Past Year Questions: Working Stress & Limit State Method | Topic wise GATE Past Year Papers for Civil Engineering - Civil Engineering (CE) PDF Download
Q1: The structural design method that does not take into account the safety factors on the design load is [2024, Set-2]
(a) working stress method
(b) load factor method
(c) ultimate load method
(d) limit state method
Ans: (a)
Sol: In working stress method, safety is accounted for by considering factor of safety in material strength only and no factor is considered in load.
Q1: Consider the singly reinforced section of a cantilever concrete beam under bending, as shown in the figure (M25 grade concrete, Fe415 grade steel). The stress block parameters for the section at ultimate limit state, as per IS 456: 2000 notations, are given. The ultimate moment of resistance for the section by the Limit State Method is ____ kN.m (round off to one decimal place). [2023, Set-2]
[Note: Here, As is the total area of tension steel bars, b is the width of the section, d is the effective depth of the bars, fck is the characteristic compressive cube strength of concrete, fy is the yield stress of steel, and xu is the depth of neutral axis.]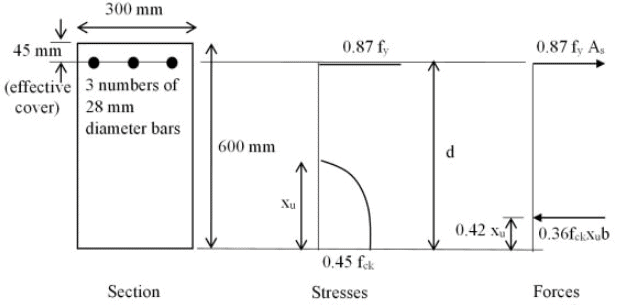 Ans: 295 to 305
Ans: 295 to 305
Sol: Given data,
Grade of concrete = M25
Grade of Steel = Fe415
Effective depth, d = 600 − 45 = 555mm
As, = 3 x π/4 x (28)2 = 1847.26 mm2
From Compression = Tension
Depth of neutral axis, xu = 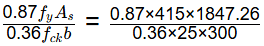 = 247.02 mm
= 247.02 mm
Limiting depth of neutral axis, xu,lim = 0.48 d = 0.48 x 555 = 266.40 mm
⇒ Section is under reinforced.
Ultimate moment of resistance
= 0.36 fck bxu (d - 0.42xu)
= 0.36 × 25 × 300 × 247.02 × (555 − 0.42 × 247.02) × 10−6
= 301.0 (after rounding off to one decimal place).
Q2: Two plates are connected by fillet welds of size 10 mm and subjected to tension, as shown in the figure. The thickness of each plate is 12 mm. The yield stress and the ultimate stress of steel under tension are 250MPa and 410MPa, respectively. The welding is done in the workshop (partial safety factor, γmw = 1.25). As per the Limit State Method of IS 800: 2007, what is the minimum length (in mm, rounded off to the nearest higher multiple of 5 mm ) required of each weld to transmit a factored force P equal to 275kN? [2023, Set-2]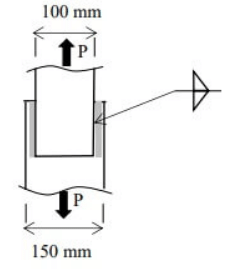
(a) 100
(b) 105
(c) 110
(d) 115
Ans: (b)
Sol: Size of weld =10 mm
Thickness of each plate =12 mm
fy = 250MPa, fu = 410MPa
γmw = 1.25
P = 275KN (Factored)
Let us assume minimum length required of each weld = l
⇒ 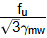 x 2l x 0.7 x size of weld = 275 x 103
x 2l x 0.7 x size of weld = 275 x 103
⇒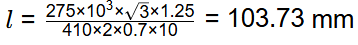
The answer has to be round off to be nearest higher multiple of 5 and hence it shall be taken as 105 mm. Hence, correct option is (B).
Q3: Creep of concrete under compression is defined as the [2023, Set-1]
(a) increase in the magnitude of strain under constant stress
(b) increase in the magnitude of stress under constant strain
(c) decrease in the magnitude of strain under constant stress
(d) decrease in the magnitude of stress under constant strain
Ans: (a)
Sol: Under sustained compressive loading, deformation in concrete increases with time even through the applied stress level is not changed. The time dependent component of strain is called creep.
