Indian Geography I | IBPS PO Prelims & Mains Preparation - Bank Exams PDF Download
Introduction
India is situated north of the equator between 8°4' north to 37°6' north latitude and 68°7' east to 97°25' east longitude. It is the seventh-largest country in the world, with a total area of 3,287,263 square kilometres. India measures 3,214 km from north to south and 2,933 km from east to west.
Location
- India is located latitudinally in the Northern Hemisphere and longitudinally in the Eastern Hemisphere.
- It extends from 8°4’ N to 37°6’ N latitude and 68°7’ E to 97°25’ E longitude.
- The Country is divided into almost equal parts by the Tropic of Cancer (passing from Jabalpur in MP).
- It is the seventh-largest country in the world.
- It occupies the south-central peninsula of Asia. Arabian Peninsula and the African continent lie on the west and Myanmar, Malaysia, and Indonesia in the east.
- The southernmost point in Indian Territory, (in Great Nicobar Island) is the Indira Point (6°45'), while Kanyakumari, also known as Cape Comorin, is the southernmost point of Indian Mainland.
- The 82°30' E longitude is taken as the standard Time Meridian of India, as it passes through the middle of India (from Naini, near Allahabad).Question for Indian Geography ITry yourself:India is the ________ largest country in the world.View Solution

Area and Boundaries
- India stretches 3,214 km from North to South & 2,933 km from East to West.
- Area: 32,87,263 sq. km. Accounts for 2.4% of the total world area and 16% of the population.
- It has a land frontier of 15,200 km. Mainland India has a coastline of 6,100 km. Including the Lakshadweep and Andaman and Nicobar, the coastline measures about 7516.6 km.
- In India, of the total landmass:
(a) Plains: 43.3 %
(b) Plateaus: 27.7%
(c) Hills:18.6%
(d) Mountains: 10.7% - In the South, on the eastern side, The Gulf of Mannar and the Palk Strait separate India from Sri Lanka.
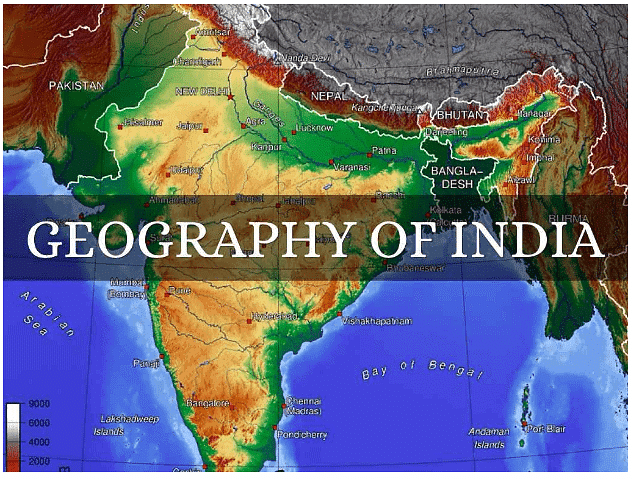
- Total land neighbours: 7 (Pakistan, Afghanistan, China, Nepal, Bhutan, Bangladesh and Myanmar).
- India’s Islands include the Andaman & Nicobar Islands in the Bay of Bengal & Lakshadweep, Minicoy & Amindive Islands in the Arabian Sea.

Radcliffe Line: Borderline between India and Pakistan, and India and Bangladesh. The border was decided by Sir Cyril Radcliffe in 1947.
McMahon Line: Borderline between India and China. This line was decided by Sir Henry McMahon in 1914.
Durand Line: Borderline between India and Afghanistan. This line was decided by Sir Henry Mortimer Durand in 1896.
Question for Indian Geography ITry yourself:The Gulf of Mannar and the Palk Strait separate India fromView Solution
Facts About Position of States of India
- Uttar Pradesh borders a maximum number of States, 8 (Eight):
Uttarakhand, Himachal Pradesh, Haryana, Rajasthan, MP, Chhattisgarh, Jharkhand, and Bihar. - Tropic of Cancer passes through 8 (Eight) States:
Gujarat, Rajasthan, MP, Chhattisgarh, Jharkhand, West Bengal, Tripura, and Mizoram. - Indian Standard Meridian (82°30´ E meridian) passes through:
UP, MP, Chhattisgarh, Odisha, and Andhra Pradesh.Question for Indian Geography ITry yourself:Tropic of Cancer passes through 8 States. Which of the following is not one of them?View Solution
Administrative Division of India
 Administrative Divisions of India
Administrative Divisions of India
- India is divided into 28 States and 8 Union Territories.
