Previous Year Short & Long Questions With Answers: Forms of Business Organisations | Business Studies (BST) Class 11 - Commerce PDF Download
Short Answer Type Questions
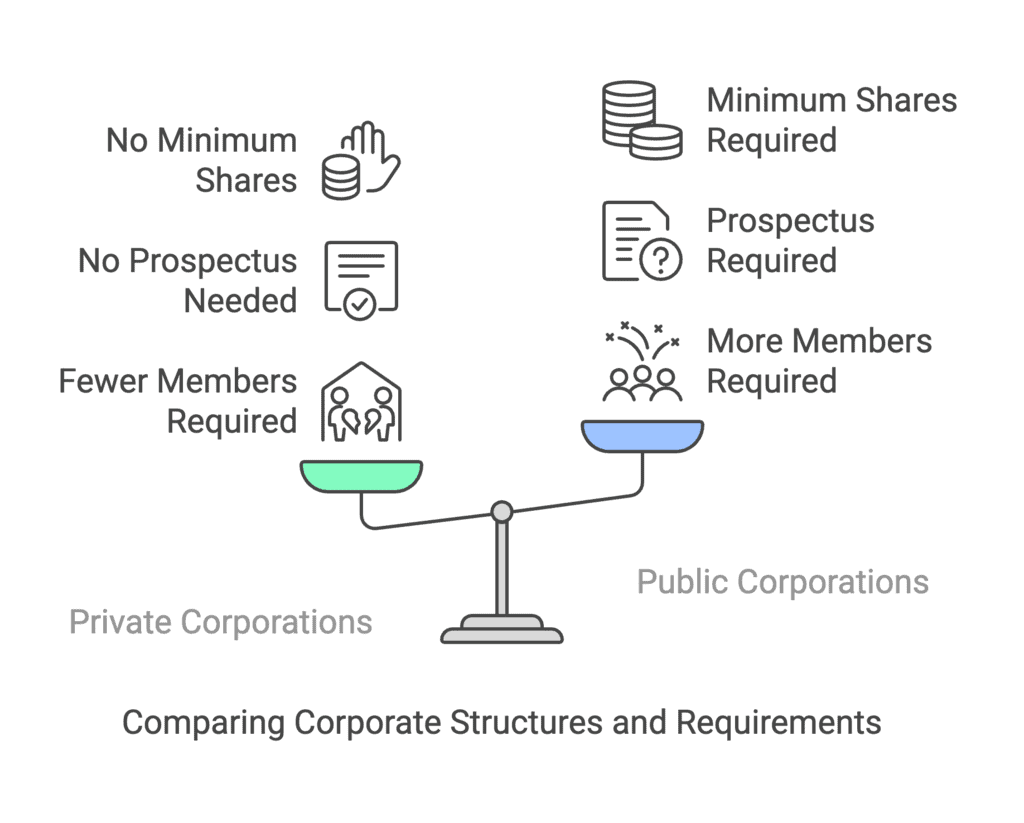
Q1: What are the important privileges available to a private company?
Ans: When a business is formed as a private corporation, it has several advantages and exemptions that are not accessible to public companies. Some of the main benefits that a private corporation has are as follows:
- A private business can be formed with as few as two members, but a public corporation requires seven.
- In private business the public is not asked to subscribe to company’s shares and hence a prospectus is unnecessary.
- Shares can be distributed without a minimum subscription requirement.
- A private company can start operating as soon as it receives its establishment certificate. On the other hand, the public company must wait until it gets the starting certificate before it may begin operations.
- A private company only needs two directors, but a public company requires at least three.
- A member index is not necessary for a private organisation but is required for a public corporation.
Q2: With a notable example, explain mutual agency in partnership.
Ans: Mutual agency refers to the legal connection between participants in a partnership who have authorization powers and the authority to engage the collaboration in business contracts. In another way, each partnership member has the authority to make business choices that commit or bind the entire partnership to a commercial contract with a third party or entity. For example, even if the partnership agreement prohibits it, a grocery store partner who acquires a delivery truck in the partnership’s name enters a legally enforceable transaction. On the other hand, such behaviour would be unlawful if a law firm partner purchased a snowmobile for the firm.
Q3: What is meant by “partner by estoppel”? Explain.
