Class 10 Maths Chapter 4 Previous Year Questions - Quadratic Equations
Previous Year Questions 2025
Q1: if 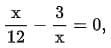 then the values of x are:
then the values of x are:
(a) ± 6
(b) ± 4
(c) ± 12
(d) ± 3
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a)
We have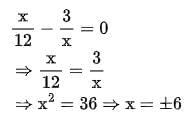
Q2: Case Study: A garden designer is planning a rectangular lawn that is to be surrounded by a uniform walkway. 
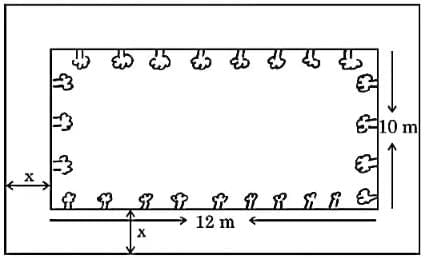 The total area of the lawn and the walkway is 360 square metres. The width of the walkway is same on all sides. The dimensions of the lawn itself are 12 metres by 10 metres. Based on the information given above, answer the following questions:
The total area of the lawn and the walkway is 360 square metres. The width of the walkway is same on all sides. The dimensions of the lawn itself are 12 metres by 10 metres. Based on the information given above, answer the following questions:
(i) Formulate the quadratic equation representing the total area of the lawn and the walkway, taking width of walkway= x m.
(ii) (a) Solve the quadratic equation to find the width of the walkway 'x'.
OR
(ii) (b) If the cost of paving the walkway at the rate of ₹ 50 per square metre is ₹ 12,000, calculate the area of the walkway.
(iii) Find the perimeter of the lawn.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans:
(i) Length of rectangular lawn, l = (12 + 2x) m
Breadth of rectangular lawn, b = (10 + 2x) m
∴ Area of rectangular lawn = 360 m2 (given)
⇒ (12 + 2x)(10 + 2x) = 360
⇒ 120 + 24x + 20x + 4x2 = 360
⇒ 4x2 + 44x - 240 = 0
x2 + 11x - 60 = 0
(ii) (a) Quadratic equation is x2 + 11x - 60 =
⇒ x2 + 15x - 4x - 60 = 0
⇒ x(x + 15) - 4(x + 15) = 0
⇒ (x + 15)(x - 4) = 0
⇒ x = -15 or 4
⇒ x = 4 ( x can't be negative)
∵ Width of the walkway= 4 m.
OR
(ii) (b)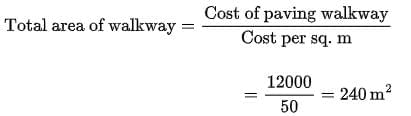
(iii) Length of lawn , l= 12 m, Breadth of lawn, b = 10 m
∴ Perimeter of lawn= 2(l + b)
= 2(12 + 10)
= 2 x 22 = 44 m
Q3: A student scored a total of 32 marks in class tests in Mathematics and Science. Had he scored 2 marks less in Science and 4 marks more in Mathematics, the product of his marks would have been 253. Find his marks in the two subjects.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans:
Let the marks scored by a student in Mathematics be x and Science be y.
According to question,
x + y = 32 ⇒ y = 32 - x ...(i)
Also, (x + 4)(y - 2) = 253
⇒ xy - 2x + 4y - 8 = 253
⇒ xy - 2x + 4y = 261
⇒ x(32 - x) - 2x + 4(32 - x) = 261 [from(i)]
⇒ 32x - x2 - 2x + 128 - 4x = 261
⇒ 26x -x2 + 128 = 261
⇒ x2 - 26x + 133 = 0
⇒ x2 - 19x - 7x + 133 = 0
⇒ x(x - 19) - 7(x - 19) = 0
⇒ (x - 19)(x - 7) = 0 ⇒ x = 7, 19
From (i) when get y = 25, 13
if x = 7, then y = 25 and if x = 19, then y = 13.
∴ Marks in mathematics and science are 7 and 25 or 19 and 13 respectively.
Q4: There is a circular park of diameter 65 mas shown in the following figure, where AB is a diameter. 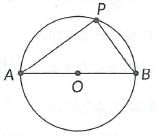 An entry gate is to be constructed at a point P on the boundary of the park such that distance of P from A is 35 m more than the distance of P from B. Find distance of point P from A and B respectively.
An entry gate is to be constructed at a point P on the boundary of the park such that distance of P from A is 35 m more than the distance of P from B. Find distance of point P from A and B respectively.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Let the distance of 'P' from 'B' be x m.
