Previous Year Short & Long Questions With Answers: Planning | Business Studies (BST) Class 12 - Commerce PDF Download
Very Short Answer Questions
Q1: Give the meaning of "Method" as a type of plan.
Ans: The prescribed approach or manner in which a work must be completed is referred to as the method.
Q2: What is planning?
Ans: Planning entails deciding what to do and how to do it ahead of time. It is a fundamental managerial function.
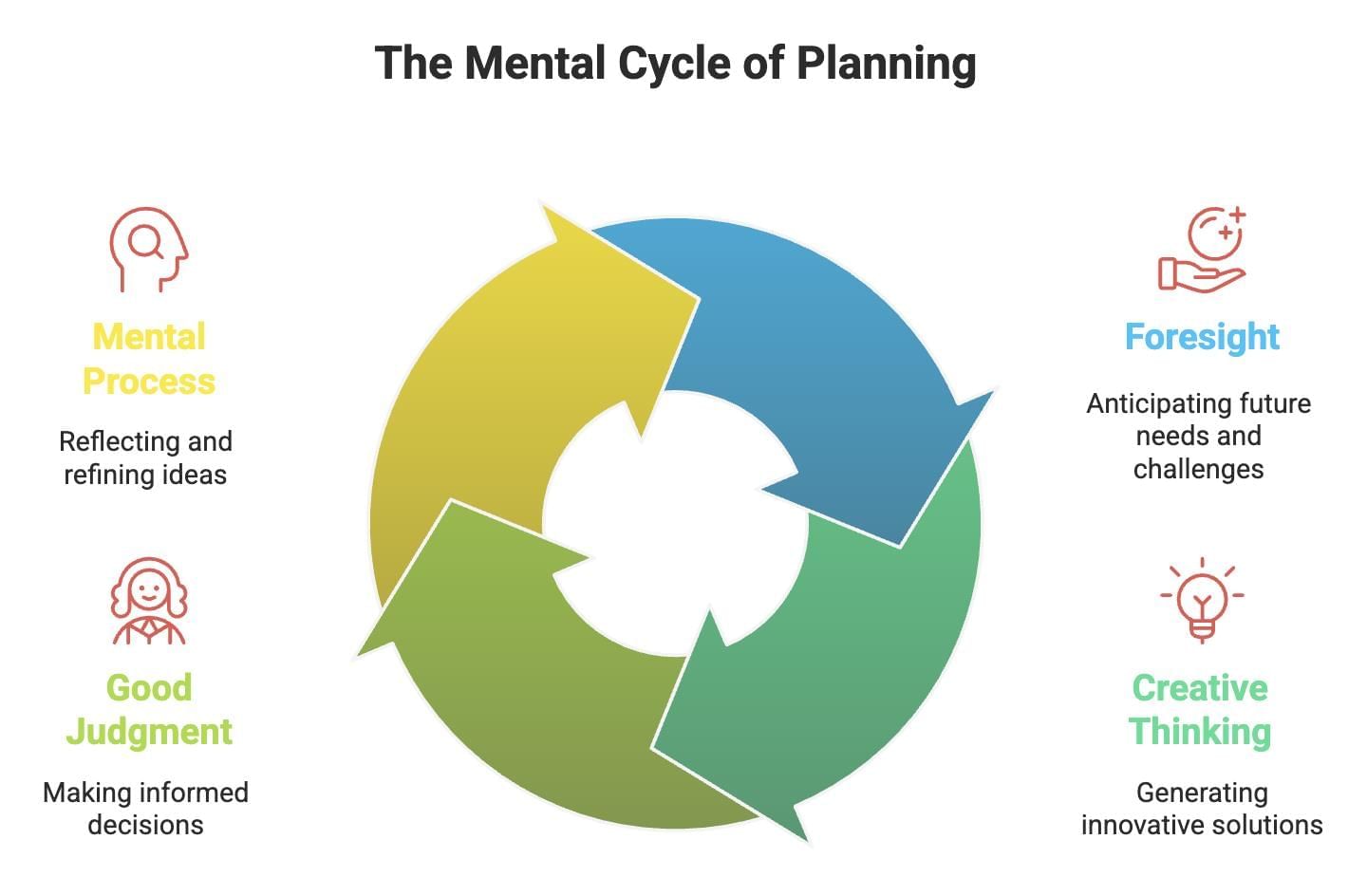
Q3: How is planning a mental exercise?
Ans: Planning involves using the mind with foresight, creative thinking, and good judgment. It is mainly a mental process of thinking rather than taking action.
Q4: How does planning create rigidity?