(a) The 28 states are:
Andhra Pradesh, Arunachal Pradesh, Assam, Bihar, Chhattisgarh, Goa, Gujarat, Haryana, Himachal Pradesh, Jharkhand, Karnataka, Kerala, Madhya Pradesh, Maharashtra, Manipur, Meghalaya, Mizoram, Nagaland, Odisha, Punjab, Rajasthan, Sikkim, Tamil Nadu, Telangana, Tripura, Uttar Pradesh, Uttarakhand and West Bengal.
(b) The 8 union Territories are:
Andaman and Nicobar Island, Chandigarh, Dadra and Nagar Haveli and Daman and Diu, NCT of Delhi, Ladakh, Lakshadweep, Jammu and Kashmir, Puducherry. Puducherry (Pondicherry) is the only Union Territory which spread in three states:
(a) Puducherry (Main) - Situated in Tamil Nadu
(b) Karaikal- Situated in Tamil Nadu
(c) Yanam- Situated in Andhra Pradesh; Mahe- Situated in Kerala.• The Indira Point, the southern point of India is situated in the southern tip of Great Nicobar Island.Barren Island is only India’s active volcano which situated in the east of Middle Andaman.
Narcondam Island is a volcanic island which is situated in the northern-eastern part of North Andaman.
Duncan pass is between South Andaman and Little Andaman.
The Grand Channel is between Great Nicobar and Sumatra (Indonesia).
The Palk Strait is situated between Tamil Nadu (India) and Sri Lanka.
The Adam’s Bridge is situated between Tamil Nadu (India) and Sri Lanka. Pamban Island is a part of the Adam’s Bridge. Rameshwaram is situated on this Island.
- The Palk Bay is to the north and the Gulf of Mannar is to the south of the Adam’s Bridge.Question for Indian Geography ITry yourself:Which Union Territory spreads in three states?View Solution
Important Rivers of India
 Major Indian Rivers
Major Indian Rivers
- Ganges: Originates from Gangotri Glacier and falls into the Bay of Bengal. It measures around 2525 km in length.
- Satluj: Originates from Mansarovar Rakas Lakes and falls into the Chenab. It measures around 1050 km in length.
- Indus: Originates near Mansarovar Lake and falls into the Arabian Sea. It measures around 2880 km in length.
- Ravi: Originates from Kullu Hills near Rohtang Pass and falls into the Chenab. It measures around 720 km in length.
- Beas: Originates near Rohtang Pass and falls into the Satluj. It measures around 470 km in length.
- Jhelum: Originates from Verinag in Kashmir and falls into the Chenab. It measures around 725 km in length.
- Yamuna: Originates from Yamunotri and falls into the Ganga. It measures around 1375 km in length.
- Chambal: Originates from M.P. and falls into the Yamuna. It measures around 1050 km in length.
- Ghagra: Originates from Matsatung Glaciers and falls into the Ganga. It measures around 1080 km in length.
- Kosi: Originates near Gosain Dham Peak and falls into the Ganga. It measures around 730 km in length.
- Betwa: Originates from Vindhyanchal and falls into the Yamuna. It measures around 480 km in length.
- Son: Originates from Amarkantak and falls into the Ganga. It measures around 780 km in length.
- Brahmaputra: Originates near Mansarovar Lake and falls into the Bay of Bengal. It measures around 2900 km in length.
- Narmada: Originates from Amarkantak and falls into the Gulf of Khambat. It measures around 1057 km in length.
- Tapti: Originates from Betul Distt. in M.P. and falls into the Gulf of Khambat. It measures around 724 km in length.
- Mahanadi: Originates from Raipur Distt. in Chhattisgarh and falls into the Bay of Bengal. It measures around 858 km in length.
- Luni: Originates from Aravallis and falls into the Rann of Kutch. It measures around 450 km in length.
