Ques 1: What do you mean by 'Seeding'?
Ans: Seeding is a method in which strong teams/players are selected to keep them at appropriate places in the fixture so that they may not meet in the earlier rounds. They usually meet at the stage of quarter-final. For the selection of strong teams, the organizers must be well aware regarding the previous performance of the teams.
Ques 2: What do you mean by food intolerance?
Ans: Food intolerance is the inability of a person to digest food properly. Its symptoms include nausea, vomiting, acidity, stomach upset, etc.
Ques 3: What is the main physiological cause of Asthma?
Ans: The physiological cause of asthma is airway narrowing and a subsequent interference with airflow.
Ques 4: What is Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD)?
Ans: It is a brain disorder that includes inattentiveness, hyperactivity and impulsiveness. It is a medical condition that affects how well can someone sit still, focus and pay attention.
Ques 5: What do you mean by Congenital Deformity?
Ans: The deformity in children that is present at birth is known as congenital deformity. For example, congenital scoliosis, which is caused by a bone abnormality present at birth, neuromuscular scoliosis which results due to abnormal muscle or nerves.
Ques 6: What is Bulimia?
Ans: Bulimia is a serious, potentially life-threatening eating disorder in which a person eats excessive amount of food. People with bulimia try to compensate or make up for the excess energy intake using a variety of techniques including vomiting, fasting, excessive exercise etc. to control body weight.
Ques 7: Explain the meaning of cardiac output.
Ans: The amount of blood pumped by the heart in one minute is known as cardiac output. It is a product of stroke volume and heart and is measured in litres/min.
Ques 8: What type of sports injury can be termed as 'Laceration' in sports?
Ans: Abrasion or am soft tissue cut in fencing is the type of sports injury that can be termed as a laceration.
Ques 9: Which field of study in sports is called 'Biomechanics'?
Ans: Biomechanics is made from two words i.e., Bio (meaning: A Living body) and?Mechanics (meaning: Field of physics which deals in the study of bodies in motion). Application of the principle of mechanics in physical education and sports is called biomechanics.
Ques 10: What do you mean by the term 'Aggression' in sports?
Ans: In sports, aggression means an intention to harm or injure a player outside the rules of game so as to gain a competitive advantage or late tackling to stop an opponent from scoring.
Ques 11: What is the coordinative ability?
Ans: Abilities of an individual which assist him to do a variety of interconnected activities correctly and competently are called coordinative abilities.
Ques 12: What are the advantages and disadvantages of food supplements for adolescents? Write briefly.
Ans: The nutrients that are added to diet to nourish the body without getting regular diet are food supplements. Food supplements include vitamins, minerals, fibres, fatty acids, amino acid etc.
Advantages:
(i) to provide the substances to the body, in case of incomplete diet.
(ii) They ensure to replenish sufficient quantity of nutrients to avoid deficiency from meal.
Disadvantages: Some body building supplements may contain steroid or like substance that could lead to serious liver injury, strokes, kidney failure etc.
Ques 13: Sushant was a good athlete. He used to practice regularly to achieve a position at the State level. But he could not get success. He got frustrated with his poor performance and started misbehaving with his teachers and friends in school. Due to depression and anxiety, he started taking drugs. The Principal counseled Sushant and called his parents.
They took him to a rehabilitation center for treatment. After a few months, he recovered and came back home. On the basis of above passage answer the following questions:
(a) Do you think that consuming drugs is a solution to emotion-focused problems?
(b) What values are shown by the Principal?
(c) What should be the attitude of the teachers and the parents after his recovery?
Ans: (a) No, consuming drug is not a solution to emotion focussed problems or failure or poor performance.
(b) The Principal shows caring, concerned nature towards his student Sushant.
(c) Teachers and parents should motivate Sushant for achieving his goal. They should try to make him understand that success comes after failure. So, he has to work hard and prove himself in front of everyone.
Ques 14: What are the types of disability? Explain briefly.
Ans: Types of disability are:
(i) Cognitive disability: Cognitive disability generally refers to anyone with lower than average intellectual functioning. A person who has a cognitive disability has trouble in performing mental tasks that the average person would be able to do.
(ii) Intellectual disability: Intellectual disability is a disability characterized by significant limitations in both intellectual functioning (such as learning, problem-solving, judgment) and in adaptive behavior (activities of daily life such as communication). This disability originates before the age of 18.
(iii) Physical disability: A physical disability is a long term loss or impairment of part of body?s physical function. It can involve difficulties in walking and mobility, sitting and standing, use of hands and arms, sight, hearing, speech, muscle control etc.
Ques 15: What are the major muscles involved in running, jumping and throwing? Explain.
Ans: Glutes, quads, calves and hamstring are the major muscles involved while running. Glutes muscles stabilizes the hips and legs. Quads propel you forward and help straighten out the leg in front so that it can make a good contact with the surface of ground. Calves muscles provide spring action in the steps and also act as shock absorber. While moving forward, hamstring helps in pulling the leg back behind.
