NEET Previous Year Questions (2014-2025): Gravitation | Physics Class 11 PDF Download
2025
Q1: The radius of Martian orbit around the sun is about 4 times the radius of the orbit of mercury. The Martian year is 687 earth days. Then which of the following is the length of 1 year on mercury? [2025]
(a) 172 earth days
(b) 124 earth days
(c) 88 earth days
(d) 225 earth days
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (c)
The radius of Mars' orbit around the Sun, R′ = 4R, where R is the radius of Mercury's orbit.
The Martian year T′ = 687 Earth days.
First, apply Kepler's Third Law to find the ratio of the orbital periods:
(T′ / T)² = (R′ / R)³ = (4R / R)³ = 4³ = 64
From this, we can solve for the ratio of the periods:
T′ / T = 8
This means that Mars takes 8 times longer to orbit the Sun compared to Mercury. Therefore, the length of one year on Mercury is:
T = T′ / 8 = 687 / 8 ≈ 85.88 days
Hence, one year on Mercury is approximately 86 Earth days. The nearest option is 88 days.
Q2: A body weight 48 N on the surface of the earth. The gravitational force experienced by the body due to the Earth at a height equal to one-third the radius of the Earth from its surface is: [2025]
(a) 32 N
(b) 36 N
(c) 16 N
(d) 27 N
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (d)
Given,
Weight on Earth’s surface = 48 N
Height from surface = (1/3) R
Total distance from Earth’s center = R + (1/3)R = (4/3)R
The gravitational force at height h is given by,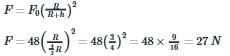
∴ The gravitational force at that height is 27 N.
2024
Q1: The mass of a planet is 1/10th that of the earth and its diameter is half that of the earth. The acceleration due to gravity on that planet is: [2024]
(a) 19.6 m s−2
(b) 9.8 m s−2
(c) 4.9 m s−2
(d) 3.92 m s−2
 View Answer
View Answer 
The acceleration due to gravity (g) on a planet is given by the formula: 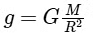
where:
- G is the universal gravitational constant,
- M is the mass of the planet, and
- R is the radius of the planet.
In this question, we know that:
- The mass of the planet Mp is 1/10 of the mass of the earth Me, so Mp
The diameter of the planet is half that of earth. Since the diameter is twice the radius, a diameter half that of earth implies the radius Rp is also half the radius of the earth Re. Therefore, Rp
Using the formula for acceleration due to gravity and substituting the above information: 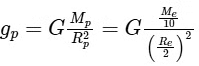 Simplify the expression:
Simplify the expression: 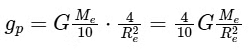 Knowing that
Knowing that 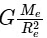 is the acceleration due to gravity on Earth
is the acceleration due to gravity on Earth 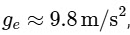 we substitute this value into the equation:
we substitute this value into the equation: 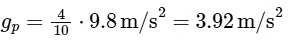 Thus, the acceleration due to gravity on the planet is 3.92m/s2, which corresponds to:
Thus, the acceleration due to gravity on the planet is 3.92m/s2, which corresponds to:
Option D:
Q2: The minimum energy required to launch a satellite of mass m from the surface of earth of mass M and radius R in a circular orbit at an altitude of 2R from the surface of the earth is: [2024]
(a)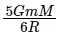 (b)
(b) 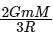 (c)
(c) 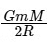 (d)
(d) 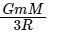
 View Answer
View Answer 
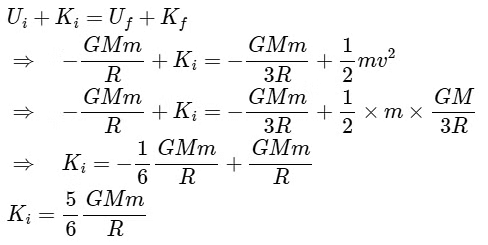
Q3: A rocket is fired vertically upward with a speed of ve/√ 2 from the Earth's surface, where ve is escape velocity on the surface of Earth. The distance from the surface of Earth upto which the rocket can go before returning to the Earth is: (given, the radius of Earth = 6400 km) [2024]
(a) 1600 km
(b) 3200 km
(c) 6400 km
(d)12800 km
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (c)
First, let's understand what happens when a rocket is launched upward.
Given:
Initial velocity = v₀ = ve/√2 (where ve is escape velocity)
Radius of Earth = R = 6400 km
To find the maximum height reached, I'll use energy conservation. At the maximum height, the kinetic energy becomes zero.
Step 1: Express the initial and final energies.
