Short & Long Answer Questions: States of Matter | Physical Chemistry for NEET PDF Download
Q.1 Out of CO2 and NH3 gases, which is expected to show more deviation from the ideal gas behaviour?
Answer: NH3 is expected to show more deviation because it can be easily liquefied being of polar nature. This shows that the attractive forces in the molecules of NH3 are more than the forces present in CO2 molecules.
Q.2 Can we apply Dalton's law of partial pressures to a mixture of carbon monoxide and oxygen?
Answer: No, the law cannot be applied because these gases readily combine to form carbon dioxide. The law can be applied only to the non reacting gases.
Q.3 Out of dry air and wet air, which is heavier?
Answer: Dry air mainly contains gases like nitrogen and oxygen along with small proportions of the other gases. The wet air on the other hand, also contains a small amount of water vapours. Now, vapour density of water vapours is less than that of nitrogen and oxygen because molar mass of H2O (18) is less than that of N2(28) and O2 (32). This means that heavier molecules of nitrogen and oxygen have been replaced by lighter molecules of water vapours when the dry air changes to wet air. Therefore, dry air is heavier than wet air.
Q.4 Carbon dioxide is heavier than oxygen and nitrogen but it does not form the lower layer of the atmosphere. Explain.
Answer: The diffusion of the gases is quite independent of the gravitational pull by the earth. The molecules of carbon dioxide remain distributed throughout the atmosphere. Therefore, carbon dioxide does not form the lower layer of the atmosphere.
Q.5 Ammonia and hydrochloric acid gases are prepared at the two extreme corners in the laboratory. Which gas will reach first to a person in the centre of the laboratory?
Answer: Ammonia gas will reach first to a person in the centre of the laboratory because it is lighter than hydrochloric acid gas. This is according to the Graham's law of diffusion which states that the rate of diffusion of a gas under given conditions of temperature and pressure is inversely proportional to the square root of its density.
Q.6 Both N2O and CO2 have similar rates of diffusion under same conditions of temperature and pressure. Explain.
Answer: Gram molar mass of both these gases are the same (44 g). According to Graham's law of diffusion, the rates of diffusion of the gases are inversely proportional to the square roots of their molar masses under similar conditions of temperature and pressure. Therefore, both these gases diffuse at the same rate.
Q.7 The molecular speeds of gaseous molecules are analogous to those of rifle bullets ; why is then odour of the gaseous molecules not detected so fast?
Answer: No doubt molecules in the gaseous state move almost with the same speed of rifle bullets. But these molecules do not follow a straight path. Since they undergo collisions with one another at a very fast rate, the path followed is zig-zag. Thus, the odour cannot be detected at the same speed at which the molecules move.
Q.8 Why are aerated water bottles kept under water during summer?
Answer: In aerated water bottles, CO2 gas is passed through the aqueous solution under pressure because the solubility of the gas in water is not very high. In summer, the solubility of the gas in water is likely to decrease because the rise in temperature decreases the solubility. Thus, in summer, more of gas will be present above the liquid surface in the glass bottle. In case, the pressure of the gas becomes too high, then glass will not be able to withstand the pressure. The bottle may explode and may lead to serious accident. To avoid this, the bottles are kept under water. As a result, the temperature is likely to decrease and the solubility of the gas is likely to increase in aqueous solution resulting in decreased pressure.
Q.9 Liquid ammonia bottle is cooled before opening the seal. Explain.
Answer: Liquid ammonia bottle contains the gas under very high pressure. If the bottle is opened as such, then the sudden decrease in pressure will lead to a large increase in the volume of the gas. As a result, the gas will come out of the bottle all of a sudden with force. This will lead to the breakage of the bottle and also some serious accident. However, if the bottle is cooled under tap water for sometime, this will lead to a decrease in the volume of the gas to a large extent. If the seal is opened now, the gas will come out of the bottle at a slow rate, thus, reducing the chances of accident.
Q.10 Why are tyres of automobiles inflated to lesser pressure in summer than in winter?
Answer: The pressure of the air is directly proportional to the temperature. Since the temperature is higher in summer than in winter, the pressure of the air in the tube of the tyre is likely to be quite high as compared to winter. It is quite likely that the tube may burst under high pressure in summer. Therefore, it is advisable to inflate the tyres to lesser pressure in summer than in winter.