- Ghaggar: Originates from the Himalayas and falls into the Near Fatehabad. It measures around 494 km in length.
- Sabarmati: Originates from Aravallis and falls into the Gulf of Khambat. It measures around 416 km in length.
- Krishna: Originates from the Western Ghats and falls into the Bay of Bengal. It measures around 1327 km in length.
- Godavari: Originates from Nasik Distt. in Maharashtra and falls into the Bay of Bengal. It measures around 1465 km in length.
- Cauvery: Originates from Brahmagir Range of Western Ghats and falls into the Bay of Bengal. It measures around 805 km in length.
- Tungabhadra: Originates from Western Ghats and falls into the Krishna River. It measures around 640 km in length.Question for Indian Geography ITry yourself:Which river originates from MP?View Solution
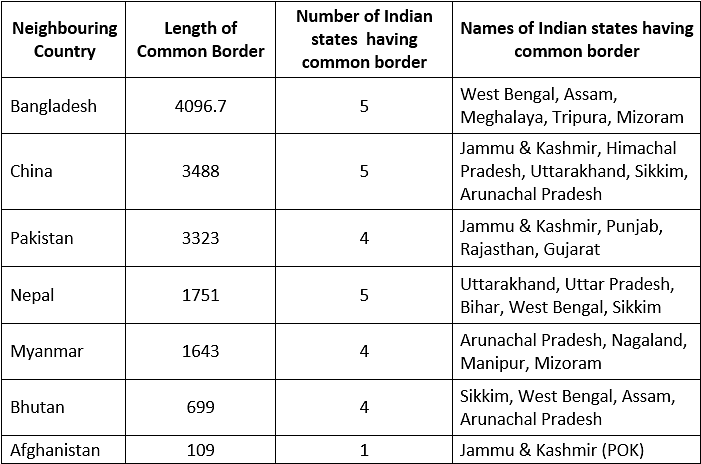
Major Ports in India
National Parks and Wild Life Sanctuaries
- Gir Forests: Home of the Asiatic lion, in Gujarat
- Kaziranga Sanctuary: One-horned Rhino, in Assam
- Manas Sanctuary: One-horned Rhino, in Assam
- Chandraprabha Sanctuary: Home of Asiatic lion, in UP
- Ghana or Keoladeo Bird Sanctuary: In Bharatpur, Rajasthan
- Dachigam Sanctuary: For Hangul, in Kashmir
- Corbett National Park: Home of Tiger, in Uttarakhand
- Kanha National Park: In MP
- Shiv Puri National Park: In MP
- Hazaribagh National Park: In Jharkhand
- Periyar Game Sanctuary: In Kerala
- Dudhwa National Park: In UP
- Vedanthangal Bird Sanctuary: In Tamil Nadu
- Nokrek National Park: In Meghalaya
- Sariska Sanctuary: In Rajasthan
- Ranthambhor National Park: In Rajasthan
- Namdapha National Park: In Arunachal Pradesh
- Keibul Lamjo Floating National Park: In Manipur
- Palamau Tiger Project: In Bihar
- Similipal National Park: In Odisha
- Ranganthittoo Bird Sanctuary: In Mysore, Karnataka
- Nagarhole National Park: In Karnataka
- Mudumalai Sanctuary: In Tamil Nadu
- Balpakram Sanctuary: In Meghalaya
- Bandipur Sanctuary: Along the Karnataka- Tamil Nadu border
- Jaldapara Sanctuary: In West Bengal. For Rhinos
- Wild Ass Sanctuary: In Rann of Kutch, Gujarat. For wild AssQuestion for Indian Geography ITry yourself:
Ghana or Keoladeo Bird Sanctuary is located in?View Solution
Important Crops of India
- Rice: West Bengal, Punjab, UP
- Wheat: UP, Punjab, Haryana
- Maize: Madhya Pradesh, Andhra Pradesh, Karnataka
- Bajra: Rajasthan, Gujarat, Maharashtra
- Jowar: Maharashtra, Karnataka, MP, AP
- Total Pulses: UP, MP, Punjab
- Total Foodgrains: UP, Punjab, West Bengal
- Rapeseed and Mustard: Rajasthan, UP, Haryana
- Groundnut: Gujarat, Tamil Nadu, Andhra Pradesh
- Soybean: Madhya Pradesh, Maharashtra, Rajasthan
- Sunflower: Karnataka, Andhra Pradesh, Maharashtra
- Total Oil Seeds: MP, Maharashtra, Rajasthan
- Sugarcane: UP, Maharashtra, Karnataka
- Cotton: Maharashtra, Gujarat, Andhra Pradesh
- Jute and Mesta: West Bengal, Bihar, Assam
- Tea: Assam, West Bengal, Himachal Pradesh
- Coffee: Karnataka, Kerala, Tamil Nadu
- Rubber: Kerala, Tamil Nadu, Karnataka
- Silk: Karnataka, Jammu & Kashmir, Andhra Pradesh,
In India, all 4 varieties of silk are available: Mulberry, tussar, eri and muga.
