DC Pandey Solutions: Laws of Motion | Physics Class 11 - NEET PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Introductory Exercise 5.1 |

|
| Introductory Exercise 5.2 |

|
| Introductory Exercise 5.3 |

|
| Introductory Exercise 5.4 |

|
| Introductory Exercise 5.5 |

|
Introductory Exercise 5.1
Q1. The diagram shows a rough plank resting on a cylinder with one end of the plank on rough ground. Neglect friction between plank and cylinder. Draw diagrams to show:
(a) the forces acting on the plank,
(b) the forces acting on the cylinder.
 View Answer
View AnswerSol.
N = Normal force on cylinder by plank
R = Normal force on cylinder by ground,
f = Force of friction by ground by cylinder,
w = Weight of cylinder.
N cosθ = f
w + N sinθ = R,
N(R) = Reaction to N,
(Force acting on plank)
i.e., normal force on plank by cylinder
R' = Normal force on plank by ground,
w = Weight of plank,
f' = frictional force on plank by ground.
Resultant of f' and R', N(R) and w pass through point O.
Q2. Two spheres A and B are placed between two vertical walls as shown in figure. Friction is absent everywhere. Draw the free body diagrams of both the spheres.
 View Answer
View AnswerSol.
R = Normal force on sphere A by left wall,
N = Normal force on sphere A by ground,
N' = Normal force on sphere A by sphere B,
wA = Weight of sphere A.
N' cos θ = R
N' sin θ + wA = N
R' = Normal force on sphere B by right wall,
N ( R) = Reaction to N i.e. normal force on sphere B by sphere A,
wB = Weight of sphere B,
R', N(R) and wB pass through point O, the centre sphere B.
Q3. A point A on a sphere of weight W rests in contact with a smooth vertical wall and is supported by a string joining a point B on the sphere to a point C on the wall. Draw free body diagram of the sphere.
 View Answer
View AnswerSol.
N = Normal force on sphere by wall,
w = Weight of sphere,
T = Tension in string.
Q4. Write down the components of four forces  along ox and oy directions as shown in Fig. 5.33.
along ox and oy directions as shown in Fig. 5.33.

 View Answer
View AnswerSol.
- F1x = 2√3 N
- F2x = -2 N
- F3x = 0
- F4x = 4 N
- F1y = 2N
- F2y = 2√3 N
- F3y = -6 N
- F4y = 0
Explanation:
Component of 
along x-axis : 4 cos 30° = 2√3 N
along y-axis : 4 sin 30° = 2 N
Component of 
along x-axis : 4 cos 120° = - 2 N
along y-axis : 4 sin 120° = 2√3 N
Component of 
along x-axis : 6 cos 270° = 0 N
along y-axis : 6 sin 270° = - 6 N
Component of 
along x-axis : 4 cos 0° = 4 N
along y-axis : 4 sin 0° = 0 N
Q5. A uniform rod AB of weight w is hinged to a fixed point at A It is held in the horizontal position by a string, one end of which is attached to B as shown in Fig. 5.34. Find in terms of w, the tension in the string.
 View Answer
View AnswerSol.
Taking moment about point A
AB = 1
(T sin 30) 1 = w 1/2
⇒ T = w
Q6. In Question 3 of the same exercise, the radius of the sphere is a. The length of the string is also a. Find the tension in the string.
 View Answer
View AnswerSol. 
Explanation:
See figure (answer to question no. 3)

T cos 30° = w
or 
or 
Q7. Find the values of the unknown forces if the given set of forces shown in figure below are in equilibrium.

 View Answer
View AnswerSol. F = 10.16 newton, R = 2.4 newton
Explanation:
R cos 30° + 3 = f cos 60°
i.e., 
or
R√3 + 6 = f …(i)
and R sin 30° + f sin 60° = 10
i.e., 
or R + f√3 = 20 …(ii)
Substituting the value of f from Eq. (i) in Eq. (ii)
R + ( R√3 + 6)√3 = 20
4 R + 6√3 = 20
⇒ 
∴ f = (2.4) √3 + 6
f = 10.16 N
Q8. Two beads of equal masses m are attached by a string of length √2a and are free to move in a smooth circular ring lying in a vertical plane as shown in Fig. 5.36. Here, a is the radius of the ring. Find the tension and acceleration of B just after the beads are released to move.
 View Answer
View AnswerSol. 
Explanation:
At point B (instantaneous vertical acceleration only)
∴ mg - T sin 45° = ma …(i)
At point A (instantaneous horizontal acceleration only)
∴ T cos 45° = ma …(ii)
Combining Eqs. (i) and (ii)
mg - ma = ma
⇒ 
T cos 45° = m(g/2)
T/√2 = m(g/2)
T = mg/√2
Introductory Exercise 5.2
Q1. Three blocks of mass 1 kg, 4 kg and 2 kg are placed on a smooth horizontal plane as shown in figure. Find:
(a) the acceleration of the system,
(b) the normal force between 1 kg block and 4 kg block,
(c) the net force on 2 kg block.