Ans: A person who shows others that they are a company partner via their actions, behaviour, or statements, is referred to as Partner by estoppel. Such a person is not a partner, and they are not responsible for providing any cash to the company, nor are they accountable for any portion of the company’s profit or loss. The same individual, however, may be held accountable for the firm’s debts. Hence, as a result, if the Business has adequate assets or finances, debt repayment can be obtained by selling off the partner’s private assets via estoppel.
Q4: What exactly is HUF?
Ans: Although the Income Tax Act does not define the Hindu Undivided Family (HUF), it is recognised under Hindu law. Unmarried daughters are included in the HUF, as are all those who are lineally settled from the same ancestor. A person does not create HUF but by a family’s standing, i.e., it is created automatically in any Hindu household.
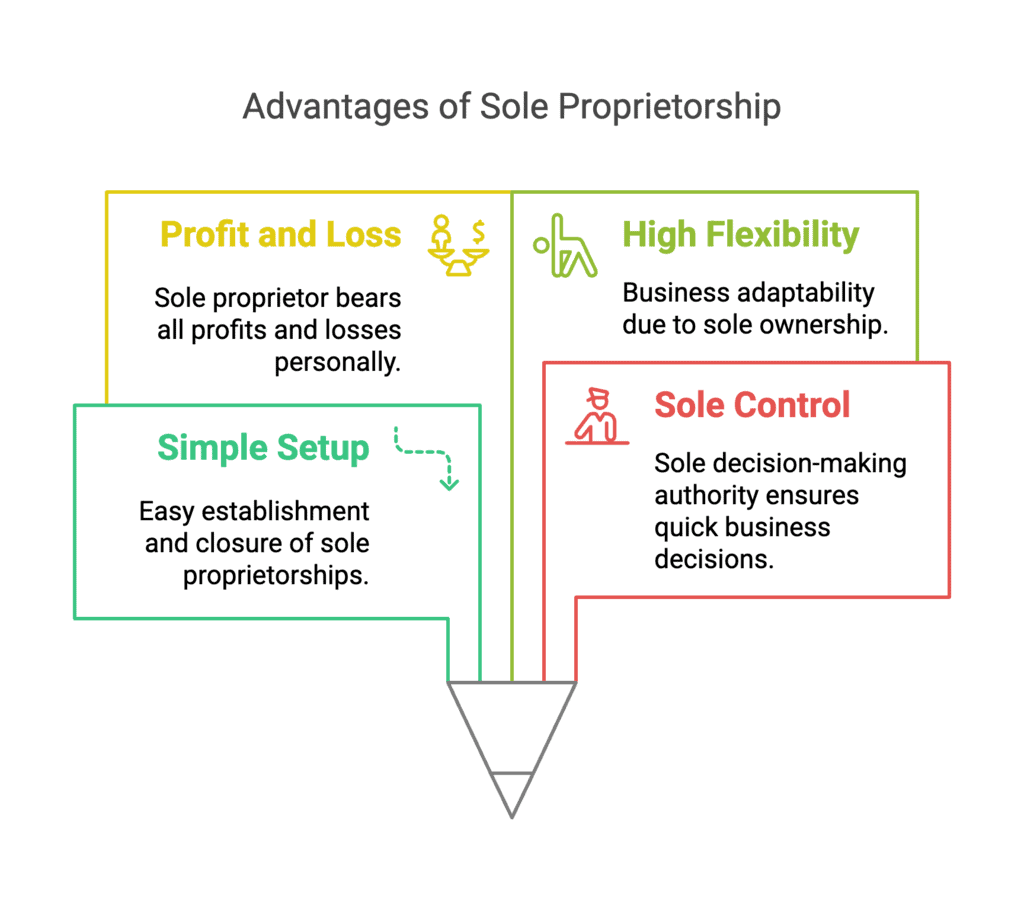
Q5: Even though there are limitations of size and resources, several people continue to prefer sole proprietorship compared to other forms of organisation? Why?
Ans: Due to the numerous sheer benefits, it provides despite the size and resource limits. The sole proprietorship is the company’s form of choice. The following are some of the advantages:
- A single proprietorship firm is simple to set up since there are few legal requirements. Similarly, closing a firm is a painless process.