Hence, correct answer is (A).
Q1: In the context of elastic theory of reinforced concrete, the modular ratio is defined as the ratio of [2022, Set-1]
(a) Young's modulus of elasticity of reinforcement material to Young?s modulus of elasticity of concrete.
(b) Youngs modulus of elasticity of concrete to Young?s modulus of elasticity of reinforcement material.
(c) shear modulus of reinforcement material to the shear modulus of concrete.
(d) Young's modulus of elasticity of reinforcement material to the shear modulus of concrete.
Ans: (a)
Sol: This is a question of working stress method i.e. elastic theory.
Modular ratio
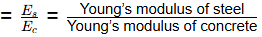
Q1: The maximum applied load on a cylindrical concrete specimen of diameter 150 mm and length 300 mm tested as per the split tensile strength test guidelines of IS 5816 : 1999 is 157kN. The split tensile strength (in MPa, round off to one decimal place) of the specimen is [2020, Set-2]
Ans: 2 to 2.4
Sol:
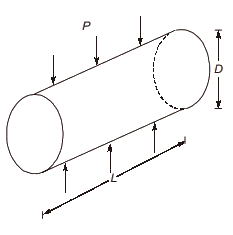 P = 157kN
P = 157kN
D = 150 mm
L = 300 mm
In split tensile strength test, split tensile strength of concrete
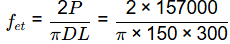
= 2.22 N/mm2
Q2: As per IS 456:2000, the pH value of water for concrete mix shall NOT be less than [2020, Set-2]
(a) 4.5
(b) 5
(c) 5.5
(d) 6
Ans: (d)
Sol: 1. Minimum pH value of water for concrete = 6.0
As per IS code provision no. 5.4.2, the pH value of water shall not less than 6.0.
Q3: During the process of hydration of cement, due to increase in Dicalcium Silicate (C2S ) content in cement clinker, the heat of hydration [2020, Set-1]
(a) increases
(b) decreases
(c) initially decreases and then increases
(d) does not change
Ans: (b)
Sol: Due to increase in C2S heat of hydration decreases.
Q1: When aspecimen of M25 concrete is loaded to a stress level of 12.5 MPa, a strain of 500 x 10-6 is recorded. If this load is allowed to stand for a long time, the strain increases to 1000 x 10-6. In accordance with the provisions of IS:456-2000, considering the long-term effects, the effective modulus of elasticity of the concrete (in MPa) is_______ . [2019, Set-2]
Ans: 12500
Sol: Effective modulus of elastic
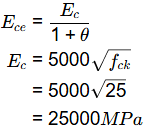
Creep coefcient
Q2: In the context of provisions relating to durability of concrete, consider the following assertions:
Assertion (1): As per IS 456-2000, air entrainment to the extent of 3% to 6% is required for concrete exposed to marine environment.
Assertion (2): The equivalent alkali content (in terms of Na2O equivalent) for a cement containing 1% and 0.6% of Na2O and K2O, respectively, is approximately 1.4% (rounded to 1 decimal place).
Which one of the following statements is CORRECT? [2019, Set-2]
(a) Assertion (1) is FALSE and Assertion (2) is TRUE
(b) Assertion (1) is TRUE and Assertion (2) is FALSE
(c) Both Assertion (1) and Assertion (2) are FALSE
(d) Both Assertion (1) and Assertion (2) are TRUE
Ans: (a)
Sol: (1) As per clause 8.2.2.3 of IS 456-2000, entrained air percentage of 3 to 6% is required to resist freezing and thawing, i.e. not for marine environment.
Hence, Assertion (1) is wrong
Equivalent alkali content is terms of Na2O
= [Na2O] + 0.685[K2O]
= 1 + 0.685 × 0.6 = 1.41%
Hence, Assertion (2) is correct
Q3: The characteristic compressive strength of concrete required in a project is 25MPa and the standard deviation in the observed compressive strength expected at site is 4MPa. The average compressive strength of cubes tested at different water-cement (w/c) ratios using the same material as is used for the project is given in the table.
