Mensuration: Solved Examples | Quantitative Aptitude (Quant) - CAT PDF Download
Question 1: A right circular cone has height H and radius R. A small cone is cut off at the top by a plane parallel to the base. At what height above the base the section has been made?
Statement (I): H = 20 cm
Statement (II): Volume of small cone: volume of large cone : 1:15
(A) If the question can be answered with statement I alone but not statement II alone, or can be answered with statement II alone but not statement I alone.
(B) If the question cannot be answered with statement I alone or with statement II alone, but can be answered if both statements are used together.
(C) If the question can be answered with either statement alone.
(D) If the question cannot be answered with the information provided.
Option B
Explanation:
From statement I, we know that the height of the initial cone is 20cm. However, nothing is said about the small cone. Hence, we cannot answer the question using statement A. So, we can eliminate choices (C).
We are down to choices, (A), (B) or (D).
From Statement II,we know that the ratio of the volume of the small cone to that of the large cone is 1 : 15.
i.e. 1/3*π*r2*h : 1/3*π*R2*H is 1 : 15 (r is the base radius of the smaller cone and h is the height of the smaller cone)
or r2 * h : R2 * H is 1 : 15
From this information, we will not be able to find the answer to h. Hence, we can eliminate choice (A).
Combining the information in the two statements:
When a section is made the two cones are similar triangles. so, h/H = r/R
R = rH/h
We know H = 20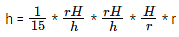
i.e., h3 = 1/15 * H3. Substituting H = 20, we can get the value for h.
Choice (B) is therefore, the correct answer.
Hence, the answer is If the question cannot be answered with statement I alone or with statement II alone, but can be answered if both statements are used together.
Question 2: A sphere of radius r is cut by a plane at a distance of h from its center, thereby breaking this sphere into two different pieces. The cumulative surface area of these two pieces is 25% more than that of the sphere. Find h.
(A) r/√2
(B) r/√3
(C) r/√5
(D) r/√6
Option A
Explanation: Area = 4πr2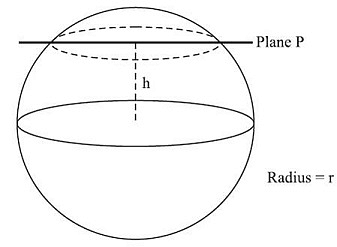
Cumulative area of the two pieces = 25%
more than that of sphere.
Area of 2 pieces = 1.25 × 4π2 = 5πr2
Extra area = πr2
Extra area = area of two new circles that are now created circles.
Area each new circle = πr2/2
Let radius of new circle be r1.
Now, πr12 = πr2/2
r1 = r/√2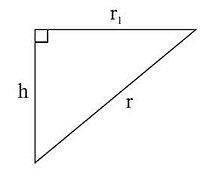
Now, r1 , h and r form a right angled triangle.
h2 + r12 = r2
h2 + (r/√2)2 = r2
h = r/√2
Choice (A) is therefore, the correct answer.
The question is " The cumulative surface area of these two pieces is 25% more than that of the sphere. Find h. "
Hence, the answer is r/√2
Question 3: Two mutually perpendicular chords AB and CD meet at a point P inside the circle such that AP = 6 cms, PB = 4 units and DP = 3 units. What is the area of the circle?
(A) 125π/4 sq cms
(B) 100π/7 sq cms
(C) 125π/8 sq cms
(D) 52π/3 sq cms
Option A
Explanation: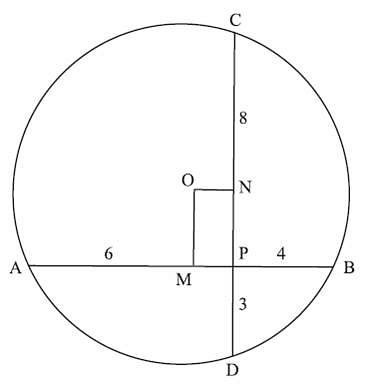
As AB and CD are two chords that intersect at O, AP * PB = CP * PD6 * 4 = CP * 3
CP = 8
From center O draw OM ⊥r AB and ON ⊥r CD.
