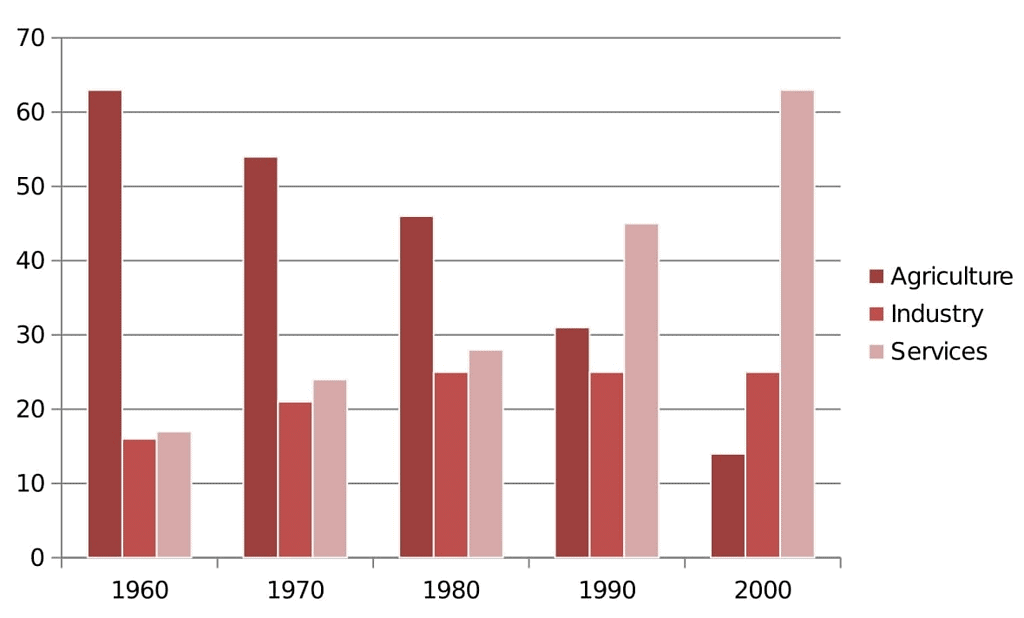SSC CHSL Exam > SSC CHSL Notes > Current Affairs & General Knowledge > Five Year Plans
Five Year Plans | Current Affairs & General Knowledge - SSC CHSL PDF Download
Five-Year Plans (FYPs) are centralized and integrated national economic programs. Joseph Stalin implemented the first Five-Year Plan in the Soviet Union in 1928. India launched its First FYP in 1951, immediately after independence, under the socialist influence of India's first prime minister, Jawaharlal Nehru.

Context
- From 1947 to 2017, the Indian economy was premised on the concept of planning.
- This was carried through the Five-Year Plans, developed, executed, and monitored by the Planning Commission (1951-2014) and the NITI Aayog (2015-2017).
- With the prime minister as the ex-officio chairman, the commission has a nominated deputy chairman, who holds the rank of a cabinet minister.
- Montek Singh Ahluwalia is the last deputy chairman of the commission (resigned on 26 May 2014).
- The Twelfth Plan completed its term in March 2017.
- Prior to the Fourth Plan, the allocation of state resources was based on schematic patterns rather than a transparent and objective mechanism, which led to the adoption for the Gadgil formula in 1969.
- The Gadgil formula is named after Dhananjay Ramchandra Gadgil, a social scientist and the first critic of Indian planning. It was evolved in 1969 for determining the allocation of central assistance for state plans in India. Gadgil formula was adopted for distribution of plan assistance during Fourth and Fifth Five Year Plans.
- Revised versions of the formula have been used since then to determine the allocation of central assistance for state plans.
- The recent government elected in 2014, has announced the dissolution of the Planning Commission, and its replacement by a think tank called the NITI Aayog (an acronym for National Institution for Transforming India).
M. Visvesvaraya Plan
- In 1934, Sir M. Visvesvaraya had published a book titled “Planned Economy in India”, in which he presented a constructive draft of the development of India in next ten years.
- His core idea was to lay out a plan to shift labor from agriculture to industries and double up National income in ten years.
- This was the first concrete scholarly work towards planning.
- The economic perspective of India’s freedom movement was formulated during the thirties between the 1931 Karachi session of Indian National Congress, 1936 Faizpur session of India National Congress.