Ans: Planning imposes rigidity by limiting managers' ability to take initiative.
Q5: What is the basis for creating a future course of action?
Ans: Forecasting.
Q6: Give one limitation of the planning function.
Ans: Planning does not guarantee success.
Q7: Which is the most crucial step in the planning process?
Ans: Setting objectives for the organisation.
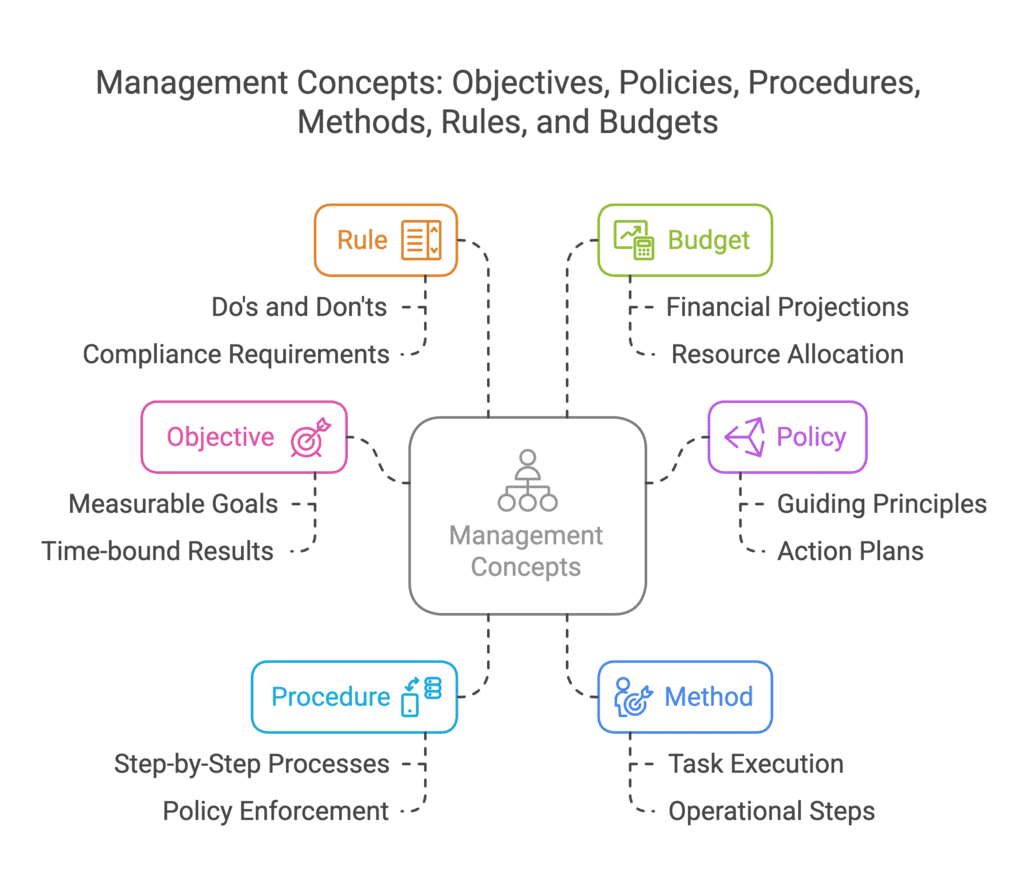
Q8: Define 'Objective'?
Ans: Objectives are desired future positions that the management would like to reach. These are quantitative and measurable in nature.
Q9: Define 'Strategy".
Ans: A strategy refers to future decisions and actions, defining the organisation's direction and scope in the long run.
Short Answer Questions
Q1: It is deciding in advance what to do and how to do it. It is one of the basic managerial functions. It requires that, before doing something, the manager must formulate an idea of how to work on a particular task. This function is closely connected with creativity and innovation. It seeks to bridge the gap between where we are and where we want to go and is performed at all levels of management.
In spite of this, the function of management referred to above has a number of limitations.
Explain any two such limitations.
OR
State any three limitations of the planning function of management.
Ans: The following are the limitations of planning.
