Coded inequalities -2 | Quantitative Aptitude (Quant) - CAT PDF Download
Question 13: For how many integer values does the following inequality hold good? (x + 2) (x + 4) (x + 6)........(x + 100) < 0?
A. 25
B. 50
C. 49
D. 47
Answer. 25
Explanation.
(x + 2) (x + 4) (x + 6) ........(x + 100) < 0
Now, the above expression will be zero for x = –2, –4, –6, – 8…..–100.
For x > – 2 all the terms will be positive and so, the product will be positive.
For x < – 100, all the terms will be negative and since there are 50 terms (even number), the product will be positive.
Now, if x = – 99, the term x + 100 would be positive, everything else would be negative, so the expression would have 49 negative terms and one positive term. So the product would be negative.
Overall the expression will be negative if there are exactly 49 negative terms, or exactly 47 negative terms, or exactly 45 terms…. Or so on, up to exactly one negative term.
Exactly 49 negative terms= x = – 99
Exactly 47 negative terms= x= – 95
Exactly 45 negative terms= x = – 91
...............
Exactly 1 negative term=. x = – 3
So, x can take values {–3, –7, –11, –15, –19…. –99}. We need to compute how many terms are there in this list.
In other words, how many terms are there in the list {3, 7, 11, ....99}. Now, these terms are separated by 4, so we can write each term as as multiple of 4 + ‘some constant’.
Or 3 = 0 * 4 + 3
7 = 1 * 4 + 3
11 = 2 * 4 + 3
......................
99=24 * 4 + 3
We go from 0 * 4 + 3 to 24 * 4 + 3, a total of 25 terms.
The question is "For how many integer values does the given inequality hold good? (x + 2) (x + 4) (x + 6)........(x + 100) < 0?"
Hence the answer is "25"
Choice A is the correct answer.
Question 14: If a, b, c are integers such that – 50 < a, b, c < 50 and a + b + c = 30, what is the maximum possible value of abc?
Answer. 4410
Explanation.
abc will be maximum when it is positive. So, a, b, c can all be positive or two of the three can be negative and one positive.
When all are positive, max product is when the numbers are 10, 10 and 10.
When two are negative and one positive, the best–case scenario would be when two negative numbers are as low as possible (magnitudes as high as possible) so that the product can be high. Now, in order for the product to be maximum, the positive number should be as high as possible. So, let the positive number be 49. Then the sum of the two negative numbers should be –19. The best– case scenario would be when numbers are 49, –9, –10.
Product would be 4410.
The question is "what is the maximum possible value of abc?"
Hence the answer is "4410"
Choice C is the correct answer.
Question 15: Solve x2 - |x + 3| + x > 0?
A. x ∊ (-∞,-1] ∪ [√3, 3)
B. x ∊ (-∞,-3] ∪ [√3, ∞)
C. x ∊ (-4,-3) ∪ (4, ∞)
D. x ∊ (-8,-3] ∪ [2, ∞)
Answer. x ∊ (-∞,-3] ∪ [√3, ∞)
Explanation.
x2 - |x + 3| + x > 0
If x + 3 > 0 ⇒ x > -3
Then equation is in the form x2 - x - 3+ x > 0 i.e., x2 -3 > 0
x2 > 3 ⇒ x < -√3 and x > √3
But x > -3, thus x > √3
Now if x + 3 > 0 ⇒ x < -3
Then equation is in the form x2 + x + 3 + x > 0 ⇒ x2 + 2x + 3 > 0
Discriminant < 0 ⇒ a > 0 and iequality > 0 exist for all value of x.
But x < -3 , thus range will be x < -3
Combining both x ∊ (-∞,-3] ∪ [√3, ∞)
The question is "what is the maximum possible value of abc?"
Hence the answer is "x ∊ (-∞,-3] ∪ [√3, ∞) "
Choice B is the correct answer.
Question 16: Find range of f(x) = x2 – 6x + 14?
A. (-∞, 8)
B. (-∞, 100)
C. (-∞, 45)
D. (5, ∞)
Answer. (5, ∞)
Explanation.
x2 - |x + 3| + x > 0
Given, f(x) = x2 – 6x + 14
f(x) can be written as x2 – 6x +9 -9 + 14
⇒ f(x) = (x-3)2 + 5
As you can see, for whatever value of x, the term (x-3)2 is always positive. The least value it can take is zero, so the minimum value of the function is 5.