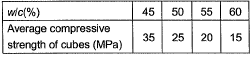 The water-cement ratio (in percent, round off to the lower integer) to be used in the mix is______. [2019, Set-2]
The water-cement ratio (in percent, round off to the lower integer) to be used in the mix is______. [2019, Set-2]
Ans: 46
Sol: Target mean strength
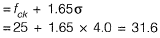
Water content required
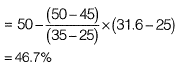
Say 46%(round off to the lower integer)
Q4: In the reinforced beam section shown in the figure (not drawn to scale), the nominal cover provided at the bottom of the beam as per IS 456-2000, is [2019, Set-1]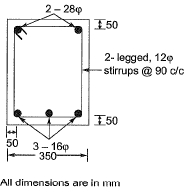
(a) 30 mm
(b) 50 mm
(c) 42 mm
(d) 36 mm
Ans. (a)
Sol:
Nominal cover = Effective cover 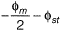
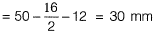
Q1: As per IS 456 : 2000, the minimum percentage of tension reinforcement (up to two decimal places) required in reinforced-concrete beams of rectangular cross-section (considering effective depth in the calculation of area) using Fe500 grade steel is _______ [2018, Set-2]
Ans: 0.17
Sol: From clause 26.5.1.1 of IS 456 : 2000, we know minimum reinforcement is given by
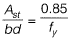
∴ Min. % of steel 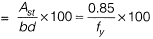
For Fe500, min. % of steel
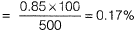
Q2: The frequency distribution of the compressive strength of 20 concrete cube specimen is given in the table. If μ is the mean strength of the specimens and o is the standard deviation, the number of specimens (out of 20) with compressive strength less than μ - 3σ is _______ . [2018, Set-1]
If μ is the mean strength of the specimens and o is the standard deviation, the number of specimens (out of 20) with compressive strength less than μ - 3σ is _______ . [2018, Set-1]
Sol: Average strength,
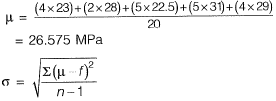
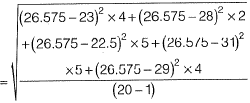
= 3.7
Now, μ - 3σ = 26.575 - 3 x 3.7 = 15.48
Thus, no specimen is having compressive strength less than μ - 3σ.
No. of specimen = 0.
Q3: The deformation in concrete due to sustained loading is [2018, Set-1]
(a) creep
(b) hydration
(c) segregation
(d) shrinkage
Ans. (a)
Sol: Creep is inelastic deformation with time due to sustained loading.
Q1: Let the characteristic strength be defined as that value, below which not more than 50% of the results are expected to fail. Assuming a standard deviation of 4 MPa, the target mean strength (in MPa) to be considered in the mix design of a M25 concrete would be [2017 , Set-2]
(a) 18.42
(b) 21.00
(c) 25.00
(d) 31.58
Ans. (c)
Sol:
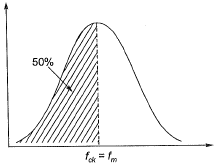
If fck is the value below which not more than 50% of test results are expected then,
fm = fck
[Mean strength = Characteristics strength]
So target mean strength of concrete to be considered in design mix.
= Mean strength
fm = fck = 25 MPa
Q.8 According to IS 456-2000, which one of the following statements about the depth of neutral axis xμbal for a balanced reinforced concrete section is correct? [2017, Set-1]
(a) xμbal depends on the grade of concrete only
(b) xμbal depends on the grade of steel only
(c) xμbal depends on both the grade of concrete and grade of steel
(d) xμbal does not depend on the grade of concrete and grade of steel
Ans: (b)
Sol:
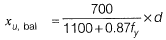
So it depends upon grade of steel only.
Q1: For M25 concrete with creep coefficient of 1.5, the long-term static modulus of elasticity (expressed in MPa) as per the provisions of IS:456-2000 IS: _______ [2016 : 2 Marks, Set-I]
Sol:
Long term static modulus of elasticity,
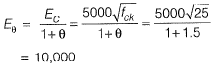
Q1: According to the concept of Limit State Design as per IS 456 : 2000, the probability of failure of a structure is _________. [2015 : 2 Marks, Set-II]
Sol:
The structure may fail when,
(i) the load exceeds the design load
(ii) the strength is less than the characteristic strength
(iii) both the load exceeds the design load and strength is less than the characteristic strength. The probability of load exceeding design load = 5%
(iv) The probability of strength less than characteristic strength = 5%.