∴ PA = (x + 35)m
In ΔAPB, ∠P = 90°
∴ AB2 = AP2 + PB2 [Using Pythagoras theorem]
(65)2 = (x + 35)2 + x2
⇒ x2 + x2 + 1225 + 70x = 4225
⇒ 2x2 + 70x - 3000 = 0
⇒ x2 + 35x - 1500 = 0
⇒ x2 + 60x - 25x - 1500 = 0
⇒ (x + 60)(x - 25) = 0
⇒ x + 60 = 0 or x - 25 = 0
⇒ x = -60, 25 [∵ Distance can't be negative]
x = 25
∴ PA = 25 + 35 = 60 m and PB = 25 m.
Q5: The discriminant of the quadratic equation bx2 + ax + c = 0, b ≠ 0 is given by:
(a) b2 - 4ac
(b) 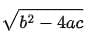
(c) 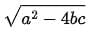
(d) a2 - 4bc
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (d)
We have, bx2 + ax + c = 0
On comparing with Ax2 + Bx + C = 0, we get
A = b, B = a and C = c
∴ D = B2 - 4AC = a2 - 4bc [∵ Discriminant = B2 - 4AC]
Q6: Which of the following quadratic equations has real and equal roots?
(a) (x + 1)2 = 2x + 1
(b) x2 +x= 0
(c) x2 - 4 = 0
(d) x2+ x + 1= 0
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a)
(x + 1)2 = 2x + 1
x2 + 2x + 1 = 2x+1
x2 + 2x + 1 - 2x - 1 = 0
x2 = 0 ⇒ x = 0, 0
Hence, the given equation has real and equal roots.
Q7: Find the value(s) of 'k' so that the quadratic equation 4x2 + kx + 1 = 0 has real and equal roots.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Given quadratic equation 4x2 + kx + 1 = 0 has real and equal roots.
Comparing with ax² + bx + c = 0, we have
a = 4, b = k, c = 1
∴ D = b2 - 4ac = k2 - 4(4)(1) = 0
⇒ k2 - 16 = 0 ⇒ k² = 16 ⇒ k = ±4
Q8: Find the smallest value of p for which the quadratic equation x2 - 2(p + 1)x + p2 = 0 has real roots. Hence, find the roots of the equation so obtained.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Given, x2 - 2(p + 1)x + p2 = 0 has real roots.
Compare it with ax2 + bx + c = 0, we get
a = 1, b = -2(p + 1), c = p2
∴ For real roots, we have D ≥ 0
(-2(p + 1))2 - 4 × 1 × p² ≥ 0
⇒ 4(p2 + 1 + 2p) - 4p2 ≥ 0 ⇒ 4p2 + 4 + 8p - 4p2 ≥ 0
⇒ 8p + 4 ≥ 0 => p ≥ -1/2
∴ Smallest value of p is -1/2.
Put value of 'p' in given equation,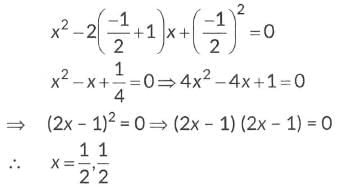
So, 1/2, 1/2 are the roots.
Previous Year Questions 2024
Q1: In a flight of 2800 km, an aircraft was slowed down due to bad weather. Its average speed is reduced by 100km/h, and by doing so, the time of flight is increased by 30 minutes. Find the original duration of the flight. (CBSE 2024) View Answer
View Answer 
Ans:
Let the speed of aircraft be x km/hr.
Time taken to cover 2800 km by speed of x km/hr = 2800/x hrs.
New speed is (x – 100) km/hr
so time taken to cover 2800 km at the speed of (x - 100) km/hr = 2800x - 100 hrs
ATQ,
2800x - 100 - 2800x = 12
⇒ 2800 (x - x + 100)x (x - 100) = 12
⇒ 100x² - 100x = 12 × 2800
⇒ 560000 = x2 – 100x
⇒ x2 – 100x – 560000 = 0
⇒ x2 – 800x + 700x – 560000 = 0
⇒ x(x – 800) + 700(x – 800) = 0
⇒ (x – 800) (x + 700) = 0
⇒ x = 800, – 700 (Neglect)
⇒ x = 800
Speed = 800 km/hr
Time = 2800/800
= 3 hr 30 min.
Q2: The denominator of a fraction is one more than twice the numerator. If the sum of the fraction and its reciprocal is 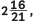 found, the fraction. (CBSE 2024)
found, the fraction. (CBSE 2024)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans:
Let the numerator of the required fraction be x.
Then, its denominator = (2x + 1).
The fraction = x / (2x + 1) and its reciprocal = (2x + 1) / x.
