Short & Long Answer Questions: Mechanical Properties of Fluids - 3 | Physics for EmSAT Achieve PDF Download
Q.101 Why do the hair of a shaving brush cling together when taking out of water?
Answer: When the brush is taken out of water, thin water film is formed at the tips of the hair. It contracts due to surface tension and so the hair cling together.
Q.102 A needle floats on the surface of pure water but goes down when detergent is added to water. Why?
Answer: Due to addition of detergent, the surface tension and hence the reaction of surface tension decreases. Hence the needle sinks due to smaller upward reaction.
Q.103 Why it becomes easier to spray the water in which some soap is dissolved?
Answer: When soap is dissolved in water, the surface tension of water decreases and so less energy is needed for spraying the water i.e., spraying of water in which soap is dissolved becomes easier.
Q.104 The clothes are better cleaned with hot water than with cold water. Why?
Answer: Surface tension decreases with the increase of temperature. Lesser the surface tension, more is the wetting (and hence the washing) power of water.
Q.105 How does soap help us to remove dirt better in washing clothes?
Answer: With the addition of soap, the surface tension of water decreases. The decrease in surface tension results in greater wetting and hence washing power.
Q.106 A oil drop on a hot cup of soup spreads over when the temperature of the soup falls. Why?
Answer: The surface tension of hot water is less than that of oil and hence oil drop does not spread over hot water. When water is cooled, its surface tension decreases. At low temperature, the surface tension of water becomes greater than that of oil and hence oil drop starts spreading over it.
Q.107 Glass marbles are made by heating the end of a glass rod until drops of molten glass fall. Explain.
Answer: When drops of molten glass fall freely, they are in state of weightlessness. As only the force of surface tension acts on them, so they acquire spherical shape which on solidification become glass marbles.
Q.108 Oil is sprinkled on sea waves to calm them. Why?
Answer: When oil is sprinkled, the breeze spreads the oil on the sea-water in its own direction. The surface tension of sea-water (without oil) is greater than oily water. Hence the water without oil pulls the oily water against the direction of breeze, and the sea waves become calm.
Q.109 A tiny liquid drop is spherical but a larger drop has oval shape. Why?
Answer: In the case of a tiny drop, the force of surface tension is large compared to its weight, so the drop has spherical shape. A large drop has oval shape because the force of gravity (weight) exceeds the force of surface tension.
Q.110 Why does a small piece of camphor dance about on the water surface?
Answer: Due to its irregular shape, the camphor piece dissolves more rapidly at some points than at others. Where it dissolves, the surface tension of water is reduced. As the force of surface tension reduces by different amounts at different points of the camphor piece, a resultant force acts on it which makes it dance about on water surface.
Q.111 The addition of flux to tin mat soldering easy. Why?
Answer: The addition of flux reduces surface tension of the molten tin. This helps it spread easily over the area of soldering.
Q.112 The paints and lubricating oils have low surface tension. Why?
Answer: The paints and lubricating oils having low surface tension can spread over a large surface area.
Q.113 Why are the droplets of mercury when brought in contact pulled together to from a bigger drop? Also state with reason whether the temperature of bigger drop will be the same, or more, or less than the temperature of the smaller drops?
Answer: Due to surface tension, liquid drops tend to have minimum surface area. When mercury droplets are brought in contact, they form one drop thereby decreasing the surface area. Due to decrease in surface, surface energy is lost by the bigger drop which appears as heat. So its temperature increases.
Q.114 The angle of contact for a solid and a liquid is less than 90∘. Will the liquid wet the solid? Will the liquid rise in the capillary made of that solid?
Answer: The liquid will wet the solid and will rise in the capillary tube made of that solid.
Q.115 Write down formula for excess pressure inside (i) a liquid drop (ii) a soap bubble.
Answer: (i) For a liquid drop: p= 2σ/R (ii) For a soap bubble: p= 4σ/R where σ is surface tension.
