NCERT Exemplar: Diversity in Living Organisms | Biology for Class 9 PDF Download
Multiple Choice Questions
Q.1. Find out incorrect sentence
(a) Protista includes unicellular eukaryotic organisms
(b) Whittaker considered cell structure, mode and source of nutrition for classifying the organisms in five kingdoms
(c) Both Monera and Protista may be autotrophic and heterotrophic
(d) Monerans have a well-defined nucleus
Ans: (d)
Explanation: Monerans include single-celled prokaryotes, actinomycetes and photosynthetic blue-green algae. Monerans don’t have a well-defined nucleus and cell organelles.
Q.2. Which among the following has specialised tissue for conduction of water?
(i) Thallophyta
(ii) Bryophyta
(iii) Pteridophyta
(iv) Gymnosperms
(a) (i) and (ii)
(b) (ii) and (iii)
(c) (iii) and (iv)
(d) (i) and (iv)
Ans: (c)
Explanation: Thallophytes and Bryophytes don’t have specialized tissues for water conduction whereas Pteridophytes and Gymnosperms have specialized tissues for conduction of water.
Q.3. Which among the following produce seeds?
(a) Thallophyta
(b) Bryophyta
(c) Pteridophyta
(d) Gymnosperms
Ans: (d)
Explanation: Gymnosperms are the flowerless plants that produce seeds. But the seeds are not covered within an ovary and are hence called “naked seeds”.
Q.4. Which one is a true fish?
(a) Jellyfish
(b) Starfish
(c) Dogfish
(d) Silverfish
Ans: (c)
Explanation: Jellyfish is a coelenterate, starfish belongs to Echinodermata and silverfish is an Arthropod.
Q.5. Which among the following is exclusively marine?
(a) Porifera
(b) Echinodermata
(c) Mollusca
(d) Pisces
Ans: (b)
Explanation: Echinodermata are exclusively found in the marine environment whereas Porifera, Molluscs and Pisces can be found in both marine and freshwater.
Q.6. Which among the following have an open circulatory system?
(i) Arthropoda
(ii) Mollusca
(iii) Annelida
(iv) Coelenterata
(a) (i) and (ii)
(b) (iii) and (iv)
(c) (i) and (iii)
(d) (ii) and (iv)
Ans: (a)
Explanation: Annelida and Coelenterata have closed circulatory system whereas Arthropods and Mollusca have an open circulatory system.
Q.7. In which group of animals, coelom is filled with blood?
(a) Arthropoda
(b) Annelida
(c) Nematoda
(d) Echinodermata
Ans: (a)
Explanation: Annelida, Nematoda and Echinodermata don’t have blood and Arthropods coelom is filled with blood.
Q.8. Elephantiasis is caused by
(a) Wuchereria
(b) Pinworm
(c) Planarians
(d) Liver flukes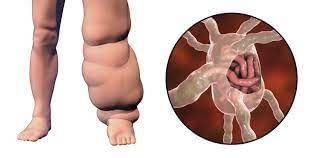 Ans: (a)
Ans: (a)
Explanation: Wuchereria is a human parasite which causes Elephantiasis. Elephantiasis is spread through mosquitos.
Pinworm is a common intestinal parasite and causes enterobiasis
Planarians are non-parasitic flatworms
Liver flukes are flatworms that cause liver rot in Humans.
Q.9. Which one is the most striking or (common) character of the vertebrates?
(a) Presence of notochord
(b) Presence of triploblastic condition
(c) Presence of gill pouches
(d) Presence of coelom
Ans: (a)
Explanation: Presence of triploblastic condition, presence of gill pouches, presence of coelom is found in both vertebrates and invertebrates but Notochord is exclusively present invertebrates.
Q.10. Which among the following have scales?
(i) Amphibians
(ii) Pisces
(iii) Reptiles
(iv) Mammals
(a) (i) and (iii)
(b) (iii) and (iv)
(c) (ii) and (iii)
(d) (i) and (ii)
Ans: (c)
Explanation: Amphibians and mammals don’t have scales on their body whereas Pisces and reptiles have scales on their body.
