Important National Activities from 1885 to 1947 | General Awareness - Bank Exams PDF Download
Introduction
The period from 1885 to 1947 marks a transformative phase in Indian history, characterized by a robust wave of nationalist activities that paved the way for India’s independence from British rule.
- Beginning with the formation of the Indian National Congress in 1885, a new political consciousness emerged, bringing together leaders and revolutionaries who sought self-governance and the end of colonial oppression.
- This era witnessed significant events, from the early moderates advocating reforms within the British framework to the assertive extremism of figures like Bal Gangadhar Tilak, the rise of Mahatma Gandhi’s nonviolent resistance movements, and the eventual Quit India Movement.
- Each milestone, whether through negotiations, civil disobedience, or revolutionary actions, contributed to the collective momentum that culminated in India's independence on August 15, 1947.
- Understanding these activities provides insight into the strategic, ideological, and grassroots efforts that shaped modern India’s identity and its struggle for freedom.
Revolt of 1857
- The Revolt of 1857 marked the first major uprising against British rule in India.
- It commenced on May 10, 1857, in the town of Meerut.
- This uprising was directed against the East India Company and was the first large-scale rebellion challenging its authority.
- Despite its failure, the revolt had a profound impact on public sentiment and invigorated the independence movement across India.
- Mangal Pandey played a pivotal role in this uprising by rebelling against his British commanders .
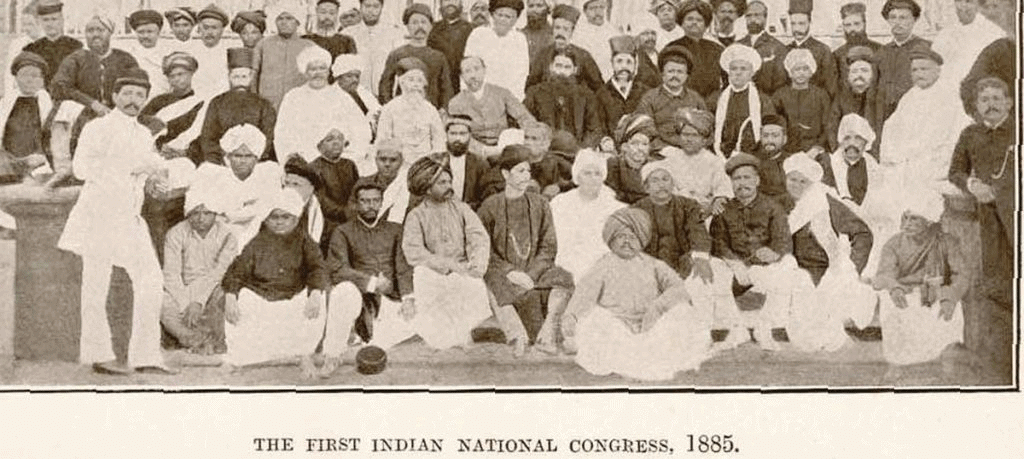
The Indian National Congress (1885)
- Formed in 1885 by A. O. Hume, an Englishman and a retired civil servant.
- First session in Bombay under W. C. Banerjee in 1885 (72 delegates attended it).
- For the first two decades, Congress adopted a moderate approach, believing in the fairness of the British government.
- But the repressive measures of the British gave rise to extremists within Congress like Bipin Chandra Pal, Bal Gangadhar Tilak and Lala Lajpat Rai ( Lal, Bal, Pal).

Partition of Bengal (1905)
- On October 16, 1905, Lord Curzon announced the partition of Bengal, aiming to create a divide between Hindus and Muslims by reducing the size of the old province of Bengal and creating East Bengal and Assam.
- This move sparked a strong nationwide movement against the partition, uniting people in opposition to the British decision.
Swadeshi Movement (1905)
- The Swadeshi Movement gained momentum with key figures like Lal-Bal-Pal and Aurobindo Ghosh leading the charge.
- The Indian National Congress first adopted the Swadeshi message at the Banaras Session in 1905, chaired by G. K. Gokhale.
- Public bonfires of foreign goods became a common sight in various locations, symbolising the rejection of foreign products and the promotion of Swadeshi (Indian-made) goods.