Q.116 Why excess pressure in a soap bubble is twice the excess pressure of a liquid drop of the same radius?
Answer: A soap bubble has two free surfaces, one internal and another external; whereas liquid drop has only one outer free surface.
Q.117 Two soap bubbles of unequal sizes are blown at the ends of a capillary tube. Which one will grow at the expense of the other and what does it show?
Answer: The bigger one will grow at the expense of the smaller one. This is because excess pressure is inversely proportional to radius and air flows from higher pressure to lower pressure.
Q.118 What is the importance of (i) wetting agents used by dyers, and (ii) water proofing agents?
Answer: (i) They are added to decrease the angle of contact between the fabric and the dye so that the dye may penetrate well. (ii) They are used to increase the angle of contact between the fabric and water to prevent the water from penetrating the cloth.
Q.119 Teflon is coated on the surface of non-sticking pans. Why?
Answer: When the surface of a pan is coated with teflon, the angle of contact between the pan and the oil used for the frying purpose becomes obtuse. Thus the frying pan becomes non-sticking.
Q.120 What makes water-proof rain coat water-proof?
Answer: The angle of contact between water and the material of the raincoat is obtuse. So the rainy water does not wet the raincoat i.e., the raincoat is water-proof.
Q.121 How does the ploughing of fields help in preservation of moisture in the soil?
Answer: This is done to break the tiny capillaries through which water can rise and finally evaporate. The ploughing of field helps the solid to retain the moisture.
Q.122 How does the cotton wick in an oil-filled lamp keep on burning?
Answer: The narrow spaces between the threads of the wick serve as capillary tubes through which oil keeps on rising due to capillary action.
Q.123 Why sand is drier than clay?
Answer: Due to narrow pores in clay, water rises in the clay due to capillary action and keeps it damp. Practically no pores or capillaries exist in sand and hence water cannot rise in sand. So sand is drier than clay.
Q.124 Why undergarments are usually made of cotton?
Answer: Cotton threads have large number of capillaries between them. These capillaries help to absorb sweat from the surface of the body due to capillarity action.
Q.125 A piece of chalk immersed in water emits bubbles in all directions. Why?
Answer: A chalk piece has a large number of capillaries. As it is immersed in water, water rises due to capillary action. The air present in the chalk is expelled out in the form of bubbles in all directions.
Q.126 Why new earthen pots keep water cooler than the old one?
Answer: Due to capillary action, water oozes out of the pores of the new earthen pot. This water takes latent heat from the pot to evaporate and so the water in the pot gets cooled. In old pots, most of the capillaries are blocked. So the cooling is not so effective.
Q.127 Why is the tip of the nib of a pen split?
Answer: The split in the tip of the nib acts as a capillary tube. The ink rises up in the nib due to capillary action. Hence we are able to write with the pen.
Q.128 Water rises in a capillary tube, whereas mercury falls in the same tube. Why?
Answer: In a capillary tube, a liquid rises to a height h given by 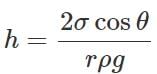 For water, θ is acute, cosθ is positive and hence h is positive. So water rises in the capillary tube. For mercury, θ is obtuse, cosθ is negative and hence h is negative. So mercury gets depressed in the capillary tube.
For water, θ is acute, cosθ is positive and hence h is positive. So water rises in the capillary tube. For mercury, θ is obtuse, cosθ is negative and hence h is negative. So mercury gets depressed in the capillary tube.
Q.129 Why is it difficult to make mercury enter a fine thermometer tube?
Answer: The meniscus of mercury in a glass tube is convex. Since there exists an excess pressure (p=2σ/r) on the concave side of the curved liquid surface, the pressure below the meniscus is greater than the atmospheric pressure. This excess pressure has a very large value for a tube of fine bore. As the pressure of mercury inside the tube is greater than that outside it, mercury instead of entering into the tube tends to flow out.
Q.130 Water gets depressed in a glass tube whose inner surface is coated with wax. Why?