- The sole owner controls the firm as the only decision-maker, allowing for swift choices.
- The sole proprietor enjoys all the Business’s gains while bearing all its misfortunes.
- Because the lone proprietor is the only person in charge of the business, it is highly flexible.
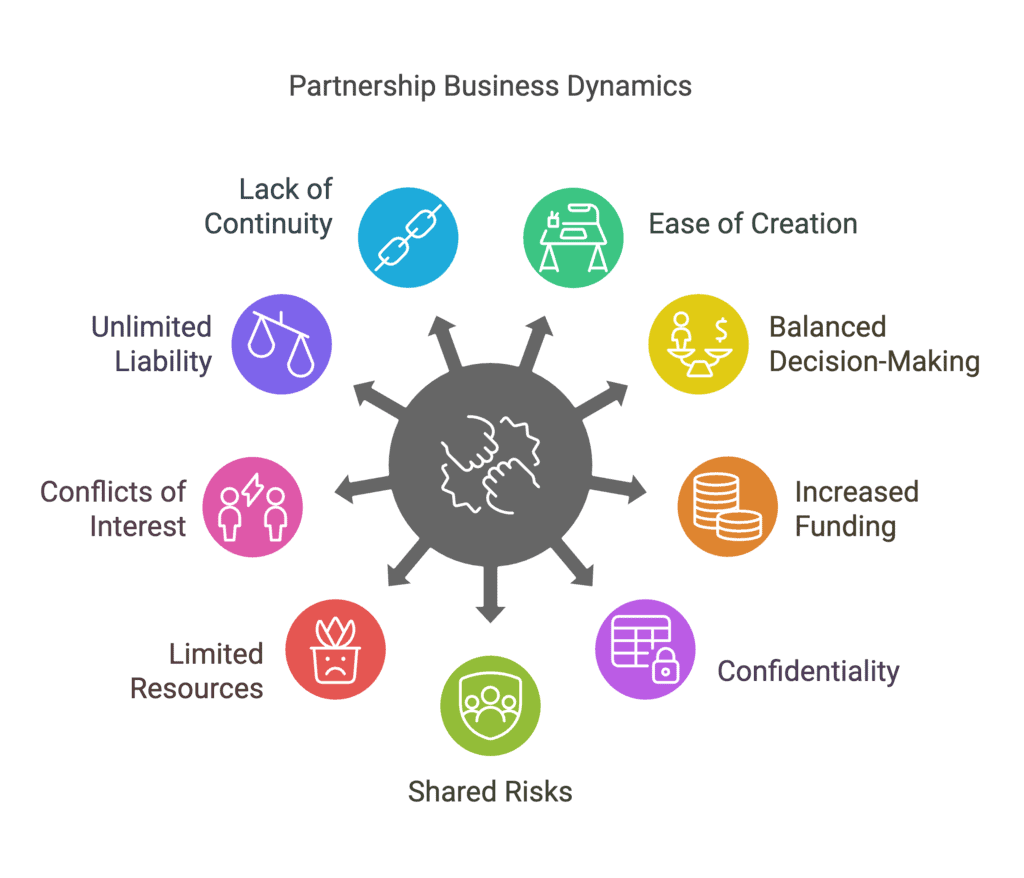
Q6: Why do some consider partnership a relatively unpopular form of business ownership? Explain the merits and limitations of partnership.
Ans: A partnership is viewed as a relatively unattractive sort of company ownership due to the inherent limitations that come with it. These limits include infinite responsibility, limited resources, the possibility of conflict, and a lack of consistency.
- Ease of closure and creation: A partnership business can be established rapidly by agreement amongst potential partners. A company doesn’t need to be registered.
- Balance decision-making: The partners might manage various responsibilities depending on their expertise. As a result, the decision-making process in a partnership business is more balanced than in any other kind of corporate ownership.
- A large amount of funds: Each partner in a partnership provides a certain amount of money. Consequently, compared to a single owner, it is feasible to collect a more considerable sum of cash and carry out additional activities as needed.
- Confidentiality: There is no legal requirement for a partnership business to publish its financial accounts or submit reports. As a result, it may maintain secrecy regarding its operations.
- Sharing the risk: The risks that come with running a partnership business are shared by all partners. As a result, individual partners experience less worry, tension, and stress.