Mulberry is the main variety, while tussar is mainly found in Bihar. - Tobacco: Gujarat, Andhra Pradesh, Karnataka
Important River Valley Projects
1. Bhakra Nangal Project
- It is situated on Satluj in Punjab.
- It is the highest in India.
- Its height is around 226 m.
- The reservoir is called Gobind Sagar Lake.
2. Mandi Project: It is situated on Beas in H.P.
3. Chambal Valley Project:
- It is situated on Chambal in MP & Rajasthan.
- There are 3 Dams in this Project:
(a) Gandhi Sagar Dam
(b) Rana Pratap Sagar Dam
(c) Jawahar Sagar Dam
4. Damodar Valley Project:
- It is situated on Damodar in Bihar.
- It is based on Tennessee Valley Project, USA.
5. Hirakud Project:
- It is situated on Mahanadi in Odisha.
- It is the world’s Longest Dam, 4801 m.
6. Rihand Project:
- It is situated on Son in Mirzapur.
- The reservoir is called Govind Vallabh Pant reservoir.
7. Kosi Project: It is situated on Kosi in North Bihar.
8. Mayurkashi Project: It is situated on Mayurkashi in West Bengal.
9. Kakrapara Project: It is situated on Tapti in Gujarat.
10. Nizamsagar Project: It is situated on Manjra in Telangana.
11. Nagarjuna Sagar Project: It is situated on Krishna in Telangana and AP.
12. Tungabhadra Project: It is situated on Tungabhadra in AP & Karnataka.
13. Shivasamudram Project:
- It is situated on Cauvery in Karnataka.
- It is the oldest river valley project in India.
14. Tata Hydel Scheme: It is situated on Bhima in Maharashtra.
15. Sharavathi Hydel Project: It is situated on Jog falls in Karnataka.
16. Kundah & Periyar Project: It is situated in Tamil Nadu.
17. Farakka Project:
- It is situated on Ganga in WB.
- Apart from power and irrigation, it helps to remove silt for easy navigation.
