Short Question Answers : Origin of Continents and Oceans | Geography Class 11 - Humanities/Arts PDF Download
Q. 1. Who and when proposed the continental drift-theory ?
Ans. Alfred Wegner in 1912.
Q. 2. Name the original super continent. When was it formed ?
Ans. Pangea, 280 million years ago. (Carboniferous period)
Q. 3. Name the Northern Continent split from Pangea.
Ans. Laurasia (Angara Land)
Q. 4. Name the Southern Continent split from Pangea.
Ans. Gondwana Land.
Q. 5. Name the landmasses included in the Gondwanaland.
Ans. South America, Africa, Australia and Antarctica.
Q. 6. Name the plant whose fossils are widely found.
Ans. Glossopteris.
Q. 7. Name the gold bearing areas of Africa and South America.
Ans. Ghana coast and Brazil.
Q. 8. What do you mean by Polar Wandering ?
Ans. Changing position of Poles in different periods.
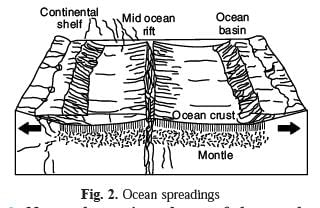
Q. 9. What do you mean by sea-floor spreading ?
Ans. The spreading of crust from oceanic ridges and widening of sea floor.
Q. 10. What is the cause of plate movement ?
Ans. Thermal convection moves the sub-crustal plates.
Q. 11. Who proposed that convection currents are the cause of plate movement ?
Ans. Arthur Holmes in 1928.
Q. 12. How many major plates are there on the earth’s crust ?
Ans. Seven.
Q. 13. Which is the largest tectonic plate ?
Ans. Pacific plate.
Q. 14. Name two volcanic tracts of hot spots in Indian Ocean.
Ans. 90° East ridge and Chagos-Lakshadweep ridge.
Q. 15. What was the cause of formation of Himalayas ?
Ans. The collision between Indian plate and Eurasian plate.
Q. 16. How much time has been taken to separate South America and South Africa.
Ans. 200 million years.
Q. 17. What do you mean by Tillite ? Where are these found ?
Ans. Tillite : Tillite are the sedimentary rocks formed out of deposits of glaciers. The Gondawana system of sediments from India is known to have its counter parts in six different landmasses of Southern Hemisphere such as Africa, Falkland Island, Madagascar, Antarctica and Australia. At the base the system has thick tillite indicating extensive and prolonged glaciation. The counter parts of this succession are found in Africa, Falkland Island, Madagascar, Antarctica and Australia. Overall resemblance of the Gondawana type sediments clearly demonstrate that these landmasses had remarkably similar histories. The glacial tillites provide unambiguous evidence of palaeoclimates and also of drifting of continents.
Q. 18. Where are Placer deposits found ?
Ans. Placer deposits. The occurrence of rich placer deposits of gold in Ghana coast and absolute absence of source rock in the region is an amazing fact. The gold bearing veins are in Brazil and it is obvious that the gold deposits of Ghana are derived from the Brazil plateau when the two continents lay side by side.
Q. 19. What do you mean by Lemuria ?
Ans. When identical species of plant and animal adapted to living on land or in fresh water are found on either sides of marine barriers a problem arises to account for such distribution. The observation that Lemurs occur in India, Madagascar and Africa, led some consider a contiguous landmass ‘Lemuria’ linking these three landmasses.
Q. 20. Describe the two main types of plates.
Ans. Plates are of two types (1) oceanic (2) continental. It can be named according to the fact that it is connected with oceans or continents. Pacific plate is an oceanic plate, while Eurasian plate is a continental plate. The lithosphere is divided into seven major plates. Young fold mountains, Trenches and faults mark their boundaries.
Q. 21. What do you mean by convergence of plates ?
Ans. When a plate pushes beneath the other plate, it is called converging plate. It is called a subduction zone. This is caused in three ways :
(i) Between a continental and oceanic plate.
