NCERT Solutions for Class 4 Maths - Chapter 13 - Fields And Fences
PAGE NO. 149
Q.1. Rahmat needs to find the length of the boundary of the field. Can you find it from this picture? See the length of each side written near it.
Rahmat bought a roll of 70 m wire for the fence.
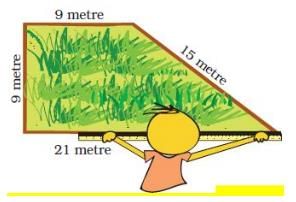
How much wire did Rahmat give to Ganpat?
Ans. Length of the boundary Rahmat’s field = 9 m + 15 m + 21 m + 9 m = 54 m.
Length of wire bought by Rahmat for fencing his field = 70 m
Rahmat used 54 m of wire for fencing his field.
∴ Length of wire left with Rahmat = 70 m − 54 m = 16 m
Working: 70 - 54 = 16
Thus, Rahmat gave 16 m wire to Ganpat.
PAGE No. 150
Q.1. Ganpat thanked Rahmat and started fencing his own field. But he needed to get more wire.
- How long is the boundary of Ganpat’s field? ______________
- How much more wire will Ganpat need for his field? _____________
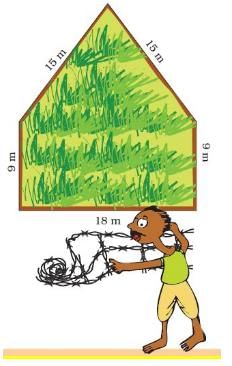
Ans. Length of the boundary of Ganpat’s field = 15 m + 15 m + 9 m + 18 m + 9 m = 66 m. Rahmat gave 16 m wire to Ganpat for fencing his field. Length of wire now needed by Ganpat for fencing his field = 66 m − 16 m = 50 m Working: 66-16 = 50.
Thus, Ganpat will require 50 more metres wire for his field.
PAGE.No 151
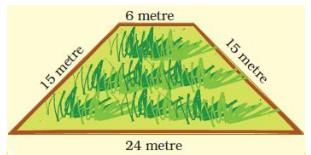
Q.1. Here are pictures of some more fields. Find out which one has the longest boundary
(a) Boundary = __________ metre.
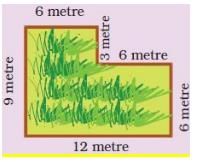
(b) Boundary = __________ metre.
(c) Boundary = __________ metre.
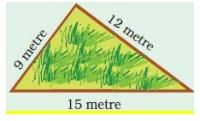
(d) Boundary = __________ metre.
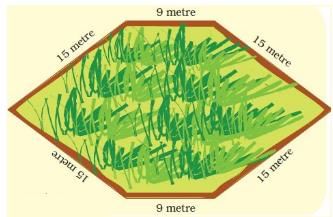
Ans.
(a) Length of the boundary = 6 m + 15 m + 24 m + 15 m = 60 m Boundary = 60 metre
(b) Length of the boundary = 6 m + 3 m + 6 m + 6 m + 12 m + 9 m = 42 m Boundary = 42 metre.
(c) Length of the boundary = 9 m + 12 m + 15 m = 36 m Boundary = 36 metre.
(d) Length of the boundary = 9 m + 15 m + 15 m + 9 m + 15 m + 15 m = 78 m Boundary = 78 metre
Thus, figure (d) has the longest boundary.
PAGE NO. 152
Q.1.
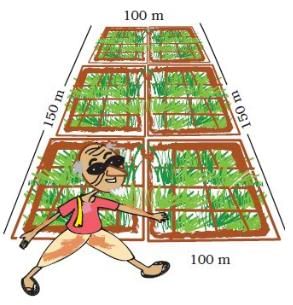
Chandu’s father is called the ‘young old man’ in his village. At 70 years of age, he is fully fit. Do you know his secret? He goes for a walk around the field every morning. Everyday he takes four rounds of Chandu’s field.