Limitations of business partnership:
- Restricted Resources: Capital investment contributions are frequently insufficient to sustain large-scale commercial activity due to the limited number of partners. As a result, partnership firms struggle to expand beyond a particular scale.
- Conflicts of Interest: The decision-making authority in a partnership business is distributed among the partners. This is also dependent on their level of competence, foresight, and ability.
- Unlimited liability: Partners are accountable for repaying debts from their assets if the Business’s assets are insufficient to fulfil its obligations.
- Lack of continuity: When one of the partners dies, retires, becomes bankrupt, or becomes mad, the partnership comes to an end. On the other side, the surviving partners might enter into a new agreement and continue to run the business.
Q7: How does a cooperative society exemplify democracy and secularism? Explain.
Ans: A cooperative society is run by persons chosen by all members through a democratic process. Each member has an equal right to vote, regardless of the amount of money they have invested. As a result, it functions as a democracy in which all members are treated equally and have similar rights. Members are not discriminated against because of their caste, religion, or gender. People of the management committee can select the members they believe best represent them. As a result, it denotes secularism.
Q8: What does it mean to have unlimited liability?
Ans: General partners and sole proprietors with unlimited liability are jointly and severally liable for the company’s debts and obligations. However, this obligation is not limited and can be paid off by seizing the owners’ assets, distinguishing it from limited liability partnerships.
Q9: Compare the status of a minor in a Hindu joint family business with that in a partnership firm.
Ans: A person under 18 is considered a minor in Indian law. By being born into a Joint Hindu household, a minor becomes a member of the family company. Like other family members, the minor has equal ownership and rights to the property and company. However, his obligation is limited to his part of the property.
As per the Indian Partnership Act of 1932, a minor cannot become a partner in a partnership business. However, if all partners agree, a minor can be initiated and partake in a firm’s profits. Still, a minor does not need to contribute capital or carry any obligation if the Business supports the firm. Therefore, minors aren’t regarded as partners. However, once they reach the age of 18, they have the option of continuing the relationship or terminating it.
Long Answer Type Questions
Q1: In what form of Business do individuals associate freely for profit, with capital dividends into transferable shares, and ownership of which is a requirement of membership? Explain in terms of characteristics.
Ans: A joint-stock company is a non-profit organisation formed by a group of people to do profitable economic activities. It has a legal status distinct from its members and a capital structure separated into transferable shares. A corporation is an independent legal entity with its legal identity, perpetual succession, and a common seal. In a corporation, the shareholders are the company’s owners, and the Board of Directors, which the shareholders elect, is the company’s central management body.
The company’s capital is divided into smaller components known as “shares,” which can be freely transferred from one shareholder to the next (except in a private company). A joint-stock firm has the following characteristics:
- A corporation is a made-up entity. It is a legal entity that exists without the participation of its members.
- The legal personality of a corporation is established. The law does not regard the Business and its owners as the same.
- Starting a business is a time-consuming, costly, and challenging endeavour. Therefore, incorporation is required for all enterprises.
- It will only be deactivated after completing a specialised operation known as winding up. Members may come and go, but the firm does not cease to exist.
- A company’s common seal may or may not exist.
- All shareholders share the risk of a company’s losses.
Q2: Which business model is best for the following businesses, and why?
- Coaching centre for the students of science subject
- A beauty salon
- A shopping centre
- Hotel
- Little repair shops
- Restaurant
Ans: The suitable business model for the businesses as mentioned earlier would be:
- Coaching center for the students of science subject: Collaboration with a science coaching facility. It’s simple to set up and run, and it’s inexpensive. Partners report their share of profit or loss on their tax returns.
- A beauty salon: A salon can be run as a sole proprietorship. Created and ran straightforwardly and cost-effectively. The owner declares profit or loss on their tax return.
- A shopping center: shopping malls are JSCs (joint-stock corporations). Personal responsibility for commercial debts is restricted for business owners.
- Hotel: In the hotel industry, there are joint-stock companies. Small businesses are drawn to LLCs and corporations because they minimize their owners’ liability for corporate debts and court judgments against the company. Another factor to consider is income taxes: you may set up a limited liability company (LLC) or a corporation to benefit from reduced tax rates. Furthermore, an LLC or company may be able to deduct the cost of a range of fringe benefits passed on to its employees (including the owners) as a business expense.