Answer: The angle of contact between water and wax is obtuse. So cosθ is negative and hence capillary rise: h=2σcosθ/rρg is also negative. That is why water gets depressed.
Q.131 If a capillary tube is immersed at first in cold water and then in hot water, the height of capillary is smaller in the second case. Why?
Answer: The height up to which a liquid rises in a capillary tube is given by 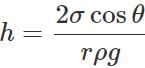 The surface tension (σ) of hot water is less than that of cold water. Moreover, capillary tube expands in hot water, so its radius r increases. So capillary rise h is smaller in hot water than in cold water.
The surface tension (σ) of hot water is less than that of cold water. Moreover, capillary tube expands in hot water, so its radius r increases. So capillary rise h is smaller in hot water than in cold water.
Q.132 If a capillary tube is put in water in a state of weightlessness how will the rise of water in a capillary tube be different to one observed under normal conditions?
Answer: In normal conditions, when the force of surface tension (due to which water rises in capillary) becomes equal to the weight of the water column raised in the tube, water stops rising. In the state of weightlessness, the effective weight of water column raised is zero. Hence water will rise up to the other end of the capillary, however long the capillary is. Water will not overflow, its surface will become flat (its radius of curvature will become infinity)
Q.133 How is the rise of liquid affected, if the top of the capillary tube is closed?
Answer: As the liquid rises in the capillary tube, the air gets compressed between the top end of the tube and the liquid meniscus. The compressed air opposes the rise of liquid due to surface tension. The liquid rises till the two opposing forces just balance each other. Hence if the top end of the capillary tube is closed, the liquid rises to a smaller height.
Q.134 A 20 cm long capillary tube is dipped in water. The water rises up to 8 cm. If the entire arrangement is put in a freely falling elevator, what will be the length of water column in the capillary tube?
Answer: In the freely falling elevator, the entire arrangement is in a state of weightlessness, i.e., g= 0. So water will rise in the tube 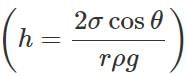 to fill the entire 20 cm length of the tube.
to fill the entire 20 cm length of the tube.
Q.135 Spherical balls of radii R are falling in a viscous fluid of viscosity η with a velocity υ. How does the retarding viscous force acting on a spherical ball depend on R and υ?
Answer: F=6πηRυi.e., retarding viscous force is directly proportional to both R and υ.
Q.136 Why do air bubbles in a liquid move in upward direction?
Answer: The density of air bubble is less than that of liquid. Initially, the resultant of up thrust and the viscous force is greater than the weight of the air bubble. So, the air bubble experiences a net upward force. Then bubble soon attains a terminal velocity in the upward direction.
Q.137 Explain why some oils spread on water, when others float as drops.
Answer: If the surface tension of oil is less than that of water, then it spreads on water. If the surface tension of oil is more than that of water, then it floats as drops on water.
Q.138 What happens when a capillary tube of insufficient length is dipped in a liquid?
Answer: When a capillary tube of insufficient length is dipped in a liquid, the liquid rises to the top. The radius of curvature of the concave meniscus increases till the pressure on its concave side becomes equal to the pressure exerted by the liquid column of insufficient length. But the liquid does not overflow.
Q.139 Problem 1. Explain why : (i) A balloon filled with helium does not rise in air indefinitely but halts after a certain height (Neglect winds). (ii) The force required by a man to raise his limbs immersed in water is smaller than the force for the same movement in air.
Answer: (i) A balloon filled with helium goes on rising in air so long as the weight of the air displaced by it (i.e., up thrust) is greater than the weight of filled balloon. We know that the density of air decreases with height. Therefore, the balloon halts after attaining a height at which density of air is such that the weight of air displaced just equals the weight of filled balloon.
(ii) Water exerts much more up thrust on the limbs of man than air. So the net weight of limbs in water is much less than that in air. Hence the force required by a man to raise his limbs immersed in water is smaller than the force for the same movement in air.