Q.11. Find out the false statement
(a) Aves are warm-blooded, egg laying and have a four-chambered heart
(b) Aves have feather-covered body, forelimbs are modified into wings and breathe through lungs
(c) Most of the mammals are viviparous
(d) Fishes, amphibians and reptiles are oviparous
Ans: (d)
Explanation: Some fishes are viviparous but Amphibians show external fertilization they can neither be kept under oviparous nor be viviparous hence statement (d) is wrong.
Q.12. Pteridophyta do not have
(a) root
(b) stem
(c) flowers
(d) leaves
Ans: (c)
Q.13. Identify a member of porifera
(a) Spongilla
(b) Euglena
(c) Penicillium
(d) Hydra
Ans: (a)
Explanation: Euglena is a protozoan.
Penicillium is a fungus
Hydra is a Coelenterata
Q.14. Which is not an aquatic animal?
(a) Hydra
(b) Jellyfish
(c) Corals
(d) Filaria
Ans: (d)
Explanation: Filaria is a disease caused by Wuchereria. It is spread by Mosquitos.
Q.15. Amphibians do not have the following
(a) Three chambered heart
(b) Gills or lungs
(c) Scales
(d) Mucus glands
Ans: (c)
Explanation: Amphibians have 3 chambered heart. Lungs are present in Adults and Gills are present in tadpoles. Mucous glands are present on the skin of Amphibians.
Q.16. Organisms without nucleus and cell organelles belong to
(i) fungi
(ii) protista
(iii) cyanobacteria
(iv) archaebacteria
(a) (i) and (ii)
(b) (iii) and (iv)
(c) (i) and (iv)
(d) (ii) and (iii)
Ans: (b)
Explanation: Cyanobacteria and archaebacteria are prokaryotes and they do not have a well-defined nucleus and cell organelles.
Fungi and Protista are Eukaryote which posses Cell organelles and nucleus.
Q.17. Which of the following is not a criterion for the classification of living organisms?
(a) Body design of the organism
(b) Ability to produce one’s own food
(c) Membrane-bound nucleus and cell organelles
(d) Height of the plant
Ans: (d)
Explanation: Height of a plant is an attribute which is related to bushes and trees which are part of Kingdom Plantae hence the height of the trees cannot be a criterion for classification of living organisms.
Q.18. The feature that is not a characteristic of protochordata?
(a) Presence of notochord
(b) Bilateral symmetry and coelom
(c) Jointed legs
(d) Presence of circulatory system
Ans: (c)
Explanation: Protochordata are triploblastic with the bilaterally symmetric body and coelom. They show notochord at some stage of life and they are marine living.
Q.19. The locomotory organs of Echinodermata are
(a) Tube feet
(b) Muscular feet
(c) Jointed legs
(d) Parapodia
Ans: (a)
Explanation: Tube feet in Echinodermata help in locomotion and respiration
Q.20. Corals are
(a) Poriferans attached to some solid support
(b) Cnidarians, that are solitary living
(c) Poriferans present at the sea bed
(d) Cnidarians that live in colonies
Ans: (d)
Q.21. Who introduced the system of scientific nomenclature of organisms
(a) Robert Whittaker
(b) Carolus Linnaeus
(c) Robert Hooke
(d) Ernst Haeckel
Ans: (b)
Explanation: Carolus Linnaeus introduced binomial nomenclature which is a simplified method of naming organisms. Binomial nomenclature gives each organism a scientific name that has two parts. The first part is a Genus and the second part is Species.
Q.22. Two-chambered heart occurs in
(a) Crocodiles
(b) Fish
(c) Aves
(d) Amphibians
Ans: (b)
Explanation: Amphibians have 3 chambered heart. Aves and crocodile have 4 chambered heart.
Q.23. Skeleton is made entirely of cartilage in
(a) Sharks
(b) Tuna
(c) Rohu
(d) None of these
Ans: (a)
Explanation: Sharks are cartilaginous fish whereas Tuna and Rohu are bony fishes.