 View Answer
View AnswerSol. (a) 10 ms-2 (b) 110 N (c) 20 N
Explanation:
Acceleration of system
= 10 m/s2
Let normal force between 1 kg block and 4 kg block = F1
∴ Net force on 1 kg block = 120 - N
∴ 
or 10 = 120 - F1
i.e., F1 = 110 N
Net force on 2 kg block = 2*a
= 2*10
=20 N
Q2. Two blocks of mass 2 kg and 4 kg are released from rest over a smooth inclined plane of inclination 30° as shown in figure. What is the normal force between the two blocks?

 View Answer
View AnswerSol. zero
Explanation:
As, 4 g sin 30° > 2 g sin 30°
The normal force between the two blocks will be zero.
Q3. What should be the acceleration ‘a’ of the box shown in figure so that the block of mass m exerts a force mg/4 on the floor of the box?
 View Answer
View AnswerSol. 3g/4
Explanation:
 ∴ N = mg/4
∴ N = mg/4
As lift is moving downward with acceleration a , the pseudo force on A will be ma acting in the upward direction. For the block to be at rest w.r.t. lift.
N + ma = mg
or 
⇒ 
Q4. A plumb bob of mass 1 kg is hung from the ceiling of a train compartment. The train moves on an inclined plane with constant velocity. If the angle of incline is 30°. Find the angle made by the string with the normal to the ceiling. Also, find the tension in the string, (g = 10 m/s2)
 View Answer
View AnswerSol. 30°, ION
Explanation:
Angle made by the string with the normal to the ceiling = θ = 30°
As the train is moving with constant velocity no pseudo force will act on the plumb-bob. Tension in spring = mg
Tension in spring = mg
= 1*10
= 10 N
Q5. Repeat both parts of the above question, if the train moves with an acceleration a = g/2 up the plane.
 View Answer
View AnswerSol. 
Explanation:
Pseudo force (= ma) on plumb-bob will be as shown in figure T cos φ = mg + ma cos (90° - θ)
T cos φ = mg + ma cos (90° - θ)
i.e., T cos φ = mg + ma sin θ …(i)
and T sin φ = ma cos θ
Squaring and adding Eqs. (i) and (ii),
T2 = m2 g2 + m2 a2 sin2 θ + 2m2 ag sin θ + m2 a2 cos2 θ …(iii)
T2 = m2 g2 + m2 a2 + m2 ag (∴ θ = 30°)

or
Dividing Eq. (i) by Eq. (ii),


i.e., 
Q6. Two blocks of mass 1 kg and 2 kg are connected by a string AS of mass 1 kg. The blocks are placed on a smooth horizontal surface. Block of mass 1 kg is pulled by a horizontal force F of magnitude 8 N. Find the tension in the string at points A and B.
 View Answer
View AnswerSol. 4 N, 6 N
Explanation: 

