Class 9 History Chapter 3 Extra Question Answers - Nazism and the Rise of Hitler
46) Describe the effects of the Treaty of Versailles on Germany. Or Discuss any three major clauses of the 'Treaty of Versailles'? Or The Treaty of Versailles sowed the seeds of the Second World War. Justify.
Answer: This treaty had a far reaching impact and paved the way for the rise of Nazism in Germany and the Second World War. (i) After signing this treaty, Germany lost its overseas colonies, a tenth of its population, 13 per cent of its territories, 75 per cent of its iron and 26 per cent of its coal to France, Poland, Denmark and Lithuania.
(ii) The war guilt clause held Germany responsible for the war and Germany was forced to pay compensation amounting to 6 billion.
(iii) The treaty made provisions for demilitarization of Germany to further weaken it. Thus, the Treaty of Versailles was harsh, humiliating and devastating for the economy and national honour of the Germans. Its clauses became the causes for the rise of Nazism.
47) What is Nazism? Why did Nazism become popular in Germany by 1930? Or What were the reasons for the rise of Nazism in Germany? Or Why did Nazism become popular in Germany by 1930? Explain.
Answer:Nazism was a political system introduced by Hitler in Germany to establish dictatorship which propagated extreme hatred against the Jews is called Nazism. Some of the main causes of the rise and popularity of Nazism in Germany are
(i) The humiliating Versailles Treaty created a need to avenge of the defeat the First World War and restore the old prestige of Germany.
(ii) Germany witnessed a grave economic crisis and Hitler promised the people prosperity and peace.
(iii) Due to the Weimar Republic being weakened. Hitler took the opportunity and inspired the people.
(iv) Hitler had a strong personality and mass appeal which contributed a lot to the popularity of Nazism in Germany.
48) Describe the problems faced by the Weimar Republic. Or Describe any three problems faced by Weimar Republic in Germany. Or Explain any five problems faced by the Weimar Republic in Germany
Answer: (i) The Weimar Republic had to sign the humiliating Treaty of Versailles.
(ii) This Republic carried the burden of war guilt and was financially crippled by being forced to pay compensation.
(iii) Hyperinflation made the German Mark valueless and caused immense hardship for the common man. This economic crisis led to widespread inflation, misery and despair. (iv) In the Weimar Republic, both the communists and socialists became irreconcilable enemies and could not make common cause against Hitler.
(v) Both revolutionaries and militant nationalists craved for radical solutions, which was not easy. Within its short life, the Weimar Republic saw twenty different cabinets and the liberal use of Article 48. All these created a political crisis in Germany.
(vi) It became very unpopular among the German, because it lost the pride of the nation in the hands of Allies powers. 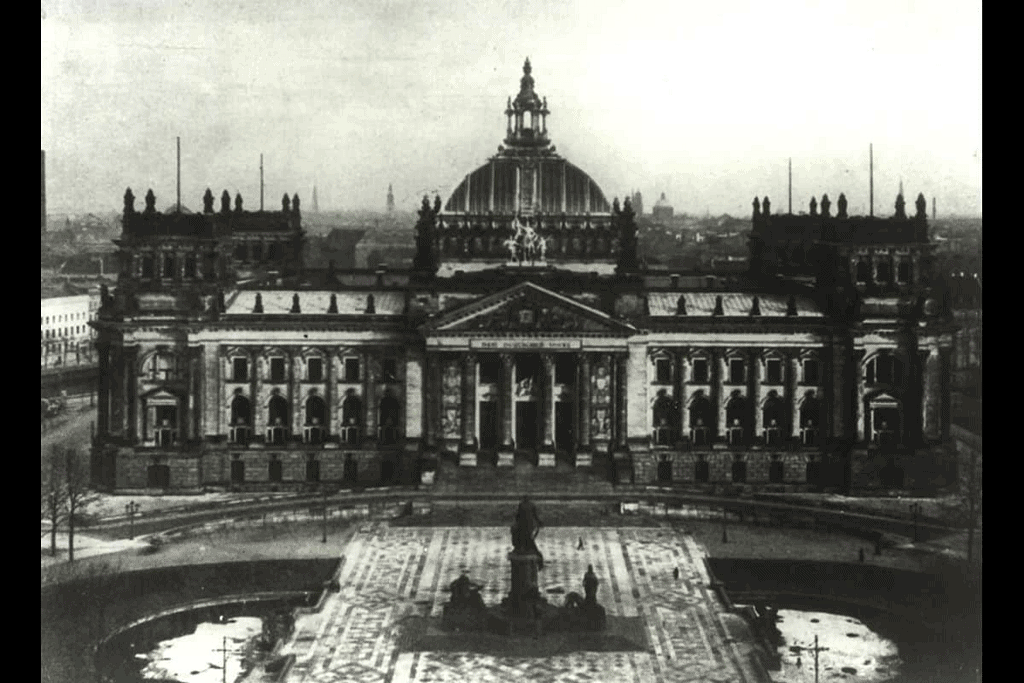 Reichstag: The lower house of the new Weimar Republic’s Parliament
Reichstag: The lower house of the new Weimar Republic’s Parliament
49) What are the peculiar features of Nazi thinking?