We are given that:
(x / (2x + 1)) + ((2x + 1) / x) = 58 / 21
Multiplying both sides by 21x(2x + 1):
21x [x² + (2x + 1)²] = 58x(2x + 1)
21x [x² + (2x + 1)²] = 58x(2x + 1)
Simplifying this:
21x [5x² + 4x + 1] = 116x² + 58x
Expanding both sides:
11x² - 26x - 21 = 0
This is a quadratic equation.
Solving the quadratic equation:
11x² - 33x + 7x - 21 = 0
11x(x - 3) + 7(x - 3) = 0
(x - 3) (11x + 7) = 0
So, x = 3 or x = -7/11.
Since the numerator cannot be negative, x = 3.
Thus, the required fraction is x / (2x + 1) = 3 / 7.
Q3: If the roots of quadratic equation 4x² - 5x + k = 0 are real and equal, then the value of k is (CBSE 2024)
(a) 5/4
(b) 25/16
(c) 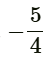
(d) 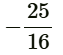
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (b) 25/16
Given that,
Roots of quadratic equation 4x2 − 5x + k = 0 are real and equal
On comparing with ax2 + bx + c = 0,
We get, a = 4, b = −5 and c = k
For real and equal roots,
⇒ b2 − 4ac = 0
⇒ (−5)2 − 4(4)(k) = 0
⇒ 16k = 25
⇒ k = 25/16
Q4: A rectangular floor area can be completely tiled with 200 square tiles. If the side length of each tile is increased by 1 unit, it would take only 128 tiles to cover the floor. (CBSE 2024)
(i) Assuming the original length of each side of a tile is x units, make a quadratic equation from the above information.
(ii) Write the corresponding quadratic equation in standard form.
(iii) (a) Find the value of x, the length of the side of a tile by factorisation.
OR
(b) Solve the quadratic equation for x using the quadratic formula.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (i) Let the original side length of each tile be x units.
The area of the rectangular floor using 200 tiles = 200 x2 unit2
The area with increased side length (each side increased by 1 unit) using 128 tiles
= 128 (x + 1)2 unit2
So, the required quadratic equation is: 200x2 = 128 (x + 1 )2
(ii) We have,
200x2 = 128 (x + 1)2
⇒ 200x2 = 128 (x2 + 2x + 1)
⇒ 200x2 = 128x2 + 256x + 128
⇒ 72x2 − 256x − 128 = 0
which is the quadratic equation is standard form.
(iii) (a) We have,
72x2 − 256x − 128 = 0
or, 9x2 − 32x − 16 = 0
or, 9x2 − 36x + 4x − 16 = 0
or, 9x (x − 4) + 4 (x − 4) = 0
or, (x − 4) (9x + 4) = 0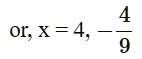
Since the side cannot be negative, thus x = 4 units.
OR
(b) We have 9x2 − 32x − 16 = 0
On comparing with ax2 + bx + c = 0, we get
a = 9, b = −32 and c = −16
Using quadratic formula,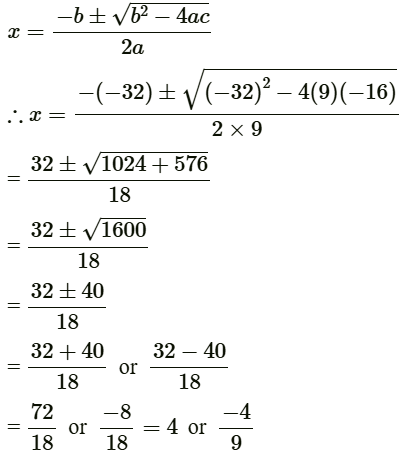
Q5: If the roots of equation ax2 + bx + c = 0, a ≠ 0 are real and equal, then which of the following relations is true? (CBSE 2024)
(a) a = b2/c
(b) b2 = ac
(c) ac = b2/4
(d) c = b2/c
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (c) ac = b2/4
If the discriminant is equal to zero, i.e., b2 − 4ac = 0 where a, b, c are real numbers and a ≠ 0, then roots of the quadratic equation ax2 + bx + c = 0, are real and equal.
Thus, b2 - 4ac = 0 or ac = b2/4
Previous Year Questions 2023
Q6: Find the sum and product of the roots of the quadratic equation 2x2 - 9x + 4 = 0. (CBSE 2023) View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Let α and β be the roots of given quadratic equation 2x2 - 9x + 4 = 0.
Sum of roots = α + β = -b/a = (-9)/2 = 9/2
and Product of roots, αβ = c/a = 4/2 = 2
Q7: Find the value of p, for which one root of the quadratic equation px2 – 14x + 8 = 0 is 6 times the other. (CBSE 2023)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Let the first root be α, then the second root will be 6a
Sum of roots = -b/a
⇒ a + 6a = 14/p
⇒ 7a = 14/p
⇒ a = 2/p
Product of roots = c/a
⇒ a x 6a = 8/p
⇒ 6a2 = 8/p
⇒ 6(2p)² = 8p
⇒ 6 x 4p² = 8p
⇒ p = 6 x 4/8
⇒ p = 3
Hence, the value of p is 3.