- What is the total distance he covers?
4 × _________ = _________ m = _________ km.
Ans. Length of the boundary of Chandu’s field = 100 m + 150 m + 100 m + 150 m = 500 m ∴ Distance covered by Chandu’s father in one round = 500 m
Chandu’s father takes four rounds of the field every morning.
Distance covered by Chandu’s father in four rounds = 4× 500 m = 2000 m.
Now, 1 km = 1 × 1000 m
∴ 2 km = 2 × 1000 m
Thus, the total distance covered by Chandu’s father is 2 km.
∴ Total distance covered = 4 × 500 m = 2000 m = 2 km.
Q.2. Ganpat’s wife works in a tailor’s shop. She has to fix lace around a table cloth. She bought a 100 metre roll of lace.
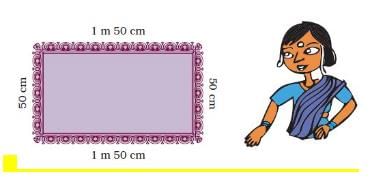
i) Look at the picture of the table cloth and tell how much lace is used for one table cloth ____________
 ii) How much lace will be used in 3 such table cloths? ____________
ii) How much lace will be used in 3 such table cloths? ____________
iii) How much lace will be left in the roll? ____________
Ans.
i) We know 1 m = 100 cm
Length of the table cloth = 1 m 50 cm = 1 × 100 cm + 50 cm = 100 cm + 50 cm = 150 cm Width of the table cloth = 50 cm Length of the boundary of the cloth = 150 + 50 + 150 + 50 = 400 cm = 4 m
Working: 150+150+50+50 = 400.
Thus, the length of lace needed for one table cloth is 4 m.
ii) Length of lace required for one table cloth = 4 m
Length of lace required for three table cloths = 4 m × 3 = 12 m
iii) Total length of the roll of lace = 100 m
Length of lace used in three table cloths = 12 m
Length of lace left in the roll = 100 m − 12 m = 88 m
Working: 100-12 = 88m
Thus, 88 m of lace is left in the roll.
PAGE NO. 153
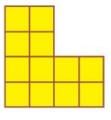
Q.1. Find out the length of the boundary of these shapes.
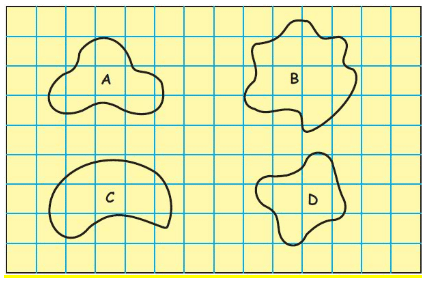
Now count the squares to find out:
- How many squares are there in each shape?
- Which shape covers the least number of squares?
- Which shape covers the most number of squares?
Ans.
Number of squares in shape A = 5
Number of squares in shape B = 9
Number of squares in shape C = 7
Number of squares in shape D = 4
- Shape D covers the least number of squares.
- Shape B covers the most number of squares.
PAGE NO. 154
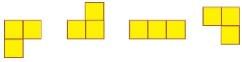
Q.1. How many different shapes can you make by joining two squares? Draw them on the squared sheet given below. How long is the boundary of each shape?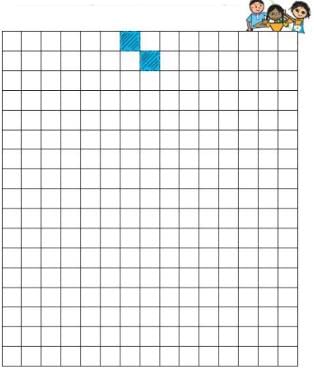
Try this activity with three squares also.
Ans.