Answer:The peculiar features of Nazi thinking were
(i) They believed that the strong should rule the world and the rest should accept their leadership.
(ii) They believed in racial hierarchy, where the Nordic German Aryans were at the top and the Jews at the lowest rung.
(iii) The Nazis believed that the Jews were their greatest enemies. So the Jews were tortured and killed.
(iv) From a very young age, children were indoctrinated both inside and outside school with the Nazi ideology of nationalism and war.
(v) The Nazis believed in the geopolitical concept of Lebensraum or living space, i.e., new territories had to be acquired for the German nation.
(vi) Womens were seen as mere bearers of the Aryan culture and race.
50) Explain why Nazi propaganda was effective in creating a hatred for Jews?
Answer:Nazi propaganda was effective in creating hatred for the Jews because Nazis successfully exploited the low position of the Jews in medieval times as there was a traditional Christian hatred against the Jews.
(ii) The Jews were affluent being mainly traders and moneylenders. The economically shattered, unemployed German people easily developed hatred against them.
(iii) The Jews lived separately in marked areas called ghettos; they therefore became easy targets.
(iv) The Nazis introduced the hatred theory against the Jews from the very beginning of the child's school life so that they grew up with this hatred.
(v) Nazi ideas were spread through visual images, posters, slogans, leaflets, films, etc. This propaganda worked on the minds and emotions of the German people.
51) In what ways did the Nazi state seek to establish total control over its people?
Answer:After becoming the Chancellor of Germany (1933), Hitler captured all powers.
(i) All political parties and trade unions were banned except the Nazi Party and its affliates.
(ii) The state established total control over the economy, media, army and judiciary.
(iii) Germany became almost a police state. Special surveillance, security forces, secret state police (Gestapo) were created to control the society.
(iv) The Nazi rule glorified war and chose the path of war as a way out of the economic crisis.
(v) The Nazi rule targeted the Jews as the cause of all miseries and undertook genocidal war against the Jews.
(vi) Hitler introduced a massive programme of militarisation to enhance the military power of Germany and to restore her international honour and glory.
52) State any five measures taken by the Nazis to create a pure German racial state. Or Explain any three steps taken by Hitler to establish racial state. Or Explain the Nazi idea of a racial state.
Answer: (i) Nazi ideology stated that the Nordic German Aryans were at the top and the Jews were located at the lowest rung of society.
(ii) The Jews, gypsies and blacks were regarded as racially impure and 'undesirable', and they were widely persecuted.
(iii) Under the Euthanasia programme, many Germans who were considered mentally or physically unfit were condemned to death.
(iv) Russians and Poles were considered as subhuman and captured civilians from Russia and Poland were forced to work as slave labour.
(v) From 1933 to 1938, the Nazis terrorised, pauperised and segregated the Jews, compelling them to leave Germany. From 1939 to 1945, a large number of them were killed in gas chambers in Poland.
53) How were the ideas of Darwin and Herbert Spencer adopted by Hitler or Nazis? Explain.
Answer: Hitler's racism borrowed from thinkers like Charles Darwin (1809-1882) and Herbert Spencer (1820-1903). Darwin was a natural scientist who tried to explain the creation of plants and animals through the concepts of evolution and natural selection. In 1859, Darwin published 'On the Origin of Species by Means of Natural Selection' in which he proposed a theory of evolution by the process of natural selection. But he never advocated human intervention in what he thought was a purely natural process of selection. His ideas were used by racist politicians to justify imperial rule over conquered peoples. Herbert Spencer was deeply influenced by Charles Darwin's 'On the Origin of Species' and gave the idea of 'Survival of the Fittest' in his book, 'Principles of Biology'. He developed an all embracing conception of evolution as the progressive development of the physical world, biological organism, the human mind and human culture and societies. According to his ideas, only those species survival on Earth that could adopt themselves to changing climatic conditions. Adopting his idea, the Nazi government suggested that the strongest race, i.e., Nordic German Aryans would survive and the weak ones would perish.
54) What were the effects of great economics depression of 1929-1932 on Germany?
Answer:The German economy was the worst hit by the economic crisis caused by the Great Economic Depression (1929-1932) in the USA. German investments and industrial was largely dependent on loan from the USA. The Wall Street Exchange crashed in 1929, the USA withdrew the support from Germany.
(i) By 1932, industrial production was reduced to 40 per cent of the 1929 level.
(ii) The number of unemployed was 6 million. People with 'willing to do any work' placard could be seen on the street. Unemployment rate reached nearly 30 per cent in 1932.
(iii) Unemployed youths sometimes involved in criminal activities. They were seen playing cards, sitting at street corners or desperately queuing up at local employment exchange. (iv) The Germany currency (mark) collapsed, prices rose phenomenally high due to hyper inflation.
(v) The economic crisis created deep anxieties and fear in people. As business got ruined, small businessmen, self-employed and retailers were filled with the fear of proletarianisation, an anxiety of being reduced to the ranks of workers or unemployed.
