Class 8 Science Chapter 12 Question Answers - Some Natural Phenomena
Short Answer Type Questions
Q1: Why does a plastic comb rubbed with dry hair attract tiny pieces of paper?
Ans: Plastic comb gets electrically charged due to rubbing and therefore it attracts tiny pieces of paper which are neutral, as charged body can attract an uncharged body.
Q2: Why a copper rod cannot be charged by friction, if held by hand?
Ans: Copper is a conducting object, as soon as it gets charged by rubbing with another material, the electric charge produced on its surface flow through our hand and body into the earth and it remains uncharged.
Q3: What do you mean by earthing? What is the purpose of providing it in buildings?
Ans: The process of transferring of charge from a charged object to the earth is called earthing. For our safety, most of the electrical appliances and the mains of the house are connected to earth, so that we can be prevented from getting an electric shock.
Q4: Suppose you are at home and an earthquake strikes. What precaution would you take to protect yourself?
Ans: The precautions that should be taken are as follow:
- Take shelter under a table and stay there only, till the shaking stops.
- Stay away from the objects which are tall and heavy that may fall on you.
- If you are on bed, do not get up and remain there only and protect your head with pillow.
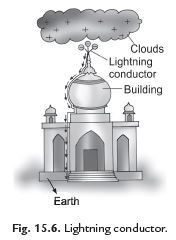
Q5: What do you mean by lightning conductor?
Ans: Lightning conductor is a device used to protect buildings from the damaging effects of lightning. It runs from the top to the bottom, along the outer wall of the buildings or any other object, which is to be protected. If lightning strikes the buildings or any other objects, then the lightning conductor provides an easy and direct path for the lightning bolt to pass to the ground without effecting them.
Q6: A crackling sound is heard while taking off sweater during winters. Explain the reason behind this.
Ans: As we know that electrical charges that are generated through friction are static, i.e they do not move by themselves and Motion of charges constitutes an electric current. When we take off our sweater there is a motion between the charges on the sweater and our body that produces electric current, which produces a crackling sound. Infact we can see a spark if we take off the sweater in the dark.
Q7: What are tectonic plates?
Ans: The earth's lithosphere is fragmented into many pieces. Each fragment is called a plate, also called tectonic plate. These plates are in continuous motion i.e. they float over hot magma.
Q8: Explain seismograph.
Ans: Tremors or vibrations caused by the earthquakes which travel in the form of waves within the earth or along the earth's surface, are called seismic waves. Seismograph is an instrument which records these seismic waves.
Q9: What happens when we touch the metal cap of a charged electroscope with our finger? What is the name of this process?
Ans: The leaves of an electroscope collapse as soon as we touch the metal cap with hand because the leaves of the charged electroscope lose charge to the earth through our body in other words leaves are discharged. This process is known as Earthing.
Q10: What is the nature of charge on the metal cap and on the leaves of the uncharged electroscope when a negatively charged body is brought in contact with its metal cap?
Ans: When a negatively charged body is brought in contact with the metal cap of an uncharged electroscope, both the metal cap and the leaves acquire a negative charge.
Q11: What are the uses of an electroscope?
Ans: An electroscope can be used for following purposes:
- To detect & measure the charge on a body.
- To determine the nature of charge on a body.
Q12: List two states in India where earthquakes are more likely to strike.
Ans: Two places in India which are most threatened by earthquake are Kashmir and Rann of kutch.
Q13: Explain why a charged balloon is repelled by another charged balloon but a charged balloon is attracted by a charged balloon?
Ans: The charged balloon has similar charges on its surfaces, since like charges repel each other thus charged balloon repels another charged balloon. When an uncharged balloon is brought near a charged balloon it acquires some opposite charge, since opposite charges attracts each other therefore a charged balloon attracts an uncharged balloon.
Q14: Why a charged body loses its charge if we touch it with our hand?
Ans: A charged body loses its charge if we touch it with our hand because the charges get transferred from our body to earth, this process is known as earthing.
Q15: What causes an earthquake?
Ans: The earth's lithosphere is fragmented into many pieces. Each fragment is called a plate, also called tectonic plate, these plates are in continual motion, when they brush past one another a plate goes under another because of collision, and they cause disturbance in earth’s crust, this disturbance shows up as an earthquake on the surface of earth.
Q16: What are the causes of sparking?
Ans. Causes of sparking:
(i) On electric pole wires become loose.
(ii) Blowing of wind and shaking the wires.
(iii) Loosenes
Q17: What happens when amber is rubbed of fur?
Ans. When amber is rubbed with fur, it attracts light objects such as hair. In the same way woollen and polyester clothes also attract light objects.
Q18: Who established the relation between sparks produced by amber and the thunderstorms?
Ans. An American Scientist Benjamin Franklin established that sparks produced by amber are similar to those produced in sky during a thunderstorm. He flew a kite tied with a silken thread, which had an iron key attached to it on a rainy day. During lightning he felt the shock through iron key, which proved that clouds also carried charges.
