Previous Year Short & Long Questions With Answers - Directing | Business Studies (BST) Class 12 - Commerce PDF Download
Very Short Answer Questions
Q1: State the difference between 'formal' and 'informal" organizations based on 'origin."
Ans: The difference between formal and informal organizations based on 'origin' is tabulated below.

Q2: What is the meaning of the term "motivation'' as an element of directing?
Ans: Motivation refers to a process of inducing and stimulating individuals to behave in a certain manner to achieve organizational objectives. That is, it refers to encouraging and urging the employees to perform to the best of their capabilities to achieve the desired organizational goals. Motivation varies as per the desires and expectations of the employees and can take various forms such as promotion, appraisal, and recognition.
Q3: What is inspiring, guiding, and instructing people in the organization to achieve its objectives?
Ans: Directing
Q4: The function of directing is performed by every manager from the top executive position. Which characteristic of directing is referred to here?
Ans: At every level of management directing takes place.
Q5: It means overseeing the subordinates at work. Which element of directing is referred to?
Ans: Supervision
Q6: What makes a Supervisor act as a link between workers and management?
Ans: The supervisor implements the plans formulated by the management by directing the workers on the one hand and informs the worker's problems to the management on the other.
Q7: Give the meaning of "supervision' as an element of directing
Ans: Supervision implies the process of overseeing the subordinates at work, so as to ensure that the work is being performed as per the requirements of the company.
Q8: Mention one barrier to effective communication.
Ans: Poor listening skills of people.
Q9: Give any one measure to improve communication.
Ans: Listening to the communicator attentively, without interrupting or making premature assumptions about his/her intentions.
Q10: State any two non-Financial incentives.
Ans: Two non-Financial incentives are:
- Status: In the organizational context, status means a ranking of positions. A person with status means a person holding a high position with increased responsibilities and other benefits.
- Job Enrichment: Job enrichment is concerned with designing jobs that include a greater variety of work content and require higher knowledge and skill.
Q11: Name the formal Communication network where each person can communicate with his adjoining two persons?
Ans: Circular communication network.
Q12: Give an example of any two organizational facilities to encourage a free flow of communication by removing organizational barriers.
Ans: The two facilities are:
- Proper feedback system.
- Employee orientation.
Q13: What is the highest level needed in the hierarchy of Abraham Maslow?
Ans: Self-Actualization
Q14: Which element in the communication process relates to the process of converting encoded symbols of the sender?
Ans: Decoding
Short Answer Questions
Q1: Neha was a regional sales manager in "Good Luck Garments Ltd' for the last ten years. During the retirement of the marketing manager, Neha applied for the same job, because she was extremely talented and had devoted all her hard work to the position of marketing manager. However, the company's top executives decided to complete this post by choosing the best person outside the company. As a result, Neha was devastated and had to lose her job. When a new marketing manager joined, one of his biggest problems was how to motivate Neha to her previous level of performance?
Suggest any three non-financial benefits a new marketing manager could use to promote Neha.
Ans: The non-financial incentives that the new marketing manager may use are:
- Status: In the organizational context, status means a ranking of positions. A person with status means a person holding a high position with increased responsibilities and other benefits.
- Job Enrichment: Job enrichment is concerned with designing jobs that include a greater variety of work content and require higher knowledge and skill
- Job Security: Employees want job security and stability about future income, as well as their job so that they don't have to worry about these aspects and they can work with greater zeal.
Q2: Mr. Mohan Kumar, owner of Jason's Enterprises, runs a hygienic business. There is a lot of dissatisfaction in the organization and the goals are not being achieved. He asked his son Ritesh, who had just finished his MBA, to find out why.
Ritesh found that his father did not trust the workers' abilities and did not seek their advice or opinion.
There was also a lack of transparency in the operations of the business. Thus, the employees were not happy.
(a) Identify any two communication barriers because of which "Jason's Enterprises' was not able to achieve its targets.
Ans: The two communication barriers because of which "Jason's Enterprises' was not able to achieve its target are:
- Organizational Barriers: The organization policy is not supportive of free flow of communication, which disrupts the effectiveness of communication. A free and effective flow of communication requires the presence of certain organizational facilities such as social gatherings, complaint boxes, and transparency in operations, etc. The absence of such facilities hinders the flow of information. Also there was no transparency in the organization, thus adding to the demotivation of the employees.
- Personal Barriers: The type of personal barrier, which is discussed above, is the lack of confidence of a superior in his subordinates. When the superior does not have confidence in the subordinates, he is unwilling to involve them in discussions and other matters. This leads to a communication gap between the superior and the subordinate.