(vi) Big businessmen were also in crisis.
(vii) The large mass of peasantry was affected by a sharp fall in agricultural prices.
(viii) Women, unable to feed their children properly, were filled with a sense of despair.
55) Or Describe the impact of economic depression of Germany? Or Describe the impact of great economic depression (1929-1932) on various sections of society in Germany?
Answer: Hitler was a powerful orator. His speech could mesmerise the masses
(i) He promised to build strong nation, undo the injustice of the Versailles Treaty and restore the dignity of the German people.
(ii) He assured employment for unemployed people and a secured future for the youths. (iii) He promised to control all foreign influence and resist all foreign conspiracies against Germany.
(iv) He introduced a new style of politics. Nazi party held massive rallies and public meetings to demonstrate the supports for Hitler and these massive mobilization created a sense of unity among German people.
(v) Nazi propaganda skillfully projected Hitler as a messiah, a saviour as someone who had arrived to save people from their distress.
(vi) Hitler came during such a period when the dignity and pride of German people were totally shattered due to the defeat in First World War and humiliating Treaty of Versailles. The crisis in the economy, polity and society formed the background of Hitler's rise to power.
56) What factors enabled the recast of Germany's political system after the First World War?
Answer:The factors which enabled the recast of German policy after the First World War were the defeat which Imperial Germany suffered in the First World War and the abdication of the German emperor.
57) Who according to Hitler topped the racial hierarchy? Who formed the lowest rung of the hierarchy?
Answer: The Nordic German Aryans were at the top, while the Jews were located at the lowest rung of the racial hierarchy.
58) Who were the signatories of the 1940 Tripartite Pact?
Answer:Germany, Italy and Japan were the signatories of the 1940 Tripartite Pact.
59) The Nazi party was renamed after which organisations?
Answer:The Nazi party was renamed after the National Socialist German Workers' Party.
60) Why did Nazis hold massive rallies and public meetings in Germany ?
Answer:Nazis held massive rallies and public meetings in Germany to demonstrate the support for Hitler and instil a sense of unity among the people.
62) When did German President Hindenburg offer the Chancellorship to Hitler?
Answer:On 30th January, 1933 President Hindenburg offered the Chancellorship to Hitler.
63) What was the significance of the Enabling Act?
Answer:The Enabling Act enabled Hitler to sideline Parliament and rule by decree.
64) What does the term 'Genocidal War' refer to?
Answer: The term 'Genocidal War' refers to the mass murder of selected groups of innocent civilians in Europe by Germany during the Second World War.
65) When did the US enter the Second World War?
Answer:When Japan extended its support to Hitler and bombed the US base at Pearl Harbour on 7th December, 1941, the US entered the Second World War.
66) Hitler's views on racialism were based on which thinkers?
Answer: Hitler's views on racialism were based on views of Charles Darwin and Herbert Spencer.
67) What was the Nazi argument for their imperialist ambitions ?
Answer:The Nazi argument for their imperialist ambitions was that the strongest race would survive and the weak perish. To retain purity of the Aryan race, they had to dominate the world.
68) Who were the worst sufferers in Nazi Germany and why ?
Answer: The Jews remained the worst sufferers in Nazi Germany. Nazi hatred for Jews had a precursor in the traditional Christian hostility towards the Jews. The Jews were considered as the killers of Christ and usurers. However, Hitler's hatred of Jews was based on pseudoscientific theories of race.
69) Name some countries which became victims of Hitler's aggressive policy.
Answer:Some countries which became victims of Hitler's aggressive policy were Poland, Austria, Czechoslovakia, Holland, Belgium, France, countries of North Africa and Russia.
70) How were the deputies of Reichstag appointed?
Answer: The deputies of the Reichstag were elected on the basis of universal adult franchise including women.
71) When was the Youth League of Nazis founded?
Answer:The Youth League of the Nazis was founded in 1922.
72) What was The Eternal Jew'?
Answer: It was the most infamous film which was made to create hatred for Jews.
73) Who was regarded as the most important citizen according to Hitler?
Answer:The mothers were regarded as most important citizens according to Hitler.
74) Who is the author of the book Third Reich of Dreams'?
Answer:Charlotte Beradt is the author of this book.
75) For what was Auschwitz notorious during the Nazi period ?
Answer: Auschwitz was notorious for gas chambers used for mass human killing.
|
53 videos|437 docs|80 tests
|
FAQs on Class 9 History Chapter 3 Extra Question Answers - Nazism and the Rise of Hitler
| 1. What is Nazism and how did it contribute to the rise of Hitler? |  |
| 2. What were the key factors that enabled Hitler's rise to power? |  |
| 3. How did Hitler consolidate his power once he became the Chancellor of Germany? |  |
| 4. What were the main goals of the Nazi Party under Hitler's leadership? |  |
| 5. What were the major consequences of Hitler's rule and the Nazi regime? |  |

|
Explore Courses for Class 9 exam
|

|


