18. Ukai Project: It is situated on Tapti in Gujarat.
19. Mahi Project: It is situated on Mahi in Gujarat.
20. Salal Project: It is situated on Chenab in J&K.
21. Mata Tila Multipurpose Project: It is situated on Betwa in UP & MP.
22. Thein Project: It is situated on Ravi in Punjab.
23. Pong Dam: It is situated on Ravi in Punjab.
24. Tehri Project: It is situated on Bhagirathi in Uttarakhand.
25. Sardar Sarovar Project: It is situated on Narmada in Gujarat & MP.
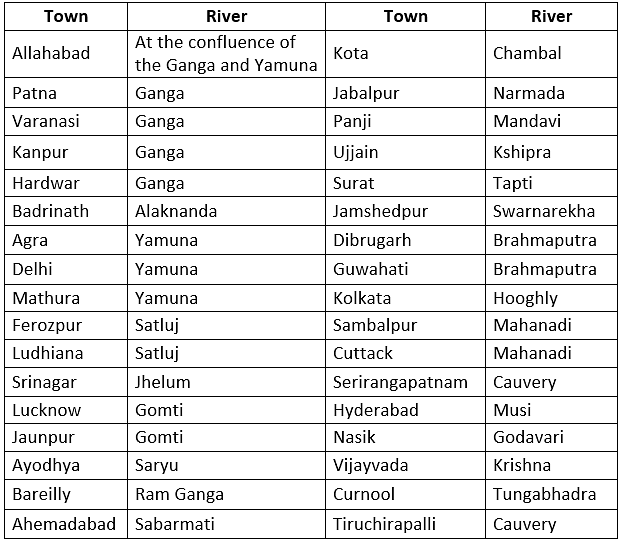
Important Indian Towns on Rivers
Largest, Longest, Highest in India
Longest
- River: Ganges
- Tributary river of India: Yamuna
- River of the South: Godavari
- Road: Grand Trunk Road
- State Coast Line: Gujarat
- Railway Route: From Jammu to Kanyakumari
- Tunnel: Pir Panjal tunnel (Jammu &Kashmir)
- National Highway: NH 44 as it covers the North-South Corridor of NHDP and it is officially listed as running over 4,112 km (2,555 mi) from Srinagar to Kanyakumari.
- Dam: Hirakud dam (Odisha)
- Bridge: Dr. Bhupen Hazarika Bridge(9.15 Km )
- River Bridge: Mahatma Gandhi Setu, Patna
- Rail Bridge: Vembanad Rail Bridge, Kerala
- Electric Railway Line: From Delhi to Kolkata via Patna
- Corridor: Rameswaram Temple corridor (Tamil Nadu)
- Railway Platform: Gorakhpur (Uttar Pradesh)
- Coastline in South India: Andhra Pradesh
- The river which forms estuary: Narmada
- Beach: Marina Beach (Chennai)
Largest
- Lake (Freshwater): Wular lake (Kashmir)
- Lake (Artificial): Dhebar lake (Udaipur, Rajasthan)
- Mosque: Jama Masjid, Delhi
- Populated city: Mumbai (12,478, 447)
- Museum: National Museum, Kolkata
- Delta: Sunderban Delta, W. Bengal
- Dome: Gol Gumbaz, Bijapur (Karnataka)
- Zoo: Zoological Garden, Alipur, Kolkata
- Desert: Thar (Rajasthan)
- Cave Temple: Kailash Temple, Ellora (Maharashtra)
- Biggest Hotel: Oberai-Sheraton (Mumbai)
- State (Area): Rajasthan
- State (Population): Uttar Pradesh
- Cantilever Span Bridge: Howrah Bridge (Kolkata)
- Forest State: M.P.
- Stadium: Salt Lake (Yuva Bharti), Kolkata
- Port: Mumbai
- Lake (Saline): Chilika Lake (Odisha)
- Gurudwara: Golden Temple, Amritsar
- Church: Saint Cathedral (Goa)
- River Island: Majuli (Brahmaputra river, Assam)
- Planetarium: Birla Planetarium (Kolkata)
- Cattle Fair: Sonepur Fair (Bihar)
Highest
- Mountain Peak: Godwin Austin (K²)
- Dam: Bhakra Dam (Punjab)
- Tower: Pitampura Tower, Delhi
- Waterfall: Kunchikal (Karnataka)
- Densely Populated State: Bihar
- Gateway: Buland Darwaza, Fatehpur Sikri (Agra)
- Straight Gravity Dam: Bhakra Dam
- Lake: Devatal (Garhwal)
- Award: Bharat Ratna
- Gallantry Award: Paramveer Chakra
- Battlefield: Silachi Glacier
- Airport: Leh (Laddakh)
- Statue: Statue of Unity (Gujarat)
Note:
- Smallest State(area): Goa
- Smallest State(Population): Sikkim
- Place of heaviest rainfall: Mausinram (Meghalaya)
- Deepest river valley: Bhagirathi & Alaknanda
- Bank, with maximum branches: State Bank of India
Difficult Words
- Latitudinally: In relation to latitude, the distance north or south from the equator.
- Longitudinally: In relation to longitude, the distance east or west from the prime meridian.
- Peninsula: A piece of land almost surrounded by water or projecting out into a body of water.
- Equator: An imaginary line around the Earth, equidistant from the North and South Poles, dividing the Earth into Northern and Southern Hemispheres.
- Frontier: A border between two countries.
- Plateaus: Elevated flat areas of land.