B. State one more barrier for each of the types identified in part (a) above.
Ans: Type of organizational Barrier:
Lack of Organizational Facilities: If the organization does not have required and sufficient communication facilities such as telephone, stationary, typewriter etc., then also communication can be obstructed and delayed.
Types of Personal Barrier:
Fear: If the subordinates fear voicing out their opinions to their superiors, and they are unwilling to communicate the negative or unsatisfactory information to the superior fearing the adverse impact it may have on their job, they try to hide or conceal the information, or sometimes provide half or incomplete information.
Q3: 'K.S. Energy Ltd.’ was an energy-efficient consultancy company. To get the business the team leader and his team used to travel to different states to give a presentation to their clients. According to company policy, the group leader used to travel by plane, and his group traveled by road / train. Not only was it time consuming but it also sometimes forced the members of the women's group to travel alone.
As a result, subordinates did not act in the desired way to achieve organizational goals.
The CEO came to know about it. He called the team leader, discussed the matter with him, and changed the travel policy of the company. It was decided that all members including the leader would travel together in the future and would use the time to talk to subordinates about presentations to be given to the clients. This made a positive impact and every member of the team started acting in a manner as desired by the team leader.
Explain the features of the element of the function of management used by the CEO.
Ans: The management function used by the CEO is “Motivation.
The earlier travel policy of the organization wasn’t appropriate as it required the leader and members to go on a different transportation medium, and also forced the women’s group to travel alone, this discourages the employees to work for the organization.
However, a change in travel policy had a positive impact on employees and they started acting in a manner desired by the leader, which is possible only with the help of motivation.
The features of motivation are as follows.
- Motivation is a Psychological Phenomenon: Motivation is an internal feeling such as urges, drives, and desires which cannot be forced on employees.
- Motivation is a Goal-Oriented Behaviour: It helps people to arrange things in a particular manner so that they can achieve their goals. A motivated person works to achieve the goals he or she wants.
- Motivation can be either positive or Negative: Positive motivation means inspiring people to work better and appreciating a work that is done well e.g., pay increases promotion recognition. Negative motivation mainly involves threats and punishment.
- Motivation is a Complex Process: It is a complex and difficult process as there is a human factor involved. Individuals differ in their needs and wants and human needs change from time to time.
Q4: "My Car Ltd. 'has decided to set up its own new automobile factory in a backward area of West Bengal where very few job opportunities were available. Locals have welcomed the initiative of "My Car Ltd." The company has also decided to provide services such as school, hospital, market, etc. to the factory premises so that people can be attracted to join the factory as workers. 'My Car Ltd." started earning a huge profit. Another competing company asked its production manager 'Arvind' to investigate the reasons for the huge profits by My Car Ltd. "Arvind found that in both companies there is systematic coordination among the various activities to achieve organizational goals. Every employee knew who was in charge and held responsible to whom. The only difference was that in his organization communication took place only through the scalar chain, whereas 'My Car Ltd.' was allowing the flow of communication in all the areas as needed, which led to faster dissemination of information and faster response.
(a) Identify the type of organization that permits the flow of communication in all the directions in 'My Car Ltd.
Ans: In My Car Ltd. Ltd., informal organization allows the flow of communication in all directions.
(b) Also mention the benefit of the type of organization identified in the area above. Name any two values 'My Car Ltd.' wanting to connect with the community.
Ans: The benefit of the informal organization are:
Fulfillment of social needs: An informal organization allows for personal communication beyond the officially defined roles. This enables the employees to interact with like-minded colleagues. This unofficial interaction provides a sense of belongingness among the employees towards one another and towards the organization.
The two values that 'My Car Ltd." wanted to communicate to society are given below.
- Fulfilling social responsibility by providing employment opportunities in the backward area of West Bengal.
- Working for the benefits of employees by providing services such as school, hospital, market, etc.
Q5: Explain any three points that highlight the importance of directing the work of managers.
Ans: The importance of directing is given below:
- Achieving objectives: The function of directing initiates the actual action in an organization. Directing helps individuals to complete the assigned task properly and on time as per the instruction of their superiors.
- Integration of efforts: Every organization comprises several employees who have different jobs assigned to them and work at different levels. Through directing, communication and motivation, their efforts get aligned for the successful achievement of organizational objectives.
- Facilitates change: There are times when the employees are reluctant regarding the changing policies and structure in the organization, thinking that the changes are not in their favor, or are very difficult to implement. In this case, through direction, the management can change the perspective of employees, by constant communication and motivation regarding the pros and benefits the change would bring to the organization, as well as to them.