National Planning Committee
- The first attempt to develop a national plan for India came up in 1938. In that year, Congress President Subhash Chandra Bose had set up a National Planning Committee with Jawaharlal Nehru as its president.
- However the reports of the committee could not be prepared and only for the first time in 1948 -49 some papers came out.
Bombay Plan
- It was presented in 1944 by Eight Industrialists of Bombay viz. Mr. JRD Tata, GD Birla, Purshottamdas Thakurdas, Lala Shriram, Kasturbhai Lalbhai, AD Shroff , Ardeshir Dalal, & John Mathai working together prepared “A Brief Memorandum Outlining a Plan of Economic Development for India”.
- This is known as “Bombay Plan”. This plan envisaged doubling the per capita income in 15 years and tripling the national income during this period.
- Nehru did not officially accept the plan, yet many of the ideas of the plan were inculcated in other plans which came later.
Gandhian Plan
- In the light of the basic principles of Gandhian economics, S. N. Agarwal authored ‘The Gandhian Plan’ in 1944 in which he put emphasis on the expansion of small unit production and agriculture.
- Its fundamental feature was decentralisation of economic structure with self-contained villages and cottage industries.
People’s Plan
- In 1945, yet another plan was formulated by the radical humanist leader M.N. Roy, chairman of the Post-War Reconstruction Committee of Indian Trade Union.
- The plan was based on Marxist socialism and advocated the need of providing the people with the ‘basic necessities of life’. Agricultural and industrial sectors, both were equally highlighted by the plan.
Sarvodaya Plan
- Sarvodaya Plan (1950) was drafted by Jaiprakash Narayan.
- This plan itself was inspired by Gandhian Plan and Sarvodaya Idea of Vinoba Bhave.
- This plan emphasized on agriculture and small & cottage industries.
- It also suggested the freedom from foreign technology and stressed upon land reforms and decentralized participatory planning.
The Wage Good Model
- Prominent Economist like, C N Vakil and P R Brahmananda advocated Wage Good model for the development of the Indian economy and Industrialisation.
- Vakil and Brahamanda differed from the Mahalanobis strategy as they believe “At the low level of consumption (this was the situation in India) the productivity of the workers depends on how much they consumed."
- According to them, if people were undernourished, they will lose their productivity and become less efficient, at this juncture it is necessary to feed them to increase their productivity. But this is not true for all consumer good; so they differentiated between Wage Good (whose consumption increase worker productivity) and Non-Wage Good (whose consumption did not).
- To sum up, Wage Good model says; worker’s productivity depends on not on whether they use machines to produce goods but also on the consumption of wage goods like, food, cloth and other basics.
- Therefore, the first step towards development is to mechanize agriculture and raise food production; once this objective is reached, one should go for Mahalanobis strategy of Heavy Industrialisation.
Twenty Point Programme (TPP)
- The second Central Plan which was launched in July 1975.
- The programme was conceived for coordinated and intensive monitoring of a number of schemes implemented by the Central and the State Governments.
- The basic objective was of improving the quality of life of the people, especially of those living below the poverty line.
- Under this, a thrust was given to schemes relating to poverty alleviation, employment generation in rural areas, housing, education, family welfare and health, protection of environment and many other schemes having a bearing on the quality of life in the rural areas.
Planning commission
- A formal body to formulate and implement Five-Year Plans was established on 15th March 1950 with the Prime Minister as the head.
- The commission nominated a Deputy Chairman which held the rank of a cabinet minister.
- In 2014, Prime Minister Narendra Modi dissolved the planning commission to replace it with the NITI Aayog which acts as a think tank for development of the nation.
National Development Council
- All the plans made by the Planning Commission need to be approved by the National Development Council first which is an extra-constitutional body. It was set up on 6th August 1952.
- Planning at the state level is done through a state planning body where the chief minister is the chairman of the body and finance and planning members along with technical members assist her/him to formulate a plan. A district planning committee also functions similarly.
NITI Aayog
- The NITI Aayog was a political think tank set up to act as an advisor the government. The NITI Aayog will not involve setting up of a plan which is designed from the perspective of the center.
- Rather, it aims to involve all states to devise systematic policies differently for all states.
- The NITI Aayog aims to implement the sustainable development goals (SDG’s) which are formulated on the global forums and make the federal structure of our nation more efficient and co-operative.