Q8: The least positive value of k for which the quadratic equation 2x2 + kx + 4 = 0 has rational roots is (2023)
(a) ±2√2
(b) 4√2
(c) ±2
(d) √2
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (c)
Sol: Put k = 2,
⇒ 2x² + 2x - 4 = 0
⇒ 2x² + 4x - 2x - 4 = 0
⇒ 2x (x + 2) - 2(x + 2) = 0
⇒ x = 1, -2
Put k = -2,
⇒ 2x² - 2x - 4 = 0
⇒ 2x² - 4x + 2x - 4 = 0
⇒ 2x (x - 2) + 2 (x - 2) = 0
⇒ x = -1, 2
Hence, to get the rational values of x, that is, to get rational roots, k must be ±2.
Q9: Find the discriminant of the quadratic equation 4x2 - 5 = 0 and hence comment on the nature of the roots of the equation. (CBSE 2023)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Given quadratic equation is 4x2 - 5 = 0
Discriminant, D = b2 - 4ac = 02 - 4(4)(-5) = 80 > 0
Hence, the roots of the given quadratic equation are real and distinct.
Q10: Find the value of 'p' for which the quadratic equation px(x - 2) + 6 = 0 has two equal real roots. (2023)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: The given quadratic equation is px(x - 2) + 6 = 0
⇒ px2 - 2xp +6 = 0
On comparing with ax2+ bx + c = 0, we get
a = p, b = -2p and c = 6
Since, the quadratic equations has two equal real roots.
∴ Discriminant D = 0
⇒ b2 - 4ac = 0
⇒ (-2p)2 - 4 x p x 6 = 0
⇒ 4p2 - 24p = 0
⇒ p2 - 6p = 0
⇒ p(p - 6) = 0
⇒ p = 0 or p = 6
But p ≠ 0 as it does not satisfy equation
Hence, the value of p is 6.
Q11: Case Study: While designing the school yearbook, a teacher asked the student that the length and width of a particular photo be increased by n units each to double the area of the photo. The original photo is 18 cm long and 12 cm wide.
Based on the above information. Answer the following Questions:
(i) Write an algebraic equation depicting the above information.
(ii) Write the corresponding quadratic equation in standard form.
(iii) What should be the new dimensions of the enlarged photo?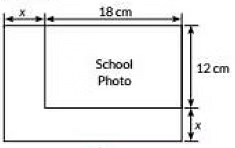
Can any rational value of x make the new area equal to 220 cm2? (2023)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Area = 18 x 12 cm = 216 cm2
Length (l) is increased by x cm
So, new length =(18 + x ) cm
New width = (12 + x) cm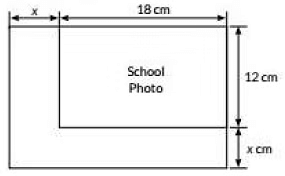
(i) Area of photo after increasing the length and width
= (18 + x)(12 + x) = 2 x 18 x 12
i.e., (18 + x) (12 + x) = 432 is the required algebraic equation.
(ii) From part (i) we get, (18 + x) (12 + x) = 432
⇒ 216 + 18x + 12x + x2 = 432
⇒ x2 + 30x - 216 = 0
(iii) x2 + 30x - 216 = 0
⇒ x2+ 36x - 6x - 216 = 0
⇒ x(x+ 36) - 6 (x+ 36) = 0 ⇒ x = 6, -36
-36 is not possible.
So, new length = (18 + 6) cm = 24 cm
New width = (12 + 6) cm = 18cm
So. new dimension = 24cm x 18 cm
According to question (18 + x) (12 + x) = 220
⇒ 216 + 30x + x2 = 220
⇒ x2 + 30x + 216 - 220 = 0
⇒ x2 + 30x - 4 = 0
For rational value of x. discriminant (D) must be perfect square.
So, D = b2 - 4ac
= (30)2 - 4(1)(-4) = 900 + 16 = 916
∴ 916 is not a perfect square.
So, no rational value of x is possible.
Q12: The roots of the equation x2 + 3x – 10 = 0 are:
(a) 2, –5
(b) –2, 5
(c) 2, 5
(d) –2, –5 (CBSE 2023)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a)
To find the roots of the quadratic equation x2 + 3x − 10 = 0, we can use the quadratic formula:
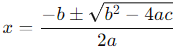
For the equation x2 + 3x − 10 = 0:
a = 1
b = 3
c = −10
Substitute these values into the formula:
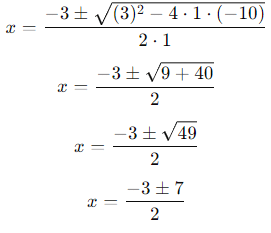
Now, calculate the two roots:
(i) For x = (-3 + 7) / 2 = 4/2 = 2
(ii) For x = (-3 - 7)/2 = -10/2 = -5
The roots of the equation are 2 and -5.