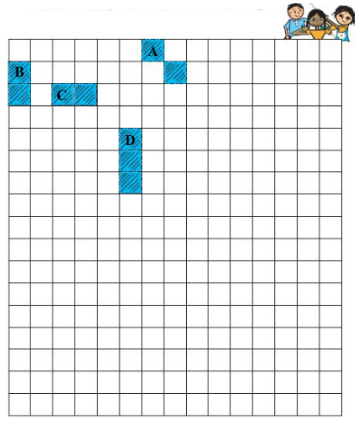
Clearly, the boundaries of B and C include 6 sides each, whereas the boundary of A includes 8 sides. Thus, A will have a larger boundary as compared to B and C.
Figure D is made using three squares.
PAGE NO. 155
Q.1. A square has a boundary of 12 cm.
(a) From the corner of this square, a small square of side 1 cm is cut off. Will the boundary of B be less or more? Find its length.
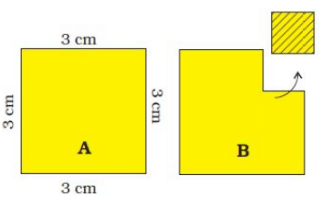
(b) If you cut a 1 cm square to get shape C, what will be the length of the boundary of C?
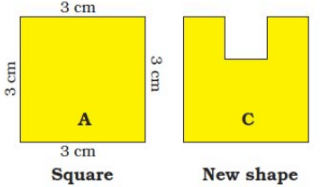
Ans.
(a) Length of each side of square A = 3 cm
Number of sides of square A = 4
Length of the boundary of square A = 4 × 3 cm = 12 cm
Now, a small square of side 1 cm is cut off from one corner of square A.
∴ Length of the boundary of B = 2 cm + 1 cm + 1 cm + 2 cm + 3 cm + 3 cm = 12 cm
Thus, the length of the boundary of square B will remain the same as that of square A.
(b) Length of the boundary of C = 1 cm + 1 cm + 1 cm + 1 cm + 1 cm + 3 cm + 3 cm + 3 cm = 14 cm.
Q.2. (a) Find the length of the boundary of square D.
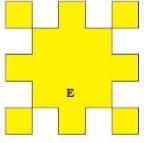
(b) 8 squares of side 1 cm are cut out of the square D. Now it looks like shape E. What is the length of the boundary of shape E?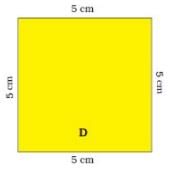
(c) The boundary of this 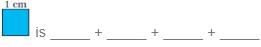 Can we also say that the boundary is 4 × 1 cm?
Can we also say that the boundary is 4 × 1 cm?
Ans:
(a) Length of each side of square D = 5 cm
Number of sides = 4
Length of the boundary of square D = 5 cm × 4 = 20 cm
(b) Length of each side of the figure that forms the boundary of shape E = 1 cm
Number of sides = 36
Length of the boundary of shape E = 1 cm × 36 = 36 cm
(c) The boundary of this 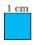 is 1 cm + 1 cm + 1 cm + 1 cm Now, 4 cm = 4 × 1 cm Thus, we can say that the length of the boundary of the given square is 4 × 1 cm
is 1 cm + 1 cm + 1 cm + 1 cm Now, 4 cm = 4 × 1 cm Thus, we can say that the length of the boundary of the given square is 4 × 1 cm
PAGE NO. 156
Q.1. A hockey field is 91 metres 40 cm long and 55 metres wide. How long is the boundary of the field?
Ans. We know 1 m = 100 cm
Length of the hockey field = 91 m 40 cm = 91 × 100 + 40 cm = 9100 + 40 cm = 9140 cm
Breadth of the hockey field = 55 m = 55 × 100 cm = 5500 cm
Now, length of the boundary = 9140 + 5500 + 9140 + 5500 cm = 29280 cm = 29200 cm + 80 cm = 292 m 80 cm
Thus, the boundary of the field is 292 m 80 cm long.