The probability of failure is
= 0.05 x 0.95 + 0.05 x 0.95 + 0.05 x 0.05
= 0.0975
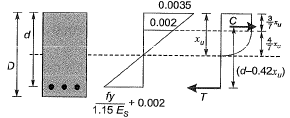
Q2: Consider the singly reinforced beam section given below (left figure). The stress block parameters for the cross-section from IS 456 : 2000 are also given below (right figure). The moment of resistance for the given section by the limit state method is________kN-m. [2015 : 2 Marks, Set-I]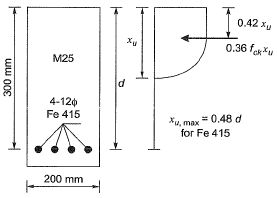
Solution:
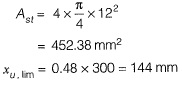
∴ C = T
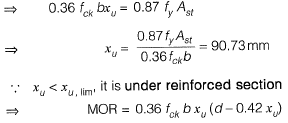
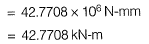
Q3: Consider ihe following statements for air-entrained concrete:
(i) Air-entrainment reduces the water demand for a given level of workability.
(ii) Use of air-entrained concrete is required in environments where cyclic freezing and thawing is expected.
Which of the following is TRUE? [2015 : 1 Mark, Set-I]
(a) Both (i) and (ii) are True
(b) Both (i) and (ii) are False
(c) (i) is True and (ii) is False
(d) (i) is False and (ii) is True
Ans. (A)
Solution:
(i) An air-entraining agent introduces air in the form of bubbles that occupy upto 5% of the volume of concrete distributed uniformly throughout the cement paste. Thus, for the same amount of water/cement ratio, we get higher workability.
(ii) Since water takes up the air voids in the concrete and its freezing and melting causes cracks in concrete, hence using air entraiment agents improves the freezing and throwing resistance.
Q4: Consider the singly reinforced beam shown in the figure below: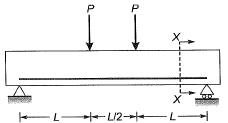
At cross-section XX, which of the following statements is TRUE at the limit state? [2015 : 1 Mark, Set-I]
(a) The variation of stress is linear and that of strain is non-linear
(b) The variation of strain is linear and that of stress is non-linear
(c) The variation of both stress and strain is linear
(d) The variation of both stress and strain is nonlinear
Ans. (C)
Solution:
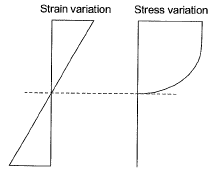
Q5: Workability of concrete can be measured using slump, compaction factor and Vee-bee time. Consider the following statements for workability of concrete
(i) As the slump increases, the Vee-bee time increases.
(ii) As the slump increases, the compaction factor increases.
Which of the following is TRUE? [2015 : 1 Mark, Set-I]
(a) Both (i) and (ii) are True
(b) Both (i) and (ii) are False
(c) (i) is True and (ii) is False
(d) (i) is False and (ii) is True
Ans. (D)
Solution:
As slump increase, water content increases means workability increases.
Compaction factor

∴ Compaction factor will also increase
The time required for complete remoulding in seconds is considered as a measure of workability and is expressed as the number of Vee-Beeseconds
∴ As workability increases, Vee-Bee time decreases.