So, the correct answer is: (a) 2,−5
Previous Year Questions 2022
Q13: If the sum of the roots of the quadratic equation ky2 – 11y + (k – 23) = 0 is 13/21 more than the product of the roots, then find the value of k. (2022) View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Given, quadratic equation is ky2 – 11y + (k – 23) = 0
Let the roots of the above quadratic equation be α and β.
Now, Sum of roots, α + β = -(-11)/k = 11/k ...(i)
and Product of roots, αβ = (k-23)/k ...(ii)
According to the question,
α + β = αβ + 13/21
∴ 11k = k - 23k + 1321 ... [From equations (i) and (ii)]
⇒ 11k = k - 23k + 1321
⇒ 11 - k + 23k = 1321
⇒ 21(34 – k) = 13k
⇒ 714 – 21k = 13k
⇒ 714 = 13k + 21k
⇒ 34k = 714
⇒ k = 714/34
⇒ k = 21
Q14: Solve the following quadratic equation for x: x2 – 2ax – (4b2 – a2) = 0
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: x2 – 2ax – (4b2 – a2) = 0
⇒ x2 + (2b – a)x – (2b + a)x – (4b2 – a2) = 0
⇒ x(x + 2b – a) – (2b + a)(x + 2b – a) = 0
⇒ (x + 2b – a)(x – 2b – a) = 0
⇒ (x + 2b – a) = 0, (x – 2b – a) = 0
∴ x = a − 2b, a + 2b
Q15: In the picture given below, one can see a rectangular in-ground swimming pool installed by a family In their backyard. There is a concrete sidewalk around the pool that is width x m. The outside edges of the sidewalk measure 7 m and 12 m. The area of the pool is 36 sq. m.
Based on the information given above, form a quadratic equation in terms of x
Find the width of the sidewalk around the pool. (2022)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Given, width of the sidewalk = x m.
Area of the pool = 36 sq.m
∴ Inner length of the pool
= (12 - 2x)m
Inner width of the pool = (7 - 2x)m
∴ Area of the pool = A = l x b
⇒ 36 = (12 - 2x) x (7 - 2x)
⇒ 36 = 84 - 24x - 14x +4x2
⇒ 4x2 - 38x + 48 = 0
⇒ 2x2 - 19x + 24 = 0, is the required quadratic equation.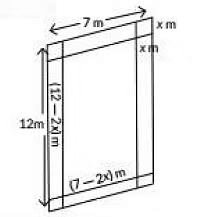
Area of the pool given by quadratic equation is 2x2 - 19x + 24 = 0
⇒ 2x2 - 16x - 3x + 24 = 0
⇒ 2x(x - 8) - 3(x - 8) = 0
⇒ (x - 8)(2x - 3) = 0
⇒ x = 8 (not possible)
Hence, x = 3/2 = 1.5
Width of the sidewalk =1.5m
Q16: The sum of two numbers is 34. If 3 Is subtracted from one number and 2 is added to another, the product of these two numbers becomes 260. Find the numbers. (2022)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Let one number be x and another number be y.
Since, x + y = 34 ⇒ y = 34 - x (i)
Now. according to the question. (x - 3) (y + 2) = 260 (ii)
Putting the value or y from (i) in (ii), we get
⇒ (x - 3)(34 - x + 2) = 260
⇒ (x - 3)(36 - x) = 260
⇒ 36x - x2 - 108 + 3x = 260
⇒ x2 - 39x +368 = 0
⇒ x2- 23x - 16x + 368 = 0
⇒ x(x - 23) - 16(x - 23) = 0
⇒ (x - 23)(x - 16) =0
⇒ x = 23 or 16
Hence; when x = 23 from (i), y = 34 - 23 = 11
When x = 16. then y = 34 - 16 = 18
Hence the required numbers are 23 and 11 or 16 and 18.
Q17: The hypotenuse (in cm) of a right-angled triangle is 6 cm more than twice the length of the shortest side. If the length of the third side is 6 cm less than thrice the length of the shortest side, then find the dimensions of the triangle. (2022)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans:
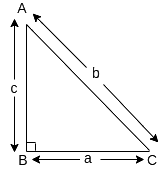
Let ΔABC be the right angle triangle, right angled at B, as shown in the figure.
