Accounting for Bills of Exchange (Part - 1) | Accountancy Class 11 - Commerce PDF Download
Page No 16.35:
Question 1: Calculate the due dates of the bills in the following cases: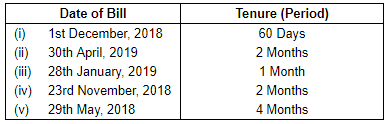
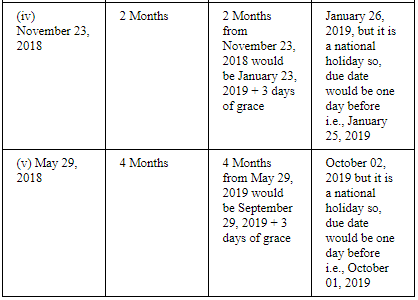
ANSWER: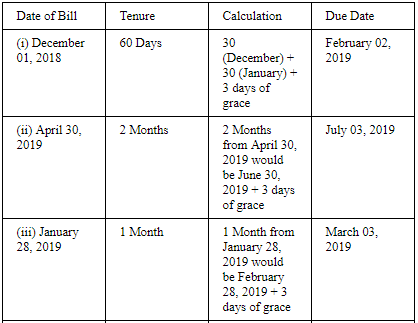
Page No 16.35:
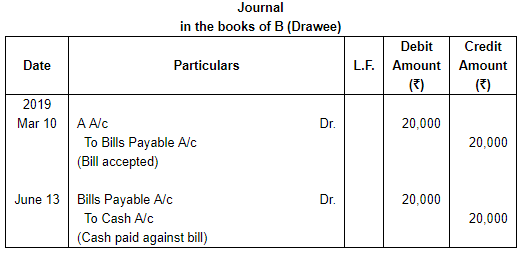
Question 2: On 10th March, 2019, A draws on B a bill at 3 months for ₹ 20,000 which B accepts immediately and returns to A. The bill is honoured due date.
Pass necessary Journal entries in the books of both the parties.
ANSWER: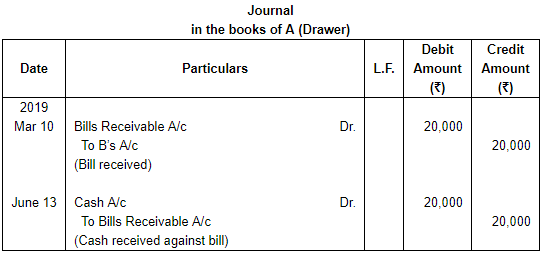
Page No 16.35:
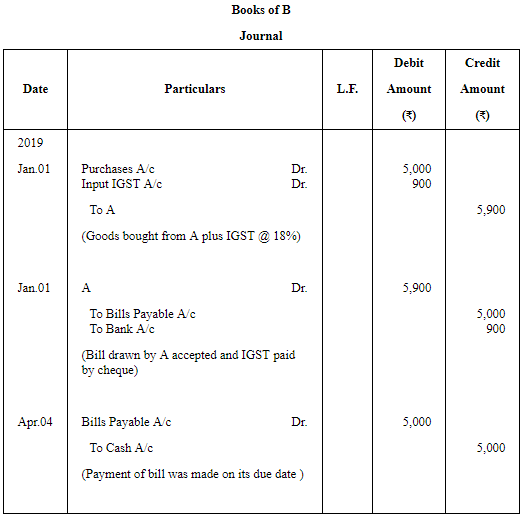
Question 3: On 1st January, 2019, A sold goods to B for ₹ 5,000 plus IGST @ 18%. A received ₹ 900 by cheque from B and drew on him a bill for the balance amount payable 3 months after date. The bill was duly accepted by B. A retained the bill till due date. On due date, the bill was paid.
Pass Journal entries in the books of A and B. Also, show necessary accounts in the books of both the parties.
ANSWER: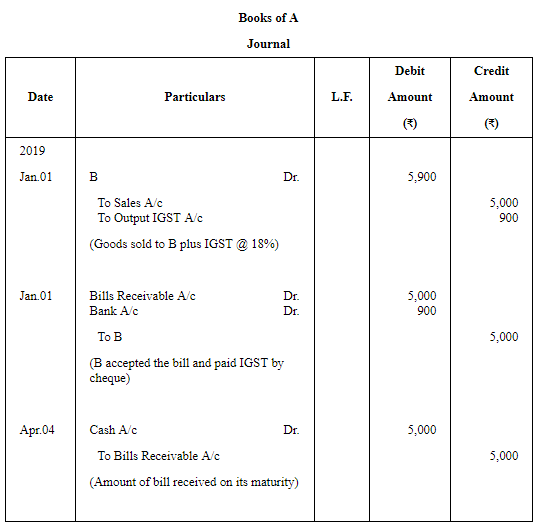
Page No 16.35:
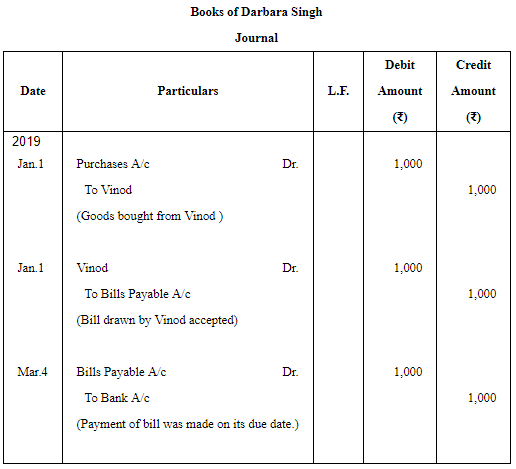
Question 4: Vinod sold goods to Darbara Singh for ₹ 1,000 on 1st January, 2019. He drew on the latter a bill for the amount payable 3 months after date.He discounted the bill with his bank for ₹ 990 on 4th January, 2019. On maturity, the bill is duly met. Make the Journal entries in the books of Vinod and Darbara Singh.