Q.11 The size of the weather balloon becomes larger and larger as it ascends up into higher altitude. Assign reason.
Answer: The volume of the gas is inversely proportional to the pressure at a given temperature according to Boyle's law. As the weather balloon ascends, the pressure tends to decrease. As a result, the volume of the gas inside the balloon or the size of the balloon is likely to increase.
Q.12 What would have happened to the molecular motion in a gas if the molecular collisions were not elastic?
Answer: There might have been decrease in the kinetic energy during the collisions because energy is likely to decrease in each collision under the circumstances. Since the collisions are very frequent, the energy of the molecules might have considerably decreased and ultimately the gas molecules might have come to rest.
Q.13 Under what conditions do real gases show maximum deviation from ideal gas behaviour?
Answer: Real gases show maximum deviation from the ideal gas behaviour when the pressure of the gas is very high and its temperature is very low.
Q.14 If the value of 'a' for a gas is zero, can it be liquefied?
Answer: If the value of 'a' for a gas is zero, this means that the attractive forces among the gas molecules are absent. In the absence of these forces, the gas cannot be liquefied.
Q.15 Gases like CO2 and CH4 show more deviation from the ideal gas behaviour as compared to gases like H2 and He. Explain.
Answer: In CO2 and CH4, the molecular size is more as compared to H2 and He. Therefore, if we neglect the molecular volume in these gases in the same way as we do for H2 and He, the deviations from the ideal gas behaviour are likely to be more.
Q.16 How will you justify that the collisions among the gas molecules are perfectly elastic?
Answer: According to the kinetic theory, the collisions of the gas molecules among themselves and also with the walls of the container are perfectly elastic. This means that the collisions are frictionless and there is no loss of kinetic energy in the collisions. Had it not been so, some energy might have been lost during each collision and the molecules must ultimately come to rest. But this does not happen. This clearly shows that the collisions are of elastic nature. However, the molecules may exchange energy during the collisions.
Q.17 What is the basic difference between boiling and evaporation?
Answer: Evaporation is a slow process and it occurs spontaneously at all temperatures. Boiling is a fast process and a liquid boils only at that temperature when its vapour pressure is equal to the applied external pressure.
Q.18 Why does the boiling point of liquid rise on increasing pressure?
Answer: Boiling point of a liquid is the temperature when its vapour pressure becomes equal to the atmospheric pressure. When pressure is increased, the vapour pressure of the liquid has to be increased to match the external pressure. Therefore, the liquid has to be heated or its boiling point increases.
Q.19 Drop of liquid assumes spherical shape. Why?
Answer: Because of the surface tension, a liquid tends to possess minimum surface area. Since for a given volume, sphere has the minimum surface area therefore, drop of the liquid assumes spherical shape.
Q.20 The level of mercury in a capillary tube is lower than the level outside when the capillary is inserted in mercury. Explain.
Answer: This is explained in terms of cohesive and adhesive forces. The attractive forces in the molecules of the same substance are called cohesive forces while those in the molecules of different substances are called adhesive forces. In case of mercury, the cohesive forces are stronger than the adhesive forces. As a result, mercury gets detached from the glass surface and its level therefore, goes down in the capillary tube.
Q.21 Water meniscus in a glass tube is concave while that of mercury is convex. Why?
Answer: In case of water, the adhesive forces in the molecules of glass and water are stronger than the cohesive forces in the water molecules. Therefore, the meniscus of water is concave. However, in mercury, the cohesive forces are stronger than the adhesive forces. As a result, its meniscus is convex.
Q.22 Liquids like ether and acetone are kept in cool places.
Answer: Both these liquids are volatile in nature which means that their boiling points are quite low. They are expected to evaporate at a fast rate in case temperature is high. Therefore, the temperature has to be lowered or they are to be kept in cool places to check their evaporation.
Q.23 Tea or coffee is sipped from a saucer when it is hot.
Answer: Evaporation causes cooling and its rate increases with the increase in surface area. Since a saucer has a large surface, the evaporation of tea or coffee is expected to be quite fast. As a result, both of them get cooled and can be sipped comfortably.
Q.24 What is the effect of temperature on : (a) Density (b) Surface tension (c) Viscosity and (d) Vapour pressure of a liquid?
Answer: (a) Density of the liquid decreases. (b) Surface tension of the liquid decreases. (c) Viscosity of the liquid decreases. (d) Vapour pressure of the liquid increases.
