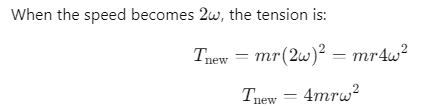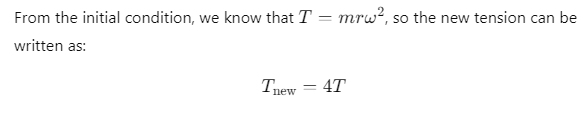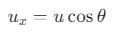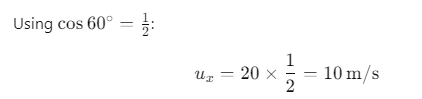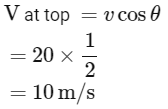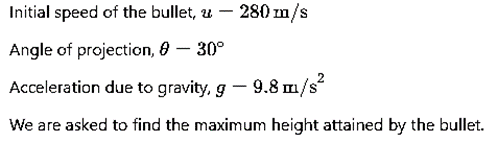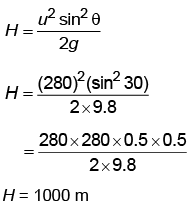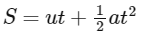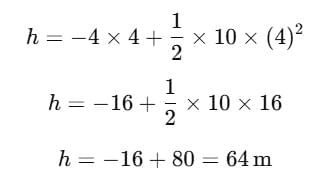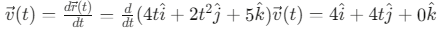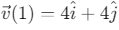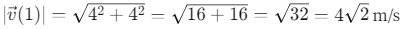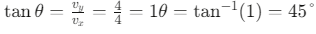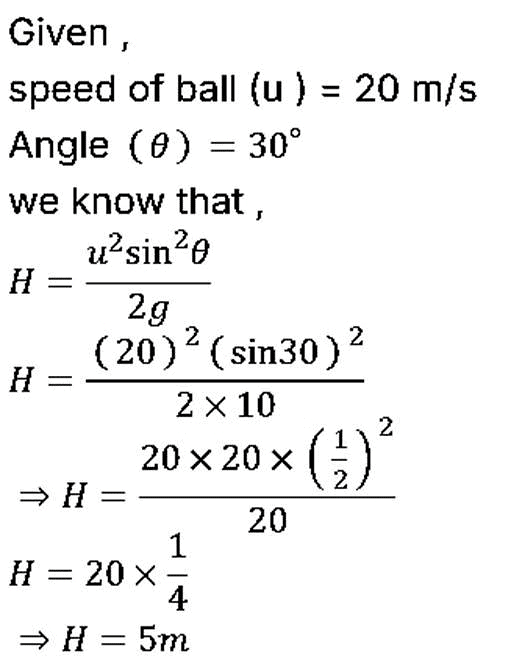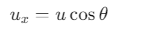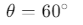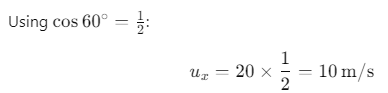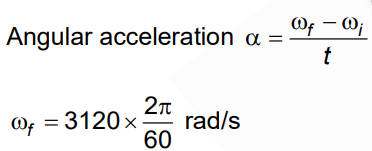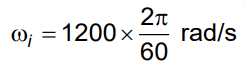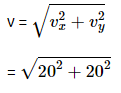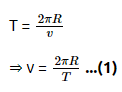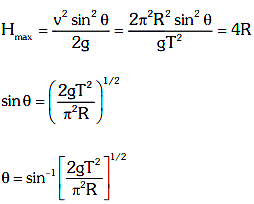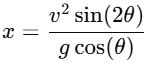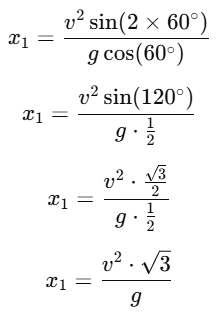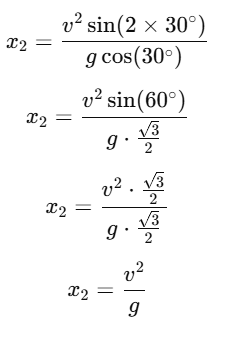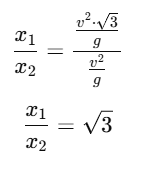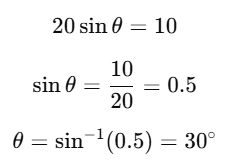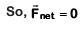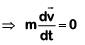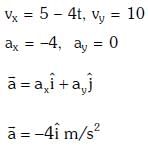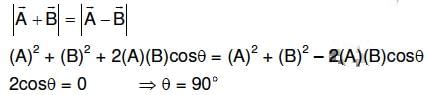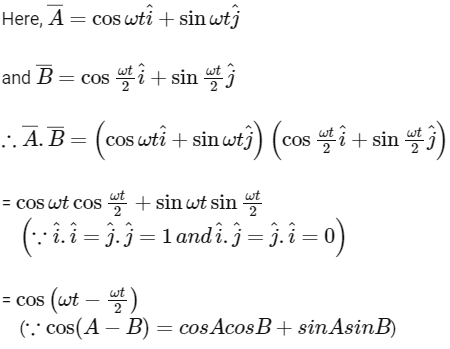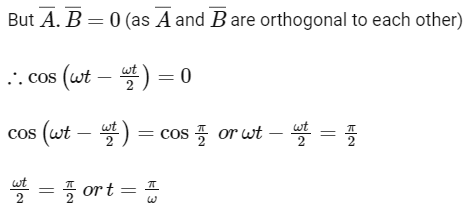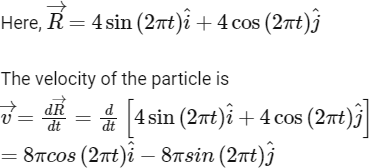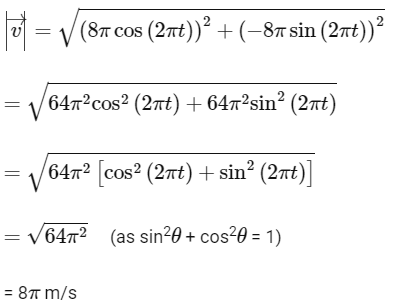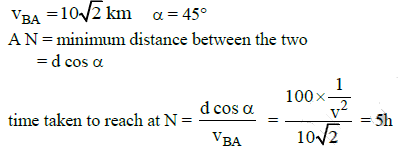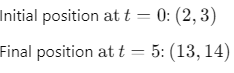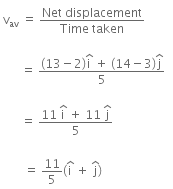NEET Previous Year Questions (2014-2025): Motion in a Plane | Physics Class 11 PDF Download
2024
Q1: A bob is whirled in a horizontal plane by means of a string with an initial speed of ω rpm. The tension in the string is T. If speed becomes 2ω while keeping the same radius, the tension in the string becomes: [2024](a) T
(b) 4T
(c) T/4
(d) √2T
Ans: (b) 4T
When the speed is ω, the tension is given by:
T=mrω 2
Q2: A particle moving with uniform speed in a circular path maintains: [2024]
(a) Constant velocity
(b) Constant acceleration
(c) Constant velocity but varying acceleration
(d) Varying velocity and varying acceleration
Ans: (d) Varying velocity and varying acceleration
Uniform speed: The magnitude of the velocity (speed) remains constant.
Circular motion: The direction of the velocity is constantly changing as the particle moves along the curved path.
Velocity: Velocity is a vector quantity, meaning it has both magnitude (speed) and direction. While the speed is constant, the direction of the velocity is always changing in circular motion.
Acceleration:
(i) In circular motion, there is always centripetal acceleration, which acts towards the center of the circular path. This acceleration changes the direction of the velocity but not its magnitude.(ii) Since the direction of the velocity is changing, the particle experiences a varying velocity.