Also, let AB = c cm, BC = a cm and AC = b cm
Then, according to the given information, we have
b = 6 + 2a .....(i) (Let a be the shortest side)
and c = 3a – 6 ...(ii)
We know that, b2 = c2 + a2 .....(Pythagoras Theorem)
Putting the values of b and c from (i) and (ii) in above equation
⇒ (6 + 2a)2 = (3a – 6)2 + a2 ...[Using (i) and (ii)]
⇒ 36 + 4a2 + 24a = 9a2 + 36 – 36a + a2
⇒ 60a = 6a2
⇒ 6a = 60 ...[∵ a cannot be zero]
⇒ a = 10 cm
Now, putting value of a in equation (i), we get
b = 6 + 2 × 10 = 26
and putting value of a in equation (ii), we get
c = 3 × 10 – 6 = 24
Thus, the dimensions of the triangle are 10 cm, 24 cm and 26 cm.
Q18: Solve the quadratic equation: x2 – 2ax + (a2 – b2) = 0 for x. (2022)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: We have, x2 – 2ax + (a2 – b2) = 0
⇒ x2 – ((a + b) + (a – b))x + (a2 – b2) = 0
⇒ x2 – (a + b)x – (a – b)x + (a + b)(a – b) = 0 ......[∵ a2 – b2 = (a + b)(a – b)]
⇒ x(x – (a + b)) – (a – b)(x – (a + b)) = 0
⇒ (x – (a + b))(x – (a – b) = 0
⇒ x = a + b, a – b
Q19: Find the value of m for which the quadratic equation (m - 1) x2 + 2 (m - 1) x + 1 = 0 has two real and equal roots. (2022)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: We have
(m - 1) x2 + 2 (m - 1) x + 1 = 0 ----(i)
On comparing the given equation with ax2 + bx + c = 0,
we have a = (m - 1), b = 2 (m - 1), c = 1
Discriminant, D = 0
⇒ b2 - 4ac = 0
⇒ (2 (m - 1))2 - 4 (m - 1)(1)
⇒ 4m2 + 4 - 8m - 4m + 4 = 0
⇒ 4m2 -12m + 8 = 0
⇒ m2 - 3m + 2 = 0 ⇒ m2 - 2m - m + 2= 0
⇒ m(m - 2) - 1 (m - 2) = 0
⇒ (m - 1)(m - 2) = 0 ⇒ m = 1, 2
Q20: The quadratic equation (1 + a2)x2 + 2abx + (b2 - c2) = 0 has only one root. What is the value of c2(1 + a2)? (2022)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (1 + a2)x2 + 2abx + (b2 - c2)= 0
Comparing on Ax2 + Bx + C = 0
A = 1 + a2, B = 2ab & C = (b2 - c2)
Now, B2 - 4AC = 0
⇒ (2ab)2 - 4 × (1 + a2) × (b2 - c2) = 0
⇒ 4a2b2 - 4(b2 - c2 + a2b2 - a2c2) = 0
⇒ 4a2b2 - 4b2 + 4c2 - 4a2b2 + 4 a2c2 = 0
⇒ - b2+ c2 + a2c2 = 0
⇒ c2 + a2c2 = b2
∴ c2 (1 + a2) = b2
Previous Year Questions 2021
Q21: Write the quadratic equation in x, whose roots are 2 and -5. (2021)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Roots of quadratic equation are given as 2 and - 5.
Sum of roots = 2 + (-5) = -3
Product of roots = 2 (-5) = -10
Quadratic equation can he written as
x2 - (sum of roots)x + Product of roots = 0
⇒ x2 + 3x - 10 = 0
Previous Year Questions 2020
Q22: Sum of the areas of two squares is 544 m2. If the difference of their perimeters is 32 m, find the sides of the two squares. (2020)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Let the sides of the two squares be x m and y m, where ; x > y.
Then, their areas are x2 and y2 and their perimeters are 4x and 4y respectively.
By the given condition, x2 + y2 = 544 --------(i)
and 4x - 4y = 32
⇒ x - y = 8
⇒ x = y + 8 ------------ (ii)
Substituting the value of x from (ii) in (i) we get
⇒ (y + 8)2 + y2 = 544
⇒ y2 + 64 + 16y + y2 = 544
⇒ 2y2 + 16y - 480 = 0
⇒ y2 + 8y - 240 = 0
⇒ y2 + 20y - 12y - 240 = 0
⇒ y(y + 20) - 12(y + 20) = 0
⇒ (y - 12) (y + 20) = 0
⇒ y = 12 (∵ y ≠ - 20 as length cannot be negative)
From (ii), x = 12 + 8 = 20 Thus, the sides of the two squares are 20 m and 12 m.