Q.25 Name the liquid with higher vapour pressure in the following pairs: (a) Alcohol, glycerine (b) Petrol, kerosene (c) mercury, water.
Answer: The vapour pressure of the liquid is inversely proportional to the magnitude of the intermolecular forces of attraction present. Based on this, the liquid with higher vapour pressure in the different pairs is: (a) Alcohol (b) Petrol (c) Water.
Q.26 If alcohol evaporates on your palm, it becomes cold. Why?
Answer: Certain molecules of alcohol acquire kinetic energy greater than the escape energy as a result of collisions. They, therefore, escape as vapours. Since the kinetic energy of the rest of the molecules decreases, their temperature gets lowered. As a result, the palm becomes cold.
Q.27 Arrange solid, liquid and gas in order of energy, giving reasons.
Answer: Solid < Liquid < Gas. This is because a solid absorbs energy to change into a liquid which further absorbs energy to change into a gas.
Q.28 Why liquids have a definite volume but no definite shape?
Answer: This is because the intermolecular forces are strong enough to hold the molecules together but not so strong as to fix them into definite positions (as in solids). Instead, they possess fluidity and hence no definite shape.
Q.29 Which type of intermolecular forces exist among the following molecules? (i)H2Smolecules (ii) H2O molecules (iii) Cl2 and CCl4 molecules (iv) SiH4 molecules (v) Helium atoms (vi) He atoms and HCl molecules
Answer: (i) Dipole-dipole interactions (because H2S is polar). (ii) Hydrogen bonding. (iii) London dispersion force (because both are non-polar). (iv) London dispersion forces (because SiH4 is non-polar). (v) London dispersion forces (because He atoms have symmetrical electron clouds). (vi) Dipole-induced dipole forces (because HCl is polar while He atom has symmetrical electron cloud).
Q.30 A gas is filled into a bulb connected to an open limb manometer. The level of mercury in the open arm is 24 cm lower than that in the other arm of the manometer. The atmospheric pressure is 740 mm. What is the pressure of the gas?
Answer: As level in the open arm of the manometer is lower than that in the arm connected to the gas bulb, this means that atmospheric pressure is greater than pressure of the gas by difference of the two levels. Hence, pressure of gas = 740 - 21 = 719 mm.
Q.31 How do you convert (a) pressure in atmospheres into SI units? (b) temperature in °C to temperature in °F?
Answer: (a) 1 atm. = 101, 325 Pa or Nm−2 or 1 bar = 105 Pa (b) oC =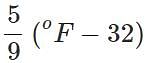
Q.32 CO2 is heavier than O2 and N2 gases present in the air but it does not form the lower layer of the atmosphere. Why?
Answer: Gases possess the property of diffusion which is independent of the force of gravitation. Due to diffusion, the gases mix into each other and remain almost uniformly distributed in the atmosphere.
Q.33 What type of graph will you get when PV is plotted against P at constant temperature.
Answer: A straight line parallel to pressure axis.
Q.34 At a certain altitude, the density of air is 1/10th of the density of the earth's atmosphere and temperature is -10°C. What is the pressure at that altitude? Assume that air behaves like an ideal gas, has uniform composition and is at S.T.P. at the earth's surface.
Answer:
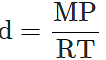
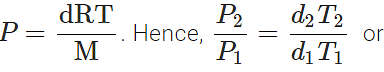
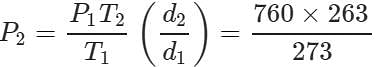
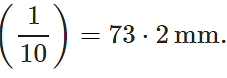
Q.35 How is the partial pressure of a gas in a mixture related to the total pressure of the gaseous mixture?
Answer: Partial pressure of a gas = Mole fraction of that gas ×Total pressure.
Q.36 Compare the rates of diffusion of 235UF6 and 238UF6.
Answer: Molecular mass of 235UF6=235+6×19=349 Molecular mass of 238UF6=238+6×19= 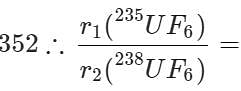
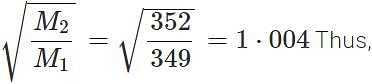 r(235UF6):r(238UF6)=1⋅004:1.
r(235UF6):r(238UF6)=1⋅004:1.