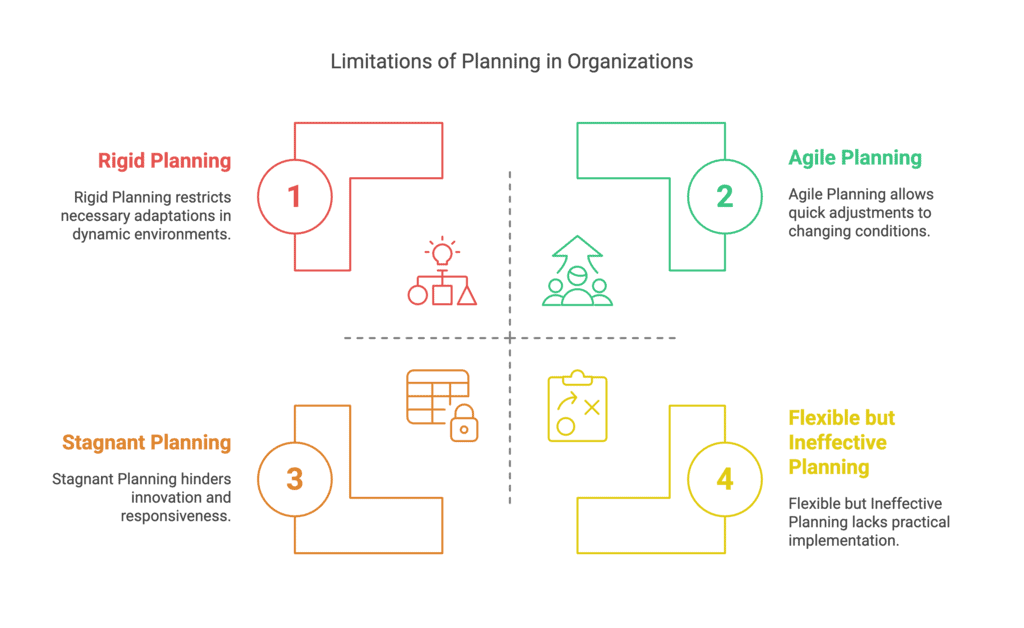
- Planning leads to rigidity: A well-defined plan is put up in an organisation with specified goals to be completed within a specific time frame, but management may not be able to change it. As the business environment is dynamic, managers need to be given some flexibility to cope with the changing circumstances.
- Planning may not work in a dynamic environment: Since planning is dependent on anticipating future events, and because the future is uncertain and dynamic, the organisation must react to changes. However, planning will not be able to adequately predict future events.
- Planning reduces creativity: Top management does Planning, and middle management does implementation of the plan, but they are not allowed to deviate from the plan, and thus, the creativity of these managers is reduced.
Q2: Explain the first three steps in the process of 'Planning'.
Ans: The following are the first three steps involved in the planning process.
- Setting the objectives: Any business enterprise needs to decide upon its objectives, and the first step in the planning process is to set the objectives. Managers are required to define objectives clearly so that they can take the right action to achieve the goals.
- Establishing the premises: Planning is based on specific future assumptions. Premises are the terms used to describe these assumptions. The assumptions concern future forecasts, which serve as the foundation for the planning process. For successful strategies, forecast accuracy is required.
- Identifying alternatives: The next step is to identify alternative courses of action. Managers must identify all the alternative courses of action for achieving the objectives of the organisation. This involves innovation and creativity.
Q3: Explain any three features of "Planning."
Ans: The features of planning are highlighted in the following points.
- Planning is centred on accomplishing goals: General and particular goals, as well as strategies and activities to attain these goals, are established by organisations. Management should create plans with specific objectives in mind. These strategies must ensure that the desired result is achieved.
- Foundation: Planning is the foundation for all other management responsibilities. That is, planning comes before everything else, including organising, directing, staffing, and managing. This is because the objectives are stated in the plans, and all other functions are carried out in accordance with the stated objectives. After the plans are set, the roles of various interconnected functions are assigned. As a result, planning serves as the foundation for all of an organisation's other functions.
- Organisational Pervasiveness: Planning is essential at all levels of management as well as in all departments. At different levels and for different departments, the extent of planning varies. For example, top-level managers must lay down policies for general management, while middle-level managers must map out the authority to be delegated to subordinates. Lower-level managers, on the other hand, set tiny goals for day-to-day operations.
Q4: "Planning focuses on achieving objectives". Explain.
Ans: Planning is a goal-oriented process that aids in the definition of objectives and the creation of action plans to attain those objectives. As a result, planning focuses on defining what has to be done and how it should be done. If the planning isn't focused on achieving predetermined organisational or corporate goals, it's pointless.
Q5: "Planning is the basic function of management". Comment.
Ans: Planning is the foundation for management. Planning underpins all other operations, including organising, staffing, directing, and controlling. It comes before all other managerial duties and lets managers better organise their teams, direct and regulate activities, as well as achieve organisational goals. All of the activities are designed in such a way that carrying out plans is simple.
Q6: What do you mean by planning premises?