The maximum value can range until infinity.
Therefore, Range = (5, ∞)
The question is "Find range of f(x) = x2 – 6x + 14?"
Hence the answer is "(5, ∞)"
Choice D is the correct answer.
Question 17: Solve 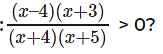
A. x ∊ (-∞,-1] ∪ [√3, 3)
B. x ∊ (-∞,-3] ∪ [√3, ∞)
C. x ∊ (-4,-3) ∪ (4, ∞)
D. x ∊ (-8,-3] ∪ [2, ∞)
Answer. x ∊ (-∞,-1] ∪ [√3, 3)
Explanation.
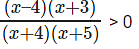
Consider this as 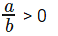
Here both a > 0 & b > 0 or a < 0 & b < 0
Case 1: (x – 4) (x + 3) > 0 & (x + 4) ( x +5) > 0
x > 4 , x > -3, x > -4 , x > -5
Combining all we get x > 4
Case 2: (x – 4) (x + 3) < 0 & (x + 4) ( x +5) < 0
x < 4, x < -3, x < -4, x < -5
Combining all x < -5
Hence range is (-∞,-5) ∪ (4, ∞)
The question is "Solve 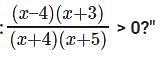
Hence the answer is "x ∊ (-∞,-1] ∪ [√3, 3)"
Choice A is the correct answer.
Question 18: Consider three distinct positive integers a, b, c all less than 100. If |a - b| + |b - c| = |c – a|, what is the maximum value possible for b?
A. 98
B. 99
C. 50
D. 100
Answer. 98
Explanation.
|q – p| is the distance between p and q on the number line. |p –q| is the same as |q –p| to begin with.
So, in this case we are told |a -b| + |b -c| = |c – a|. Think about this. What does this mean? There are three points on the number line. We are talking about 3 distances on the number line here. We know that sum of some two of the distances is equal to the third. What does this tell us?
This tells us that the point b has to be in between a and c. With this we are done. We can have a or c to be 99 and b to be 98.
Maximum value b can take is 98. Classic question.
The question is "If |a - b| + |b - c| = |c – a|, what is the maximum value possible for b?"
Hence the answer is "98"
Choice A is the correct answer.
Question 19: Consider integers m, n such that -5 < m < 4 and -3 < n < 6. What is the maximum possible value of m2 - mn + n2?
A. 65
B. 60
C. 50
D. 61
Answer. 61
Explanation.
Points to note
1. m2 and n2 are always positive
2. -mn will be maximum when m and n have opposite signs
After this, it is pretty simple. We are better off with m being negative and n positive as in this case they can take higher values. m = -4, n = 5 works best. Note that as far as absolute value is concerned maximum |m| can be is 4 and maximum |n| can be is 5. This is important, otherwise we may have a scenario where even sacrificing –mn we might be able to maximise this.
So, m = -4, n = 5 works
m2 - mn + n2 = 16 + 20 + 25 = 61.
The question is "What is the maximum possible value of m2 - mn + n2?"
Hence the answer is "61"
Choice D is the correct answer.
Question 20: Consider integers p, q, r such that |p| < |q| < |r| < 40. P + q + r = 20. What is the maximum possible value of pqr?
A. 3600
B. 3610
C. 3510
D. 3500
Answer. 3510
Explanation.
We need to maximise pqr. So, we should shoot for either all three positive or two negative and one positive. Given p + q + r = 20, two positive and one negative works better. Let us say we choose p, q to be negative and r to be positive. Maximum value r can take is 39. p + q now becomes -19.
P = -9, q = -10 and r = 39 works best.
So, the product should be -9 * -10 * 39 = 3510.
The question is "What is the maximum possible value of pqr?"
Hence the answer is "3510"
Choice C is the correct answer.
Question 21: What is the minimum value of f(x) = x2 – 5x + 41?
A. 139/4
B. 149/4
C. 129/4
D. 119/4
Answer. 139/4
Explanation.
This question is present for one reason and one reason only. To talk about the idea of “completion of squares”. There are two ways of solving this question
The ugly differentiation based method and the beautiful completion of squares method.
Always pick the elegant method. You might not prefer VVS Laxman over Gary Kirsten, or Federer over Nadal. But these are matters of sport. When it comes to math solutions – elegant solutions kick ass every time.
What is this famous completion of squares method ?