Q.140 What height of water column produces the same pressure as a 760 mm high column of Hg?
Answer: Pressure exerted by h height of water column =Pressure exerted by 760 mm of Hg column ∴h×1000×9.8=0.760×13.6×103×9.8 [P=hρg] or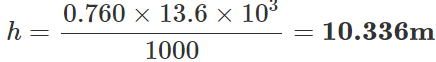
Q.141 A small ball of mass m and density ρ is dropped in a viscous liquid of density ρ. After some time, the ball falls with a constant velocity. Calculate the viscous force on the ball.
Answer: Volume of the ball, V= m/ρ Mass of the liquid displaced, m′=Vρ0=m/ρ .ρ0 When the body falls with a constant velocity, Viscous force = Effective weight of the ball F=Weight of the ball ? Up thrust =mg−m′g or
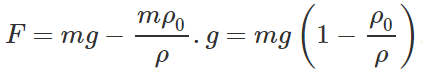
Q.142 A tank filled with fresh water has hole in its bottom and water is flowing out of it. If the size of the hole is increased what will be the change in: (a) Volume of water flowing out per second? (b) Velocity of the out coming water? (c) If in the above tank, the fresh water is replaced by sea water, will the velocity of out coming water change?
Answer: (a) The volume of water flowing out per sec will increase as its volume depends directly on the size of hole.
(b) The velocity of outflow of water remains unchanged because it depends upon the height of water level and is independent of the size of the hole.
(c) No, though the density of sea water is more than that of fresh water, but the velocity of outflow of water is independent of the density of water.
Q.143 In a bottle of narrow neck, water is poured with the help of an inclined glass rod. Why?
Answer: If water is directly poured into a bottle of narrow neck, the stream of water blocks the neck due to the pressure of inside air and the strong force of adhesion between glass and water. If a small part of the glass rod is placed inside the bottle and water is poured along the length of the rod outside the bottle, water molecules cling to the glass rod and the force of gravity pulls down these molecules into the bottle.
Q.144 The excess pressure inside a soap bubble is thrice the excess pressure inside a second soap bubble. What is the ratio between the volume of the first and the second bubble?
Answer: Given: P1=3P2 or r2=3r1
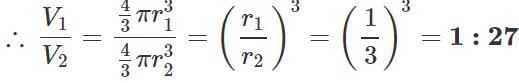
Q.145 The viscous force 'F' acting on a body of radius 'r' moving with a velocity ' υ' in a medium of coefficient of viscosity ?η? is given by F=6πηrυ. Check the correctness of the formula.
Answer: [F]=[MLT−2] [6πηrυ]=[ML−1T−1][L][T−1]=[MLT−2]
∴ Dimensions of LHS = Dimensions of RHS.
Hence the given formula for viscous force F is dimensionally correct.
Q.146 A tornado consists of rapidly whirling air vortex. Why is the pressure always much lower in the centre than at the outside? How does this condition account for the destructive power of tornado?
Answer: The angular velocity of air in a tornado increases as it goes towards the centre. As the air moves towards the centre, its moment of inertia (I) decreases and to conserve angular momentum (L=Iω), the angular velocity co increases. Because of the enormous increase in velocity of inner layers, the air pressure at the centre reduces greatly in accordance with Bernoulli's theorem. This sudden reduction in pressure may prove highly disastrous both for life and property in the vicinity of a tornado.
|
209 videos|327 docs|212 tests
|
FAQs on Short & Long Answer Questions: Mechanical Properties of Fluids - 3 - Physics for EmSAT Achieve
| 1. What are the mechanical properties of fluids? |  |
| 2. How does viscosity affect the flow of fluids? |  |
| 3. What is the significance of surface tension in fluids? |  |
| 4. How does density affect the buoyancy of objects in fluids? |  |
| 5. What is the difference between compressibility and elasticity in fluids? |  |





