Q19: How can charging take place when the substances are rubbed?
Ans. When a plastic refill is rubbed with polythene, it acquires a small electric charge. Similarly, when a plastic comb is rubbed with dry hair, it also acquires a small charge. These objects are called charged objects. In this process of charging the refill and the plastic comb, polythene and hair also get charged.
Q20: How many different types of charges are there? Write the nature of charges on glass rod and silk cloth when they are rubbed each other?
Ans. There are two types of charges:
(i) Positive charge and
(ii) Negative charge
Charge acquired by a glass rod rubbed with silk is called positive charge and the charge acquired by silk cloth is called negative charge.
Q21: What is static electricity? How is it different from electric current?
Ans. The electrical charges generated by rubbing produce static electricity. The charges do not move in static electricity while charges move in current electricity.
Q22: What is electric discharge? How does it occur?
Ans. The negative and positive charges meet, producing streaks of bright light and sound. This process is called electrical discharge, the process of electric discharge can occur between two or more clouds or between clouds and earth.
Q23: How does electric discharge occur in clouds?
Ans. At the time of thunder negative charges get accumulated near the clouds and positive charges accumulate near ground. When these charges meet electric discharge takes place between ground and clouds. In this process a large amount of energy is released as thunder and lightning.
Q24: During lightning what should we do?
Ans. (i)Hearing thunder is an alert to rush to a safer place.
(ii) After hearing the last thunder wait for some time before coming out.
Q25: What is lightning conductor? How does it protect building from lightning?
Ans. Lightning conductor is a device used to protect building from the effect of lightning. A metallic rod taller than the building is installed in the walls of the building during its construction. One end of the rod is kept out in the air and the other is buried deep in the ground. The rod provides easy route for transfer of electric charge to the ground.
Q26: Define the following:
- Richter scale
- Seismograph
Ans:
- Richter scale: The Richter scale is used to rate the magnitude of an earthquake that is the amount of energy it released. This is calculated using information gathered by a seismograph.
- Seismograph: Tremors or vibrations caused by the earthquakes which travel in the form of waves within the earth or along the earth's surface, are called seismic waves. Seismograph is an instrument which records these waves.
Q27: Write about two last major earthquakes in India.
Ans. (i) A major earthquake occurred on 26 January 2001 in Bhuj district of Gujarat.
(ii) A major earthquake also occurred in India on 8 October 2005 in Uri and Tangdhar towns of North Kashmir.
Q28: Name the regions of the earth more prone to earthquakes.
Ans. Earthquakes are caused by the movement of plates. The regions which fall on the boundaries of these plates are called danger zones. Earthquakes are most likely to happen in these danger zones.
Q29: What are fault zones? Name the fault zones in India.
Ans. The areas fall between the boundaries of two plates are called weak zones or seismic or fault zones. In india the most threatened areas are Kashmir, Western and Central Himalayas, whole of North-East, Rann of Kutch, Rajasthan, Indo-Gangetic plain and some areas of south India.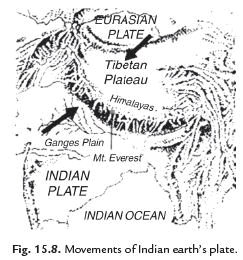
Q30: What are the protections to be taken against lightning?
Ans: During lightning avoid going at an open place, try to rush towards safe place like in a house or building, if you are travelling in nay vehicle like car or bus, you are safe inside with windows and doors of the vehicle closed. If you are in a forest take shelter under a smaller tree.
Q31: List the things that you should do while thunderstorm.
Ans: During lightning avoid going at an open place, try to rush towards safe place like in a house or building, if you are travelling in nay vehicle like car or bus, you are safe inside with windows and doors of the vehicle closed. If you are in a forest take shelter under a smaller tree.
Q32: List the things that you should not do while thunderstorm.
Ans: During lightning avoid going at an open place, try to rush towards safe place like in a house or building, if you are travelling in nay vehicle like car or bus, you are safe inside with windows and doors of the vehicle closed. If you are in a forest take shelter under a smaller tree.
Long Answer Type Questions
Q1: Mention three ways by which a body can be charged.
Ans: There are three methods of charging objects:
1. Rubbing: Charging through rubbing involves transferring electrons between objects. When two objects are rubbed together, one loses electrons (positive charge) and the other gains electrons (negative charge).
2. Conduction: Conduction charging occurs when a charged object comes into direct contact with a neutral object. The charges are transferred, and the neutral object becomes charged with the same type of charge as the charged object.
3. Induction: Induction charging happens when a charged object is brought near a neutral object without direct contact. The presence of the charged object induces a separation of charges in the neutral object, creating a temporary imbalance.
Q2: Suppose you are outside your home and an earthquake strikes. What precaution would you take to protect yourself?