Q.24. One of the following is not an Annelid
(a) Nereis
(b) Earthworm
(c) Leech
(d) Urchins
Ans: (d)
Explanation: Urchins are Coelenterates
Q.25. The book Systema Naturae was written by
(a) Linnaeus
(b) Haeckel
(c) Whittaker
(d) Robert Brown
Ans: (a)
Q.26. Karl Von Linne was involved with which branch of science?
(a) Morphology
(b) Taxonomy
(c) Physiology
(d) Medicine
Ans: (b)
Q.27. Real organs are absent in
(a) Mollusca
(b) Coelenterata
(c) Arthropoda
(d) Echinodermata
Ans: (b)
Explanation: Coelenterates have tissue level organization hence they lack real organs.
Q.28. Hard calcium carbonate structures are used as skeleton by
(a) Echinodermata
(b) Protochordata
(c) Arthropoda
(d) Nematoda
Ans: (a)
Explanation: Echinodermata are spiny skinned organisms which are exclusively free-living marine animals. They are triploblastic and have a coelomic cavity. They use a unique water-driven tube from moving and they contain calcium carbonate structures which are used as a skeleton.
Q.29. Differentiation in segmental fashion occurs in
(a) Leech
(b) Starfish
(c) Snails
(d) Ascaris
Ans: (a)
Explanation: Leech belongs to Annelids and it shows metameric body segmentation.
Q.30. In taxonomic hierarchy family comes between
(a) Class and Order
(b) Order and Genus
(c) Genus and Species
(d) Division and Class
Ans: (b)
Explanation: Taxonomic hierarchy
Species
Genus
Family
Order
Class
Phylum
Kingdom
Q.31. 5-Kingdom classification is given by
(a) Morgan
(b) R. Whittaker
(c) Linnaeus
(d) Haeckel
Ans: (b)
Explanation: R. Whittaker proposed 5 kingdom classification which includes Monera, Protista, Fungi, Plantae and Animalia.
Q.32. Well-defined nucleus is absent in
(a) Blue green algae
(b) Diatoms
(c) Algae
(d) Yeast
Ans: (a)
Explanation: Blue-green algae belong to prokaryotes which do not have a well-defined nucleus and cell organelles.
Q.33. The ‘Origin of Species’ is written by
(a) Linnaeus
(b) Darwin
(c) Hackel
(d) Whittaker
Ans: (b)
Q.34. Meena and Hari observed an animal in their garden. Hari called it an insect while Meena said it was an earthworm. Choose the character from the following which confirms that it is an insect.
(a) Bilateral symmetrical body
(b) Body with jointed legs
(c) Cylindrical body
(d) Body with little segmentation
Ans: (b)
Explanation: Body with jointed legs is a characteristic feature of Kingdom Arthropoda and all the insects belong to this kingdom.
Short Answer Questions
Q.35. Write true (T) or false (F)
(a) Whittaker proposed five kingdom classification.
(b) Monera is divided into Archaebacteria and Eubacteria.
(c) Starting from Class, Species comes before the Genus.
(d) Anabaena belongs to the kingdom Monera.
(e) Blue-green algae belong to the kingdom Protista.
(f) All prokaryotes are classified under Monera.
Solution:
a-True
b- True
c- False
d-True
e-False
f- True
Explanation:
c) Taxonomic hierarchy
Species
Genus
Family
Order
Class
Phylum
Kingdom
e) Blue-green algae belonged to Kingdom Monera
Q.36. Fill in the blanks
(a) Fungi show———mode of nutrition.
(b) Cell wall of fungi is made up of ———.
(c) Association between blue-green algae and fungi is called as———.
(d) Chemical nature of chitin is ———.
(e) ———has smallest number of organisms with maximum number of similar characters
(f) Plants without well-differentiated stem, root and leaf are kept in ———.
(g) ———are called as amphibians of the plant kingdom
Solution:
- Fungi shows Saprophytic mode of nutrition.