Formation of the Muslim League (1906)
- Set up in 1906 under the leadership of Aga Khan, Nawab Salimullah of Dhaka and Nawab Mohsin-ul-Mulk.
- It was a loyalist, communal and conservative political organisation which supported the partition of Bengal, opposed the Swadeshi movement, demanded special safeguards to its community and a separate electorate for Muslims.
Demand for Swaraj (1906)
- In December 1906, at Calcutta the INC under Dadabhai Naoroji adopted ‘Swaraj’ (Self-government) as the goal of the Indian people.
Surat Session of the Indian National Congress (1907)
- At the Surat session of the Indian National Congress in 1907, the INC divided into two factions: the extremists and the moderates.
- The extremists, led by Bal, Pal, and Lal, advocated for more direct and aggressive methods of protest.
- The moderates, led by G. K. Gokhale, preferred a more gradual and reformist approach.
Indian Councils Act (Minto- Morley Reforms) (1909)
- The Minto-Morley Reforms, part of the Indian Councils Act of 1909, introduced various constitutional measures, including a separate electorate for Muslims.
- This separate electorate aimed to divide the nationalist movement and align the Moderates and Muslims with the government, thereby weakening the united front of nationalists.
Ghadar Party (1913)
- The Ghadar Party was established by Lala Hardayal, Taraknath Das, and Sohan Singh Bhakna in 1913.
- The headquarters of the Ghadar Party were located in San Francisco, USA.
Home Rule Movement (1916)
- Started by B. G. Tilak (April, 1916) at Poona and Annie Besant and S. Subramania Iyer at Adyar, near Madras (Sept, 1916).
- Objective: Self-government for India in the British Empire.
- Tilak linked up the question of Swaraj with the demand for the formation of linguistic States and education in vernacular language. He gave the slogan ‘Swaraj is my birthright, and I shall have it’.
Satyagraha Movement(1917)
- The first Satyagraha Movement, led by Mahatma Gandhi in 1917, took place in the Champaran District of Bihar.
- The Champaran district was home to many landless serfs who faced severe hardships.
- Pandit Raj Kumar Shukla, an indigo cultivator facing oppression, played a crucial role in convincing Gandhi to lead this movement.
- The success of the Champaran Satyagraha marked the beginning of a series of Satyagraha Movements across India, demonstrating the effectiveness of non-violent resistance.
Lucknow Pact (1916)
- The Lucknow Pact was a significant agreement reached in 1916 between the Indian National Congress (INC) and the Muslim League.
- This pact came in the wake of rising anti-British sentiments among Muslims due to the conflict between Britain and Turkey.
- The Congress party agreed to the demand for separate electorates for Muslims, and together with the Muslim League, they called for a representative government and dominion status for India.
August Declaration (1917)
Following the Lucknow Pact, the British government made the August Declaration in 1917, promising to increase Indian participation in all areas of administration.
This declaration aimed to gradually establish responsible governance within the framework of the British Empire.
Rowlatt Act (1919)
- The Rowlatt Act, enacted in 1919, granted the government sweeping powers to arrest and imprison suspects without trial for up to two years.
- It also allowed the suspension of the Habeas Corpus right, a fundamental civil liberty in Britain, leading to widespread outrage across various communities.
- This act sparked the first major nationwide protest led by Mahatma Gandhi and marked the beginning of the Non-Cooperation Movement.