Ans: If caught outside during an earthquake, consider these precautions:
1. Find an Open Area: Move away from buildings, trees, and any structures that could collapse. Find an open space, like an empty field or a park.
2. Stay Grounded: Sit or crouch down to reduce the chance of being knocked over. Protect your head and neck with your arms.
3. Avoid Hazards: Stay away from streetlights, power lines, and anything that could fall during the tremor.
4. Stay Inside a Vehicle: If you're in a car, pull over to a safe area, away from buildings, bridges, and power lines. Stay inside the vehicle until the shaking stops.
5. Stay Calm: Try to stay calm and avoid panicking. Keep your distance from buildings to prevent any falling debris from harming you.
Q3: How an electroscope can be charged through conduction?
Ans: Charging an electroscope through conduction involves transferring charge from a charged object to the electroscope. For instance, rubbing a plastic comb on hair makes the comb charged. When the charged comb touches the electroscope's plate, the static charges move through the conducting wire and reach the aluminum foil leaves. As both leaves acquire similar charges, they repel each other, indicating the presence of charge. This process, where an uncharged object gains charge by direct contact with a charged object, is known as charging by conduction. This way, an electroscope can be charged through conduction.
Q4: Touch the disc of an electroscope with an ebonite rod rubbed with fur. Now bring a glass rod rubbed with silk close to the disc of this electroscope. Explain what do you observe?
Ans:
- Rubbing an ebonite rod with fur gives it a negative charge.
- When this charged rod touches the metal cap of the electroscope, it transfers its negative charge to the cap and the leaves via conduction.
- Both the metal cap and leaves acquire a negative charge, causing the leaves to repel and diverge.
- Next, rubbing a glass rod with silk charges it positively.
- Bringing the positively charged glass rod close to the metal cap of the negatively charged electroscope causes an effect called induction.
- Due to induction, the leaves acquire a temporary positive charge while the metal cap remains negative.
- The positive and negative charges attract each other, leading to the collapse of the previously diverged leaves.
Q5: How would you use an electroscope to determine the nature of charge of a charged body?
Ans: Let the electroscope get charged with negative charge, by touching a negatively charged ebonite rod to the metal disc of the electroscope. The leaves of the electroscope open up (diverge). Now touch the body to be tested with the metal disc of the charged electroscope.
- If the divergence of the leaves increases, the body has similar charge that is the given body is also negatively charged.
- If the divergence of the leaves decreases, the body has unlike charge that is the given body is positively charged.
Q6: Explain a lightning conductor and its function.
Ans: Lightning conductor is the device that protects a tall building from lightning strike, by providing an easier path for current to flow to earth than through the building. It consists of a thick copper strip of very low resistance connected to the ground below. A good connection to the ground is essential and is made by burying a large metal plate deep in the damp earth. In the event of a direct lightning strike, the current in the conductor may be great as to melt or even vaporize the metal, but the damage to the building will nevertheless be limited.
Q7: What are the protections to be taken against earthquakes?
Ans: If you are at home:
1. Take shelter under the table and stay there until the stoppage of shaking
2. Keep yourself away from the tall or heavy objects that may fall on you and damage you.
3. If you are on bed, do not get up and keep a pillow on your head
If you are outside the home:
1. Find a clear spot, away from buildings, trees, poles and electric poles, signboards and overhead power lines and drop to the ground.
2. Do not use elevators if they are available at some place outside your house
3. If you are in a car or a bus, do not come out and drive slowly to a clear spot.
Q8: Define the following
- Lightning
- Earthing
Ans:
- Lightning: Lightning is a natural phenomenon that has fascinated people for ages. Several people thought and researched about the cause of lightning and its process. Benjamin Franklin discovered for the first time that there is an electric discharge between clouds that produces a spark, and it is the electric spark between the clouds and the earth that appears as lightning. His famous kite experiment proved this fact. The occurrence of lightning is as follows. The formation of clouds involves friction between water particles in the atmosphere. The friction charges the particles. Among the positive and negative charges, the negative charge accumulates at the bottom of the cloud and the positive charges in its top. As the accumulation of the charge increases, the cloud will create a positive charge on the ground nearby. As the amount of charge increases, the negative charge on the cloud tends to make a path towards the ground, and it results in a narrow streak of electrical discharge, which we call lightning.
- Earthing: The process of transferring of charge from a charged object to the earth is called as earthing. For our safety, most of the electrical appliances and the mains of the house are connected to earth, so that we can be prevented from getting an electric shock.
|
90 videos|415 docs|44 tests
|
FAQs on Class 8 Science Chapter 12 Question Answers - Some Natural Phenomena
| 1. What are the different types of natural phenomena? |  |
| 2. How are natural phenomena formed? |  |
| 3. Can natural phenomena be predicted? |  |
| 4. How can we stay safe during natural phenomena? |  |
| 5. What is the role of technology in studying natural phenomena? |  |

