- The chairperson of the NITI Aayog is the Prime Minister.
- The CEO of the planning commission is Amitabh Kant at present. The chief Ministers of all states are a part of the governing council of the NITI Aayog.
- Structure under NITI Aayog
- NITI Aayog will be headed by the Prime Minister and will have a Governing Council, comprising Chief Ministers of states and Heads of all Union Territories.
- The Governing Council replaces the earlier National Development Council.
- In addition, there will also be a regional council comprising of Chief Ministers and Lieutenant Governors of Union Territories, which will be mandated to develop plans that are region specific.
- The Aayog will have 7 or 8 full time members and two well- known and accomplished part- time members, drawn from leading research organisations and major universities.
- Four Union Ministers, nominated by the Prime Minister, will also be included in ex-officio capacity
First Plan (1951-56)
- It was based on Harrod-Domar Model.
- Community Development Program was launched in 1952.
- Emphasized on agriculture, price stability, power & transport.
- It was more than a success because of good harvests in the last two tears.Question for Five Year PlansTry yourself: The main objective of the first five year plan of India was?View Solution
Second Plan (1956-61)
- Also called Mahalanobis Plan after its chief architect.
- Its objective was rapid industrialization.
- Advocated huge imports which led to the emptying of funds leading to foreign loans. It shifted basic emphasis from agriculture to industry far too soon. During this plan, the price level increased by 30% against a decline of 13% during the First Plan.
Third Plan (1961-66)
- At its conception time, it was felt that Indian economy has entered a take-off stage. Therefore, its aim was to make India a ‘self-reliant’ and ‘self-generating’ economy.
- Also, it was realized from the experience of the first two plans that agriculture should be given the top priority to suffice the requirements of export and industry.
- This plan is also called ‘Gadgil Yojna’, after the Deputy Chairman of Planning Commission D.R. Gadgil.
 Sector Wise Growth Rate (1960-2000)
Sector Wise Growth Rate (1960-2000) - Complete failure due to unforeseen misfortunes, viz. Chinese aggression (1962), Indo-Pak war (1965), severest drought in 100 years (1965-66).
Three Annual Plan (1966-69)
- Plan holiday for 3 years. The prevailing crisis in agriculture and serious food shortage necessitated the emphasis on agriculture during the Annual Plans.
- During these plans a whole new agriculture strategy involving the wide-spread distribution of High-Yielding Varieties of seeds, the extensive use of fertilizers, exploitation of irrigation potential and soil conservation was put into action to tide-over the crisis in agricultural production.
- During the Annual Plans, the economy basically absorbed the shocks given during the third Plan, making way for a planned growth.
Question for Five Year PlansTry yourself:Which five year plan was called ‘Gadgil Yojna’?
View Solution
Plan Holidays (1966–1969)
- Due to miserable failure of the Third Plan the government was forced to declare “plan holidays” (from 1966 to 1967, 1967–68, and 1968–69).
- Three annual plans were drawn during this intervening period. During 1966–67 there was again the problem of drought. Equal priority was given to agriculture, its allied activities, and industrial sector.
- The government of India declared “Devaluation of Rupee” to increase the exports of the country. The main reasons for plan holidays were the war, lack of resources and increase in inflation.
Fourth Plan (1969-74)
- Main emphasis on agriculture’s growth rate so that a chain reaction can start.
- Fared well in the first two years with record production, last three years failure because of poor monsoon.
- Had to tackle the influx of Bangladeshi refugees before and after 1971 Indo-Pak war.
- Implementation of Family Planning Programmes was amongst major targets of the Plan
- This plan failed and could achieve a growth rate of 3.3% only against the target of 5.7%.
Fifth Plan (1974-79)
- The fifth plan prepared and launched by D.D. Dhar proposed to achieve two main objectives viz, ‘removal of poverty’ (Garibi Hatao) and ‘attainment of self-reliance’, through promotion of high rate of growth, better distribution of income and a very significant growth in the domestic rate of savings.
- The plan was terminated in 1978 (instead of 1979) when Janata Govt. came to power.
- The Electricity Supply Act was amended in 1975, a Twenty-point program was launched in 1975, the Minimum Needs Programme (MNP) and the Indian National Highway System was introduced.
- Overall this plan was successful which achieved a growth of 4.8% against the target of 4.4%.
- This plan was terminated in 1978 by the newly elected Moraji Desai government.