Jallianwala Bagh Massacre (1919)
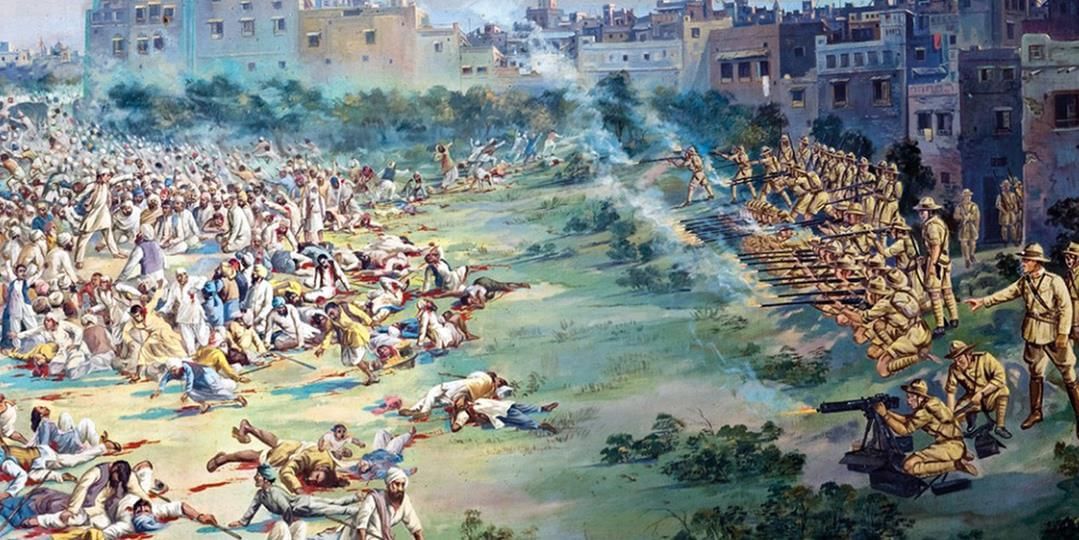

- The Jallianwala Bagh Massacre occurred on April 13, 1919, when General Dyer ordered his troops to fire on a large crowd gathered at Jallianwala Bagh in Amritsar.
- The crowd had gathered to protest the arrests of Dr. Kitchlu and Dr. Satyapal, and the firing resulted in the deaths of hundreds of people, including men, women, and children, with thousands more injured.
- In response to the massacre, Rabindranath Tagore returned his knighthood, and Sir Shankaran Nair resigned from the Viceroy’s Executive Council.
- The Hunter Commission was established to investigate the incident, and the outrage over the massacre led to long-term repercussions, including the assassination of Michael O’Dwyer (Lt. Governor of Punjab during the massacre) by Sardar Udham Singh on March 13, 1940.
Khilafat Movement (1920)
- The Khilafat Movement was launched in 1920 to protest against the dismemberment of the Ottoman Empire, particularly following the harsh terms imposed by the Treaty of Sèvres in August 1920.
- The movement aimed to protect the position of the Caliph, the spiritual leader of Muslims worldwide, who was seen as a symbol of Islamic unity and authority.
- The Indian leaders involved in the movement believed that preserving the Caliph's authority was crucial for maintaining the socio-political fabric of the Muslim community, both in India and globally.
- This movement gained significant support among Indian Muslims, who were motivated by a mix of religious sentiment and anti-colonial nationalism.
Non-Cooperation Movement (1920)
- It was the first mass-based political movement under Gandhi Ji.
- Congress passed the resolution in its Calcutta session in September 1920.
Chauri Chaura Incident (1922)
- On February 5, 1922, a clash occurred between a crowd in Chauri–Chaura (near Gorakhpur) and the police.
- During this incident, 22 policemen lost their lives.
- This incident prompted Gandhi to call off the Non-Cooperation Movement on February 12, 1922.
Simon Commission (1927)
 Protests Against the Simon Commission
Protests Against the Simon Commission - The commission was established by John Simon to evaluate the political situation in India.
- Its goal was to propose new reforms and enhance parliamentary democracy.
- Indian leaders opposed the commission because it lacked Indian members.
- The government responded with severe repression and police violence against protestors.
- In Lahore, Lala Lajpat Rai was injured by police brutality and later died from his injuries on November 17, 1928.
Lahore Session(1929)
- On Dec. 19, 1929, under the Presidentship of J.L. Nehru, the INC at its Lahore session declared Poorna Swaraj (complete Independence) as its ultimate goal.
- On Dec. 31, 1929, the newly adopted tri-colour flag was unfurled, and Jan 26, 1930 was fixed as the first Independence Day, which was to be celebrated every year.
Revolutionary Activities
- The first political murder of a European was committed in 1897 at Poona by the Chapekar brothers, Damodar and Balkishan. Their target was Mr. Rand, President of Plague Commission, but Lt. Ayerst was accidentally shot.