 Net force on 1 kg mass = 8 - T2
Net force on 1 kg mass = 8 - T2
∴ 8 - T2 = 1*2
⇒ T2 = 6 N
Net force on 1 kg block = T1
∴ T1 = 2a = 2*2 = 4 N
Introductory Exercise 5.3
Q1. In the arrangement shown in figure what should be the mass of block A, so that the system remains at rest? Neglect friction and mass of strings.
 View Answer
View AnswerSol. 3 kg
Explanation:
F = 2 g sin 30° = g For the system to remain at rest
For the system to remain at rest
T2 = 2 g …(i)
T2 + F = T1 …(ii)
or T2 + g = T1 …[ii (a)]
T1 = mg …(iii)
Substituting the values of T1 and T2 from Eqs. (iii) and (i) in Eq. [ii(a)]
2 g + g = mg
i.e., m = 3 kg
Q2. In the arrangement shown in figure, find the ratio of tensions in the strings attached with 4 kg block and that with 1 kg block.
 View Answer
View AnswerSol. 4
Explanation:
As net downward force on the system is zero, the system will be in equilibrium ∴ T1 = 4 g
∴ T1 = 4 g
and T2 = 1 g
∴ 
Q3. Two unequal masses of 1 kg and 2 kg are connected by a string going over a clamped light smooth pulley as shown in figure. The system is released from rest. The larger mass is stopped for a moment 1.0 s after the system is set in motion. Find the time elapsed before the string is tight again.
 View Answer
View AnswerSol. 1/3 s
Explanation:
2 g - T = 2a T - 1 g = 1a
T - 1 g = 1a
Adding above two equations
1 g = 3 a
∴ a = g/3
Velocity of 1kg block 1 section after the system is set in motion
v = 0 + at
On stopping 2 kg, the block of 1kg will go upwards with retardation g. Time ( t' ) taken by the 1 k g block to attain zero velocity will be given by the equation.
⇒ 
If the 2 kg block is stopped just for a moment (time being much-much less than 1/3 s), it will also start falling down when the stopping time ends.
In  time upward displacement of 1 kg block
time upward displacement of 1 kg block
Downward displacement of 2 kg block
As the two are just equal, the string will again become taut after time 1/3 s.
Q4. Two unequal masses of 1 kg and 2 kg are connected by an inextensible light string passing over a smooth pulley as shown in figure. A force F = 20 N is applied on 1 kg block. Find the acceleration of either block. (g = 10 m/s2).
 View Answer
View AnswerSol.
Explanation:
F + 1g - T = 1a … (i) and T - 2g = 2a …(ii)
and T - 2g = 2a …(ii)
Adding Eqs. (i) and (ii),
F - 1g = 3a
∴ 
Introductory Exercise 5.4
Q1. Consider the situation shown in figure. Both the pulleys and the string are light and all the surfaces are smooth.
(a) Find the acceleration of 1 kg block.
(b) Find the tension in the string.
(g = 10 m/s 2).
 View Answer
View AnswerSol. (a) 2g/3, (b) 10/3 N
Explanation:
2T = 2*a … (i) and 1g - T = 2a …(ii)
and 1g - T = 2a …(ii)
Solving Eqs. (i) and (ii),
α = g/3
∴ Acceleration of 1 kg block
Tension in the string
Q2. Calculate the acceleration of either blocks and tension in the string shown in figure. The pulley and the string are light and all surfaces are smooth.
 View Answer
View AnswerSol. 
Explanation:
Mg - T = Ma …(i) T = Ma …(ii)
T = Ma …(ii)
Solving Eqs. (i) and (ii)
α = g/2
and T = Mg
Q3. Find the mass M so that it remains at rest in the adjoining figure. Both the pulley and string are light and friction is absent everywhere, (g = 10 m/s 2).
 View Answer
View AnswerSol. 4 . 8 kg
Explanation:
Block of mass M will be at rest if T = Mg …(i)
T = Mg …(i)
For the motion of block of mass 3 kg ....(ii)
....(ii)
For the motion of block of mass 2 kg ....(iii)
....(iii)
Adding Eqs. (ii) and (iii),
g = 5a
i.e., α = g/5
Substituting above value of a in Eq. (iii),
T/2 = 2(g+a)
or 
= 24g/5
Substituting value of above value of T in Eq. (i),
M = 24/5
= 4.8 kg
Q4. In figure assume that there is negligible friction between the blocks and table. Compute the tension in the cord connecting m2 and the pulley and acceleration of m2 if m1 = 300 g, m2 = 200g and F = 0.401V.
 View Answer
View AnswerSol. 
Explanation:
T/2 = m1.2a i.e., T = 4 m1a …(i)
i.e., T = 4 m1a …(i)
F - T = m2a …(ii)
or F - 4m1a = m2a
or 