From the center a line ⊥r to a chord bisects the chord.
So, we have AM = MB = 5 cm
MP = 1 cm, ON = 1 cm, CD = 11 cm, CN = 5.5 cm
ON2 + CN2 = OC2
12 + 5.52 + r2
1 + 30.25 = r2
Area = πr2
π * 31.25
31.25π = 125π/4 sq cms
The question is "What is the area of the circle?"
Hence, the answer is 125π/4 sq cms.
Question 4: Cylindrical cans of cricket balls are to be packed in a box. Each can has a radius of 7 cm and height of 30 cm. Dimension of the box is l = 76 cm, b = 46 cm, h = 45 cm. What is the maximum number of cans that can fit in the box?
(A) 15
(B) 17
(C) 22
(D) 21
Option D
Explanation:
This question requires a good deal of visualization. Since, both the box and cans are hard solids, simply dividing the volume won’t work because the shape can’t be deformed.
Each cylindrical can has a diameter of 14 cm and while they are kept erect in the box will occupy height of 30 cm
Number of such cans that can be placed in a row = l/Diameter = 76/14 = 5 (Remaining space will be vacant)
Number of such rows that can be placed = Width/Diameter = 46/14 = 3
Thus 5 * 3 = 15 cans can be placed in an erect position.
However, height of box = 45cm and only 30 cm has been utilized so far
Remaining height = 15 cm > 14 cm (Diameter of the can)
So, some cans can be placed horizontally on the base.
Number of cans in horizontal row = Lengthofbox/Heightofcan = 76/30 = 2
Number of such rows = Widthofbox/Diameterofcan = 46/14 = 3
∴ 2 * 3 = 6 cans can be placed horizontally
∴ Maximum number of cans = 15+6 = 21
The question is "What is the maximum number of cans that can fit in the box?"
Hence, the answer is 21.
Question 5: PQRS is a square of sides 2 cm & ST = 2 cm. Also, PT=RT. What is the area of ∆PST?
(A) 2 cm2
(B) √3 cm2
(C) √2 cm2
(D) 1/√2cm2
Option C
Explanation:
Notice, ∆PST ~ ∆SRT (all three sides equal). So, TS extended will meet PR at cross points of diagonal as shown:- 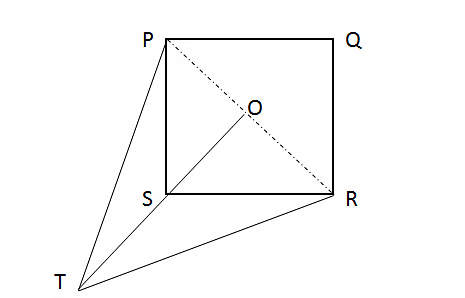
Now, A ∆ PST = A ∆ POT – A ∆ POS ---------- Equation(1)A ∆POT = 1/2 * PO * OT = 1/2 * 2√2/2 (PO = 2√2/2 as diagonal of square = 2√a) * (OS + ST)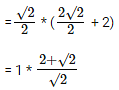
= √2 + 1
A ∆ POS = 1/4 * Area of Square
= 1/4 * 22 = 1cm2
=> A ∆ POT = √2 +1 - 1 = √2cm2
The question is " What is the area of ∆PST? "
Hence, the answer is √2cm2
Question 6: A string is wound around two circular disk as shown. If the radius of the two disk are 40 cm and 30 cm respectively. What is the total length of the string?
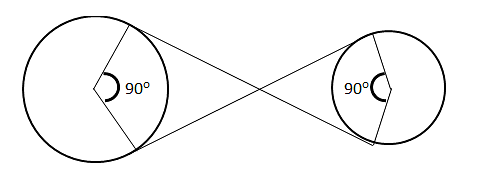
(A) 140 cm
(B) 140 + 165π cm
(C) 140 + 120π cm
(D) 140 + 165π/2 cm
Option D
Explanation: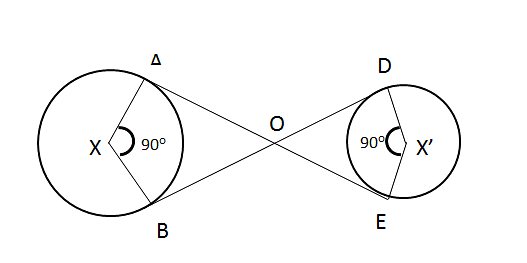
As, tangent from an exterior point makes right angle with the radius.