(iii) The magnitude of the centripetal acceleration remains constant as long as the speed is constant, but the direction of the acceleration changes as the particle moves along the circular path.
Conclusion:
(i) The velocity of the particle is varying because its direction is constantly changing.
(ii) The acceleration is varying because its direction (towards the center of the circle) changes as the particle moves along the path.So, option (d) Varying velocity and varying acceleration is the correct answer.
Q3: For a smoothly running analog clock, the ratio of the number of rotations made in a day by the hour hand to the second hand, respectively, is: [2024]
(a) 24 : 1
(b) 1 : 720
(c) 1 : 60
(d) 2 : 5
Ans: (b)
Number of rotations by the hour hand:
- The hour hand completes 1 full rotation every 12 hours.
- Therefore, in 24 hours, the hour hand completes 2 full rotations.
Number of rotations by the second hand:
- The second hand completes 1 full rotation every 60 seconds, which is 1 minute.
- In 1 hour (60 minutes), the second hand completes 60 rotations.
- Therefore, in 24 hours, the second hand completes:
60 rotations/hour × 24 hours = 1440 rotations.Ratio of rotations:
The ratio of rotations made by the hour hand to the second hand is:
- Hour hand rotations: 2
- Second hand rotations: 1440
- So, the ratio is: 2 : 1440 = 1 : 720
Thus, the correct answer is (b) 1 : 720.
Q4: A body is falling freely in a resistive medium. The motion of the body is described by dv/dt = (4 − 2v), where v is the velocity of the body at any instant (in ms–1). The initial acceleration and terminal velocity of the body, respectively, are: [2024]
(a) 4 m/s2, 2 m/s
(b) 2 m/s2, 4 m/s
(c) 6 m/s2, 2 m/s
(d) 2 m/s2, 6 m/s
Ans: (a)
We are given the differential equation describing the velocity of the body falling in a resistive medium:
dv/dt = (4 - 2v)
where v is the velocity at any instant and dv/dt is the acceleration.
Step 1: Initial acceleration
To find the initial acceleration, substitute the initial velocity v = 0. When the body starts falling, its velocity is zero. Thus,
dv/dt = 4 - 2(0) = 4 m/s²
So, the initial acceleration is 4 m/s².
Step 2: Terminal velocity
The terminal velocity is the velocity at which the acceleration becomes zero, i.e., when dv/dt = 0.
Set dv/dt = 0 in the equation:
0 = 4 - 2v
Solving for v:
2v = 4 → v = 2 m/s
So, the terminal velocity is 2 m/s.
Final Answer:
- Initial acceleration: 4 m/s²
- Terminal velocity: 2 m/s
Thus, the correct answer is (a) 4 m/s², 2 m/s
2023
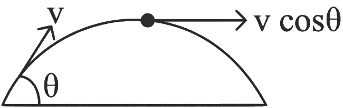
Q1: A ball is projected from point A with velocity 20 ms−1 at an angle 60∘ to the horizontal direction. At the highest point B of the path (as shown in figure), the velocity vms−1 of the ball will be: [2023]
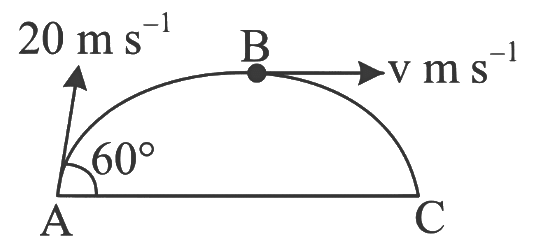
(a) 20 m/s
(b) 10√3 m/s
(c) Zero m/s
(d) 10 m/s
Ans: (d) 10 m/s
Given:
Initial velocity of the ball: u=20 m/s
Angle of projection: 60º
At the highest point B, the velocity of the ball is v m/s.We are asked to find the velocity B.