- In 1907, Madam Bhikaiji Cama, a Parsi revolutionary, unfurled the flag of India at the Stuttgart Congress (International Socialist Conference).
- In 1908, Khudiram Bose and Prafulla Chaki threw a bomb at the carriage of Kingsford, the unpopular judge of Muzaffarpur. Khudiram, Kanhaiyalal Dutt and Satyendra Nath Bose were hanged (Alipur case ).
- In 1909, M L Dhingra shot dead Col. William Curzon Whyllie, the political advisor of ‘India Office’ at London.
- In 1912, Rasbihari Bose and Sachindra Nath Sanyal threw a bomb at Lord Hardinge at Delhi (Delhi Conspiracy Case).
- In Oct 1924, a meeting of revolutionaries from all over the country was called at Kanpur. They set up Hindustan Socialist Republican Association / Army (HSRA).
- They carried out a dacoity on the Kakori bound train on the Saharanpur–Lucknow railway line on Aug. 9, 1925.
- Bhagat Singh, with his colleagues, shot dead Saunders (Assistant S.P. of Lahore, who ordered lathi-charge on Lala Lajpat Rai ) on Dec. 17, 1928.
- Then Bhagat Singh and Batukeshwar Dutt threw a bomb in Central Assembly on Apr. 8, 1929. Thus, he, Rajguru and Sukhdev were hanged on March 23, 1931, at Lahore Jail (Lahore Conspiracy Case) and their bodies cremated at Hussainiwala near Ferozepur.
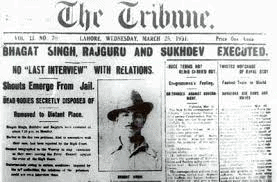
- In 1929, Jatin Das died in Lahore Jail after 63 days fast to protest against horrible conditions in jail.
- Surya Sen, a revolutionary of Bengal, formed the Indian Republican Army in Bengal. In 1930, he masterminded the raid on Chittagong armoury. He was hanged in 1933.
- In 1931, Chandrasekhar Azad shot himself at Alfred Park in Allahabad.
Dandi March (1930)
- The Salt March, also referred to as the Salt Satyagraha, was a pivotal event in India’s struggle for independence.
- On March 12, 1930, Gandhiji, along with 78 followers, set out from the Sabarmati Ashram to protest against the British salt law.
- The march aimed to reach the coastal village of Dandi, where Gandhiji planned to make salt from seawater, defying the law.
- After a long and arduous journey, Gandhiji and his followers reached the seashore on April 6, 1930.
- There, Gandhiji picked up a handful of salt, symbolising the start of the Civil Disobedience Movement and inspiring millions to join the cause.
 Gandhi leading the Dandi March
Gandhi leading the Dandi March First Round Table Conference(1930)
- The First Round Table Conference was held in London on November 12, 1930 to discuss constitutional reforms.
- It was convened in response to the Simon Commission’s criticism in India.
- The meeting signified a step where the British acknowledged the need for Indian participation in governance.
- The Indian National Congress (INC) boycotted the conference, calling it inadequate.
- Other groups like the Hindu Mahasabha, Liberals, and minority representatives attended, reflecting divided Indian politics.
- The conference opened the way for future discussions on India’s constitutional future but also revealed sharp divisions in Indian society over governance and representation.
Gandhi-Irwin Pact (1931)
- The Gandhi-Irwin Pact was a crucial agreement aimed at improving relations between Mahatma Gandhi and the British Government during India’s struggle for independence.
- Initiated by moderate leaders like Sapru, Jayakar, and Srinivas Shastri, the pact was signed on March 5, 1931, marking a significant step towards dialogue.
- Under the agreement, Gandhi, representing the Indian National Congress (INC), agreed to call off the Civil Disobedience Movement and participate in the second Round Table Conference in London.
- In return, the government, represented by Irwin, promised to release political prisoners and allow coastal villages to produce salt for personal use, easing some of the harsh restrictions imposed earlier.
- The pact was seen as a pragmatic move, reflecting the complex dynamics of the independence movement, where various factions sought to negotiate their positions while maintaining pressure on the colonial government.