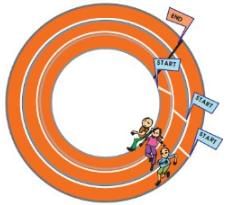
Q.2. Usha and Valsamma are running a race. Usha is running on the inner circle. Valsamma is running on the outer circle.
- Valsamma runs faster than Usha. But still she loses the race. Can you guess why? __________

- Have you seen any race where runners start from different places — like in this picture? Guess why?
 Ans.
Ans.
- The starting and the ending points of the race coincide. Now, since the radius of the outer circle is greater than the radius of the inner circle, the length of the boundary of the outer circle will be greater than the length of the boundary of the inner circle. Hence, Valsamma covers more distance than Usha while taking one round of the circular track. Thus, she loses the race even if she runs faster than Usha.
- Usually circular tracks have different starting point because the radius of the track of the different runner are different.
PAGE NO. 157
Q.1. How will Neetu find out if the two gardens are equally big?
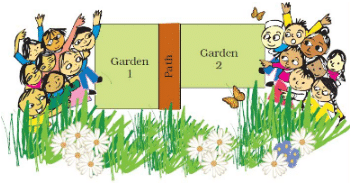
Ans: Neetu will calculate the area of both the gardens to check whether they are equally big.
PAGE NO. 160
Q.1. (a) How many small squares of size 1 cm are there in this big green square?
(b) Can you think of a faster way to know the total number of small squares without conting each?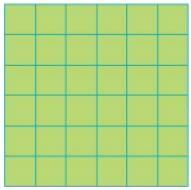 Ans:
Ans:
(a) There are 36 small squares in the big green square.
(b) Number of squares in the first row = 6
Number of rows = 6
Now, we see that each row contains the same number of squares.
∴ Total number of squares in 6 rows = 6 × 6 = 36
Q.2. Guess how many squares of one centimetre can fill this blue rectangle.

Write your guess here. ____________________ Check your guess by filling it with small squares.
Ans. The blue rectangle can be filled with 32 squares of one centimetre.
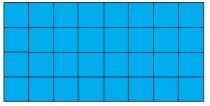
Q.3. Look at the picture. Can you divide it into 4 equal pieces? Each piece should have the same number of squares.
Ans:
PAGE NO.161
Q.1. Puzzle: A House and the Well Raghavan has a piece of land. There are 4 houses on his land and in the middle there is a well. He wants to divide this land equally among his four children. Each should get one house and be able to use the well without entering the other’s land. Can you help him divide the land? Give different colours to each one’s share.
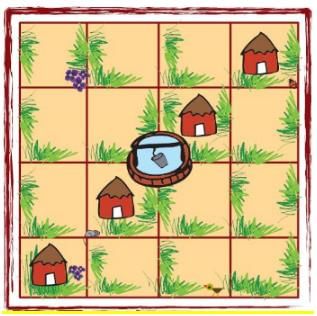
Ans. The image given below shows how the land can be equally divided among the four children so that each gets one house and is able to use the well without entering any other’s land.
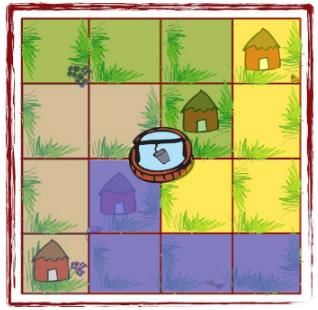
|
25 videos|123 docs|39 tests
|
FAQs on NCERT Solutions for Class 4 Maths - Chapter 13 - Fields And Fences
| 1. What is the significance of fields and fences in agriculture? |  |
| 2. What are the different types of fences used in agriculture? |  |
| 3. How can farmers ensure the effectiveness of their fences? |  |
| 4. Are there any regulations or guidelines regarding the construction of fences in agriculture? |  |
| 5. How do fields and fences contribute to sustainable agriculture practices? |  |

|
Explore Courses for Class 4 exam
|

|

