The horizontal component of the velocity is given by:
where, u = 20 m/s and θ = 60°
At the top most point of its trajectory particle will have only horizontal component of velocity
Q2: A particle is executing uniform circular motion with velocity 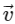 and acceleration
and acceleration 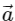 . [2023]
. [2023]
Which of the following is true?
(a) 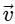 is a constant;
is a constant; 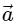 is not a constant
is not a constant
(b) 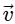 is not a constant;
is not a constant; 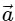 is not a constant
is not a constant
(c) 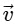 is a constant;
is a constant; 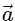 is a constant
is a constant
(d) 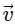 is not a constant;
is not a constant; 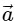 is a constant
is a constant
Ans: (b) 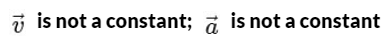
Velocity is not constant: While the speed (the magnitude of velocity) is constant, the direction of velocity is continuously changing as the object moves around the circular path.
Velocity is a vector, so any change in direction results in a change in velocity, even if the speed is the same.
Acceleration is not constant: The acceleration in uniform circular motion is called centripetal acceleration, and its direction is always pointing toward the center of the circular path.
Since the particle's position on the circular path changes continuously, the direction of the acceleration vector also changes constantly.
This means that while the magnitude of the acceleration (centripetal force) is constant, its direction is not, so overall, the acceleration is not constant.
Q3: A bullet is fired from a gun at the speed of 280 m s–1 in the direction 30° above the horizontal. The maximum height attained by the bullet is (g = 9.8 m s–2, sin30° = 0.5) [2023]
(a) 2800 m
(b) 2000 m
(c) 1000 m
(d) 3000 m
Ans: (c) 1000 m
Given:
We Know that,
Q4: The angular acceleration of a body, moving along the circumference of a circle, is [2023]
(a) Along the radius, away from centre
(b) Along the radius towards the centre
(c) Along the tangent to its position
(d) Along the axis of rotation
Ans: (d) Along the axis of rotation
Angular acceleration refers to the rate of change of angular velocity. In circular motion, angular acceleration is related to the change in how fast the body rotates around the center of the circle, rather than the linear acceleration, which deals with motion along the circle itself.
Angular acceleration acts along the axis of rotation and is perpendicular to the plane of the circle in which the body is moving.
Linear acceleration (tangential or radial) deals with motion in the plane of the circle, but angular acceleration always points along the axis of rotation (which is perpendicular to the plane of motion).
So, the correct option is (d) Along the axis of rotation.
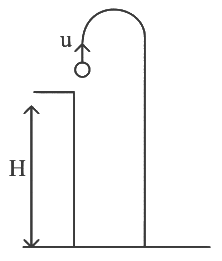
Q5: A horizontal bridge is built across a river. A student standing on the bridge throws a small ball vertically upwards with a velocity 4 m s−1. The ball strikes the water surface after 4 s. The height of bridge above water surface is (Take g = 10 m s−2 ) [2023]
(a) 60 m
(b) 64 m
(c) 68 m
(d) 56 m
Ans: (b) 64 m
Given:
Initial vertical velocity of the ball: u = 4 m/s (thrown upwards)Time taken to hit the water surface: t = 4 seconds
Gravitational acceleration: g = 10 m/s2
We need to find the height of the bridge above the water surface.
The equation for vertical displacement is:
Here, s is the net vertical displacement from the bridge to the water (so it’s positive downwards), u = 4m/s upward, and g = 10m/s2 downward.
So,
Q6: The position of a particle is given by; 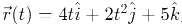 , where t is in seconds and r in metres. Find the magnitude and direction of the velocity v(t), at t = 1 s, with respect to the x - axis. [2023]
, where t is in seconds and r in metres. Find the magnitude and direction of the velocity v(t), at t = 1 s, with respect to the x - axis. [2023]
(a) 4√2 ms − 1, 45∘
(b) 4√2 ms − 1, 60∘
(c) 3√2 ms − 1, 30∘
(d) 3√2 ms − 1, 45∘
Ans: (a)
Given: Position vector
, where t is in seconds and
in meters.