=> ADXB and ODX’E are squares,
∴ AO = BO = 40 cm
OD = DE = 30 cm
Length of string wound around circle x => 270°/360° ∗ 2 ∗ π ∗ 80
=120π
Similarly, Length of string wound around circle x’ => 270°/360° ∗ 2 ∗ π ∗ 30
= 3/4 ∗ 30π
= 45π/2
∴ Length of the string = 80 + 60 + 120π + 45π/2 ∗ π
= 140 + 165π/2
The question is "What is the total length of the string?"
Hence, the answer is 140 + 165π/2 cm.
Question 7: Figure below shows a box which has to be completely wrapped with paper. However, a single Sheet of paper need to be used without any tearing. The dimension of the required paper could be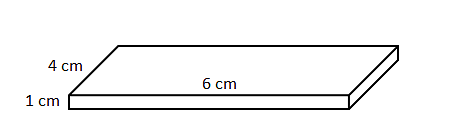
(A) 17 cm by 4 cm
(B) 12 cm by 6 cm
(C) 15 cm by 4 cm
(D) 13 cm by 4 cm
Option B
Explanation:
Total surface area of the box = 2(4 * 6 + 1 * 6 + 1 * 4)
= 2(24 + 6 + 4)
= 68 cm2
As the problem says, paper can’t be torn/cut a portion of paper will need to be fold, so, the area of paper required would be greater than 68 cm2.
Only option b) gives the area greater 68 cm2
The question is " The dimension of the required paper could be"
Hence, the answer is 12 cm by 6 cm
Question 8: An inverted right circular cone has a radius of 9 cm. This cone is partly filled with oil which is dipping from a hole in the tip at a rate of 1cm2/hour. Currently the level of oil 3 cm from top and surface area is 36π cm2. How long will it take the cone to be completely empty?
(A) 72π hours
(B) 1 hour
(C) 3 hours
(D) 36π hours
Option A
Explanation: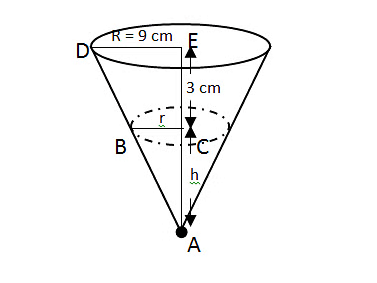
Given,
Surface area of oil = 36 π = πr2
=> r = 6 cm
Now,
∆ABC ~ ∆AED
=> DE/BC = AE/AC
=> 96 = (3+h)h
=> h = 6 cm
∴ Volume of oil in the cone = (1/3)πr2h
= (1/3) π62 x 6
= 72π
=> Time taken = 72π/1 = 72π hours.
The question is " How long will it take the cone to be completely empty? "
Hence, the answer is 72π hours.
Question 9: A square PQRS has an equilateral triangle PTO inscribed as shown:
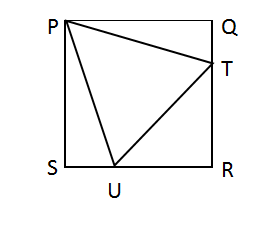
What is the ratio of A∆PQT to A∆TRU?