Q6: Umang Gupta is the Managing Director of Denver Ltd. The company has built a reputation for excellence and success.. It was known for the timely completion of orders. The Production Manager, Ms.Kanta was very careful with the order processing and had a team of fourteen employees working under him. Everything was going well. Unfortunately, she met with an accident. Umang knew that in the absence of Ms. Kanta, the company may not be able to meet the deadlines. He also knew that failure to meet deadlines could lead to customer dissatisfaction with the risk of losing business and interest. Therefore, he held a meeting with his staff at which an accurate and quick processing of orders was arranged. Everybody agreed to work as a team because the behavior of Umang Gupta was positive towards the employees of the organization. Hence everyone put in extra time and effort and the targets were met on time. Not only this, Umang visited Ms. Kanta advised her to take sufficient rest.
(a) Identify the leadership style of Umang Gupta and draw a diagram depicting the style.
Ans: The leadership style of Umang Gupta is democratic or participative leadership style. A democratic leader is the one who passes orders and makes decisions after consulting the employees and works out the policies with the acceptance of the group.
The diagram is shown below:
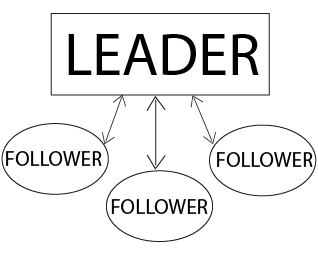 (b) State any two values highlighted by the behavior of Umang Gupta.
(b) State any two values highlighted by the behavior of Umang Gupta.
Ans: Values involved are as follows
- Positive attitude towards employees.
- Considerate attitude towards employees health and their well-being.
Q7: Explain briefly any three semantic barriers to communication.
Ans: Semantics is a branch of linguistics that studies the meaning of words and sentences. Semantic barriers are problems and impediments in the process of encoding and decoding messages into words or impressions. Typically, such barriers arise as a result of the use of incorrect words, erroneous translations, or differing interpretations. Some of the causes of semantic barriers are as follows.
- Badly Expressed Message: The information may not be clearly expressed at times due to a lack of vocabulary or incorrect word usage.
- Symbols with Different Meanings: A word may have more than one meaning at times, or two or more words may have the same pronunciation (such as idle and idol). The correct interpretation of the word remains ambiguous in such cases.
- Faulty Translations: In some cases, the proficiency of a language varies between workers and managers. In such cases, a translation of the information into a language that the workers can understand is required. However, some words or sentences may be misinterpreted during the translation process. For example, the meaning of certain words may change in a translation of an instruction from English to Hindi.
Q8: What is meant by 'Esteem needs' and 'Self-actualization needs' about the motivation of the employees?
Ans: The meanings are
- Esteem Needs: There are ego needs of a person that are fulfilled by authority, responsibility, position, status etc. For example: Self-respect, self-confidence, etc. These include elements such as respect, dignity, recognition, and so on, as every individual wishes to command respect and acknowledgement from their peers. It is the fourth need in the Maslow’s need hierarchy.
- Self-Actualization Needs: This need refers to achieving one's goals or dreams. It is the highest level requirement in the hierarchy. Such needs pertain to an employee's growth, job satisfaction, and so on. This is the need to be what one is capable of becoming and includes needs for optimal development. It comes at the last in Maslow's need hierarchy.
Long Answer Type Questions
Q1: Explain any five points of importance of the directing function of management.
Ans: Importance of directing is given below:
- Directing Initiates Action: It helps us to initiate action by the people in the organization towards the achievement of desired objectives. Until and unless the employees are told and informed about what and how they are supposed to do, all the previous three functions that are planning, organizing and staffing seem fruitless.
- Directing Integrate Employee's Efforts: Coordination of all the activities of an organization is very necessary. Hence through directing, motivating and communicating , a manager tries to bring together all the employees and make them work as a team.
- Motivation to Employees: It motivates the subordinates to work efficiently as well as effectively to contribute their maximum efforts towards the achievement of organizational goals.
- Directing Helps in Stability and Balance in the Organization: Effective directing fosters cooperation and commitment among employees and helps in striking a balance between various activities and departments.
- Facilitates Change: There are times when the employees are reluctant regarding the changing policies and structure in the organization, thinking that the changes are not in their favor, or are very difficult to implement. In this case, through direction, the management can change the perspective of employees, by constant communication and motivation regarding the pros and benefits the change would bring to the organization, as well as to them.
Q2: Ansh is working in a multinational company in Jaipur. He has running temperature for the last few days. When his blood was tested, he found a positive for chikungunya. He was admitted to the hospital and a blood transfusion was advised by the doctors as his condition was very serious. One of his colleagues sent a text message to his immediate superior "Vineet', Vineet immediately sent a text message to the employees of the organization requesting them to donate blood for Yash. When the General Manager came to know about it, he ordered fumigation in the company premises and cleanliness of the surroundings.