Step 1: Find the velocity vector by differentiating the position vector with respect to time.Step 2: Evaluate the velocity at t = 1s.
Step 3: Calculate the magnitude of the velocity vector.
Step 4: Find the direction with respect to the x-axis.
The angle θ between the velocity vector and the x-axis is:
Therefore, at t = 1s, the velocity has a magnitude of 4√2 m/s and makes an angle of 45° with the x-axis.
This confirms that option (a) 4√2 m/s, 45° is the correct answer.
2022
Q1: A cricket ball is thrown by a player at a speed of 20 m/s in a direction 30∘ above the horizontal. The maximum height attained by the ball during its motion is (g = 10 m/s2) [2023]
(a) 25 m
(b) 5 m
(c) 10 m
(d) 20 m
Ans: (b) 5m
Q2: A ball is projected with a velocity, 10 ms–1 , at an angle of 60° with the vertical direction. Its speed at the highest point of its trajectory will be [2022]
(a) 5√3 ms–1
(b) 5 ms–1
(c) 10 ms–1
(d) Zero
Ans: (a) 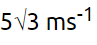
Given:
Initial velocity of the ball: u=20m/s
Angle of projection: 60∘
At the highest point B, the velocity of the ball is v m/s.We are asked to find the velocity v at the highest point B.
The horizontal component of the velocity is given by:
where, u = 20 m/s and
Since only the horizontal component of the velocity remains at the highest point, the velocity v at point B is equal to the horizontal velocity: v =10 m/s
Q3: The angular speed of a fly wheel moving with uniform angular acceleration changes from 1200 rpm to 3120 rpm in 16 seconds. The angular acceleration in rad/s2 is [2022]
(a) 4𝝅
(b) 12𝝅
(c) 104𝝅
(d) 2𝝅
Ans: (a) 4𝝅
Given:
Initial angular speed: ω1=1200 rpm
Final angular speed: ω2 = 3120 rpmTime taken for the change: t = 16 seconds
We are asked to find the angular acceleration α in rad/s².
We know that,
4𝝅
2021
Q1: A car starts from rest and accelerates at 5 m/s2. At t = 4 s, a ball is dropped out of a window by a person sitting in the car. What is the velocity and acceleration of the ball at t = 6 s ? [2021]
(a) 20√2m/s, 0 m/s2
(b) 20√2m/s, 10 m/s2
(c) 20 m/s,5 m/s2
(d) 20 m/s, 0
Ans: (b) 20√2m/s, 10 m/s2
Velocity of car at t = 4 sec is
v = u + at v = 0 + 5(4)
= 20 m/s
At t = 6 sec
acceleration is due to gravity
∴ a = g = 10 m/s
vx = 20 m/s (due to car)
vy = u + at
= 0 + g(2) (downward)
= 20 m/s (downward)
= 20√2 m/s.
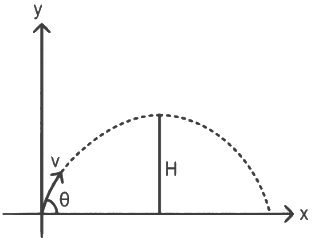
Q2: A particle moving in a circle of radius R with a uniform speed takes a time T to complete one revolution. If this particle were projected with the same speed at an angle 'θ'to the horizontal, the maximum height attained by it equals 4R. The angle of projection,θ, is then given by: [2021]
(a) 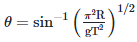
(b) 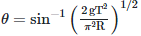
(c) 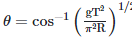
(d) 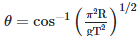
Ans: (b) 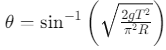
The time period of the particle in circular motion is given by
The maximum height H attained by a projectile is given by:
2019
Q1: When an object is shot from the bottom of a long smooth inclined plane kept at an angle 60o with horizontal, it can travel a distance x1 along the plane. But when the inclination is decreased to 30o and the same object is shot with the same velocity, it can travel x2 distance. Then x1 : x2 will be : [2019]
(a) 1 : √2
(b) √2 : 1
(c) 1 : √3
(d) 1 : 2√3
Ans: (c) 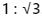
When an object is shot on an inclined plane at an angle θ with respect to the horizontal, the distance traveled x along the plane is given by the equation:
Where:
v is the initial velocity of the object.
