Waste And Sources of Waste, (Class 6) PDF Download
Introduction
Waste is defined as unwanted and unusable materials and is regarded as a substance which is of no use. Waste that we see in our surroundings is also known as garbage. Garbage is mainly considered as a solid waste that includes wastes from our houses (domestic waste), wastes from schools, offices, etc (municipal wastes) and wastes from industries and factories (industrial wastes).
Sources of Waste
Sources of waste can be broadly classified into four types: Industrial, Commercial, Domestic, and Agricultural.
Industrial Waste
These are the wastes created in factories and industries. Most industries dump their wastes in rivers and seas which causes a lot of pollution.
Example: plastic, glass, etc.
Commercial Waste
Commercial wastes are produced in the schools, colleges, shops, and offices.
Example: plastic, paper, etc.
Domestic Waste
The different household wastes which are collected during household activities like cooking, cleaning, etc. are known as domestic wastes.
Example: leaves, vegetable peels, excreta, etc.
Agricultural Waste
Various wastes produced in the agricultural field are known as agricultural wastes.
Example: cattle waste, weed, husk, etc.
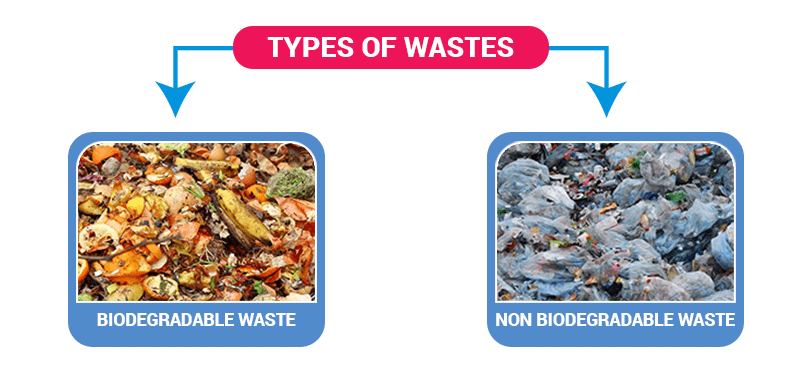
Commonly waste is classified into two types: Biodegradable and Non-biodegradable waste. These two kinds of wastes are explained below:
Types of Waste
Biodegradable waste
These are the wastes that come from our kitchen and it includes food remains, garden waste, etc. Biodegradable waste is also known as moist waste. This can be composted to obtain manure. Biodegradable wastes decompose itself over a period of time depending on the material.
Non-biodegradable waste
These are the wastes which include old newspaper, broken glass pieces, plastics, etc. Non-biodegradable waste is known as dry waste. Dry wastes can be recycled and can be reused. Non-biodegradable wastes do not decompose by themselves and hence are major pollutants.
Recycling of Waste
Recycling of waste product is very important as this process helps in processing waste or used products into useful or new products. Recycling helps in controlling air, water, and land pollution. It also uses less energy. There are a number of items that can be recycled like paper, plastic, glass, etc. Recycling helps in conserving natural resources and also helps in conserving energy. Recycling helps in protecting the environment as it helps in reducing air, water, and soil pollution.
Decomposition of Biodegradable Waste
Biodegradable waste can be decomposed and converted into the organic matter with the help of different processes.
Composting
This is the method in which waste can be decomposed and converted into organic matter by burying them in the compost pits. The wastes are composed by the action of bacteria and fungi.
Vermicomposting
This method involves decomposition of organic matter into fertile manure with the help of red worms. This manure is known as vermicompost.
Chemical waste
Chemical wastes are wastes that are made from harmful chemicals which are mostly produced in large factories. Chemical wastes may or may not be hazardous. A chemical waste which is hazardous can be solid, liquid or gaseous and will show hazardous characteristics like toxicity, corrosivity, ignitability, and reactivity.
FAQs on Waste And Sources of Waste, (Class 6)
| 1. What is waste and what are the different sources of waste? |  |
| 2. How can household waste be managed effectively? |  |
| 3. What are the environmental impacts of improper waste disposal? |  |
| 4. How can industrial waste be minimized? |  |
| 5. What are the health risks associated with biomedical waste? |  |

|
Explore Courses for Class 6 exam
|

|

