- A little repair shop: A sole proprietorship is appropriate for a small repair shop. Created and ran straightforwardly and cost-effectively. The owner declares profit or loss on their tax return.
- Restaurant: Ownership of a restaurant as a sole proprietor. Created and ran straightforwardly and cost-effectively. The owner declares profit or loss on their tax return.
Q3: Who has equal ownership rights to an ancestor’s property? Emphasise its most important aspects
Ans: A Joint Hindu Family is a form of business owned and operated by members of the Hindu Undivided Family (HUF). The company’s membership is based on birth in a specific family, and three generations of the same family can be members. The family’s business is run by the eldest member of the family, known as Karta. Joint Hindu Family Business members with equal ownership rights over an ancestor’s property are known as coparceners.
A combined Hindu family company has the following characteristics:
- Because membership is by birth, there is no requirement for an agreement.
- Except for the Karta, all members are only responsible for their portion of the Business’s co-coparcenary property. The Karta’s responsibility is boundless.
- Karta oversees the family company, and his choices bind everyone.
- After Karta’s death, the business is carried on by the next eldest son, Karta.
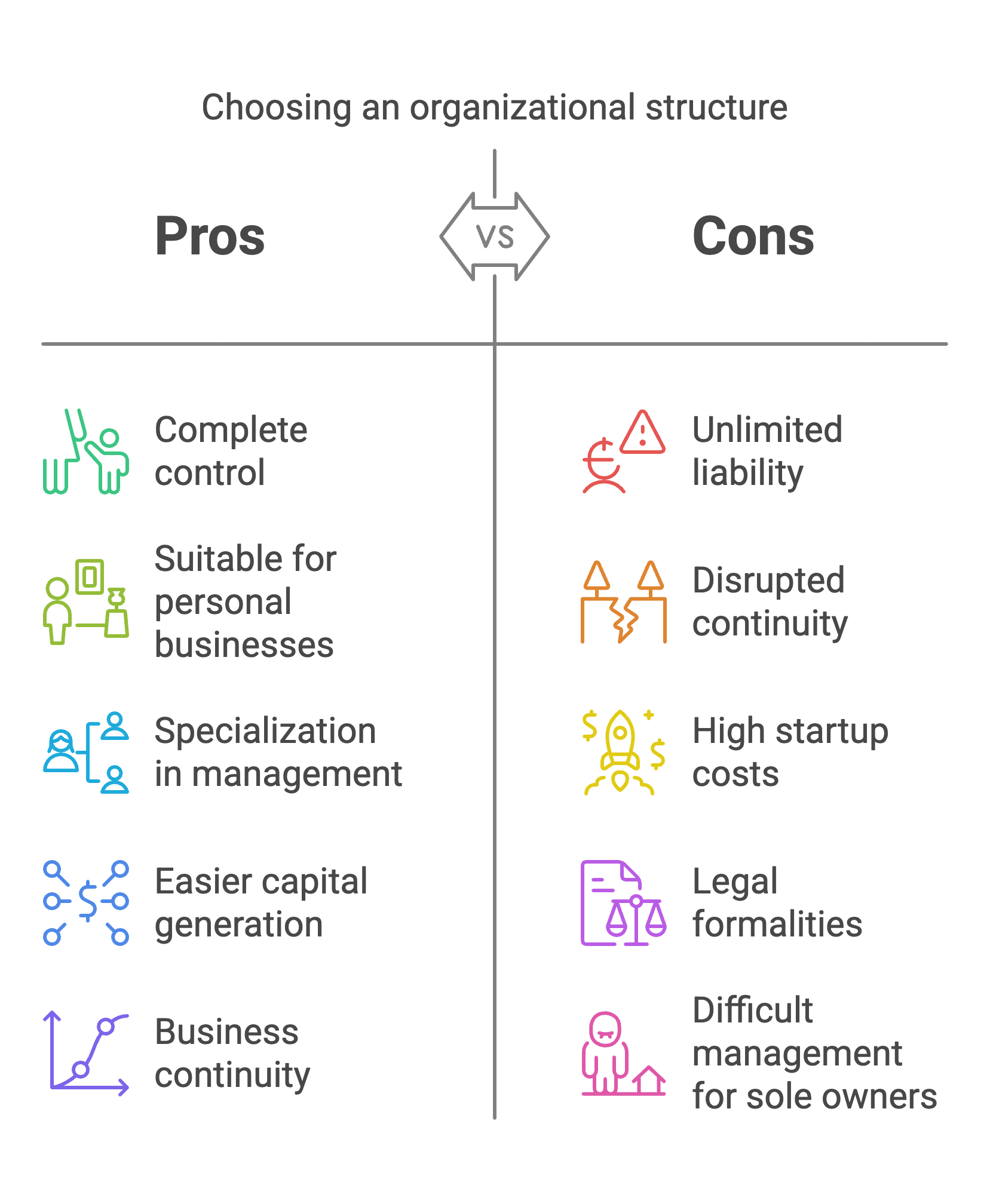
Q4: Why is it important to choose an appropriate form of organisation? Discuss the factors that determine the choice of form of organisation.