ANSWER: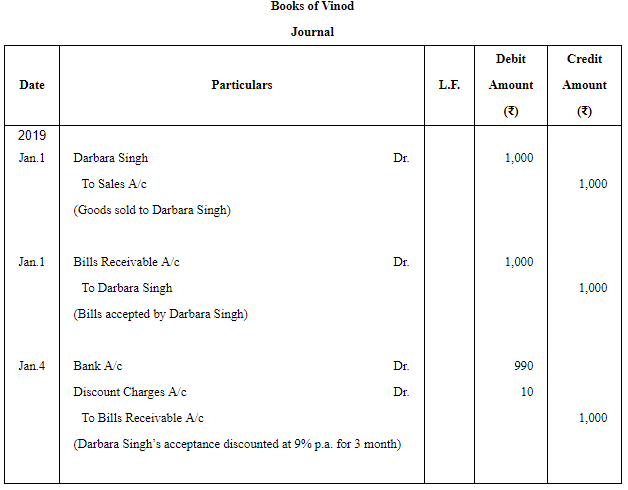
Page No 16.36:
Question 5: On 1st January, 2019, X sold goods of ₹ 20,000 to Y and drew a bill on Y at three months for the amount. Y accepted the bill. The bill is met on maturity. Pass the necessary Journal entries in the books of X and Y, if X discounted the bill @ 12% p.a. from bank on 4th January.
ANSWER: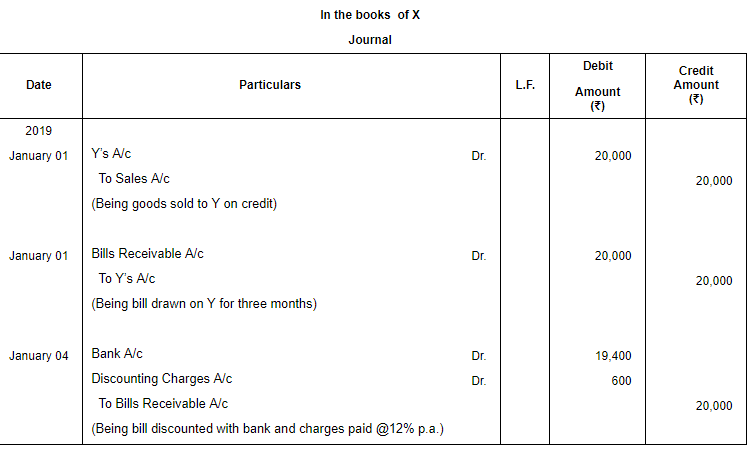 Working Notes:
Working Notes:
Discounting Charges = ₹ (20,000 × 12/100 × 3/12) = ₹ 600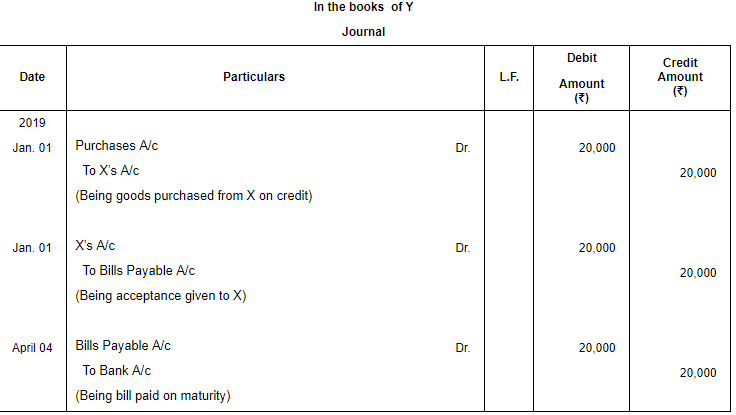
|
64 videos|152 docs|35 tests
|
FAQs on Accounting for Bills of Exchange (Part - 1) - Accountancy Class 11 - Commerce
| 1. What is a bill of exchange? |  |
| 2. What are the parties involved in a bill of exchange? |  |
| 3. What is the purpose of a bill of exchange? |  |
| 4. How does a bill of exchange work? |  |
| 5. What are the advantages of using a bill of exchange? |  |

|
Explore Courses for Commerce exam
|

|

