The leg, feet and glutens muscle groups are used in jumping. Specific muscles which are involved in jumping are gluteus maximus, hamstrings, quadriceps and soleus.
In throwing, major muscles are pectoralis major, latissimus dorsi, anterior deltoid and teres major are involved. These muscles are comparatively responsible for velocity during the throw.
Ques 16: Keeping in view the Indian ideology, critically analyse the sociological aspect of participation by women athletes in sport.
Ans: It has been decades that gender ideology has had a tremendous impact on the way people view the game and its athletes. Over the generations, it has been considered that sports are predominantly for men and woman are not that adept at such physical acts. In India till recent years, a woman has been treated and accorded only for their roles of being wife, mother and home-maker. It has only in 1930, that woman began to participate in sports.
Time and again, the government policies have helped rural women of different regions but then several drawbacks still occurred. The belief that men are much stronger, faster and more capable than women, and more entertain to watch has been a major provoking influence to the mindset of people over generations. Some of the ways through which the sociological aspect of women athletes in sports participation has highlighted are equality in society, motivation from parents encouragement from institutions, respect in society, developed confidence, safe playing environment, good coaching and training facility, financial aid, government policies etc.
Ques 17: What do you understand by 'First Aid'? Discuss briefly the aims and objectives of First Aid.
Ans: First Aid: It is the immediate care given to an injured or ill person. It does not take the place of proper medical treatment. It is a temporary assistance before actual medical care is obtained.
Aims & Objectives: The most obvious objective of first aid is to save one's life before the victim gets actual medical help. The objective can be simplified into the five Ps:
(i) Preserve life
(ii) Protect the unconscious
(iii) Prevent injury or illness becoming worse.
(iv) Promote recovery.
(v) Procure medical aid.
If a life-threatening situation does exist, the first aider should have knowledge of procedures to keep the casualty alive. A casualty should be isolated from all further dangers and placed in a position where their injury or illness will not become worse. The casualty's injuries or illness should be attended to in order to prevent complications arising from his or her injury or illness.
Ques 18: Explain the 'Eight Foot Up and Go' test for measuring agility and dynamic balance.
Ans: The eight foot up and go test is a coordination and agility test for the elderly. The purpose of this test is to measure speed, agility and balance while moving. The procedure of this test is:
(i) Place the chair next to a wall and mark 8 feet in front of the chair.
(ii) The subject starts by fully seated, hand resting on knees and feet flat on ground.
(iii) On the command GO, timing starred and the subject stands and walks as quickly as possible (no running) around the cone, returning to initial position and sit on the chair.
(iv) As the person sirs down, me timer is stopped.
(v) Perform two trials.
(vi) The score is better time of the two trials 10 die nearest 1/10th of a second. Regular exercise increases agility and dynamic balance.
Ques 19: What are the causes of back pain? Explain the procedures, benefits and contra-indications of two asanas recommended to cure back pain.
Ans: Causes of Back Pain: The human back is composed of a complex structure of muscles, ligaments, tendons, disks and bones. Problem with any of these components can lead to back pain. The most common causes of back pain are strained muscles, strained ligaments and a muscle spasm which arises due to:
(i) Incorrect body posture
(ii) Lifting something that is too heavy
Back pain can be reduced by regular exercise, correcting the posture and doing proper asanas like Tadasana and Bhujangasana.
Tadasana: Tadasana is an asana in which the posture appears like standing in the form or shape of a mountain.
Procedure: Stand erect and place your thighs, slightly apart, with your hands hanging alongside your body. Strengthen the inner arches of inner ankles as you lift them. Look slightly upward. Now breathe in and stretch your shoulders, arms and chest upwards. Raise your heels, making sure that your body is on your toes. Hold the pose for a few seconds. Then exhale and release.
Benefits:
(i) It is helpful in developing physical and mental balance,
(ii) It improves body posture.
Contra-indication: It is best to avoid this pose if someone is having problems like severe migraine, insomnia or low blood pressure.
Bhujangasana: Bhujangasana is a basic Hatha pose that strengthens the entire shoulder and upper back.
Procedure: Lie flat on your stomach. Place your hands on the side and ensure that toes touch each other. Then move your hands to the front, placing your body's weight on your palms. Inhale and raise your head and trunk. Press your hips, thighs and feet to the floor. Hold the asana for 15 to 30 seconds then release the pose by slowly bringing your hands back to the sides.
Benefits:
(i) It makes spine stronger and more flexible.
(ii) It gives lungs, shoulder, chest and abdomen a good stretch.
Contra-indication: People should avoid this asana if they suffer from problems like hernia and back injuries. Pregnant women should not perform this pose in any case.
Ques 20: Describe exercise guidelines at different stages of growth in children. Give suitable examples for every stage.
Ans: Exercise guidelines at different stages of growth: Development is a never ending process whereas growth refers to an increase caused by physiological change in which the child becomes bigger in size and heavier in weight. As every individual is unique in himself, individual differences and specificity of activity should be considered.
