Class 9 Science Chapter 9 Previous Year Questions - Gravitation
Short Answer Type Questions
Q.1. (a) Name the balances used to measure mass and weight.(b) Weight of an object will be lessor or more at Antarctica as compared to the weight of object at Delhi. Give reason for your answer.
Ans. (a) Mass is measured by beam balance. Weight is measured by spring balance.
 Spring Balance
Spring Balance Beam Balance
Beam Balance
(b) Earth is flattened at poles. So distance of the body from its centre is less. As 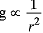 hence value of ‘g’ in Antarctica will be more as compared to that in Delhi. Consequently, its weight will be more in Antarctica than in Delhi.
hence value of ‘g’ in Antarctica will be more as compared to that in Delhi. Consequently, its weight will be more in Antarctica than in Delhi.
Q.2. Mona weighs 750 N on Earth.
(i) On the planet Mars, the force of gravity is 38% of that of Earth. How will Mona weigh on Mars?
(ii) What will be Mona’s mass on Earth (g = 10 m/s2)?
Ans. Value of g on Mars, gm = 0.38 times value of g on Earth = 0.38 x 9.8
∴ Weight on Mars = 0.38 x Weight on Earth
= 0.38 x 750 = 285 N
Mass of Earth = 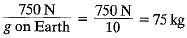
Q.3. The gravitational force between two objects is 100N. How should the distance between these objects be changed so that the force between them becomes 50 N?
Ans. F = 100 N. When distance between objects in R.
If F becomes (F/2), then let distance becomes R'.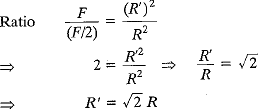
i.e. distance is increased √2 times.
Q.4. The weight of a body on the surface of the earth is 392 N. What will be the weight of this body on a planet whose mass is double that of the earth and radius is four times that of the earth?
Ans. 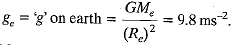
where Me = Mass of earth,
Re = Radius of earth
Mass of planet = 2Me; Radius of planet = 4Re
∴ 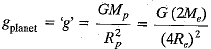
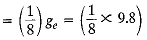
Weight on plane 
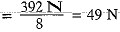
Q.5. “Several phenomena of celestial bodies were believed to be unconnected but universal law of gravitation was successful to explain them”. Mention any two phenomena.
Ans. Two phenomena explained by universal law of gravitation are:
(a) motion of planets around the sun in their orbits.
(b) presence of an atmosphere around the earth.
Q.6. (a) Suggest two ways to decrease pressure on a surface.
(b) The density of an object is 1.8 g/cm3. Express it in kg/m3.
Ans. (a) Two suggested ways so as to decrease pressure on a surface are:
(i) decrease the force acting on the surface, and
(ii) increase the surface area of given surface.
(b) The density of an object in CGS system is d = 1.8 g/cm3
∵ 1 g/cm3 = 103 kg/m3, hence density in SI system will be
d = 1.8 x 103 kg/m3
Q.7. A steel needle sinks in water kut a steel ship floats. Explain, how.
Ans. A steel needle sinks in water because density of steel is more than the density of water. The ship is made up of steel. But interior of ship is made hollow by giving it a special shape. When immersed in water, the ship displaces large volume of water and its effective density becomes less than density of water. As a result, the weight of displaced water i.e., the upward thrust due to water becomes more than the weight of the ship. So, the ship floats and may even carry a lot of cargo.
Q.8. The ratio of gravitational force on Neptune to the gravitational force on earth is 9:8. Ramesh weighs 792 N on earth. Calculate his weight on Neptune.
Ans. We know that the gravitational force acting on a given object due to a planet is called the weight of that object on the planet.
In present question weight of Ramesh on earth 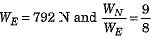
⇒ Weight of Ramesh on Neptune, 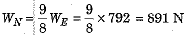
Q.9. The value of ‘g’ on earth’s surface is 9.8 m s-2. Suppose the earth suddenly shrinks to one-third of its present size without losing any mass. What is the value of on the surface of shrinked earth?
Ans. If radius of earth be R and mass of earth be M, then
If suddenly earth shrinks to one-third of its present size without any change in mass then 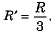 Hence new value of g will be
Hence new value of g will be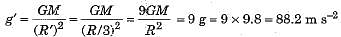
Q.10. A man feels himself lighter on moon than on earth. Why?
Ans. Since the value of acceleration due to gravity at the surface of moon is only 1/6th of its value on the earth, so the weight of a person on moon is only 1/6th of its value on earth. As a result, a man feels lighter on moon.
Q.11. The gravitational force between two small spheres is F. What will happen if masses of the two spheres, as well as distance between them, is doubled?
Ans. Force will remain unchanged.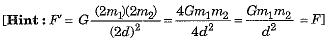
Q.12. Mass is scalar but weight is a vector. Why?
Ans. Mass of an object is a measure of its inertia and hence it is a scalar. On the other hand, weight of an object is the gravitational force due to gravity acting on it and is, therefore, a vector quantity.
Q.13. Why is G called an universal constant?
Ans. Because value of G is independent of the two objects or the distance between them or intervening medium between them.
Q.14. Which force is responsible for stability of our universe?
Ans. The force of gravitation.
Q.15. A ball projected vertically upwards with an initial velocity u goes to a maximum height h. What is its velocity at the highest point?
Ans. Zero.
Q.16. When an object is dropped from a height, it accelerates while falling. Name the force which accelerates the object.
Ans. The force of gravity causes an acceleration in the falling object.
Q.17. What is force of buoyancy?
Ans. Force acting vertically upward due to a fluid on a solid immersed completely or partly in that fluid.
Q.18. Name the SI unit of pressure.
Ans. A pascal (1 Pa), where 1 Pa = 1 N m-2.
Q.19. How is pressure related to thrust?
Ans. 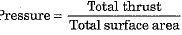
Q.20. An object of mass 2 kg is taken to the surface of moon. What will be its mass there and why?
Ans. The mass of the object will remain 2 kg because mass of an object cannot change.
Q.21. A ball is thrown vertically upwards and reaches a maximum height in 3 s. Find (i) the velocity with which it was thrown upwards, (ii) the maximum height attained by the ball. Take g = 10 m s-2.
Ans. Here final velocity of ball at highest point v = 0, time of ascent of ball t = 3 s and a = - g = - 10 m s-2
(i) As per relation v = u + at, we have
0 = u + ( - 10) x 3 ⇒ u = + 30 m s-1
(ii) As per relation v2 - u2 = 2as, we have
(0)2 - (30)2 = 2 x ( - 10) x h ⇒ h = 45 m
Q.22. A particle is released from rest from a height.
(a) Find the distance it falls through in 1 second?
(b) Find the distance it falls through in 3 seconds. Also, find the speed with which it strikes the ground after 3 seconds.
Ans. Here initial velocity of particle u = 0 and acceleration a = g = 9.8 m s-2.
(a) Distance h1 through which the particle falls in time t1 = 1 s is: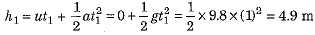
(b) Distance h through which particle falls in time t = 3 s will be: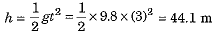
and speed with which it reaches the ground after time t = 3 s, will be:
v = u + gt = gt = 9.8 x 3 = 29.4 m s-1.
Q.23. If the distance between two masses be increased by a factor of 6, by what factor would the mass of one of them hence to be altered to maintain the same gravitational force?
Ans. By law of gravitation, of F ∝ mass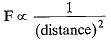
If the distance is increased by a factor of 6, F decreases by 1/36 times.
Thus, mass should be increased by (6)2 times i.e. 36 times.
Thus mass also has to be increased.
Q.24. What happens to the magnitude of the force of gravitation between two objects if
(i) distance between the objects is tripled?
(ii) mass of both objects is doubled?
(iii) mass of both objects as well as distance between them is doubled?
Ans. (i) If distance is tripled, i.e. R → 3R
By Newtons law, 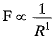
Thus F becomes (1/3)2 = one-ninth of its original value
(ii) Masses are doubled i.e. 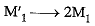
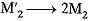
By Newton’s law, F ∝ M1M2
Thus F becomes (2) x (2) = 4 times its original value.
(iii) Masses 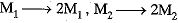
Distance 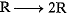
By Newton’s law, 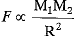
Or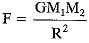
On changing masses and distance,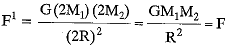
Thus force remains unchanged.
Long Answer Type Questions
Q.1. (a) A body floats in kerosene of density 0.8 x 103 kg/m3 up to a certain mark. If the same body is placed in water of density 1.0 x 103 kg/m3, will it sink more or less? Give reason for your answer.(b) If a fresh egg is put into a beaker filled with water, it sinks. On dissolving a lot of salt in the water the egg begins to rise and then floats. Why?
Ans. (a) The body will sink less in water. When a body of weight W floats on a liquid of density p with a volume V immersed in the liquid, the upthrust must balance the weight and hence