Rolling Plan (1978-80)
- In 1980, Congress rejected the Rolling Plan and a new sixth Five Year Plan was introduced.
- Three plans were introduced under the Rolling plan: (1) For the budget of the present year (2) this plan was for a fixed number of years-- 3,4 or 5 (3) Perspective plan for long terms-- 10, 15 or 20 years.
- There were 2 Sixth Plans. One by Janata Govt. (for 78-83) which was in operation for 2 years only and the other by the Congress Govt when it returned to power in 1980.
The Janta Govt. Plans are also called Rolling Plans.
Sixth Plan (1980-85)
- Objective: Increase in national income, modernization of technology, ensuring a continuous decrease in poverty and unemployment, population control through family planning, etc.
Seventh Plan (1985-90)
- The seventh plan emphasized policies and programs which aimed at rapid growth in food-grains production, increased employment opportunities and productivity within the framework of basic tenants of planning.
- It was a great success; the economy recorded 6% growth rate against the targeted 5%.
Annual Plans (1990–1992)
- The Eighth Plan could not take off in 1990 due to the fast changing economic situation at the centre and the years 1990–91 and 1991–92 were treated as Annual Plans. The Eighth Plan was finally formulated for the period 1992–1997.
Eighth Plan (1992-97)
- The eighth plan was postponed by two years because of political upheavals at the Centre and it was launched after a worsening Balance of Payment position and inflation during 1990-91.
- The plan undertook various drastic policy measures to combat the bad economic situation and to undertake an annual average growth of 5.6%.
- Some of the main economic performances during eighth plan period were rapid economic growth, high growth of agriculture and allied sector, and manufacturing sector, growth in exports and imports, improvement in trade and current account deficit.
Ninth Plan (1997-2002)
- It was developed in the context of four important dimensions: Quality of life generation of productive employment, regional balance and self-reliance.
- The main focus of this plan was “Growth with Social Justice and Equality”.
- It was launched in the 50th year of independence of India.
- This plan failed to achieve the growth target of 6.5% and achieved a growth rate of 5.6%.
Tenth Plan (2002-2007)
- Its objectives included achieving the growth rate of 8%, reduction of poverty ratio to 20% by 2007 and to 10% by 2012, universal access to primary education by 2007, increase in literacy rate to 72% within the plan period and to 80% by 2012.
Eleventh Plan (2007-2012)
- Accelerate the growth rate of GDP from 8% to 10% and then maintain at 10% in the 12th Plan in order to double per capita income by 2016-17.
- Increase agricultural GDP growth rate of 4% per year to ensure a broader spread of benefits.
- Increase literacy rate for persons of age 7 years or more to 85%.
- Reduce infant mortality rate (MR) to 28 and maternal mortality ratio (MMR) to 1 per 1000 live births.
- Raise the sex ratio for age group 0-6 to 935 by 2016-17.Question for Five Year PlansTry yourself: The main aim of the Eleventh Five Year Plan wasView Solution
Twelfth Plan (2012-2017)
- Growth rate of GDP targeted at 8%
- To achieve a growth of 4% in agriculture and 10% in manufacturing sector per year.
- To reduce poverty by 10 percentage points by 2017.
- To create 5 crore new job in the non-agriculture sectors.
- To reduce infant mortality rate to 25 maternal mortality rate to 1 per 1000 live births and increase sex ratio in the 0-6 age group to 950. Question for Five Year PlansTry yourself:What was the period of the 12th five-year plan of India?View Solution
Table: Growth During Five Year Plans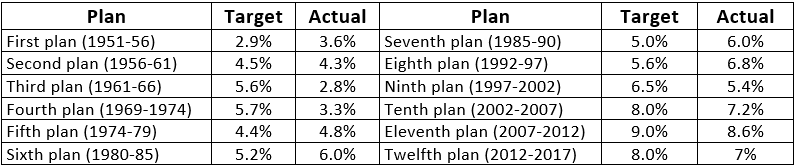
The document Five Year Plans | Current Affairs & General Knowledge - SSC CHSL is a part of the SSC CHSL Course Current Affairs & General Knowledge.
All you need of SSC CHSL at this link: SSC CHSL
|
128 videos|293 docs|30 tests
|
|
128 videos|293 docs|30 tests
|
Download as PDF

|
Explore Courses for SSC CHSL exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.
Related Searches