Long Question Answers : Origin of Continents and Oceans | Geography Class 11 - Humanities/Arts PDF Download
Q. 1. Explain the Plate Tectonic Theory and its mechanism.
Ans. According to global plate tectonic theory, the lithosphere is broken into a number of moderately rigid plates, The plates move continually and have relative direction of motion.
Types of Plate Boundaries. Based on the relative motion of plates, three kinds of plate boundaries or marginal zones are recognised—
(i) zones or margins of divergence or spreading,
(ii) zones or margins of convergence; and
(iii) fracture zones or transform faults.
(i) Zones of divergence. These are boundaries along which plates separate and in this process of separation molten material upwells. This is commonly observed along linear ocean ridges where new lithosphere is created in the form of new ocean floors.
Active volcanism and shallow focus earthquakes mark such boundaries.
(ii) Zones of convergence. These are boundaries along which the edge of one plate overrides the other. The overrridden plate slips down into the mantle and is absorbed. This process is known as subduction. Besides volcanism and shallow to deep focus earthquakes, these boundaries also produce deep trenches/basins and folded mountain chains.
(iii) Fracture Zones. There is neither creation not destruction along the transform fault. The lithospheric plates slide past each other.
Causes of Plate Movement (Mechanism)
1. Thermal Convection. Arthur Holmes, in 1928, proposed that subcrustal convection currents invoke the mechanism of thermal convection. It acts as driving force for the movement of plates.
2. Movement of currents. Hot currents rise, then cool as they reach the surface. At the same time, cooler currents sink down. This convectional movement moves the crustal plates.
3. Floating of Plates. Owing to current movements, the rigid plates of the lithosphere, which ‘float’ on more mobile asthenosphere, are in constant motion.
4. Hot spots of Volcanic activity. However, small centres of past volcanic activity are often located far from any active plate boundary suggest the effect of convection currents on the lithosphere. These centres of volcanic activity are called the hot spot.
5. Volcanoes. W. Jason Morgan proposed the hypothesis of hot spot in 1971. According to him, the source of magma in the mantle remains fixed in position while the lithospheric plate above it moves steadily. In this way, volcanoes are fomed over a hot spot but then move away from the magma source and become extinct. These extinct volcanoes form a chain that is record of the plate motion.
Plate Boundaries
Plate boundaries are the most significant structural features of the earth.
Plate boundaries are not difficult to identify ; they are marked by major topographic features.
The lithosphere—is divided into a mosaic of seven major plates and a number of smaller sub-plates. The major plates are outlined by young mountain systems, oceanic ridges and trenches. These include :
(i) Pacific Plate;
(ii) Eurasian Plate;
(iii) Indo-Australian Plate;
(iv) African Plate;
(v) North American Plate;
(vi) South American Plate;
(vii) Antarctic Plate.
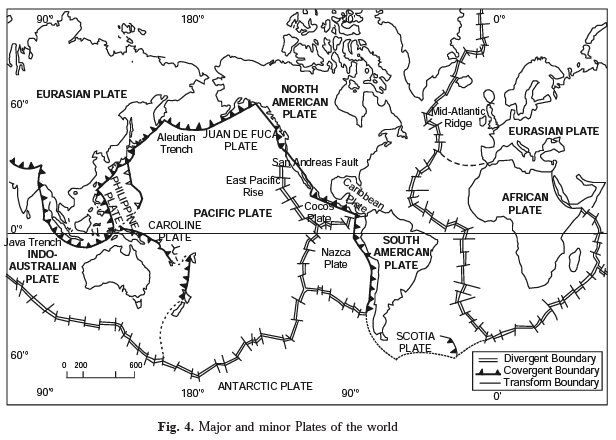
Main Features
1. The Pacific Plate which is composed of oceanic crust almost entirely and covers about 20 per cent of the earth’s surface.
2. No plate consists of only continental crust.
3. Plates range in thickness from about 70 km. beneath oceanic areas to 150 km. beneath continents.
4. Plates are not permanent features. They change in size and shape and the ones which do not contain continental crust can become victims of subduction.
5. A plate can split or weld with another adjoining plate.
6. Each tectonic plate is rigid and moves as a single unit.
7. Nearly all major tectonic activity occurs along the plate boundaries and that is why geologists and geographers focus their attention on the plate boundaries.
Q. 2. Describe the main characteristics of Indian Plate.
Ans. Movement of the Indian Plate.
Boundaries. The Indian plate includes Peninsular India and Australian continental portions. The northern plate boundary is marked by the subduction zone along Himalayas (continent-continent convergence) and it extends through Arakanyoma of Burma towards the island arc along Java Trench. The eastern margin is a spreading site lying to the east of Australia in the form of oceanic ridge in SW Pacific. The Western margin follows Kirtar Mountain of Pakistan and extending through Makrana coast coincides with the spreading site extending from Red seas rift southeastward along Chagos Archipelago. The boundary between India and Antarctic plate is also marked by oceanic ridge running in roughly W-E direction and merging into the spreading site little south of New Zealand.
Position of Indian Sub-continent. It is now a well established fact that indian subcontinent, or to be precise the Peninsular India, formed a part of Gondawana land, the southern protocontinent. This includes South America, Africa-India, Antarctica and Australia. The assembly of these continents as suggested by Smith and Hallam (1970) has received wider acceptance. India is the northern most member of this southern configuration and thus is supposed to have undergone maximum amount of northward drift.
The Tethys lying in the north of this assembly appears not as a major ocean but a narrow sea.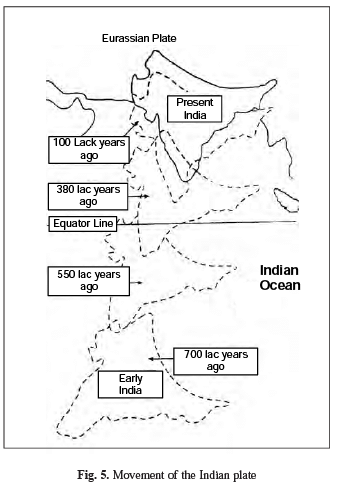
It is assumed that 20 crore years ago, when Pangea was sub-divided, Indian plate started drifting northward. About 4-5 crore years ago, Indian plate collided with Eurasian plate and Himalayas were uplifted out of the Tethys.
About 14 crore years ago, Indian subcontinent was located at 50° south latitudes. Tethys separated two plates. Tibetan block was nearer to Asian land mass. An import even took place during drifting of Indian plate. Deccan trap was formed out of lava. It started about 6 crore years ago and continued for a long time. About 4 crore years ago Himalayas were formed and the process is still going on. The Himalayas are still rising.
Q.3 What were the forces suggested by Wegner for the movement of continents ?
Ans. Force for Drifting. Wegner suggested that the movement-drifting of continents was caused by (1) pole fleeing force and (2) tidal force. Wegner believed that these forces would become effective when applied over many million years. However, most of the scholars considered these forces to be totally inadequate.
The shape of the earth is not a perfect sphere. It is bulging on equator. This is due to rotation of earth. Tidal force is related with sun and the Moon which cause Tides in oceans.
|
71 videos|245 docs|44 tests
|
FAQs on Long Question Answers : Origin of Continents and Oceans - Geography Class 11 - Humanities/Arts
| 1. What is the theory of continental drift? |  |
| 2. How do tectonic plates contribute to the formation of continents and oceans? |  |
| 3. What evidence supports the theory of continental drift? |  |
| 4. How does plate tectonics explain the formation of oceanic features like mid-ocean ridges and trenches? |  |
| 5. How does the movement of tectonic plates impact the Earth's surface? |  |


