Ans:
- The planning premises are assumptions about future conditions and events that are expected to affect goal attainment.
- These are the pillars around which the entire planning framework is built.
- Every strategy is built on a foundation of assumptions.
- The premises must be based on accurate estimates, existing plans, or any past information regarding policies, among other things, to make planning effective.
- For instance, demand for a product, raw material costs, financing rates, technological advancements, competition intensity, government policies and so on.
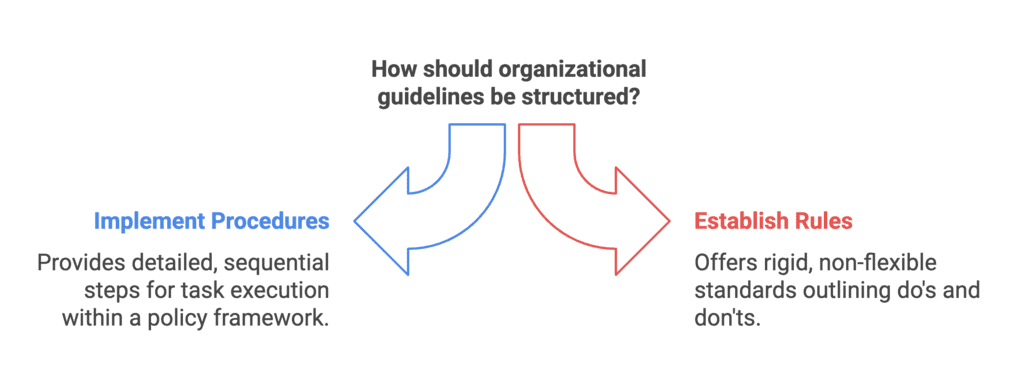
Q7: Give the meaning of "procedure' and "rule' as types of plans.
Ans: The meanings are given below:
Procedure:
- A procedure is a series of steps that are listed in order to follow for carrying out a policy.
- It provides a clear description of how to perform a specific task.
- Procedures are typically created for the employees within an organisation.
- They consist of steps that are arranged in a sequence to apply a policy or complete a certain job.
- In simple terms, procedures are the actions that need to be taken within the framework of a broader policy.
Rule:
- A rule refers to a standard or specific statement that gives information about what is to be done and what is not to be done.
- Rules are the most basic plans and do not allow for any flexibility.
- They denote a managerial decision on whether or not to carry out a specific task or action.
- Such rules do not allow any scope for compromise or change unless the managers take a policy decision.
Q8: Give the meaning of 'Strategy' and 'Rule' as types of plans.
Ans: The meanings are:
- Strategy: Strategy refers to long-term decisions that define an organisation's direction and scope. Setting goals, deciding on a path of action, and allocating the necessary resources, all these are frequently defined as future decisions that, in the end, reveal the organisation's direction and scope. A manager must analyse all components of the corporate environment while establishing a strategy, and then make strategic decisions based on all of these considerations.
- Rule: A rule is a particular statement that tells you what to do and what not to do in certain situations. They denote a managerial decision on whether or not to carry out a specific task or action. There is no room for compromise or reform under such standards.
Q9: "Planning reduces creativity." How?
Ans: In most organisations, top management is in charge of planning, while the rest of the team is responsible for putting the plans into action. As a result, middle management and other members are not allowed to deviate from plans, nor are they granted authority to act on their own. As a result, they lose a lot of their initiative and originality.
Q10: What is meant by budget?
Ans: A budget is a numerically based strategy that quantifies desired data. A budget is a numerical description of projected results for a specific time period in the future. A sales budget, for example, aids in estimating the sales of a specific product in several places over the course of a month.
Q11: How can (i) Political climate and (ii) Policies of competitors obstruct planning?
Ans: The following are the explanations:
- Planning stymied by the political climate: When the government restricts corporate practices or implements new trade regulations, business plans may be disrupted. Furthermore, political unrest has an impact on corporate strategies. Consider a change in taxation policy, it may obstruct all the plans that a firm has prepared.
- Planning can be obstructive owing to rival policies: Changes in corporate policy may be influenced by competitor policies. For example, a corporate enterprise's pricing policy may alter as a result of competitors' discounting practices.
Long Answer Questions
Q1: Two years ago, Nishant completed his degree in Textile Engineering. He worked for some time in a company manufacturing readymade garments. He was not happy in the company and decided to have his own readymade garments manufacturing unit. He set the objectives and the targets and formulated an action plan to achieve the same. One of his objectives was to earn 80% profit on the amount invested in the first year. It was decided that raw materials like cloth, thread, buttons, etc., will be purchased on two months' credit. He also decided to follow the steps required for marketing the products through his own outlets.
