Chapter 22 - Mensuration - III (Part - 4), Class 8, Maths RD Sharma Solutions | RD Sharma Solutions for Class 8 Mathematics PDF Download
PAGE NO 22.27:
Question 37:
Find the cost of sinking a tubewell 280 m deep, having diameter 3 m at the rate of Rs 3.60 per cubic metre. Find also the cost of cementing its inner curved surface at Rs 2.50 per square meter.
ANSWER:
Cost of sinking a tube well = Volume of the tube well × Cost of sinking a tube well per cubic meter
= 22/7 x (1.52) x (280) m³ x Rs 3.6/m³ = Rs 7128.
Cost of cementing = Inner surface area of the tube well × Cost of cementing per square meter
= ((2 x 22/7 x 1.5x 280) m2) x Rs 2.5/m2 = Rs 6600
Question 38:
Find the length of 13.2 kg of copper wire of diameter 4 mm, when 1 cubic cm of copper weighs 8.4 gm.
ANSWER:
Since we know the weight and the volume of copper, we can calculate its density.
density of copper = 
If the weight of copper wire is 13.2 kg and the density of copper is 8.4 g/cm³, then:
Volume = Weight / Density = 13.2 kg x 1000 gram/kg / 8.4 gram/cm³ = 1571.43 cm³
The radius of copper wire is 2 mm or 0.2 cm.
So, the length of the wire can be determined in the following way:
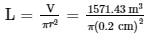 = 125050.01 cm = 125 m
= 125050.01 cm = 125 m
Thus, the length of 13.2 kg of copper is 125 m.
Question 39:
2.2 cubic dm of brass is to be drawn into a cylindrical wire 0.25 cm in diameter. Find the length of the wire.
ANSWER:
Let r cm be the radius of the wire and h cm be the length of the wire.
Volume of brass = Volume of the wire
We know that the volume of brass = 2.2 dm³ = 2200 cm³
Volume of the wire = πr²h = (0.125 cm)2 (h)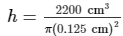 = 44800 cm = 448 mThus, length of the wire is 448 m.
= 44800 cm = 448 mThus, length of the wire is 448 m.
Question 40:
A well with 10 m inside diameter is dug 8.4 m deep. Earth taken out of it is spread all around it to a width of 7.5 m to form an embankment. Find the height of the embankment.
ANSWER:
Let r m be the radius and d m be the depth of the well that is dug.
Volume of the well = πr2d = π(5 m)2(8.4 m) = 660 m³
An embankment has the shape of hollow cylinder with thickness. Its inner radii is equal to the well's radii,
i.e. r = 5 m, and its outer radii is R = (5 + 7.5 ) = 12.5 cm.
Then, the volume of the embankment = πh(R − r2)
Volume of the well = Volume of the embankment
659.73 m³ = πh((12.5 m)2 − (5 m)2)
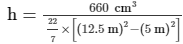 = 1.6 m
= 1.6 m
Hence, the height of the embankment is 1.6 m.
Question 41:
A hollow garden roller, 63 cm wide with a girth of 440 cm, is made of 4 cm thick iron. Find the volume of the iron.
ANSWER:
Here, R = Outer radius
r = Inner radius
t = Thickness = 4 cm
w = Width = 63 cm
Girth = 440 cm = 2πR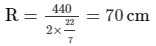 r = R − t = 70 cm − 4 cm = 66 cm
r = R − t = 70 cm − 4 cm = 66 cm
Volume of the iron = π (R2 − r2) w = 22/7 − (702 − 662) − (63) = 107712 cm³
Hence, volume of the iron is 107712 cm³.
Question 42:
What length of a solid cylinder 2 cm in diameter must be taken to recast into a hollow cylinder of length 16 cm, external diameter 20 cm and thickness 2.5 mm?
ANSWER:
Here, r = Internal radius
R = External radius = 10 cm
h = Length of the cylinder
t = Thickness = 0.25 cm
Volume of the hollow cylinder = πh(R2 - r2)
= π (16) (102 - (10-0.25)2) = 79 π cm³
Volume of the solid cylinder = Volume of the hollow cylinder
We know that the radius of the solid cylinder is 1 cm.
∴ π(12)h = 79 π
h = 79 cm
Hence, length of the solid cylinder that gives the same volume as the hollow cylinder is 79 cm.
Question 43:
In the middle of a rectangular field measuring 30m × 20m, a well of 7 m diameter and 10 m depth is dug. The earth so removed is evenly spread over the remaining part of the field. Find the height through which the level of the field is raised.
ANSWER:
Let r m be the radius and h m be the depth of the well that is dug.
Volume of the well = ππr2h = 22/7 × (3.5 m)2 × (10 m) = 385 m³
Volume of the well = Volume of the rectangular field
Volume of the rectangular field = 385 m³ = 30 m × 20 m × height
Height = 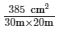 = 0.641 m = 64.1 cmHence, the height through which the level of the field is raised is 64.1 cm.
= 0.641 m = 64.1 cmHence, the height through which the level of the field is raised is 64.1 cm.
FAQs on Chapter 22 - Mensuration - III (Part - 4), Class 8, Maths RD Sharma Solutions - RD Sharma Solutions for Class 8 Mathematics
| 1. What is Mensuration and why is it important in mathematics? |  |
| 2. How can I find the volume of a cylinder using mensuration? |  |
| 3. What is the difference between surface area and volume in mensuration? |  |
| 4. How can I calculate the area of a triangle using mensuration? |  |
| 5. Can mensuration be used to solve problems related to 3D objects? |  |

|
Explore Courses for Class 8 exam
|

|

