∴ T = 4 m1a
= 4*0.3* 2/7
= 2.4/7
= 12/35 N
Introductory Exercise 5.5
Q1. In figure m1 = 1 kg and m2 = 4 kg. Find the mass M o f the hanging block which will prevent the smaller block from slipping over the triangular block. All the surfaces are friction less and the strings and the pulleys are light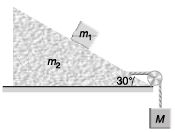
Note In exercises 2 to 4 the situations described take place in a box car which has initial velocity v = 0 but acceleration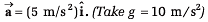
 View Answer
View AnswerSol. 6 .83 kg
Explanation:
Block on triangular block will not slip if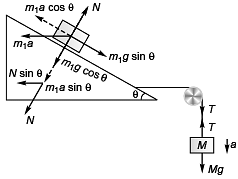
m1a cos θ= m1g sin θ
i.e., a = g tanθ …(i)
N = m1g cosθ + m1asinθ …(ii)
For the movement of triangular block
T - N sinθ = m2α …(iii)
For the movement of the block of mass M
Mg - T = Ma …(iv)
Adding Eqs. (iii) and (iv),
Mg - N sinθ = ( m2 + M )α
Substituting the value of N from Eq. (ii) in the above equation
Mg - (m1g cosθ + m1α sinθ) sinθ
=( m2α + Mα)
i.e., M (g - α) = m1g cosθ sinθ + (m2 + m1 sin2θ)α
Substituting value of a from Eq. (i) in the above equation,
M(1 - tanθ) = m1 cosθ sinθ + ( m2 + m1 sin2 θ) tanθ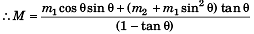
Substituting θ = 30° , m1 = 1 kg and m2 = 4 kg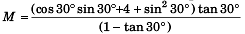
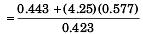
= 6.82 kg
Q2. A 2 kg object is slid along the friction less floor with initial velocity (10 m/s)î (a) Describe the motion of the object relative to car (b) when does the object reach its original position relative to the box car.
 View Answer
View AnswerSol. (a) x = x0 + 10t - 2.5t2 , v = 10 - 5t (b) t = 4s
Explanation:
(a) Using 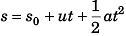
Displacement of block at time t relative to car would be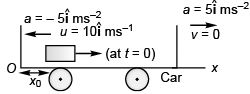
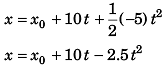
Velocity of block at time t (relative to car) will be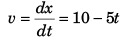
(b) Time (t) for the block to arrive at the original position (i.e., x = x0) relative to car
x0 = x0 + 10 t - 2.5 t2
⇒ t = 4s
Q3. A 2 kg object is slid along the friction less floor with initial transverse velocity (10 m/s)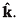 . Describe the motion (a) in car’s frame (b) in ground frame.
. Describe the motion (a) in car’s frame (b) in ground frame.
 View Answer
View AnswerSol. (a) x = x0 - 2.5t2, z = z0 + 10t, vx = - 5t, vz = 10 ms-1
(b) x = x0, z = z0 + 10t, vx = 0, vz = 10 ms-1
Explanation:
(a) In car’s frame position of object at time t would be given by
In car’s frame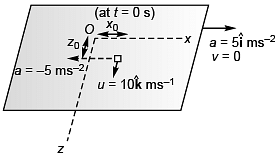
x = x0 + 0*t + 1/2(-5)t2
i.e., x = x0 - 2.5 t2 …(i)
and z = z + 10t …(ii)
Velocity of the object at time t would be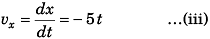
and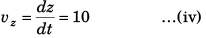
(b) In ground frame the position of the object at time t would be given by
In ground frame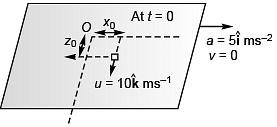
x = x0
and z = z0 + 10t
Velocity of the object at time t would be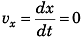
ans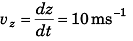
Q4. A 2 kg object is slid along a rough floor (coefficient of sliding friction = 0.3) with initial velocity (10 m/s)î. Describe the motion of the object relative to car assuming that the coefficient of static friction is greater than 0.5.
 View Answer
View AnswerSol. x = x0 + 10f - 4t2 , K = 10 - 8 t for 0<f<1.25 s object stops at t = 1.25 s and remains at rest relative to car.
Explanation:
m = 2 kg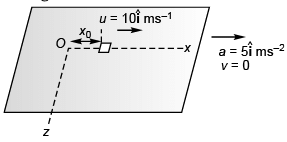
Normal force on object = mg
Maximum sliding friction = μsmg
= 0.3*2*10 = 6 N
Deceleration due to friction = 6/2 =3 m/s2
Deceleration due to pseudo force = 5 m/s2
∴ Net deceleration = (3 + 5) m/s2
= 8 m/s2
∴ Displacement of object at any time t (relative to car)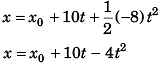
Thus, velocity of object at any time t (relative to car)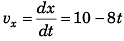
The object will stop moving relative to car when
10 - 8t = 0 i.e., t = 1.25s
∴ vx = 10 - 8t for 0<t<1.25 s
Q5. A block is placed on an inclined plane as shown in figure. What must be the frictional force between block and incline if the block is not to slide along the incline when the incline is accelerating to the right at 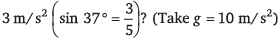
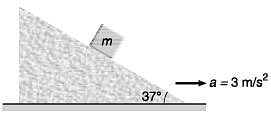
 View Answer
View AnswerSol. 9/25 mg
Explanation:
For block not to slide the frictional force ( f ) would be given by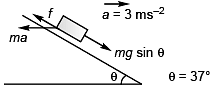
f + ma cosθ = mg sinθ
or
f = mg sinθ - ma cosθ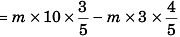
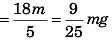
|
97 videos|378 docs|103 tests
|
FAQs on DC Pandey Solutions: Laws of Motion - Physics Class 11 - NEET
| 1. What are the basic concepts of laws of motion? |  |
| 2. How do I apply Newton's laws of motion to solve problems? |  |
| 3. What is the significance of the concept of inertia in the laws of motion? |  |
| 4. Can you provide examples of real-world applications of Newton's laws of motion? |  |
| 5. What are some common mistakes students make when studying laws of motion? |  |

|
Explore Courses for NEET exam
|

|


