Q23: A motorboat whose speed is 18 km/h in still water takes 1 hour more to go 24 km upstream than to return downstream to the same spot. Find the speed of the stream. (2020)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans:
Speed of boat = 18 km/hr
Distance = 24 km
Let x be the speed of the stream.
Let t1 and t2 be the time for upstream and downstream.
As we know that, SpeedDistance = TimeDistance ⇒ Time = DistanceSpeed
For upstream:
Speed = (18 - x) km/hr
Distance = 24 km
Time = t1
t1 = 2418 - x
For downstream:
Speed = (18 + x) km/hr
Distance = 24 km
Time = t2
t2 = 2418 + x
Now according to the question:
t1 = t2 + 1
Substitute the values:
2418 - x = 2418 + x + 1
Simplify:
118 - x - 118 + x = 124
Combine the fractions:
(18 + x) - (18 - x)(18 - x)(18 + x) = 124
⇒ 2x(18 - x)(18 + x) = 124
Cross-multiply:
48x(18 - x)(18 + x) = 1
Expand:
48x = 324 + 18x - 18x - x²
x² + 48x - 324 = 0
Rearrange:
x² + 54x - 6x - 324 = 0
(x + 54) - 6(x + 54) = 0
(x + 54)(x - 6) = 0
Solve for x:
x = -54 or x = 6
Since speed cannot be negative:
x = 6
Q24: The value(s) of k for which the quadratic equation 2x2 + kx + 2 = 0 has equal roots, is
(a) 4
(b) ± 4
(c) - 4
(d) 0 (2020, 1 Mark)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (b)
Given Quadratic equation is 2x2 + kx + 2 = 0
Since, the equation has equal roots.
∴ Discriminant = 0
= b2 - 4ac
⇒ k2 - 4 x 2 x 2 = 0
⇒ k2- 16 = 0
⇒ k2 = 16
⇒ k = ±4
Q25: Solve for x: 1x + 4 - 1x - 7 = 1130, x ≠ -4, 7. (CBSE 2020)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Given,
⇒ 1x + 4 - 1x - 7 = 1130
⇒ (x -7) - (x + 4)(x + 4)(x - 7) = 1130
⇒ -11(x + 4)(x - 7) = 1130
⇒ (x + 4)(x – 7) = –30
⇒ (x + 4) (x – 7) + 30 = 0
⇒ x2 + 4x – 7x – 28 + 30 = 0
⇒ x2 – 3x – 28 + 30 = 0
⇒ x2 – 3x + 2 = 0
⇒ x2 – 2x – x + 2 = 0
⇒ x(x – 2) – 1(x – 2) = 0
⇒ (x – 2) (x – 1) = 0
i.e., x – 1 = 0 or x – 2 = 0
⇒ x = 1 or 2
Q26: A train covers a distance of 480 km at a uniform speed. If the speed had been 8 km/h less, it would have taken 3 hours more to cover the same distance. Find the original speed of the train. (CBSE 2020)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Let the original speed of the train be x km/h.
Then, time taken to cover the journey of 480 km , t = 480 / x hours
Time taken to cover the journey of 480 km with speed of (x – 8) km/h = 480 / x − 8 hours
Now, according to question,
480x - 8 - 480x = 3
⇒ 480 [x - x + 8x(x - 8)] = 3
⇒ 480 (8) = 3x(x - 8)
⇒ 3x(x – 8) = 3840
⇒ x(x – 8) = 1280
⇒ x2 – 8x – 1280 = 0
⇒ x2 – 40x + 32x – 1280 = 0
⇒ x(x – 40) + 32(x – 40) = 0
⇒ (x + 32) (x – 40) = 0
⇒ x + 32 = 0 or x – 40 = 0
∴ x = – 32 (not possible)
∴ x = 40 Thus, the original speed of the train is 40 km/h.
Previous Year Questions 2019
Q27: Find the value of k for which x = 2 is a solution of equation kx2 + 2x - 3 = 0. (CBSE 2019) View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Since x = 2 is a solution of kx2 + 2x - 3 = 0
k(2)2 + 2(2) - 3 = 0
= 4k + 4 - 3 = 0
⇒ k = -1/4
Q28: The sum of the areas of two squares is 157 m2. If the sum of their perimeters is 68 m, find the sides of the two squares. (CBSE 2020)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Let the length of the side of one square be x m and the length of the side of another square be y m.
Given, x2 + y2= 157 _(i)
and 4x + 4y=68 _(ii)
x + y = 17
y = 17 - x _(iii)
On putting the value of y in (i), we get
x2 + (17 - x)2 = 157
⇒ x2 + 289 + x2 - 34x = 157
=> 2x2 - 34x +132 = 0
⇒ x2 - 17x + 66 = 0
⇒ x2 - 11x - 6x + 66 =0
⇒ x(x - 11) - 6(x - 11) = 0
⇒ (x - 11) (x - 6) = 0
⇒ x = 6 or x = 11
On putting the value of x in (iii), we get
y = 17 - 6 = 11 or y = 17 - 11 = 6
Hence, the sides of the squares be 11 m and 6 m.