Any quadratic expression of the form x2 + px + q can be written in the form (x +a)2 + b.
Write in that form, enjoy the equation and have some fun.
x2 – 5x + 41 = (x + a)2 + b. what value should ‘a’ take? Forget about b for the time being.
(x + a)2 = x2 + 2ax + a2. The 2ax term should correspond to -5x. Done and dusted.

x2 – 5x + 41 can be written as 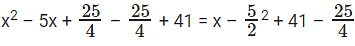
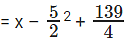
The minimum value this expression can take is 139/4
The question is "What is the minimum value of f(x) = x2 – 5x + 41?"
Hence the answer is "139/4"
Choice A is the correct answer.
Question 22: x4 – 4x3 + ax2 – bx = 1 = 0 has positive real roots. What is the maximum possible value of a + b?
A. 20
B. 12
C. 8
D. 10
Answer. 10
Explanation.
Fabulous question.
If we have an equation of the form ax4 + bx3 + cx2 + dx + e = 0 with Roots p, q, r and s.
We can say sum of the roots p + q + r + s = -b/a
Sum of the products taken two at a time pq + pr + ps + qr + qs + rs = 
Sum of the products taken three at a time pqr + pqs + prs + qrs = -d/a
Product of the roots pqrs = 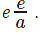
Note 1: We alternate between - and +
Note 2: Start with the immediate lower power for sum of roots, stick a negative symbol and then alternate.
So, if p, q, r, s were roots of this equation
p + q + r + s = 4,
pqrs = 1
Or, Arithmetic mean of p,q, r, s = 1 and geometric mean of pqrs = 1.
P, q, r s are positive real numbers. AM = GM. What does this mean?
This means that all 4 numbers are equal.
Or, this expression is (x-1)4
a = pq + pr + ps + qr + qs + rs = 6
-(-b) = pqr + pqs + prs + qrs = 4
a = 6, b = 4. a + b = 10
The question is "What is the maximum possible value of a + b?"
Hence the answer is "10"
Choice D is the correct answer.
Question 23: |x3 – 3x + 5| > -4. What range of x satisfies this?
A. [0,∞)
B. [-4, ∞)
C. All real values of x
D. [4,∞)
Answer. All real values of x
Explanation.
It may be late in the night when you solve this question. Overload of details might have dulled your senses. Mathematical ideas might be playing games with you. But that does not mean you should share a gift horse in the mouth.
Modulus of something > - 4. When can this not happen?
Who said CAT Preparation cannot be fun ?
This can never happen.
All real values of x satisfy the above inequality.
The question is "|x3 – 3x + 5| > -4. What range of x satisfies this?"
Hence the answer is "All real values of x"
Choice C is the correct answer.
Question 24: What are the maximum and minimum possible values for 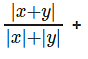
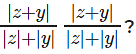
A. 3 and 1
B. 3 and 0
C. 4 and 0
D. 4 and 1
Answer. 3 and 1
Explanation.
We know that |x + y| < |x| + |y|.
So, each of these fractions lies between 0 and 1. So, all three added together should go from 0 to 3?
Is that the case? Is 2IIM running questions that are this simple?
When would this be 3? If x, y and z all have the same sign. Each fraction would be 1 and we would get 3 overall. Spot on! So, the maximum value is 3.
When can this go to zero.
When x=-y this fraction goes to 0. When x and y have opposite signs, the first term would go to zero. Likewise for the second and third terms as well.
So, what is the catch.
Among x, y, and z at least two will have the same sign.
So, of the three terms maximum of two can go to zero. One will be +1.
So, the minimum total overall = 1 (not 3)
The question is "What are the maximum and minimum possible values for 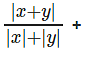
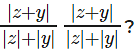
Hence the answer is "3 and 1"
Choice A is the correct answer.
|
196 videos|131 docs|110 tests
|
FAQs on Coded inequalities -2 - Quantitative Aptitude (Quant) - CAT
| 1. What are coded inequalities in the context of exams? |  |
| 2. How can I effectively solve coded inequalities questions during exams? |  |
| 3. Are there any tips or strategies for mastering coded inequalities for exams? |  |
| 4. What are some common symbols used in coded inequalities questions for exams? |  |
| 5. Where can I find practice questions and resources to improve my skills in solving coded inequalities for exams? |  |

|
Explore Courses for CAT exam
|

|

