(A) 1 : 3
(B) 1 : √3
(C) 1 : √2
(D) 1 : 2
Option D
Explanation:
Let PQ, a side of equilateral triangle be b
By symmetry QT=ST=z (say)
A ∆ PQT = 1/2 * PQ * QT
= 1/2 * a * z
A ∆ TRU = 1/2 * RT * OR
= 1/2 * (a-z) * (a-z)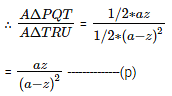
Since PQT and PTO are right angled triangles
PQ2 + QT2 = PT2
RT2 + RU2 = UT2
a2 + z2 = b2 --------- (1)
And, (a-z)2 + (a-z)2 = b2--------- (2)
=> a2 + z2 = 2(a-z)2
=> a2 + z2 = 2a2 + 2z2 – 4az
=> a2 + z2- 4az = 0
=> a2 + z2 – 2az = 2az (Please note how the solution is being managed here. You must always be aware of what you are looking for. Here, as equation -℗ we are looking for (a-z)2 in terms of az)
=> (a-z)2 =2az
Putting in equation (p) = az/2(az) = 1/2
The question is "What is the ratio of A∆PQT to A∆TRU?"
Hence, the answer is 1 : 2.
Question 10: A spherical shaped sweet is placed inside a cube of side 5 cm such that the sweet just fits the cube. A fly is sitting on one of the vertices of the cube. What is the shortest distance the fly must travel to reach the sweet?
(A) 2.5 cm
(B) 5(√3 – 1) cm
(C) 5(√2 – 1) cm
(D) 2.5(√3 – 1) cm
Option D
Explanation:
Distance = (Diagonal of cube–Diameter of sphere)/2 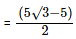 (Since the diagonal of the cube is given as √3 x l)
(Since the diagonal of the cube is given as √3 x l)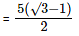
= 2.5(√3 – 1)
The question is "What is the shortest distance the fly must travel to reach the sweet? "
Hence, the answer is 2.5(√3 – 1) cm
Directions for questions 11 & 12: Answer the questions based on the following information:
A cow is tethered at point A by a rope. Neither the rope nor the cow is allowed to enter the triangle ABC Angle BAC = 30· Also AB =AC =10m.
Question 11: What is the area that can be grazed by the cow if the length of the rope is 8 m?
(A) 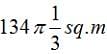
(B) 121π sq.m
(C) 132π sq.m
(D) 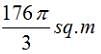
Option D
Explanation: 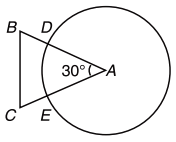
The figure shows the prohibited area for the cow and the area the cow can graze. The length of the rope is 8 m whereas the length of the sides id 10 m. Hence the scenario is as explained in the figure above. The height of this triangle can be calculated and is approx 9.6m. So clearly greater than 8 m. So the area grazed by the cow = Area of the circle – Area of the sector of 30o 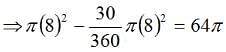
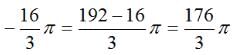
Question 12: What is the area that can be grazed by the cow if the length of the rope is 12 m?
(A) 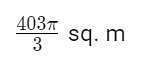
(B) 121π sq.m
(C) 132π sq.m
(D) 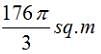
Option A
Explanation: 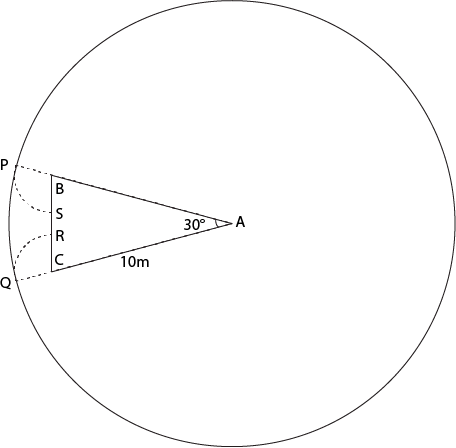
Area grazed by cow will be = Area of the larger circle - Sector APQ + Sector PBS + Sector CQR
Area of larger circle - Sector APQ = 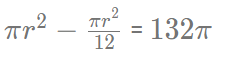
Sectors PBS and CQR are symmetrical and hence will have equal area.
In triangle ABC, AB = AC => ABC is isosceles triangle.