Q.37 N2O and CO2 have the same rate of diffusion under same conditions of temperature and pressure. Why?
Answer: Both have same molar mass (= 44 g mol−1). According to Graham's law of diffusion, rates of diffusion of different gases are inversely proportional to the square root of their molar masses under same conditions of temperature and pressure.
Q.38 What would have happened to the gas if the molecular collisions were not elastic?
Answer: On every collision, there would have been loss of energy. As a result, the molecules would have slowed down and ultimately settle down in the vessel. Moreover, the pressure would have gradually reduced to zero.
Q.39 What is the relationship between average kinetic energy and the temperature of a gas?
Answer:
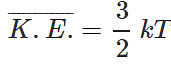 where k is Boltzmann constant=
where k is Boltzmann constant= 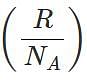
Q.40 What is the ratio of average kinetic energy of oxygen molecules to that of ozone molecules at 27°C?
Answer: Average kinetic energy of any gas depends only on temperature and not upon the nature of the gas. Hence, both the gases will have same average kinetic energy at 27°C, i.e., the ratio will be 1 : 1.
Q.41 What is the difference between total kinetic energy and translational kinetic energy? For what type of molecules, the two are equal?
Answer: Total kinetic energy is the sum of translational, vibrational and rotational kinetic energies. The total kinetic energy is equal to the translational kinetic energy for monoatomic gases (He, Ne etc.) as they do not possess vibrational and rotational motion but have only translational motion.
Q.42 The van der Waals constants for two gases are as follows : Gas a(atmL2mol−2) b(Lmol−1) X 1.39 0.0391 Y 3.59 0.0427 Which of them is more easily liquefiable and which has greater molecular size?
Answer: Greater the value of 'a', more easily the gas is liquefiable. Similarly, greater the value of 'b', greater is the molecular size. Hence, gas Y will be more easily liquefiable and will have greater molecular size.
Q.43 Out of N2 and NH3, which one will have greater value for van der Waals constant 'a' and which one will have greater value for van der Waals constant 'b'?
Answer: (i) As NH3 is more easily liquefiable (due to hydrogen bonding), intermolecular forces of attraction are stronger than in N2. Hence, NH3 will have greater value for 'a'. (ii) As NH3 molecule is larger in size than N2, hence NH3 will have greater value for 'b'. (For NH3,a=4.17L2atm mol−2,b=0.0371Lmol−1 For N2,a=1.39L2 atm mol−2,b=0.0319Lmol−1)
Q.44 At a particular temperature, why vapour pressure of acetone is less than that of ether?
Answer: This is because the intermolecular forces of attraction in acetone are stronger than those present in ether.
Q.45 A liquid is transferred from a smaller vessel to a bigger vessel at the same temperature. What will be the effect on the vapour pressure?
Answer: No effect as it depends only on the nature of the liquid and temperature.
Q.46 Why vegetables are cooked with difficulty at a hill station?
Answer: The atmospheric pressure is less and so the boiling point is lowered.
Q.47 What is the difference between normal boiling pint and standard boiling point?
Answer: When the external pressure is equal to one atmosphere pressure, the boiling point is called normal boiling point. When the external pressure is 1 bar, it is called standard boiling point.
Q.48 Explain why temperature of a boiling liquid remains constant?
Answer: At the boiling point, the heat supplied is used up in breaking off the intermolecular forces of attraction of the liquid to change it into vapour and not for raising the temperature of the liquid.
Q.49 What happens if a liquid is heated to the critical temperature of its vapours?
Answer: The meniscus between the liquid and the vapour disappears (surface tension of the liquid becomes zero).
Q.50 Why liquids diffuse slowly as compared to gases?
Answer: In liquids, the molecules are less free than in a gas, i.e., the intermolecular forces (van der Waals forces) in a liquid are greater than in a gas.
|
117 videos|225 docs|239 tests
|
FAQs on Short & Long Answer Questions: States of Matter - Physical Chemistry for NEET
| 1. What are the three states of matter? |  |
| 2. How do substances change from one state of matter to another? |  |
| 3. What is the difference between evaporation and boiling? |  |
| 4. What is sublimation? |  |
| 5. How does pressure affect the states of matter? |  |

|
Explore Courses for NEET exam
|

|

