Q.15 In a reinforced concrete section, the stress at the extreme fibre In compression is 5,80 MPa. The depth of neutral axis in the section is 58 mm and the grade of concrete is M25. Assuming linear elastic behavior of the concrete, the effective curvature of the section (in per mm) is [2014 : 2 Marks, Set-I]
(a) 2.0 x 10-6
(b) 3.0 x 10-6
(c) 4.0 x 10-6
(d) 5.0 x 10-6
Ans. (C)
Solution:
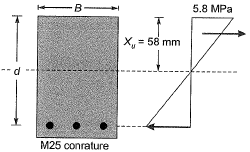
Modulus of elasticity of concrete,
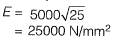
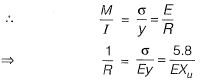
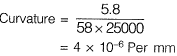
⇒ Curvature = 4 x 10-6 per mm
Q.16 The flexural tensile strength of M25 grade of concrete, in N/mm2, as per IS 456 : 2000 is ____. [2014 : 1 Mark, Set-II]
Solution:
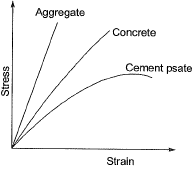
Flexural strength = 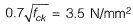
Q.17 Group-I contains representative stress-strain curves as shown in the figure, while Group-I I gives the list of materials. Match the stress-strain curves with the corresponding materials. [2014 : 1 Mark, Set-II]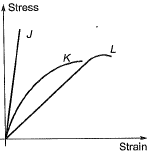
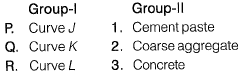
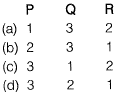
Ans. (B)
Solution:
The learner or less stiller the material, lesser is the slope of stress-strain curve, which is a measure of modulus of elasticity. Hence the diagram is self explanatory.
Q.18 While designing, for a steel column of Fe250 grade, a base plate resting on a concrete pedestal of M20 grade, the bearing strength of concrete (in N/mm2) in limit state method of design as per IS 456 : 2000 i s _______ . [2014 : 1 Mark, Set-I]
Solution:
Permissible bearing stress = 0.45 fck
= 0.45 x 20 = 9 N/mm2
Q.19 Maximum possible value of compaction factor for fresh (green) concrete is [2013 : 1 Mark]
(a) 0.5
(b) 1.0
(c) 1.5
(d) 2.0
Ans. (B)
Solution:
Compaction factor

Hence, its maximum value for fresh concrete can be 1.
Q.20 As per IS 456: 2000, in the Limit State Design of a flexural member, the strain in reinforcing bars under tension at ultimate state should not be less than [2012 : 1 Mark]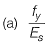
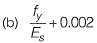
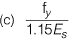
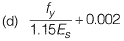
Ans. (D)
Solution:
Q.21 The cross-section of a thermo-mechanically treated (TMT) reinforcing bar has [2011 : 1 Mark]
(a) soft ferrite-pearlite throughout.
(b) hard martensite throughout.
(c) a soft ferrite-pearlite core with a hard martensitic rim.
(d) a hard martensitic core with a soft pearlite- bainitic rim.
Ans. (C)
Solution:
TMT or thermo mechanicaly treated bars are high strength reinforcement bars having a tough outer core and a soft inner core.
They provide strength is well as enough ductility to the structure.
Q.22 Match List-I (List of test methods for evaluating properties of concrete) with List-ll (List of properties) and select the correct answer using the codes given below the lists: [2010 : 2 Marks]
List-I
A. Resonant frequency test
B. Rebound hammer test
C. Split cylinder test
D. Compacting factor test
List-ll
1. Tensile strength
2. Dynamic modulus of elasticity
3. Workability
4. Compressive strength
Ans. (A)
Solution:
A. Resonant frequency test is used to determine dynamic modulus of elasticity whereas destructive test like cube test etc measures the static modulus of elasticity.
B. Rebound hammer test is a non-destructive test used for compressive strength of concrete.
C. Split cylinder test is used to determine the direct tensile strength of concrete.
D. Compaction factor test is used to measure workability of concrete.
FAQs on Past Year Questions: Working Stress & Limit State Method - Topic wise GATE Past Year Papers for Civil Engineering - Civil Engineering (CE)
| 1. What is the difference between the Working Stress Method and the Limit State Method in structural design? |  |
| 2. How do you determine the factor of safety in the Working Stress Method? |  |
| 3. What are the main advantages of using the Limit State Method over the Working Stress Method? |  |
| 4. What factors are considered in the Limit State Method when designing a structure? |  |
| 5. Can the Working Stress Method still be used in contemporary engineering practices? |  |
