- Cell wall of fungi is made up of Chitin.
- Association between blue green algae and fungi is called as Lichens.
- Chemical nature of chitin is Carbohydrate.
- Species has the smallest number of organisms with a maximum number of similar characters.
- Plants without well-differentiated stem, root and leaf are kept in Thallophyta.
- Bryophytes are called amphibians of the plant kingdom.
Q.37. You are provided with the seeds of gram, wheat, rice, pumpkin, maize and pea. Classify them whether they are monocot or dicot.
Solution: Gram-Dicot
Wheat-Monocot
Rice- Monocot
Pumpkin- Dicot
Maize- Monocot
Pea—Dicot
Q.38. Match items of column (A) with items of column (B)
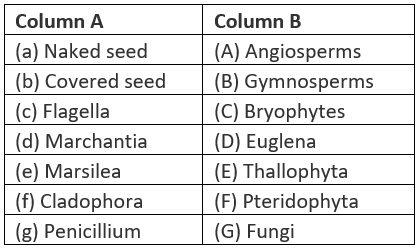
Solution: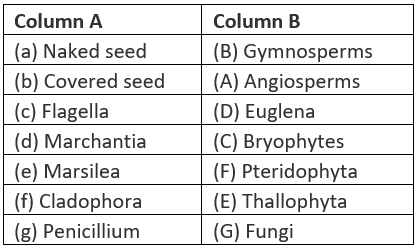
Q.39. Match items of column (A) with items of column (B)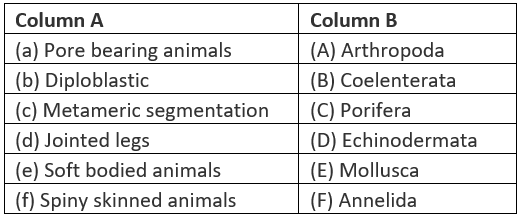
Solution: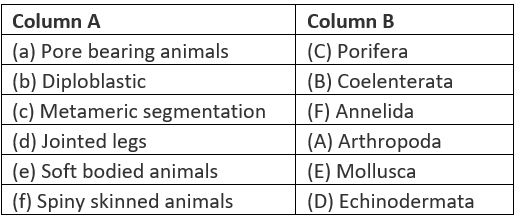
Q.40. Classify the following organisms based on the absence/presence of true coelom (i.e., acoelomate, pseudocoelomate and coelomate)
Spongilla, Sea anemone, Planaria, Liver fluke
Wuchereria, Ascaris, Nereis, Earthworm,
Scorpion, Birds, Fishes, Horse
Solution: Spongilla- acoelomate
Sea anemone- acoelomate
Planaria- acoelomate
Liver fluke- acoelomate
Wuchereria-pseudocoelomate
Ascaris-pseudocoelomate
Nereis- coelomate
Earthworm- coelomate
Scorpion- coelomate
Birds- coelomate
Fishes- coelomate
Horse- coelomate
Q.41. Endoskeleton of fishes are made up of cartilage and bone; classify the following fishes as cartilaginous or bony
Torpedo, Sting ray, Dogfish,
Rohu, Angler fish, Exocoetus
Solution: Torpedo- cartilaginous
Stingray- cartilaginous
Dogfish- cartilaginous
Rohu- bony
Angler fish- bony
Exocoetus- bony
Q.42. Classify the following based on number of chambers in their heart. Rohu, Scoliodon, Frog, Salamander, Flying lizard, King Cobra, Crocodile, Ostrich, Pigeon, Bat, Whale.
Solution: Rohu- 2 chambered
Scoliodon-2 chambered
Frog-3 chambered
Salamander-3 chambered
Flying lizard-3 chambered
King Cobra-3 chambered
Crocodile-4 chambered
Ostrich-4chambered
Bat-4chambered
Whale-4 chambered
Q.43. Classify Rohu, Scolidon, Flying lizard, King Cobra, Frog, Salamander, Ostrich, Pigeon, Bat, Crocodile and Whale into the cold-blooded/warm-blooded animals.