Ans: Choosing an appropriate business organisation is necessary since it is one of the most important decisions to make when beginning a business or expanding an existing one. A business can be owned and run in several ways. It’s challenging to modify a company model after it’s been decided. As a result, the type of business company chosen should be done with care and consideration.
The following factors influence organisational structure selection:
- Control: With a sole proprietorship, you have complete control over your operations and decision-making authority. If the owners, on the other hand, want to share ownership to make better judgments, they can form a partnership or a corporation.
- Nature of Business: Businesses that involve direct personal connection with customers, such as beauty salons or grocery stores, are better suited to a single proprietorship. The corporate kind of structure benefits large manufacturing units. The partnership structure is significantly more served in the case of professional services.
- Management Skills: Being informed in all firm parts is difficult for a sole owner. Members split their labour in other organisations, such as partnerships and businesses, allowing management to specialise in specific areas and make better judgments.
- Capital Requirements: The corporation form is suitable for large-scale activity since it may generate a large amount of money by issuing shares. There are two options for medium and small firms: partnership or sole proprietorship. In the framework of a company, expansion capital requirements may be managed more easily.
- Continuity: The continuity of sole proprietorship and partnership enterprises can be disrupted by events such as the owners’ death, insolvency, or insanity. In organisations like joint Hindu family companies, cooperative societies, and corporations, such factors, on the other hand, have minimal influence on the business’s survival.
- Liability: The liability of the owners/partners of a sole proprietorship or partnership is unlimited. This might lead to the owners’ assets being used to repay the debt.
- Cost and Convenience of Starting a Company: A sole proprietorship is straightforward to start in terms of initial business costs and legal procedures, but because of its more minor activities, a partnership has the advantage of less legal formalities and lower prices. Registration is necessary in the case of cooperative societies and companies. The process of founding a company takes time and money.
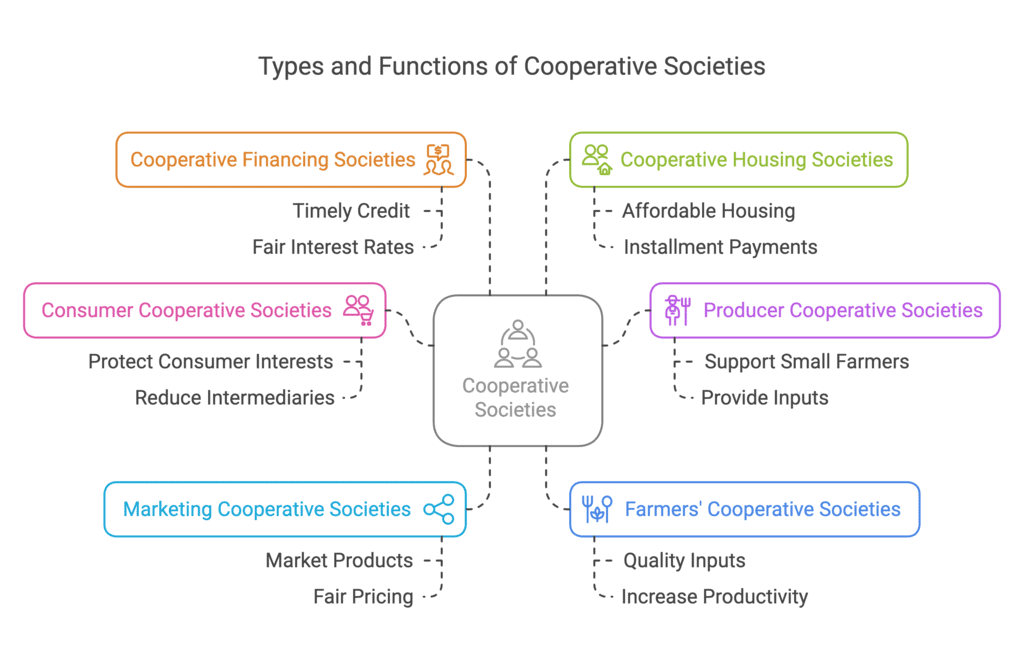
Q5: What are the reasons for the formation of cooperative forms of organisation? Describe the different sorts of cooperative societies.