Previous Year Questions 2017
Q29: If one root of the quadratic equation 6x2 – x – k = 0 is 2/3, then find the value of ‘k’. (CBSE 2017) View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Given quadratic equation is:
6x2 – x – k = 0.
It's one root is 2/3
If x = 2 / 3 is root of the given equation, then it will satisfy the given equation,
∴ 6 (23)2 - 23 - k = 0
⇒ 6 × 49 - 23 - k = 0
⇒ 83 - 23 - k = 0
⇒ k = 2
Hence, the value of k is 2.
Q30: If the equation (1 + m2)x2 + 2mcx + c2 – a2 = 0 has equal roots then show that c2 = a2 (1 + m2). (CBSE 2017)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Given, quadratic equation is,
(1 + m2 )x2 + 2mc x + c2 – a2 = 0
On comparing it with Ax2 + Bx + C = 0,
we get A = 1 + m2, B = 2mc and C = c2 – a2
The roots of the given equation are equal, then
Discriminant, D = 0
∴ B2 – 4AC = 0
(2mc)2 – 4 × (1 + m2) × (c2 – a2) = 0
⇒ 4m2c2 – 4(c2 + c2m2 – a2 – a2m2) = 0
⇒ 4m2c2 – 4c2 – 4c2m2 + 4a2 + 4m2a2 = 0
⇒ m2a2 + a2 – c2 = 0
⇒ c2 = m2a2 + a2
⇒ c2 = a2 (1 + m2)
Hence, proved
Q31: A line segment AB of length 2 m is divided at point C into two parts such that AC2 = AB × CB. Find the length of CB. (CBSE 2017)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Let the length of AC be x
Then, BC = (2 – x) m
Now, AC2 = AB × CB (given)
Putting the value of AC and BC in above equation, we get
∴ x2 = 2 × (2 – x) [∴ AB = 2 m (given)]
⇒ x2 = 4 – 2x
⇒ x2 + 2x – 4 = 0
Now, if we compare the above equation with ax2 + bx + c = 0.
Then, a = 1, b = 2, c = –4
Roots of the equation are
-b ± √b² - 4ac2a
= -2 ± √(2)² - 4 × 1 × (-4)2 × 1
= -2 ± √202
= -2 ± 2√52
= -1 ± √5
When x = -1 + √5, or x = -1 - √5
Then, BC = 2 - (- 1 + √5) = 3 - √5
BC = 3 - 2.24 = 0.76 m
When x = -1 - √5
BC = 2 - (-1 - √5) = 3 + √5
BC = 3 + 2.24 = 5.24 m
(which is not possible)
Hence, the length of BC is 3 − √5 or 0.76 m.
Previous Year Questions 2011
Q32: The roots of the equation x2 – 3x – m(m + 3) = 0, where m is a constant, are:(a) m, m + 3
(b) –m, m + 3
(c) m, –(m + 3)
(d) –m, –(m + 3) (CBSE 2011)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (b)
To find the roots of the equation x2 − 3x − m(m + 3) = 0, we can use the quadratic formula:
x = -b ± √b² - 4ac2a
For the equation x2 − 3x − m(m + 3) = 0:
a = 1
b = −3
c = −m(m + 3)
Substitute these values into the formula:
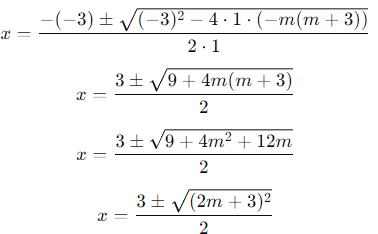
Since 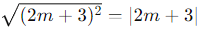 , we get two cases for the roots based on the sign:
, we get two cases for the roots based on the sign:
Case 1: 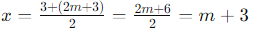
Case 2: 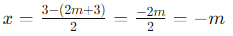
Thus, the roots of the equation are -m and m + 3.
So, the correct answer is: (b) −m, m + 3
|
127 videos|584 docs|79 tests
|
FAQs on Class 10 Maths Chapter 4 Previous Year Questions - Quadratic Equations
| 1. What are quadratic equations and how are they generally represented? |  |
| 2. What methods can be used to solve quadratic equations? |  |
| 3. How can I determine the number of real solutions a quadratic equation has? |  |
| 4. Can you provide a real-world application of quadratic equations? |  |
| 5. What are some common mistakes to avoid when solving quadratic equations? |  |






