- Meridian: An imaginary line of longitude on the Earth's surface.
- Asiatic: Relating to Asia.
- Rhino: Short for Rhinoceros, a large herbivorous mammal with one or two horns on the nose.
- Chenab: A river in South Asia, one of the major rivers in the Indian subcontinent.
- Estuary: The tidal mouth of a large river, where the tide meets the stream.
- Cantilever: A long projecting beam or girder fixed at only one end, used in bridge construction.
- Gallantry: Heroic courage, bravery.
- Garhwal: A region and administrative division in the northern part of the Indian state of Uttarakhand.
- Paramveer Chakra: The highest wartime military decoration of India.
- Tropic of Cancer: The circle of latitude approximately 23.5° north of the equator, marking the northernmost position where the sun appears directly overhead at the solstice.
- Radcliffe Line: The boundary demarcation line between India and Pakistan drawn by Sir Cyril Radcliffe during the partition of India in 1947.
- McMahon Line: The boundary line between India and China, demarcated by Sir Henry McMahon in 1914.
- Durand Line: The border between Afghanistan and Pakistan, established by Sir Henry Mortimer Durand in 1896.
- Union Territories: Regions in India that are governed directly by the Central Government of India.
- Indira Point: The southernmost point of India, located on Great Nicobar Island.
- Barren Island: The only active volcano in India, situated in the east of Middle Andaman.
- Narcondam Island: A volcanic island in the northern-eastern part of North Andaman.
- Duncan Pass: A strait between South Andaman and Little Andaman.
- Gulf of Mannar: A large shallow bay forming part of the Laccadive Sea in the Indian Ocean.
- Palk Strait: A strait between Tamil Nadu (India) and Sri Lanka.
- Adam’s Bridge: A chain of limestone shoals between Tamil Nadu (India) and Sri Lanka.
- Pamban Island: An island that is part of Adam’s Bridge, where Rameshwaram is situated.
- Bhakra Nangal Project: A multipurpose river valley development project on the Satluj River in Punjab.
- Zoological Garden: A facility where animals are kept for public viewing, commonly known as a zoo.
- Silachi Glacier: A glacier located in a battlefield context mentioned in the text.
- Meridian: An imaginary circle of constant longitude passing through a given place on the earth's surface and the poles.
- Archipelago: A group or chain of islands.
- Tributary: A river or stream that flows into a larger river.
- Corridor: A strip of natural habitat that connects separated populations of a species.
- Saline: Containing or resembling common table salt; salty.
- Delta: A landform that forms at the mouth of a river, where the river flows into an ocean, sea, or lake.
- Densely: Closely compacted in substance.
- Estuary: The tidal mouth of a large river, where the tide meets the stream.
- Dome: A rounded vault forming the roof of a building or structure, typically with a circular base.
- Desert: A dry, barren area of land, often sandy, with little or no vegetation.
- Cantilever: A long projecting beam or girder fixed at only one end, used in bridge construction.
- Gallantry: Heroic courage or bravery, especially in battle.
- Heaviest: Of great weight; difficult to lift or move.
- Deepest: Extending a great distance downward; very deep.
- Buland Darwaza: A monumental gateway in Fatehpur Sikri, Uttar Pradesh, India.
- Statue of Unity: A statue of Indian political leader Vallabhbhai Patel, located in the Indian state of Gujarat.
- Bharat Ratna: The highest civilian award of the Republic of India, awarded for exceptional service towards the advancement of Art, Literature, and Science.
- Paramveer Chakra: The highest wartime military decoration in India for the display of conspicuous gallantry in the presence of the enemy.
|
541 videos|683 docs|263 tests
|
FAQs on Indian Geography I - IBPS PO Prelims & Mains Preparation - Bank Exams
| 1. What are the major rivers of India and their significance ? |  |
| 2. What is the administrative division of India and how is it structured ? |  |
| 3. What are the important national parks and wildlife sanctuaries in India ? |  |
| 4. What are the important crops grown in India and their economic impact ? |  |
| 5. What are some significant river valley projects in India and their benefits ? |  |
|
541 videos|683 docs|263 tests
|

|
Explore Courses for Bank Exams exam
|

|