Solution: Rohu- Cold Blooded
Scolidon- Cold Blooded
Flying lizard- Cold Blooded
King Cobra- Cold Blooded
Frog- Cold Blooded
Salamander- Cold Blooded
Ostrich- Warm Blooded
Pigeon- Warm Blooded
Bat- Warm Blooded
Crocodile- Cold Blooded
Whale- Warm Blooded
Q.44. Name two egg-laying mammals.
Solution: Billed platypus and the echidna are two egg-laying mammals
Q.45. Fill in the blanks
(a) Five kingdom classification of living organisms is given by ———.
(b) Basic smallest unit of classification is ———.
(c) Prokaryotes are grouped in Kingdom ———.
(d) Paramecium is a protista because of its ———.
(e) Fungi do not contain ———.
(f) A fungus ——— can be seen without microscope.
(g) Common fungi used in preparing the bread is ———.
(h) Algae and fungi form symbiotic association called ———.
Solution:
(a) Five kingdom classification of living organisms is given by Robert Whittaker.
(b) Basic smallest unit of classification is Species.
(c) Prokaryotes are grouped in Kingdom Monera.
(d) Paramecium is a protista because of its Eukaryotic unicellular morphology.
(e) Fungi do not contain Chlorophyll.
(f) A fungus Mushroom can be seen without microscope.
(g) Common fungi used in preparing the bread is Yeast.
(h) Algae and fungi form symbiotic association called Lichens.
Q.46. Give True (T) and False (F)
(a) Gymnosperms differ from Angiosperms in having covered seed.
(b) Non-flowering plants are called Cryptogamae.
(c) Bryophytes have conducting tissue.
(d) Funaria is a moss.
(e) Compound leaves are found in many ferns.
(f) Seeds contain an embryo.
Solution:
- False
- True
- True
- True
- True
Q.47. Give examples for the following
(a) Bilateral, dorsiventral symmetry is found in———.
(b) Worms causing disease elephantiasis is———.
