyclic reactions? |  |
| 3. How do pericyclic reactions differ from other types of organic reactions? |  |
| 4. What is the significance of pericyclic reactions in organic chemistry? |  |
| 5. How can pericyclic reactions be used in the design of new pharmaceuticals? |  |

|
Explore Courses for Chemistry exam
|

|


