Initial energy (at Earth's surface): Kinetic energy + Potential energy
E₀ = (1/2)mv₀² - GMm/R
Final energy (at maximum height h from surface): Potential energy only
E₀ = -GMm/(R+h)
Step 2: By conservation of energy, E₀ = E₀
(1/2)mv₀² - GMm/R = -GMm/(R+h)
Step 3: Substitute v₀ = ve/√2 and use the relation for escape velocity ve = √(2GM/R)
(1/2)m(ve/√2)² - GMm/R = -GMm/(R+h)
Step 4: Simplify the equation
(1/2)m(ve²/2) - GMm/R = -GMm/(R+h)
(1/2)(GMm/R) - GMm/R = -GMm/(R+h)
GMm/(2R) - GMm/R = -GMm/(R+h)
-GMm/(2R) = -GMm/(R+h)
Step 5: Solve for h
R+h = 2R
h = R = 6400 km
Therefore, the maximum height reached by the rocket from the Earth's surface is 6400 km, which corresponds to option (c).
Q4: A body weighing 100 N on the surface of the Earth weights x kg-ms−2 at a height 1/9 RE above the surface of Earth. The value of x is: (take g = 10 ms−2 at the surface of Earth and RE is the radius of Earth) [2024]
(a) 72 72
(b) 54 54
(c) 81 81
(d) 62 62
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (c)
Given:
- Weight on Earth's surface = 100 N
- g = 10 m/s² (acceleration due to gravity on Earth's surface)
- Height above Earth's surface = 1/9 RE
Formula:
The formula for gravity at a height h is: g' = g × (RE / (RE + h))²
Step-by-Step Calculation:
- The new distance from Earth's center at height 1/9 RE is: RE + h = 10/9 RE
- The gravity at this height is: g' = g × (9/10)² = 10 × 81/100 = 8.1 m/s²
- The weight at height h is: W' = 100 × 8.1/10 = 81 N
Final Answer:
The weight at height 1/9 RE is 81 N.
So, the correct answer is (c) 81.
Q5: The escape velocity for Earth is v. A planet having 9 times the mass of Earth and a radius, 16 times that of Earth, has the escape velocity of: [2024]
(a) v/3
(b) 2v/3
(c) 3v/4
(d) 9v/4
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (c)
To solve the problem:
Given:
Escape velocity for Earth is v.
The new planet has:
- 9 times the mass of Earth, so its mass is 9 times Earth's mass.
- 16 times the radius of Earth, so its radius is 16 times Earth's radius.
Formula for escape velocity:
Escape velocity is given by the formula:
v_e = √(2GM / R)
where:
- G is the gravitational constant,
- M is the mass of the planet,
- R is the radius of the planet.
Step-by-step Calculation:
For the new planet:
- The mass is 9 times Earth's mass.
- The radius is 16 times Earth's radius.
So, the escape velocity for the new planet will be:
v'_e = √(2G × (9 × M_E) / (16 × R_E))
This simplifies to:
v'_e = √(9 / 16) × v
v'_e = (3/4) × v
Final Answer: The escape velocity for the new planet is 3v/4.
So, the correct answer is (c) 3v/4.
Q6: An object of mass 100 kg falls from point A to B as shown in the figure. The change in its weight, corrected to the nearest integer (RE is the radius of the Earth), is: [2024]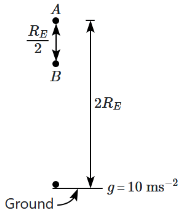 (a) 49 N
(a) 49 N
(b) 89 N
(c) 5 N
(d) 10 N
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a)
The weight of an object at a distance r from the center of Earth is:
W = G·M·m/r²
Where:
- G is the gravitational constant
- M is the mass of Earth
- m is the mass of the object (100 kg)
- r is the distance from Earth's center
The change in weight when moving from point A to point B would be:
ΔW = G·M·m(1/rB² - 1/rA²)
Since the answer is (a) 49 N, I'll work backward to determine the relationship between rA and rB.
Let's denote Earth's radius as RE.
At Earth's surface, the weight would be:
W_surface = G·M·m/RE² = m·g (where g ≈ 9.8 m/s²)
Therefore:
G·M/RE² = g
For a 100 kg object, the change in weight is 49 N, which means:
49 = 100·g·(1/rB² - 1/rA²)/g
49/100 = (1/rB² - 1/rA²)·RE²
If we assume point B is at Earth's surface (rB = RE) and point A is at height h above Earth's surface (rA = RE + h), then:
0.49 = (1 - RE²/(RE + h)²)
0.49 = (1 - 1/(1 + h/RE)²)
Solving for h/RE:
1/(1 + h/RE)² = 0.51
1 + h/RE = 1/√0.51 ≈ 1.4
h/RE ≈ 0.4
This suggests that point A is at a height of approximately 0.4RE above Earth's surface, and point B is at Earth's surface.
The change in weight is 49 N when an object of mass 100 kg falls from a height of 0.4 times Earth's radius to Earth's surface, confirming answer (a).