As A = 30° => B = C =75°
Hence, angle PBS = 180-75 = 105°

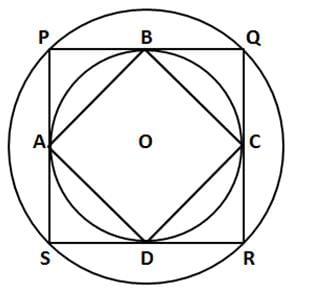
Question 13: The figure below shows two concentric circles with centre O. PQRS is a square inscribed in the outer circle. It also circumscribes the inner circle, touching it at point B, C, D and A. What is the ratio of the perimeter of the outer circle to that of polygon ABCD?
(A) π/4
(B) 3π/2
(C) π/2
(D) π
Option C
Explanation:
Let r be the radius of the inner circle. A, B, C and D are points on its circumference where the sides of the square PQRS touch it imply that the sides are tangent to the circle. The radius and tangent are perpendicular at the point of contact. Thus if we join the radius OB and OC then OB is perpendicular to PQ, OC is perpendicular to QR, OB = OC = r, Hence OBQC is a square of side r. OQ is the diagonal = √2r = R = radius of outer circle.
BC is also the diagonal of OQ = R
Clearly ABCD, is a square of side R and radius of outer circle is also R
Perimeter of ABCD = 4R
Perimeter of circle = 2πR
Hence ratio = 2πR/4R = π/2
Question 14: What is the number of distinct triangles with integral valued sides and perimeter as 14?
(A) 6
(B) 5
(C) 4
(D) 3
Option C
Explanation:
An important property of the triangle is that the sum of its two sides should be greater than the third side
Let the sides of the triangle be a, b and c
Given a + b + c = 14 and by property of triangle: a + b > c, b + c >a, c + a > b
Let one side be 1, sum of rest will be 13. Possible combinations are (1,12),(2,11),(3,10),(4,9),(5,8),(6,7)
In all the combinations the property of triangle is violated. Hence 1 cannot be the side of the triangle
Then if one side is 2, only combination satisfied is (6,6).
Accordingly, following 4 combinations can only be formed –
(4,4,6), (5,5,4), (6,5,3) and (6,6,2).
Question 15: A rectangular pool 20 meter wide and 60 meter long is surrounded by a walkway of uniform width. If the total area of the walkway is 516 square meter, how wide, in meter, is the walkway?
(A) 5
(B) 4·5
(C) 3
(D) 3·5
Option C
Explanation: Let the width of the path be x meters.
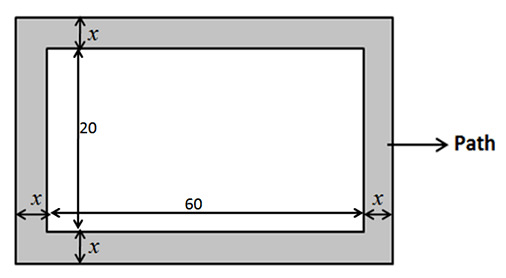
Given, Area of the path = 516 m22
Area of the path = Area of the outer rectangle – Area of the pool
Area of pool = 60×20
Area of outer rectangle = (60 + 2x)(20+2x)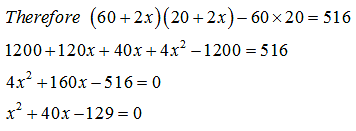
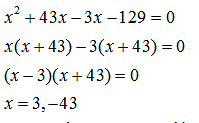
x cannot be negative and hence x = 3 meters.
So the path is 3 meters wide.
|
196 videos|131 docs|110 tests
|
FAQs on Mensuration: Solved Examples - Quantitative Aptitude (Quant) - CAT
| 1. What is mensuration? |  |
| 2. What are the common formulas used in mensuration? |  |
| 3. How can mensuration be applied in real-life situations? |  |
| 4. What is the difference between perimeter and area in mensuration? |  |
| 5. Can mensuration concepts be used in construction and architecture? |  |

|
Explore Courses for CAT exam
|

|


