He appointed Ritesh as a production manager, who decides the exact manner in which the production activities are to be carried out. Ritesh also prepared a statement showing the requirement of workers in the factory throughout the year. Nishant informed Ritesh about his sales target for different product areas for the forthcoming quarter.
A penalty of Rs. 200 per day was announced for the workers who were found smoking in the factory premises.
Quoting lines from the above paragraph, identify and explain the different types of plans discussed.
Ans: The different types of plans discussed in the paragraph are listed below.
- Objective: The final results that management aims to attain through its activities are referred to as objectives. It is to be expressed in specific terms, i.e., they should be measurable in quantitative terms, in the form of a written statement of desired results to be achieved within a given time period.
Quotation: "One of his objectives was to earn 80% profit on the amount invested in the first year" - Policy: Policies are broad pronouncements that steer people's thoughts or energies in a specific direction. It serves as the foundation for interpreting strategy. It expresses a general attitude or a plan of action to take in a specific situation.
Quotation: "It was decided that raw materials like cloth, thread, buttons, etc. will be purchased on two months' credit.” - Procedure: A process is a set of routine steps that must be done in a specific order in order to enforce a policy.
Quotation: “He also decided to follow the steps required for marketing the products through his own outlets.” - Method: Methods define the prescribed ways or manners in which a work can be completed in light of the goal. It evaluates one stage of a larger operation and specifies the next step to complete the given task.
Quotation: “Who decides the exact manner in which the production activities are to be carried out?” - Rule: A rule is a set of instructions or a precise declaration that specifies what should be done and what should not be done. The simplest sort of plan is a rule.
Quotation: “A penalty of Rs. 200 per day was announced for the workers who were found smoking in the factory premises.” - Budget: A budget is a numerical description of projected results for a specific time period in the future.
Quotation: "Ritesh also prepared a statement showing the requirement of workers in the factory throughout the year"
Q2: Is planning actually worth the huge costs involved? Explain.
Ans: Planning comes at a high price in terms of both time and money. It involves analysis, research and scientific calculations that involve huge costs. However, despite being an expensive function, it is a very basic and essential function of an organisation.
Despite the astronomical expenditures, we may assert that planning is a critical action due to the emphasised factors.
- Renders Direction: The aims and objectives that must be met are clearly stated in the planning. As a result, it serves as a guide for future activities. It directs the activities of several departments inside the organisation. They advise managers on what has to be done, what path to take, and how to attain the goals. It ensures that the path taken to achieve objectives is the proper one. Planning also ensures that the organisation's many departments work together to attain the desired goals.
- Risk Prevention: By steering an organisation in the proper path, it empowers its leaders to analyse and predict changes. As a result, the probability of the anticipated events is reduced. Planning shows how to deal with situations which may arise in the course of management, though it does not fully eliminate the problems.
- Minimise Overlapping: As the managers are well comprehended with the policies and plans of the organisation, they coordinate their activities together to reach the objectives. As a result, work overlap is reduced. Furthermore, any resource waste that occurs as a result of overlapping is decreased. Planning ahead of time ensures that there will be no misunderstandings and that the activity will be completed successfully.
- Promotes Creativity: Planning is an important part of any organisation's success. It entails establishing strategies and plans, which necessitates creativity. It is a key activity that necessitates the highest thinking talents and inventiveness from managers. It encourages management to come up with fresh ideas in order to achieve the objectives.
- Assists in Decision Making: Planning is the foundation for making decisions. Planning entails analysing the future, evaluating potential courses of action, and selecting the best option based on the goal. As a result, managers can make more sensible judgments by following a proper planning procedure.
- Planning Is Necessary For Controlling: Planning lays out the goals that must be met. As a result, it establishes the benchmarks against which the performance is measured. It also aids in detecting whether there is any divergence from the stated objectives, making remedial action easier. As a result, we may conclude that, notwithstanding the expenditures, planning plays a critical role in management that is well worth the investment.
|
51 videos|339 docs|74 tests
|
FAQs on Previous Year Short & Long Questions With Answers: Planning - Business Studies (BST) Class 12 - Commerce
| 1. What is the importance of planning in management? |  |
| 2. What are the key steps involved in the planning process? |  |
| 3. How does strategic planning differ from operational planning? |  |
| 4. What are the common challenges faced in the planning process? |  |
| 5. How can technology aid in the planning process? |  |

