(a) From the above, para quote lines that indicate formal and informal communication.
Ans: The quoted lines are:
- Informal Communication
- "One of his colleagues sent a text message to his immediate superior "Vineet”
- “Vineet immediately sent a text message to the employees of the organization requesting them to donate blood for Yash”.
- Formal Communication: "When the General Manager came to know about it, he ordered fumigation in the company premises and cleanliness of the surroundings."
(b) State any two features of informal communication.
Ans: The features of informal communication are as follows:
- It is a communication that flows without following a formally defined path.
- It comes out of social interactions among the employees.
(c) Identify any two values that are being communicated by Vineet to society.
Ans: The two values that are being communicated to society are as follows:
- Cleanliness of the surroundings.
- Sympathy for employees.
Q3: "The post of supervisor should be abolished in the hierarchy of managers". Do you agree? Give any three reasons in support of your answer.
Ans: No, I don't agree, because a supervisor plays an important role in the achievement of organizational goals, and hence his position should not be abolished.
Functions of the supervisor are:
- Planning the Work: The supervisor is responsible for determining the work schedule for every job, as well as to allocate the right resources and people to the right job.
- Providing Guidance: The supervisor constantly provides guidance to the workers of his department, and motivates them to work to the best of their abilities so as to achieve the organizational goals. Also, he is responsible for explaining the policies and programs of the organization to his subordinates
- Ensure Optimum Utilization of Resources: The supervisor makes necessary arrangements for the physical, and human resources and ensure they are efficiently utilized.
- Helps in Recruitment: The supervisor also helps the personnel departments in recruitment and selection of workers. There are situations where the personnel department takes the suggestions of the supervisor before making the selection decision.
- Multiple Roles: A supervisor plays multiple roles in an organization, such as of a:
- Key Man: Because the supervisor supervises the non-managerial employees who are ultimately responsible for the execution of the plans
- Mediator: The supervisor acts as a link between the management and workers. He puts forward the suggestions and issues of the workers to the management, as well as conveys the orders, objectives, policies of the management to the workers.
- Human Resource Specialist: A supervisor also assists the HR or personnel department of the organization, and helps them in recruitment and selection. Also, he provides solutions to the varied problems encountered by the workers.
Q4: What are the various types of leadership styles? Explain.
Ans: The various leadership styles are:
- Autocratic or Authoritarian Leader: An autocratic leader gives orders and expects others to obey them. The decision-making power is centralized. It is best applied in situations where there is little time for group decision-making or where the leader is the most intellectual member of the group.
Merits:
- No delay in decision making as the leader itself makes the decisions, and no consultations and suggestions are taken by him.
- The work performed is satisfactory due to constant control of the leader.
Demerits:
- Employees feel demotivated and discouraged due to the leader's unwillingness to take their suggestions.
- The productivity is also impacted due to demotivated employees.
Democratic or Participative Leader: A democratic leader gives order after consulting the group and works out the policies with the acceptance of the group. It is suitable in situations, when the members are skilled and competent.
Merits:
- There is a sense of cooperation between the leader and the employees, thus leading to peace and harmony in the organization.
- There is efficiency in the work performed by the employees.
Demerits:
- Decisions can be delayed due to differences of opinions between the leader and employees, or between the employees themselves.
- This style works well only when the employees are educated, skilled and competent. In case of the opposite, the productivity and efficiency may get hampered.
Laissez-Faire or Free Rein Leader: The followers are given a high degree of independence to formulate their objectives and ways to achieve them. In this the leader fully trusts his followers, and gives them complete autonomy to make decisions.
Merits:
- The employees are highly motivated due to freedom to make decisions.
- It leads to overall development of the employees as a sense of self confidence is inculcated in them to take decisions on their own.
Demerits:
- There can be a lack of coordination due to no control of the leader on the employees.
- It is only suitable when the employees are extremely educated and highly skilled. If not, there can be issues of lack of coordination, workplace conflicts, lack of productivity, etc.
|
51 videos|339 docs|74 tests
|
FAQs on Previous Year Short & Long Questions With Answers - Directing - Business Studies (BST) Class 12 - Commerce
| 1. What are the key principles of directing in theatre? |  |
| 2. How does a director prepare for a production? |  |
| 3. What is the role of a director during rehearsals? |  |
| 4. What challenges do directors face in the directing process? |  |
| 5. How does staging impact the directing of a play? |  |

