Infant activity (0 to 3 yrs.): In this stage, the growth pattern involves control over big muscles. Clean, safe and hygienic environment is the need in this stage. In this tender age, the activities have to be done under the observation of parents and guardians. Main exercises for this tender age are practice of balancing, walking and hearing from different directions.
Early childhood activity (3 to 8 yrs): During this stage of growth, the pattern involves control over small muscles and bone development. The environment needed at this stage should be clean and safe, moreover proper checks by parents and teachers are required. Suggested sports-Running, throwing in. He or she does not fall on ground to avoid injuries.
Later childhood activities (8 to 12 yrs): During this stage, flexibility and coordinated activity of growth occurs. During this stage of growth, good quality apparatus and safety measures should be considered. Wrong habits should be checked. Suggested exercise and sports-100 meters races, hanging from horizontal bars. Cricket, Football, Tennis, Judo, Karate etc.
Ques 21: Write in detail about the various tests items and their administration of the American Alliance for Health, Physical Education and Recreation (AAPHER) Test.
Ans: The AAPHER (American Alliance for Health, Physical Education and Recreation) youth fitness test was formed in 1965 and got revised in 1976. The test was administered on school students of 17 years of age.
This test consists of the following six items:
Administration of Test: These tests can be done in a gymnasium or outdoors. Apparatus required in these tests is horizontal bar of approximately 1.5 inches and a stop watch.
Test: 1
Flexed arms hang: In this test, the student is required to hang from the bar with flexed arms and overhead grasp. The student should raise his/her body to a position where the chin is above the bar and chest is close to the bar. Time is measured how much a student can remain in that position.
Test: 2 Sit ups: The student should lie on his/her back with knees bent, feet on the floor with heels not more than 12 inches from the buttocks. The hand should be placed at the back of neck, fingers elasped and elbow touching the mat. From this position, student should raise his/her head and elbow towards knees. This constitutes one sit-up. Measurement is maximum number of sit-up a given time.
Test: 3 Shuttle run: For this test, two parallel lines are drawn at a distance of 30 feet from each other and two blocks of wood are placed behind one of the lines. Students have to run from one line to other and back to starting line and place the block behind the line. He should again turn back to pick up the second block and bring it behind the starting line. Two trials are given. Time in one tenth of second is accepted as a score.
Test: 4 Standing Long Jump: Student is asked to stand behind a take-off line with the feet parallel to each other. The subject is instructed to take the jump forward by extending his bent knees and swinging the arms forward. Out of three trials, best jump is recorded.
Test: 5 50 yard Dash: Two lines are drawn at a distance of 50 yards from each other. The student is made to run from the starting line to finish line and time is recorded.
Test: 6 600 yard Run: This run can be organised in a proper track. Finish line is marked at 600 yards from starting point. The objective is to complete the distance in shortest time.
Ques 22: What are the long term effects of regular exercise on the cardiovascular system? Explain.
Ans: Effect of exercise on the cardio-vascular system:
(i) Cardiac output increases: The cardiac output tends to increase as a result of regular exercise.
(ii) Resting heart rate decreases: The resting heart rate decreases due to regular exercise. After a duration of 10-week training program, the resting rate may reduce up to 10 beats/min from the normal 72 beats/min.
(iii) Stroke volume increases at resting condition: The stroke volume at rest remains up to 50-70 ml/beat in untrained individuals, but in trained individuals it ranges from 70-90 ml/beat.
(iv) Blood volume increases: The blood volume increases due to regular exercises. Actually, as the blood volume increases, there is an increase in plasma volume. Also, the body produces a greater number of red blood cells.
(v) Blood flow increases: The body increases its number of capillaries to the requirement of supplying more oxygen during exercise to the muscles. The existing capillaries open wider as well.
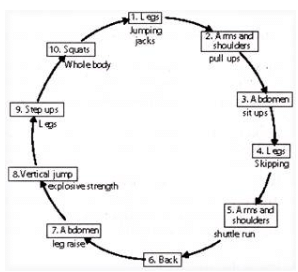
Ques 23: What is circuit training? Draw a diagram of 10 stations to improve general fitness. How can load be increased in circuit training?
Ans: Circuit training is a formal type of training in which an athlete goes through a series of selected exercises that are arranged in a circuit with 5 to 10 stations. In circuit training, several exercises are done one after the another. Completion of one set of each exercise in rotation is called one round. It was designed by GT Adamson and RE Morgan in 1957. It is very effective method for strength, speed and endurance development.
Diagram with 10 Station
 In circuit training, the load can be increased in the following two ways:
In circuit training, the load can be increased in the following two ways:
(i) By increasing the duration
(ii) By enhancing the intensity of sportsperson.
 In circuit training, the load can be increased in the following two ways:
In circuit training, the load can be increased in the following two ways:




