θ is the angle of inclination.
g is the acceleration due to gravity.
Case 1: Inclination = 60°
For θ=60∘, the distance traveled is x1:
Case 2: Inclination = 30°
For θ=30∘, the distance traveled is x2:
Ratio of distances traveled:
Now, to find the ratio x1/x2, we simply divide x1 by x2:
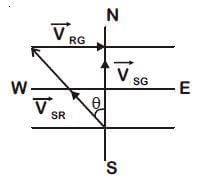
Q2: The speed of a swimmer in still water is 20 m/s. The speed of river water is 10 m/s and is flowing due east. If he is standing on the south bank and wishes to cross the river along the shortest path, the angle at which he should make his strokes w.r.t. north is given by: [2019]
(a) 30° west
(b) 0° west
(c) 60° west
(d) 45° west
Ans: (a) 30° west
Given:
The swimmer's velocity in still water is 20 m/s.
The river's velocity is 10 m/s, flowing due east. The swimmer should swim at an angle to counteract the river’s flow and move directly north.
Let the angle the swimmer needs to make with the north be θ (measured with respect to the north).The swimmer's velocity has two components:Vertical (northward) component: vscosθ
Horizontal (westward) component: vssinθ
For the swimmer to cancel the eastward current of the river, the swimmer’s westward component must equal the river's eastward speed.
Thus, we can write:
vssinθ = 10 m/swhere vs = 20 m/s (the swimmer’s speed in still water).
Solving:
Thus, the swimmer should make an angle of 30° west of north to cancel out the eastward current and cross the river along the shortest path.
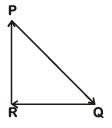
Q3: A particle moving with velocity 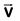 is acted by three forces shown by the vector triangle PQR. The velocity of the particle will: [2019]
is acted by three forces shown by the vector triangle PQR. The velocity of the particle will: [2019]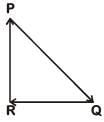
(a) Increase
(b) Decrease
(c) Remain constant
(d) Change according to the smallest force
Ans: (c) Remain constant
As forces are forming closed loop in same order
2017
Q1: The x and y coordinates of the particle at any time are x = 5t – 2t2 and y = 10t respectively, where x and y are in meters and t in seconds. The acceleration of the particle at t = 2s is:- [2017]
(a) 5 m/s2
(b) – 4 m/s2
(c) – 8 m/s2
(d) 0
Ans: (b) – 4 m/s2
Given:
We know that,
Q2: One end of string of length l is connected to a particle of mass 'm' and the other end is connected to a small peg on a smooth horizontal table. If the particle moves in circle with speed 'v' the net force on the particle (directed towards centre) will be (T represents the tension in the string):- [2017]
(a) 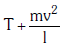
(b) 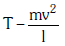
(c) Zero
(d) T
Ans: (d) T
Centripetal force is the force which makes a body move in a circular path. If a body of mass "m" moves with a velocity "v" in a circular path of radius "r", then Centripetal force, F is equal to:
F = mv²/r
If a particle connected to a string revolves in a circular path around a centre, the centripetal force is provided by the tension produced in the string.
Centripetal force (mv²/r) is provided by the tension so the net force will be equal to tension i.e. T.