2023
Q1: The escape velocity of a body on the earth surface is 11.2 km/s. If the same body is projected upward with velocity 22.4 km/s, the velocity of this body at infinite distance from the centre of the earth will be: [2023](a) 11.2√2 Km/s
(b) Zero
(c) 11.2 Km/s
(d) 11.2√3 Km/s
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (d)
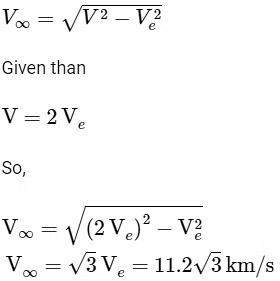
Q2: If R is the radius of the earth and g is the acceleration due to gravity on the earth surface. Then the mean density of the earth will be : [2023]
(a) 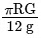
(b) 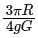
(c) 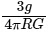
(d) 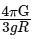
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (c)
Understand the relationship between gravity, mass, and radius:
The acceleration due to gravity g at the surface of the Earth can be expressed using the formula: 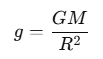
where G is the universal gravitational constant, M is the mass of the Earth, and R is the radius of the Earth.
Express mass in terms of density: The mass M of the Earth can also be expressed in terms of its mean density ρ and volume. The volume V of the Earth (assuming it is a sphere) is given by: 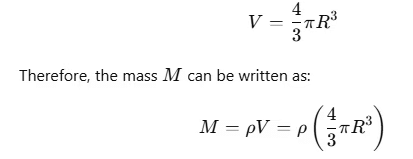
Substitute mass back into the gravity equation: Now, substitute the expression for M into the gravity equation: 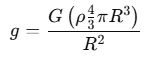
Simplifying this gives: 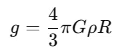
To find the mean density ρ, rearrange the equation: 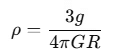
Q3: Two bodies of mass m and 9m are placed at a distance R. The gravitational potential on the line joining the bodies where the gravitational field equals zero, will be (G = gravitational constant) [2023]
(a) 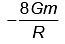 (b)
(b) 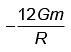 (c)
(c) 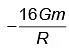 (d)
(d) 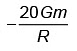
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (c)
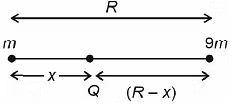 Let electric field at point Q be zeroSo,
Let electric field at point Q be zeroSo,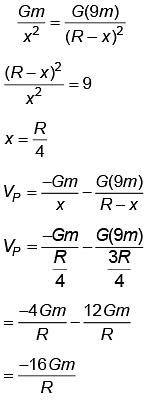
Q4: A satellite is orbiting just above the surface of the earth with period T. If d is the density of the earth and G is the universal constant of gravitation, the quantity [2023]
[2023]
(a) T
(b) T2
(c) T3
(d) √T
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (b)
Time period of satellite above earth surface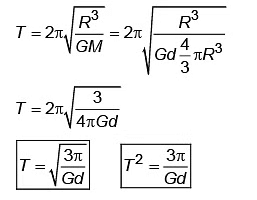
2022
Q1: A body of mass 60 g experiences a gravitational force of 3.0 N, when placed at a particular point. The magnitude of the gravitational field intensity at that point is [2022]
(a) 50 N/kg
(b) 20 N/kg
(c) 180 N/kg
(d) 0.05 N/kg
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a)
Given:
- Mass of the body m = 60g = 0.06 kg,
- Gravitational force F= 3.0 N.
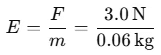
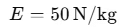
The magnitude of the gravitational field intensity at that point is: 50N/kg
Q2: Match List - I with List - II
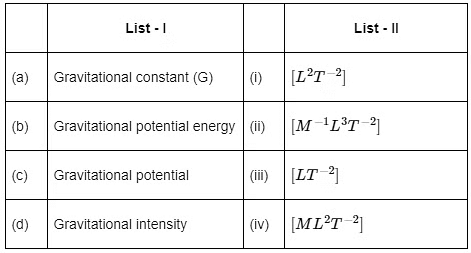
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) (a)-(ii), (b)-(i), (c)-(iv), (d)-(iii)
(b) (a)-(ii), (b)-(iv), (c)-(i), (d)-(iii)
(c) (a)-(ii), (b)-(iv), (c)-(iii), (d)-(i)
(d) (a)-(iv), (b)-(ii), (c)-(i), (d)-(iii) [2022]
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (b)
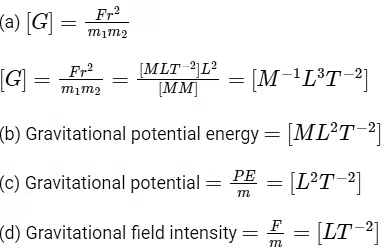
Q3: A gravitational field is present in a region and a mass is shifted from A to B through different paths as shown. If W1, W2and W3represent the work done by the gravitational force along the respective paths, then : [2022]
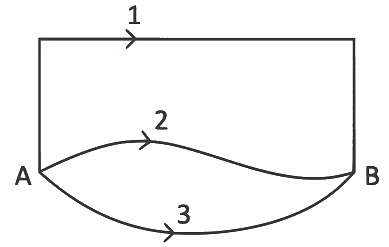
(a) W1< W2< W3
(b) W1= W2= W3
(c) W1> W2> W3
(d) W1> W3> W2
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (b)
Since the gravitational field is conservative in nature hence the work done would depend only on the initial and final positions and not on the path followed by the mass.