Second Round Table Conference (1931)
- The Second Round Table Conference in 1931 was a continuation of discussions between the British government and Indian leaders regarding constitutional reforms and the future of India.
- Mahatma Gandhi represented the Indian National Congress (INC) at this conference, which took place in London, meeting with British Prime Minister Ramsay MacDonald and other officials.
- One of the major issues at the conference was the demand for separate electorates, which was not only raised by Muslims but also by other groups such as the Depressed Classes, Indian Christians, and Anglo-Indians.
- This demand highlighted the complexities of Indian society and the differing needs and aspirations of various communities.
- The conference faced challenges in reaching an agreement due to these conflicting demands, reflecting the ongoing struggle to balance the interests of different groups within India while addressing the concerns of the British government.
The Communal Award (1932)
- The Communal Award was announced by British Prime Minister Ramsay MacDonald in 1932, reflecting the British policy of divide and rule in India.
- The award proposed separate representation for various groups, including Muslims, Sikhs, Indian Christians, Anglo-Indians, women, and Backward Classes.
- Gandhi, who was in Yeravada jail at the time, strongly opposed this policy and began a hunger strike to protest against it.
Poona Pact (1932)
- The Poona Pact was a significant agreement reached in 1932 concerning the representation of the Depressed Classes, also known as the Scheduled Castes, in the legislative assemblies of British India.
- The pact was a response to the Communal Award, which had proposed separate electorates for the Depressed Classes, a move opposed by Mahatma Gandhi, who feared it would further divide Hindu society.
- To resolve the deadlock and ensure a united Hindu front, Gandhi and Dr. B.R. Ambedkar, a prominent leader of the Depressed Classes, negotiated the Poona Pact.
- Eventually Poona pact was reached and Gandhi broke the fast on the sixth day (Sept. 25, 1932).
- The agreement provided for joint electorates for the Depressed Classes with a certain number of reserved seats in the legislative assemblies, ensuring their political representation while maintaining Hindu unity.
- The Poona Pact was a crucial step in the political integration of the Depressed Classes into the broader Indian society and laid the groundwork for their eventual inclusion in the constitutional framework of independent India.
The Third Round Table Conference(1932)
- This conference was unproductive as most national leaders were in prison.
- It resulted in the passage of the Government of India Act, 1935.
Demand for Pakistan (1933)
- In the 1930 Allahabad Address, Iqbal suggested a Muslim state in North-Western India (Punjab, Sindh, NWFP, Baluchistan).
- Chaudhary Rehmat Ali introduced the term Pakistan in 1933.
- Muhammad Ali Jinnah from Bombay played a role in promoting this concept.
- The Muslim League formally advocated for a separate Pakistan during its Lahore Session in 1940.
The Cripps Mission (1942)
- In December 1941, Japan entered World War II and moved towards India.
- By March 7, 1942, Rangoon had fallen to Japanese forces, who occupied Southeast Asia.
- The British government sent Sir Stafford Cripps, leader of the House of Commons, to negotiate with Indian leaders.
- He proposed a draft offering dominion status after the war.
- This proposal was rejected by the Congress, as it did not want to depend on future promises.
- Gandhi criticised it as a post-dated cheque from a failing bank.
The Revolt of 1942 & The Quit India Movement
- Called the Wardha proposal and the Leaderless Revolt.
- On 8th August 1942, the resolution was passed in Bombay, marking a crucial moment in the movement.
- Mahatma Gandhi played a pivotal role by coining the slogan " Do or Die," urging people to take decisive action.
- However, the situation escalated on 9th August when the Congress was banned, and many prominent leaders were arrested.
- This crackdown fueled public anger, leading to a spontaneous and violent outburst across the country.
- Despite the initial fervour, the movement was eventually suppressed by the authorities.
The Indian National Army (1942)
- The Indian National Army (INA) was originally founded by Capt Mohan Singh in Singapore in September 1942 with Japan's Indian POWs.
- In January 1941, Subhas Chandra Bose escaped from India and reached Berlin.
- In July 1943, Bose joined the INA in Singapore, where he took over leadership from Rasbehari Bose.
- The INA was primarily made up of Indian soldiers from the British army who had been captured by the Japanese in East Asia.
- The INA had its headquarters in Rangoon and Singapore.