(ii) Between two oceanic plates.
(iii) Between two continental plates.
Q. 22. What is Pangea ?
Ans. About 280 million years ago, all the land masses of the world formed one super continent called Pangea. It evolved in carboniferous period.
Q. 23. What is meant by sea floor spreading ?
Ans. The mid-oceanic ridges are cracks on the floor of ocean. There emits lava actively. Molten matter forms a new crust. The crust spreads away from the ridges. Thus the ocean basin widens. This is called sea floor spreading. In 1961, Atlas proposed a hypothesis known as sea floor spreading. According to this, volcanic erruption bring about huge amounts of lava to the surface though faults.
Q. 24. Name the major plates of the earth.
Ans. There are seven major plates :
(i) Pacific Plate
(ii) Eurasian Plate
(iii) Indo-Australian Plate
(iv) African Plate
(v) North American Plate
(vi) South American Plate
(vii) Antarctic Plate.
Q. 25. What is Pangea ? When was it evolved ? Name the landmasses constituting it. Describe the breaking up of Pangea.
Ans. Alfred Wegner, in 1912, proposed that all land masses of the world had formed from one supercontinent, called Pangea. The supercontinent, Pangea had evolved some 280 million years ago, at the end of the Carboniferous Period and by midJurassic, 150 million years ago, Pangea had split into a northern continent called Laurasia, and a southern continent called Gondwana land. About 65 million years ago, i.e. at the end of Cretaceous, Gondwana land further broke up to give rise to several other continents such as South America, Africa, Australia, and Antarctica. India broke apart and followed an independent route moving towards north-east.
Q. 26. What do you mean by Jig-Saw-fit ? Describe the similarities found on the east and west coasts of Atlantic Ocean. What do these suggest ?
Ans. Jig-Saw-fit means that the land masses on the East and West coast of Atlantic Ocean can be fitted together. Many similarities are found on the two coasts.
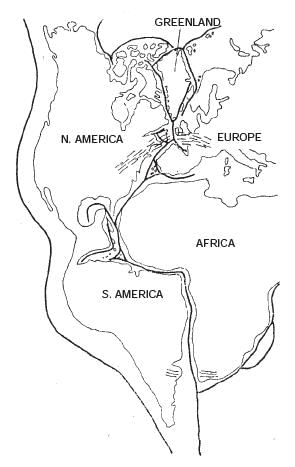
Fig. 3. Jig-saw-Fit.
(i) The Gulf of Guinea can be fitted into cape-SanRoque of Brazil. The shoulder of Africa can befitted into Gulf of Mexico. Western Europe and Eastern coast of N. America alongwith Greenland can be fitted together.
(ii) Gold deposits are found in Ghana on the East and in Brazil on the West.
(iii) The glacial deposits are found in all land masses of Gondwana land.
All these similarities suggest that these continents were together in the geological past.
Q. 27. What is meant by Polar Wandering ?
Ans. Polar Wandering. One of the strongest lines of evidence that the continents were formely united in the Pangea came from palaeomagnetism. There has been periodic change in the position of magnetic pole that is recorded in rocks by way of permanent magnetism. Unraveling the signatures of such changes in the geologically old rocks by scientific methods provides the changing position of poles in geological time scale. This is known as polar wandering. The polar wandering clearly demonstrates that the continents have frequently moved and changed directions of their motion from time to time.
|
70 videos|289 docs|44 tests
|
FAQs on Short Question Answers : Origin of Continents and Oceans - Geography Class 11 - Humanities/Arts
| 1. What is the theory of continental drift? |  |
| 2. How do scientists study the movement of continents? |  |
| 3. What evidence supports the theory of continental drift? |  |
| 4. How does the movement of continents affect the Earth's climate? |  |
| 5. Can continents collide or move closer together in the future? |  |





