⇒
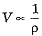
As density of water (pw = 1.0 x 103 kg/m3) is greater than density of kerosene (ph = 0.8 x 103 kg/m3), hence volume of body immersed in water will be less than that in kerosene.
(b) A fresh egg put into a beaker filled with water sinks because density of egg is more than the density of water.
When a lot of salt is dissolved in the water, the density of salt solution becomes more than the density of egg. As a result, now the egg starts floating in highly saltish water.
Q.2. (i) State two factors on which the gravitational force between two objects depends.
(ii) Why is ‘G’ called a universal constant?
(iii) What happens to the gravitational force between two objects if masses of both the objects are doubled and the distance between them is also doubled?
(iv) What is the value of ‘G' on moon?
(v) What is the value of 'g' on moon?
Ans. (i) The gravitational force between two objects is (a) directly proportional to the product of their mases, and (b) inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them.
(ii) G is called a universal constant because its value never changes under any condition.
(iii) The force remains unchanged.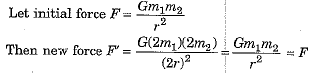
(iv) Value of G on moon is same as bn earth having a value 6.673 x 10-11 N m2 kg-2.
(v) Value of g on moon is 1/6 that of its value on the earth.
|
88 videos|369 docs|67 tests
|
FAQs on Class 9 Science Chapter 9 Previous Year Questions - Gravitation
| 1. What is the law of universal gravitation and who formulated it? |  |
| 2. How does gravity affect the motion of planets? |  |
| 3. What is the difference between mass and weight? |  |
| 4. What are the effects of gravity on objects in free fall? |  |
| 5. How does gravity influence tides on Earth? |  |

|
Explore Courses for Class 9 exam
|

|


















