Long Type Questions - Enterprise Growth Strategies, Entrepreneurship, Class 12 | Additional Study Material for Commerce PDF Download
Q1. What are the different types of value added ? (TBQ) (6 marks)
Ans.
(i) Quality added value : Quality added value is basically adding convenience, ease of use or other desirable characteristics that customers value. For example, turning a commodity into a branded product or design enhancements like pull tabs for easy opening or sipper tops on beverage bottles.
(ii) Environmental added value : Environmental added value employs methods or systems that do not harm the environment or are less harmful than those commonly used. For example, using less electricity, using less fuel and using recycled material for packaging.
(iii) Cause-related added value : Cause-related added value is a social marketing strategy where business contributes part of the revenue from a product or service to a cause. For example, a business may donate a percentage of revenue from each transaction to a cause such as an educational facility for disadvantaged children or a wildlife sanctuary.
(iv) Cultural added value : Cultural added value is also a social marketing stragety that employs methods or systems of production involving cultural aspects or allow for the needs and sensitivities of cultural groups. For example, using a combination of English and the language of other ethnic groups in a community in written communications.
Q2. Explain in detail Porter’s Generic Value Cahin with the help of a diagram. (TBQ) (6 marks)
Ans. Inbound logistics : Goods being obtained from the organisation’s suppliers and to be used for producing the end product.
Operations : Raw materials and goods are manufactured into the final product. Value is added to the product at this stage as it moves through the production line.
Outbound logistics : Once the products have been manufactured, they are ready to be distributed to distribution centres, wholesalers, retailers or customers. Distribution of finished goods is known as outbound logistics.
Marketing and sales : Marketing must make sure that the product is targeted towards the correct customer group. The Marketing mix is used to establish an effective strategy. Any competitive advantage is clearly communicated to the target group through the promotional mix.
Services : After the product/service has been sold, what support services does the organisation offer customers ? This may come in the form of after sales training, guarantees and warranties.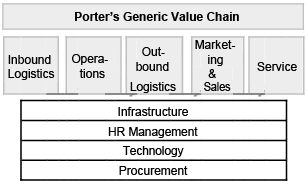
Q3. Explain the requirements of value chain management. (TBQ) (6 marks)
Ans.
(i) Coordination and collaboration : To increase efficiency within an organisation, coordination and collaboration is essential. Coordinate the work groups to ensure efforts are not duplicated. Utilize the theory that the whole is greater than the sum of its parts by collaborating with other groups and individuals to achieve a common goal.
(ii) Technology investment : Technology plays a large role in manufacturing and distribution. With outdated technology, such as old computers or machinery, an organisation’s competitiveness is weakned due to a loss in productivity.
(iii) Organisational process : In value chain management, every aspect of an organisation’s process is identified. Improvement in processes through better technology and greater procedural knowledge is important to the present and future success of a company.
(iv) Leadership : Strong leaders are crucial to the success in value chain management. Conflict management, motivation and direction are traits that strong leaders display.
(v) Employee/human resources : Without a knowledgeable and active human resources department, employees may feel they don’t have a voice within the company.
(vi) Organisational Culture and Attitudes : Organisations that foster strong cultural identity with positive attitudes tend to attract and retain top employees.
Q4. Explain the “support activities” of an organization. (6 marks)
Ans. Support activities assist the primary activities in helping the organization achieve its competitive edge. They include :
(i) Procurement : This department must source raw materials for the business and obtain the best price for doing so.
(ii) Technological Development : Technology can be used in may ways, including production, to reduce cost and thus adding value, research and development to new products on the internet so that customers can have 24×7 access to the firm.
(iii) Human Resource Management : The organization will have to recurit, train and develop the right people for the organization to be successful. Staff will have to be motivated and paid the “market rate”, if they are to stay with the organization and add value.
(iv) Firm Infrastructure : Every organization needs to ensure that their finances, legal structure and management structure work efficiently and help drive the organization forward. Inefficient infrastructure’s waste resources could affect the firm’s reputation and even leave it open to fines and sanctions.
|
4 videos|168 docs
|