- The INA formed three fighting brigades named after prominent leaders: Gandhi, Azad, and Nehru.
- The Rani Jhansi Brigade was a special unit composed of women.
- Despite their efforts, the INA could not withstand the British army and eventually surrendered.
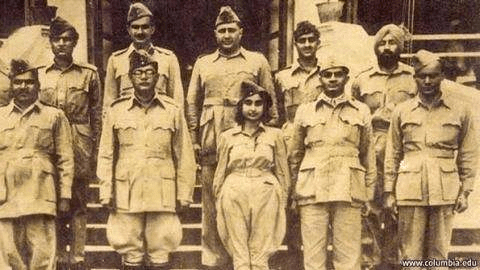 Leaders of the Indian National Army
Leaders of the Indian National ArmyThe Cabinet Mission Plan (1946)
- The struggle for freedom reached a crucial point in 1945-46.
- On March 15, 1946, the new Labour Party Prime Minister, Lord Attlee, announced that the British Cabinet Mission would visit India.
- This mission included Lord Pethick Lawrence as the chairman, along with Sir Stafford Cripps and A.V. Alexander.
- The mission aimed to discuss proposals with the Indian National Congress (INC) and the Muslim League (ML) to gain their acceptance.
- On May 16, 1946, the mission presented its proposals.
- They rejected the demand for a separate Pakistan and instead recommended a federal union of British India and the Princely States.
- While the Congress accepted these proposals, the Muslim League had reservations and continued to push for a separate Pakistan.
Formation of the Interim Government (1946)
- Following the Cabinet Mission Plan, an interim government led by Congress nominees was formed on September 2, 1946.
- J.L. Nehru was appointed Vice-President of this government, while the Governor-General continued as President.
Jinnah's Direct Action Resolution (1946)
- Fearing unfavourable election results and potential marginalisation in the constituent assembly, Jinnah and the Muslim League took a drastic step.
- On July 29, 1946, the Muslim League retracted its acceptance of the Cabinet Mission Plan.
- They called for a 'Direct Action' resolution, criticising the British Government and the Congress on August 16, 1946.
- This resolution triggered violent communal riots across the country.
- To assert the demand for Pakistan, Jinnah observed Pakistan Day on March 23, 1947.
Formation of Constituent Assembly (1946)
- The Constituent Assembly met for the first time on December 9, 1946, with Dr. Rajendra Prasad elected as its President.
Mountbatten Plan (1947)
- On June 3, 1947, Lord Mountbatten put forward his plan to resolve the political deadlock in India.
- The key points of the Mountbatten Plan included:
i) The division of India into two separate nations: India and Pakistan.
ii) The partition of Bengal and Punjab.
iii) A referendum in the North-West Frontier Province (NWFP) and the Sylhet district of Assam to determine their future.
iv) The establishment of a separate constitutional assembly for Pakistan to draft its constitution.
v) The option for Princely States to join either India or Pakistan or remain independent.
vi)The target date for transferring power to the new nations was set for August 15, 1947. - In July 1947, the British government passed the Independence Act of 1947, incorporating the main provisions of the Mountbatten Plan.
Partition and Independence (1947)

- All political parties accepted the Mountbatten Plan.
- At the time of Independence, India was made up of 562 princely states, both large and small.
- Sardar Vallabh Bhai Patel, the first home minister, managed this situation firmly.
- By August 15, 1947, most states, with a few exceptions like Kashmir, Hyderabad, and Junagarh, had signed the Instrument of Accession.
- Additionally, it is important to note that Goa was under Portuguese rule, while Pondicherry was a French territory.
|
365 videos|701 docs|149 tests
|
FAQs on Important National Activities from 1885 to 1947 - General Awareness - Bank Exams
| 1. What were the main causes of the Revolt of 1857 in India? |  |
| 2. What role did the Indian National Congress play in the Indian independence movement? |  |
| 3. What was the significance of the Partition of Bengal in 1905? |  |
| 4. How did the Swadeshi Movement contribute to India's struggle for independence? |  |
| 5. What were the key outcomes of the Indian Councils Act of 1909? |  |

