Ans: A cooperative society is a collection of individuals who get together voluntarily for the common welfare of its members. They are motivated by a desire to defend their economic interests from potential exploitation by intermediaries looking to increase their profits. The process of founding a cooperative organisation is simple, and all that is necessary is the agreement of at least ten adults. A society’s capital is raised by selling shares to its members. An organisation acquires a distinct legal character when it is registered.
One sort of cooperative society is the consumer cooperative society.
- It was designed to protect consumers’ interests.
- To improve operational savings, society strives to eliminate intermediaries. Instead, it purchases things in bulk from wholesalers and resells them to its members.
- Profits are dispersed depending on capital contributions to the organisation or purchases made by individual members.
Producer Cooperative Societies are a specific sort of producer cooperative society.
- It was established to protect the interests of small farmers.
- Members are producers looking for inputs to create commodities to fulfil customer demands.
- Profits are distributed according to their contributions to the society’s overall pool of products produced or sold.
Cooperative Societies Marketing-this organisation was established to help small manufacturers market their products.
- Producers that demand fair pricing for their commodities are among the group’s members.
- It combines individual members’ production and marketing activities such as shipping, storage, and packaging to sell the commodities for the best feasible price. Profits are dispersed according to the amount of money each member puts in.
Farmers’ Cooperative Societies were formed to protect farmers’ interests by providing high-quality inputs at a reasonable price.
- Members are farmers who want to collaborate on farming projects.
- The idea is to increase productivity while reaping the benefits of large-scale farming. Improving farmer output and returns while addressing challenges associated with farming on fragmented land holdings.
Cooperative Financing Societies were established to give members timely credit at reasonable rates.
- Members are individuals seeking financial assistance in the form of loans.
- The purpose of such groups is to protect members from being taken advantage of by lenders who demand high-interest rates on loans.
A cooperative housing organisation is a sort of Cooperative Housing Societies.
- It was established to assist low-income people in constructing homes at a reasonable cost.
- These societies are people looking for a cheaper location to reside in.
- The purpose is to alleviate members’ housing issues by constructing homes and allowing them to pay in instalments.
Q6: If registration is optional, why do partnership firms willingly go through this legal formality and register themselves? Explain.
Ans: Although partnership business registration is optional, many firms choose to do so. This is owing to the severe legal consequences of failing to register. Listed below are a few examples:
- The partners of a non-registered business cannot sue a third party, but the non-registration of a partnership firm does not prevent other firms from hiring it.
- The company is forbidden from filing a lawsuit against any of its partners. Similarly, a partner in a non-registered firm cannot sue their co-partners or the company.
- Claims against a third party by a non-registered partnership entity cannot be enforced in court. As a result, partnerships are established to overcome these disadvantages.
|
38 videos|180 docs|28 tests
|
FAQs on Previous Year Short & Long Questions With Answers: Forms of Business Organisations - Business Studies (BST) Class 11 - Commerce
| 1. What are the different forms of business organization? |  |
| 2. What are the advantages of a sole proprietorship? |  |
| 3. How does a partnership differ from a corporation? |  |
| 4. What is a limited liability company (LLC) and its benefits? |  |
| 5. What factors should one consider when choosing a form of business organization? |  |

