(c) Open circulatory system is found in———where coelomic cavity is filled with blood.
(d) ———are known to have pseudocoelom.
Solution:
(a) Bilateral, dorsiventral symmetry is found in Liver Fluke.
(b) Worms causing disease elephantiasis is Filarial worm.
(c) Open circulatory system is found in Arthropods where coelomic cavity is filled with blood.
(d) Nematodes are known to have pseudocoelom.
Q.48. Label a, b, c and d. given in Fig. 7.1 Give the function of (b)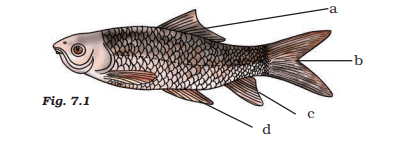
Solution:
- Dorsal fin
- Caudal fin
- Pelvic fin
- Pectoral fin
Q.49. Fill in the boxes given in Fig. 7.2 with appropriate characteristics/plant group (s)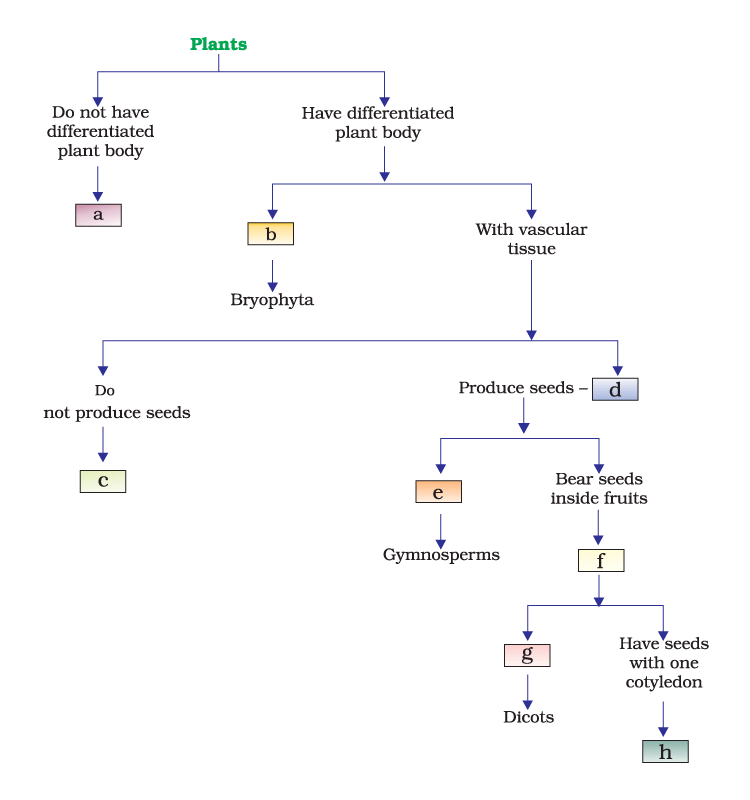
Solution:
- Thallophyta
- Vascular tissue without specialization
- Pteridophyta
- Phanerogams
- Bare naked seeds
- Angiosperms
- Seeds with two cotyledons
- Monocots
Long Answer Questions
Q.50. Write names of few thallophytes. Draw a labelled diagram of Spirogyra.
Solution: Ulothrix, Spirogyra, Cladophara, Ulva and Chara are few of the examples for Thallophytes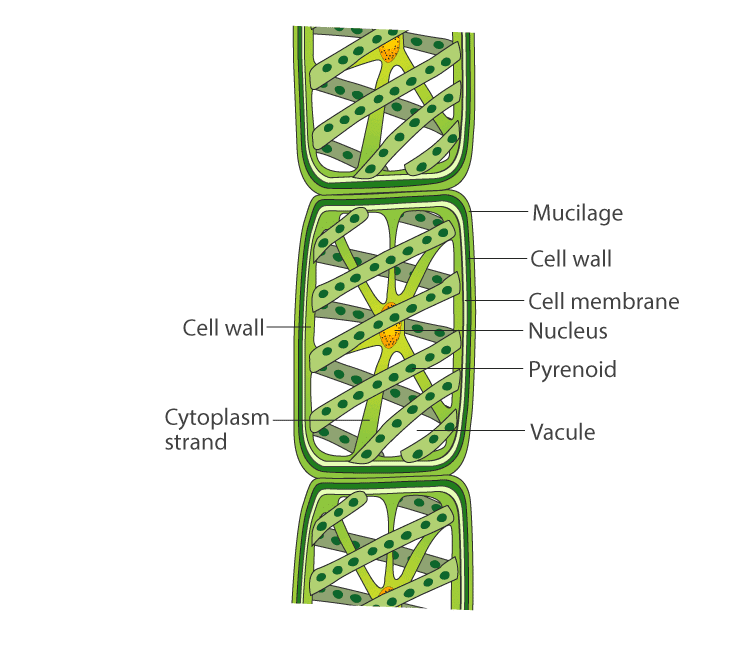
Q.51. Thallophyta, bryophyta and pteridophyta are called as ‘Cryptogams’. Gymnosperms and Angiosperms are called as ‘phanerogams’. Discuss why? Draw one example of Gymnosperm.
Solution: Thallophyta, bryophyta and pteridophyta are called as ‘Cryptogams’ because the reproductive organs of plants in all these three groups are very inconspicuous, and they are therefore called ‘cryptogams’, or ‘those with hidden reproductive organs’. In these plants seeds are absent.
Example : Pinus
Gymnosperms and Angiosperms are called as ‘phanerogams’ because these are the plants with well-differentiated reproductive parts that ultimately make seeds.
