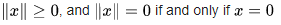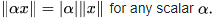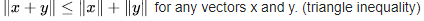Introduction:- Normed vector space | Additional Topics for IIT JAM Mathematics PDF Download
In mathematics, a normed vector space is a vector space over the real or complex numbers, on which a norm is defined. A norm is the formalization and the generalization to real vector spaces of the intuitive notion of distance in the real world. A norm is a real-valued function defined on the vector space that has the following properties:
- The zero vector, 0, has zero length; every other vector has a positive length.

- Multiplying a vector by a positive number changes its length without changing its direction. Moreover,

- The triangle inequality holds. That is, taking norms as distances, the distance from point A through B to C is never shorter than going directly from A to C, or the shortest distance between any two points is a straight line.

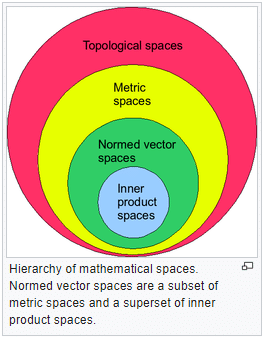
The generalization of these three properties to more abstract vector spaces leads to the notion of norm. A vector space on which a norm is defined is then called a normed space or normed vector space. Normed vector spaces are central to the study of linear algebra and functional analysis.
Definition:- A normed vector space is a pair 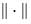 V.
V.
A seminormed vector space is a pair (V,p) where V is a vector space and p a seminorm on V.
We often omit p or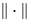 and just write V for a space if it is clear from the context what (semi) norm we are using.
and just write V for a space if it is clear from the context what (semi) norm we are using.
In a more general sense, a vector norm can be taken to be any real-valued function that satisfies the three properties above.
A useful variation of the triangle inequality is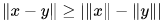 for any vectors x and y.
for any vectors x and y.
This also shows that a vector norm is a continuous function.
Note that property 2 depends on a choice of norm 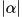 on the field of scalars. When the scalar field is
on the field of scalars. When the scalar field is 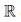 (or more generally a subset of
(or more generally a subset of 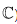 ), this is usually taken to be the ordinary absolute value, but other choices are possible. For example, for a vector space over
), this is usually taken to be the ordinary absolute value, but other choices are possible. For example, for a vector space over 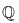 one could take
one could take 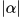 to be the p-adic norm, which gives rise to a different class of normed vector spaces.
to be the p-adic norm, which gives rise to a different class of normed vector spaces.
Topological structure:-
If (V, ‖·‖) is a normed vector space, the norm ‖·‖ induces a metric (a notion of distance) and therefore a topology on V. This metric is defined in the natural way: the distance between two vectors u and v is given by ‖u−v‖. This topology is precisely the weakest topology which makes ‖·‖ continuous and which is compatible with the linear structure of V in the following sense:
1. The vector addition + : V × V → V is jointly continuous with respect to this topology. This follows directly from the triangle inequality.
2. The scalar multiplication · : K × V → V, where K is the underlying scalar field of V, is jointly continuous. This follows from the triangle inequality and homogeneity of the norm.
Similarly, for any semi-normed vector space we can define the distance between two vectors u and v as ‖u−v‖. This turns the seminormed space into a pseudometric space (notice this is weaker than a metric) and allows the definition of notions such as continuity and convergence. To put it more abstractly every semi-normed vector space is a topological vector space and thus carries a topological structure which is induced by the semi-norm.
Of special interest are complete normed spaces called Banach spaces. Every normed vector space V sits as a dense subspace inside a Banach space; this Banach space is essentially uniquely defined by V and is called the completion of V.
All norms on a finite-dimensional vector space are equivalent from a topological viewpoint as they induce the same topology (although the resulting metric spaces need not be the same).And since any Euclidean space is complete, we can thus conclude that all finite-dimensional normed vector spaces are Banach spaces. A normed vector space V is locally compact if and only if the unit ball B = {x : ‖x‖ ≤ 1} is compact, which is the case if and only if V is finite-dimensional; this is a consequence of Riesz's lemma. (In fact, a more general result is true: a topological vector space is locally compact if and only if it is finite-dimensional. The point here is that we don't assume the topology comes from a norm.)
The topology of a seminormed vector space has many nice properties. Given a neighbourhood system N(0) around 0 we can construct all other neighbourhood systems as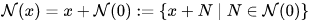
with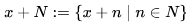
Moreover there exists a neighbourhood basis for 0 consisting of absorbing and convex sets. As this property is very useful in functional analysis, generalizations of normed vector spaces with this property are studied under the name locally convex spaces.
Linear maps and dual spaces:-
The most important maps between two normed vector spaces are the continuous linear maps. Together with these maps, normed vector spaces form a category.
The norm is a continuous function on its vector space. All linear maps between finite dimensional vector spaces are also continuous.
An isometry between two normed vector spaces is a linear map f which preserves the norm (meaning ‖f(v)‖ = ‖v‖ for all vectors v). Isometries are always continuous and injective. A surjective isometry between the normed vector spaces V and W is called an isometric isomorphism, and V and W are called isometrically isomorphic. Isometrically isomorphic normed vector spaces are identical for all practical purposes.
When speaking of normed vector spaces, we augment the notion of dual space to take the norm into account. The dual V ' of a normed vector space V is the space of all continuous linear maps from V to the base field (the complexes or the reals) — such linear maps are called "functionals". The norm of a functional φ is defined as the supremum of |φ(v)| where v ranges over all unit vectors (i.e. vectors of norm 1) in V. This turns V ' into a normed vector space. An important theorem about continuous linear functionals on normed vector spaces is the Hahn–Banach theorem.
Normed spaces as quotient spaces of seminormed spaces:-
The definition of many normed spaces (in particular, Banach spaces) involves a seminorm defined on a vector space and then the normed space is defined as the quotient space by the subspace of elements of seminorm zero. For instance, with the Lp spaces, the function defined by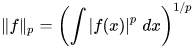
is a seminorm on the vector space of all functions on which the Lebesgue integral on the right hand side is defined and finite. However, the seminorm is equal to zero for any function supported on a set of Lebesgue measure zero. These functions form a subspace which we "quotient out", making them equivalent to the zero function.
Finite product spaces:-
Given n seminormed spaces Xi with seminorms qi we can define the product space as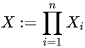
with vector addition defined as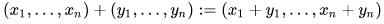
and scalar multiplication defined as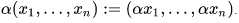
We define a new function q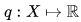
for example as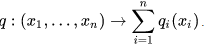
which is a seminorm on X. The function q is a norm if and only if all qi are norms.
More generally, for each real p≥1 we have the seminorm: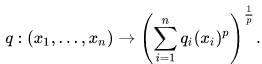
For each p this defines the same topological space.
A straightforward argument involving elementary linear algebra shows that the only finite-dimensional seminormed spaces are those arising as the product space of a normed space and a space with trivial seminorm. Consequently, many of the more interesting examples and applications of seminormed spaces occur for infinite-dimensional vector spaces.
FAQs on Introduction:- Normed vector space - Additional Topics for IIT JAM Mathematics
| 1. What is a normed vector space in mathematics? |  |
| 2. What are the key properties of a normed vector space? |  |
| 3. How is a normed vector space different from a vector space? |  |
| 4. What is the significance of normed vector spaces in mathematics? |  |
| 5. Can all vector spaces be equipped with a normed structure? |  |

|
Explore Courses for Mathematics exam
|

|