2016
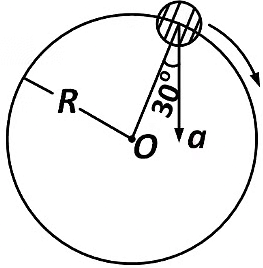
Q1: In the given figure, a = 15 m s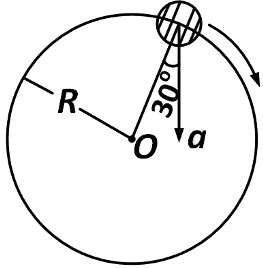
(a) 4.5 m s
(b) 5.0 m s
(c) 5.7 m s
(d) 6.2 m s
Ans: (c) 5.7 m s
Q2: If the magnitude of sum of two vectors is equal to the magnitude of difference of the two vectors, the angle between these vectors is: [2016]
(a) 180 degree
(b) 0 degree
(c) 90 degree
(d) 45 degree
Ans: (c)
2015
Q1: If vectors 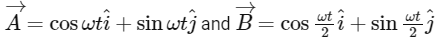 are functions of time, then the value of t at which they are orthogonal to each other is [2015]
are functions of time, then the value of t at which they are orthogonal to each other is [2015]
(a) t = π/ω
(b) t = 0
(c) t = π/4ω
(d) t = π/2ω
Ans: (a) 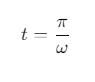
Q2: The positions vector of a particle 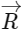 as a function of time is given by
as a function of time is given by 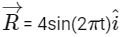 +
+ 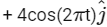 . Where R is in meters, t is in seconds and
. Where R is in meters, t is in seconds and 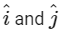 denote unit vectors along x-and y-directions, respectively. Which one of the following statements is wrong for the motion of particle?
denote unit vectors along x-and y-directions, respectively. Which one of the following statements is wrong for the motion of particle?
(a) Magnitude of the velocity of particle is 8 meter/second.
(b) Path of the particle is a circle of radius 4 meter.
(c) Acceleration vector is along - 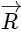
(d) Magnitude of acceleration vector is v2 / R, where v is the velocity of particle. [2015]
Ans: (a) Magnitude of the velocity of particle is 8 meter/second
Its magnitude is
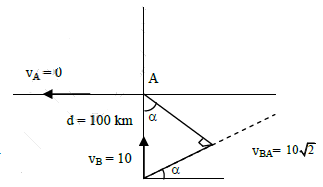
Q3: A ship A is moving Westwards with a speed of 10 km h-1 and a ship B 100 km South of A, is moving Northwards with a speed of 10 km h-1. The time after which the distance between them becomes shortest, is: [2015]
(a) 10√2h
(b) 0 h
(c) 5h
(d) 5√2h
Ans: (c) 5h
2014
Q1: A particle is moving such that its position coordinates (x, y) are (2m, 3m) at time t = 0, (6m, 7m) at time t = 2s and (13m, 14m) at time t= 5s. Average velocity vector 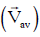 from t = 0 to t = 5s is: [2014]
from t = 0 to t = 5s is: [2014]
(a) 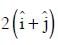
(b) 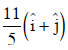
(c) 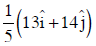
(d) 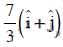
Ans: (b)
Given:
Average velocity Vector,
Q2: A projectile is fired from the surface of the earth with a velocity of 5 ms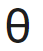 with the horizontal. Another projectile fired from another planet with a velocity of 3 ms
with the horizontal. Another projectile fired from another planet with a velocity of 3 ms
(Given g = 9.8 m s
(a) 3.5
(b) 5.9
(c) 16.3
(d) 110.8
Ans: (a) 3.5
The equation of trajectory is
y = x tan θ − (gx²)/(2u² cos² θ)
where θ is the angle of projection and u is the velocity with which projectile is projected.
For equal trajectories and for same angles of projection,
u²/g = constant
⇒ 0.8/g' = 5²/g
where g' is acceleration due to gravity on the planet.
g' = (0.8 × 9)/25 = 3.5 m s⁻²
|
119 videos|494 docs|98 tests
|
FAQs on NEET Previous Year Questions (2014-2025): Motion in a Plane - Physics Class 11
| 1. What is the importance of Motion in a Plane in NEET exams? |  |
| 2. Which formulas are essential for solving Motion in a Plane problems? |  |
| 3. How can I effectively prepare for Motion in a Plane for NEET? |  |
| 4. What types of questions can I expect from Motion in a Plane in NEET? |  |
| 5. Are there any common mistakes to avoid while solving Motion in a Plane problems? |  |