Example: Cycas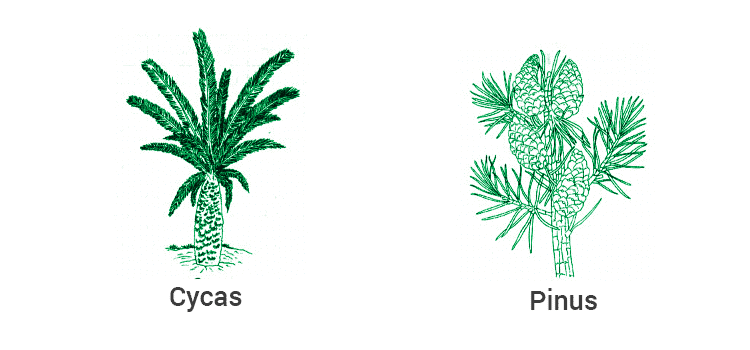
Q.52. Define the terms and give one example of each
(a) Bilateral symmetry
(b) Coelom
(c) Triploblastic
Solution:
- An organism with body shapes that are mirror images along a middle line. The internal organs, however, are not necessarily distributed symmetrically. Example: Liver fluke
- The coelom is a body cavity filled with fluid. Fluid runs the complete length of vertebrates to divide the body of an organism into the inner tube and outer tube is called Coelom Example: Butterfly
- Animals that have 3 embryonic cell layers from which differentiated tissues are made are called triploblastic organisms. Ex: Star Fish
Q.53. You are given leech, Nereis, Scolopendra, prawn and scorpion; and all have segmented body organisation. Will you classify them in one group? If no, give the important characters based on which you will separate these organisms into different groups.
Solution: The organisms given in the question does not belong to a common group of organisms. Leech and Nereis are annelids but Scolopendra, prawn and scorpion are arthropods Annelids have a metamerically segmented body. Metamerically segmented body is divided into many segments internally by septa. From head to tail body segments are lined up one after the other. Arthropods have jointed legs and open circulating system.
Q.54. Which organism is more complex and evolved among Bacteria, Mushroom and Mango tree. Give reasons.
