Class 5 Exam > Class 5 Notes > Science Class 5 > Detailed Notes: Rocks & Minerals - 2
Rocks and Minerals - 2 Class 5 Notes Science
| Table of contents |

|
| What are Minerals? |

|
| What are Fossil Fuels? |

|
| Uses of Rocks and Minerals |

|
| Need to Conserve Natural Resources |

|
What are Minerals?
- If you look closely at a rock with a magnifying glass, you will notice that it consists of tiny pieces known as minerals.
- All rocks are formed from these minerals.
- Minerals are natural substances that can be found on Earth.
- You can think of minerals as the basic parts that make up rocks.
- There are two types of minerals: metallic and non-metallic.

Metallic Minerals
- Metallic minerals include metals like gold, iron, aluminium, and copper.
- These minerals are referred to as ores.
- The mineral deposits are extracted to obtain the ores, from which the metals are separated.
- Metallic minerals are typically found in igneous rocks.
- They are known for being hard and having a natural shine.

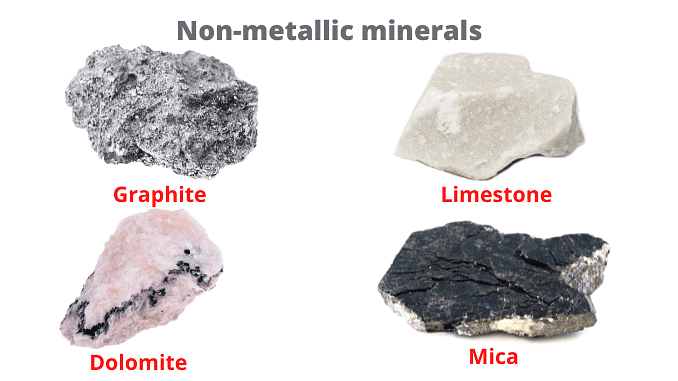
Non-metallic Minerals
- Non-metallic minerals are mostly found in sedimentary rocks.
- These minerals are typically soft and do not have a shiny appearance.
- Examples of non-metallic minerals include graphite, mica, asbestos, potassium, magnesium, and feldspar.
- This type of mineral is easy to mine and is extracted in large quantities.
- Precious stones, such as diamonds and rubies, are also classified as non-metallic.
What are Fossil Fuels?
- Fossil fuels, such as coal and petroleum, are valuable natural resources found underground and serve as our primary energy sources.
- As our country has developed since independence, the need for energy has risen significantly.
- Consequently, the significance of fossil fuels like coal and petroleum as essential energy sources has grown.
- Let's learn about coal and petroleum in detail.
Coal
- Coal is a black mineral found in the earth and is an important energy source. It can be used directly or converted into other forms like coal gas and oil.
- Formed about 300 million years ago from dead plants, coal was created when thick forests in swampy areas got buried under sand, clay, and water. Over time, high pressure and temperature transformed these remains into coal.
- In India, coal mines are located in Suhagpur (Madhya Pradesh), Raniganj (West Bengal), Dhanbad (Jharkhand), Neyveli (Tamil Nadu), and Singareni (Andhra Pradesh). The four types of coal are peat, lignite, bituminous, and anthracite.
- Uses of coal:
- Fuel: for cooking, generating electricity, powering engines, and in blast furnaces.
- Chemicals: used to produce drugs, medicines, nylon, and fertilizers.
- Metals: helps extract metals from their ores.
Thus, coal has stored the sun's energy from millions of years ago. When we burn coal as fuel we use this trapped energy of the sun.
Petroleum
- Petroleum is a thick, black liquid found beneath the earth, often referred to as rock oil, black gold, or liquid sunlight.
- It is believed to have formed from the remains of sea plants and animals buried millions of years ago, where heat and pressure transformed them into petroleum.
- To obtain petroleum, holes are drilled into the earth’s crust, and pipes are sunk to pump it out of oil wells, a process known as mining. In India, petroleum is sourced from places like Ankleshwar and Kalol in Gujarat, Digboi in Assam, and the Bombay High offshore area.
- Uses of petroleum:
- Fuel: It is used in various forms such as petrol, diesel, and kerosene, providing half of the world’s energy needs.
- Dry Cleaning: Used for cleaning woollen and silk clothes and as lubricating oil.
- Paraffin Wax: Extracted from petroleum, it is used to make candles, wax paper, Vaseline, and ointments.
- Asphalt: Also derived from petroleum, it is used for road surfaces and in paints.
Question for Detailed Notes: Rocks & Minerals - 2Try yourself: Which type of mineral is typically found in sedimentary rocks?View Solution
Uses of Rocks and Minerals
- Rocks and minerals are important construction materials.
- Our homes, schools, roads, and bridges are built using rocks and minerals.
- Rocks are sources of fuels such as coal, petroleum, and uranium.
- Uranium is a mineral that is used to generate nuclear energy.
- Rocks also provide us with valuable metals.
- Aluminium and iron are metals used to make various utensils.
- Copper is used to produce electric wires.
- Rocks are also the source of beautiful gemstones.
- Minerals like diamonds, rubies, emeralds, and sapphires are classified as gemstones.
Need to Conserve Natural Resources
- Coal and petroleum are natural resources that come from the earth.
- These resources are extremely valuable, but they are also limited.
- If we continue to use them at the current rate, they will run out quickly.
- Burning large amounts of these fuels releases harmful substances, including smoke and poisonous gases.
- This process leads to pollution, which can cause serious health issues.
- To help save coal and petroleum, we should use other types of energy that do not pollute and are available for free.
- The energy from the sun is abundant and will never be depleted.
- Using solar energy does not create pollution.
- Solar energy can be harnessed to cook food using a solar cooker.
- Additionally, solar cells can convert sunlight directly into electricity.
The document Rocks and Minerals - 2 Class 5 Notes Science is a part of the Class 5 Course Science Class 5.
All you need of Class 5 at this link: Class 5
|
43 videos|198 docs|45 tests
|
FAQs on Rocks and Minerals - 2 Class 5 Notes Science
| 1. What are minerals and how are they formed? |  |
Ans. Minerals are naturally occurring, inorganic solids with a definite chemical composition and a crystalline structure. They are formed through various geological processes, including cooling of magma, evaporation of water, and pressure changes in the Earth's crust.
| 2. What are fossil fuels and how are they created? |  |
Ans. Fossil fuels are natural substances formed from the remains of ancient plants and animals that have been buried and subjected to heat and pressure over millions of years. Common fossil fuels include coal, oil, and natural gas.
| 3. What are some common uses of rocks and minerals? |  |
Ans. Rocks and minerals are used in various ways, including construction (like granite and limestone), manufacturing (such as quartz in electronics), and in everyday products (like talc in baby powder). They are also essential in agriculture and energy production.
| 4. Why is it important to conserve natural resources? |  |
Ans. Conserving natural resources is crucial to ensure the sustainability of our environment and to prevent depletion of valuable materials. It helps maintain biodiversity, protects ecosystems, and ensures that future generations have access to essential resources like clean water, air, and energy.
| 5. How can we conserve minerals and fossil fuels? |  |
Ans. We can conserve minerals and fossil fuels by reducing waste, recycling materials, using renewable energy sources, and promoting energy efficiency. Additionally, supporting sustainable practices and technologies can help minimize the impact on these natural resources.

|
Explore Courses for Class 5 exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.
Related Searches




















