LEARNING OUTCOMES
At the end of this unit, you should be able to:
- Explain how the prices are generally determined.
- Describe how changes in demand and supply affect prices and quantities demanded and supplied.
INTRODUCTION
Prices of goods express their exchange value. Prices are also used for expressing the value of various services rendered by different factors of production such as land, labour, capital and organization in the form of rent, wages, interest and profit. Therefore, the concept of price, especially the process of price determination, is of vital importance in Economics.
In this unit, we shall learn how demand and supply interact to strike a balance so that equilibrium price is determined in a free market. A free market is one in which the forces of demand and supply are free to take their own course and there is no intervention from outside by government or any other entity. It is to be noted that, generally, it is the interaction between demand and supply that determines the price, but sometimes Government intervenes and determines the price either fully or partially. For example, the Government of India fixes the price of petrol, diesel, kerosene, coal, fertilizers, etc. which are critical inputs. It also fixes the procurement prices of wheat, rice, sugarcane, etc. in order to protect the interests of both producers and consumers. While determining these prices, the Government takes into account factors like cost of inputs, risks of business, nature of the product etc.
One of the main reasons for studying the demand and supply model is that the model is particularly useful in explaining how markets work. A comprehensive knowledge of the movements of these market forces enables us to explain the observed changes in equilibrium prices and quantities of all types of products and factors. We will be able to anticipate the possible market outcomes in real markets by applying the principles underlying the interactions of demand and supply. Business firms can use the model of demand and supply to predict the probable effects of various economic as well as non economic factors on equilibrium prices and quantities. For example, the market outcomes of government intervention in the form of taxation, subsidies, price ceiling and floor prices etc. can be analysed with the help of equilibrium analysis.
DETERMINATION OF PRICES - A GENERAL VIEW
In an open competitive market, it is the interaction between demand and supply that tends to determine equilibrium price and quantity. In the context of market analysis, the term equilibrium refers to a state of market in which the quantity demanded of a commodity equals the quantity supplied of the commodity. In an equilibrium state, the aggregate quantity that all firms wish to sell equals the total quantity that all buyers in the market wish to buy and therefore, the market clears. Equilibrium price or market clearing price is the price at which the quantity demanded of a commodity equals the quantity supplied of the commodity i.e. at this price there is no unsold stock or no unsupplied demand.
To analyse how equilibrium price is determined in a market, we need to bring together demand for and supply of the commodity in the market. Combining the tables of demand and supply (on page 2.30 and 2.75 respectively) of Chapter-2, we have the following schedule:
Table – 3: Determination of Price
| Sr. No. | Price (₹) | Demand Units
| Supply (Units)
|
| 1 | 1 | 60 | 5 |
| 2 | 2 | 35 | 35 |
| 3 | 3 | 20 | 45 |
| 4 | 4 | 15 | 55 |
| 5 | 5 | 10 | 65 |
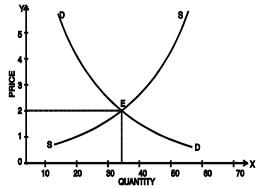
When we plot the above points on a single graph with price on Y-axis and quantity demanded and supplied on X-axis, we get a figure as shown below:

Fig. 6: Determination of Equilibrium Price
It is easy to see what will be the market price of the article. It cannot be ₹ 1, because at that price there would be 60 units in demand, but only 5 units on offer. Competition among buyers would force the price up. On the other hand, it cannot ₹ 5, for at that price, there would be 65 units on offer for sale but only 10 units in demand. Competition among sellers would force the price down. At ₹ 2, demand and supply are equal (35 units) and the market price will tend to settle at this figure. This is equilibrium price and quantity – the point at which price and output will tend to stay. Once this point is reached, we will have stable equilibrium. Equilibrium is said to be stable if any disturbance to it is self adjusting so that the original equilibrium is restored. In other words, if the equilibrium be disrupted, the market returns to equilibrium. It should be noted that it would be stable only if other things are equal.
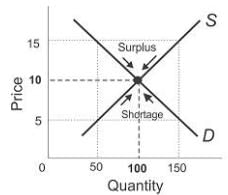
The following diagram (Fig 7) will demonstrate how stable equilibrium is achieved through price mechanism or market mechanism. If the market price is above the equilibrium price, say ₹ 15, the market supply is greater than market demand and there is an excess supply or surplus in the market. Competing sellers will lower prices in order to clear their unsold stock. As we know, other things remaining constant, as price falls quantity demanded rises and quantity supplied falls. In this process the supply-demand gap is reduced and eventually eliminated thus restoring equilibrium.

Fig 7: Stable Equilibrium
Likewise, if the prevailing market price is below equilibrium, say ₹ 5 in our example, a shortage arises as quantity demanded exceeds the quantity supplied. The shortage prompts the price to rise, as the buyers, who are unable to obtain as much of the good as they desire, bid the price higher. The market price tends to increase. Other things remaining the same, the price rise causes a decrease in the quantity demanded by the buyers and an increase in the quantity supplied by the sellers and vice versa. This process will continue as long as demand exceeds supply. The market thus achieves a state where the quantity that firms sell is equal to the quantity that the consumers desire to buy. At equilibrium price (₹ 10), the supply decisions of the firms tend to match the demand decisions of the buyers. Thus, the equilibrium is restored automatically, through the fundamental working of the market and price movements eliminate shortage or surplus