Solution: Among Bacteria, Mushroom and Mango tree; Mango tree is the complex and evolved organism Because it is Eukaryotic, multicellular, autotrophic terrestrial plant. It is an angiosperm and its seeds are covered within the ovary. Its reproductive organs and accumulated in the flower hence it is called as a flowering plant. Bacteria are prokaryotic unicellular organisms and fungi are heterotrophic thallophytes with no body differentiation. Hence mango tree is evolved more than bacteria and fungi.
Q.55. Differentiate between flying lizard and bird. Draw the diagram.
Solution: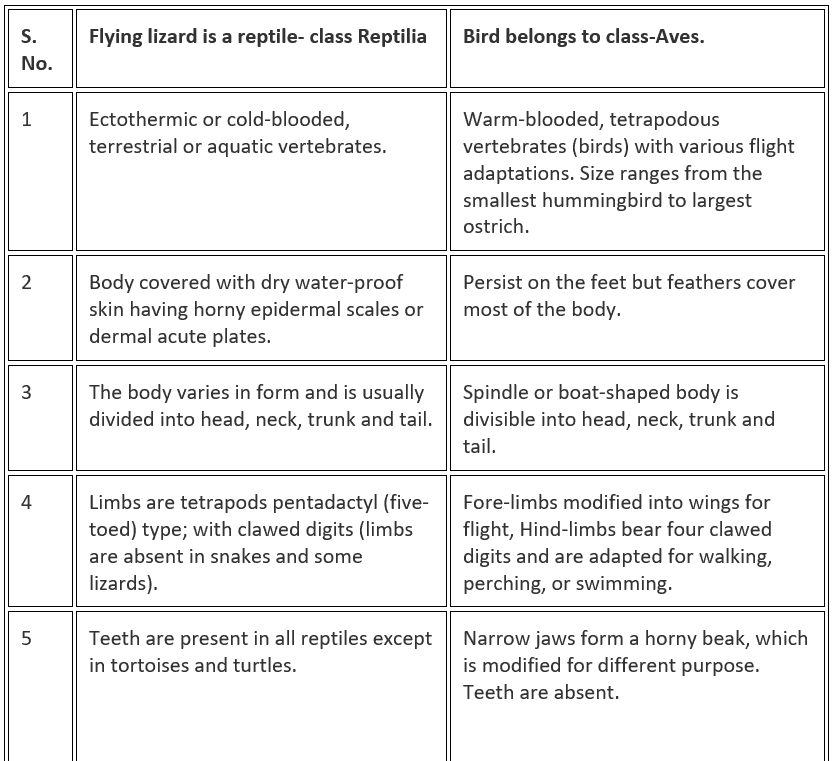
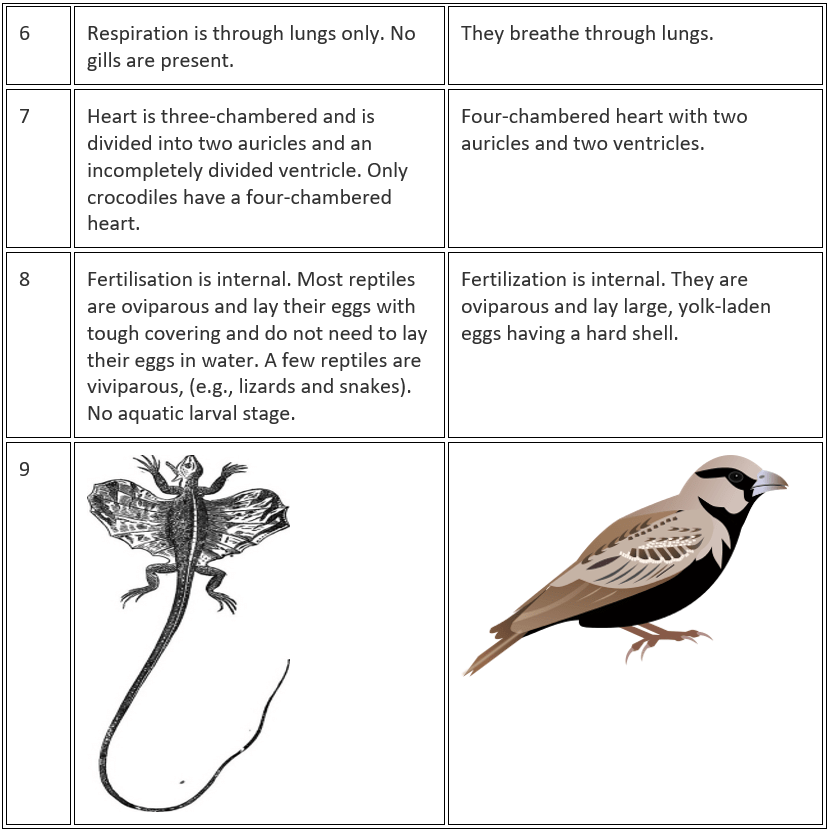
Q.56. List out some common features in cat, rat and bat.
Solution:
- All are Eukaryotes
- They are multicellular
- They are heterotrophic in nature
- All Have Notochord
- Presence of four-chambered heart
- Have a dorsal nerve cord
- All are triploblastic
- Have paired gill pouches
- They are coelomate.
Q.57. Why do we keep both snake and turtle in the same class?
Solution: Because both have a certain common feature which is listed below.
- These animals are cold-blooded
- They have scales and breathe through lungs
- Both of them have a three-chambered heart
- Both of them lay eggs with tough coverings and do not need to lay their eggs in water
|
23 videos|69 docs|55 tests
|
FAQs on NCERT Exemplar: Diversity in Living Organisms - Biology for Class 9
| 1. What is the importance of studying diversity in living organisms? |  |
| 2. How does the concept of diversity apply to living organisms? |  |
| 3. What are the different levels of classification used to study diversity in living organisms? |  |
| 4. How does understanding diversity in living organisms contribute to conservation efforts? |  |
| 5. What are the challenges in studying diversity in living organisms? |  |

|
Explore Courses for Class 9 exam
|

|

