Hence, W1 = W2 = W3
Q4: In a gravitational field, the gravitational potential is given by, V = -K/x (J/Kg). The gravitational field intensity at point (2, 0, 3) m is
(a) +K/4
(b) +K/2
(c) -K/2
(d) -K/4 [2022]
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (d)

2021
Q1: The escape velocity from the Earth's surface is v. The escape velocity from the surface of another planet having a radius, four times that of Earth and same mass density is: [2021]
(a) 3v
(b) 4v
(c) v
(d) 2v
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (b)
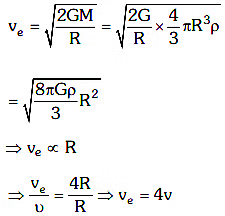
Q2: A particle of mass 'm' is projected with a velocity v = kVe (k < 1) from the surface of the earth. (Ve = escape velocity) The maximum height above the surface reached by the particle is : [2021]
(a) 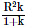
(b) 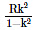
(c) 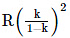
(d) 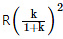
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (b)
Step 1: Kinetic and Gravitational Potential Energy
Initial Kinetic Energy (KE): The initial kinetic energy when the particle is projected with velocity v=kve is:
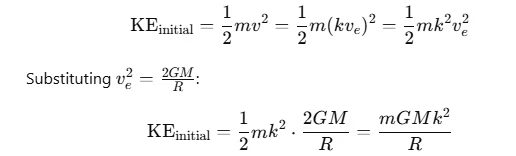
Initial Gravitational Potential Energy (PE): The initial gravitational potential energy at the Earth's surface (distance R from the center of the Earth) is:
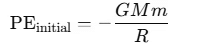
At the maximum height h above the Earth's surface, the particle's final velocity is zero. Let the total distance from the center of the Earth at this height be R+h.
By the conservation of energy, the total initial energy (kinetic + potential) is equal to the total final energy (potential energy at distance R+h): 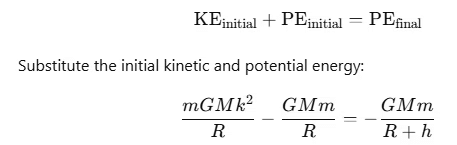
3. Simplify the Equation
Factor out G M m on the left side: 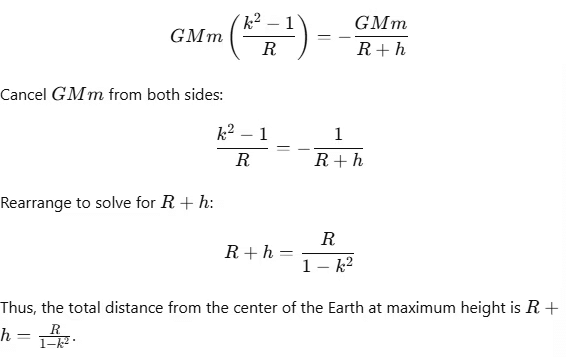
Solve for the Maximum Height h Above the Earth's Surface
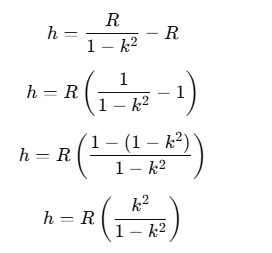
2020
Q1: A body weighs 72 N on the surface of the earth. What is the gravitational force on it, at a height equal to half the radius of the earth? [2020]
(a) 30 N
(b) 24 N
(c) 48 N
(d) 32 N
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (d)
Given:
Weight of the body on the Earth's surface, 72 N.
Height h above the Earth's surface is equal to half the Earth's radius, .
The gravitational force (or weight) W on the surface of the Earth is given by: 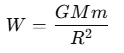
where:
- G is the gravitational constant,
- M is the mass of the Earth,
- m is the mass of the body,
- R is the radius of the Earth.
Since the weight on the Earth's surface is given as 72 N, we can use this to determine the gravitational force at a height.
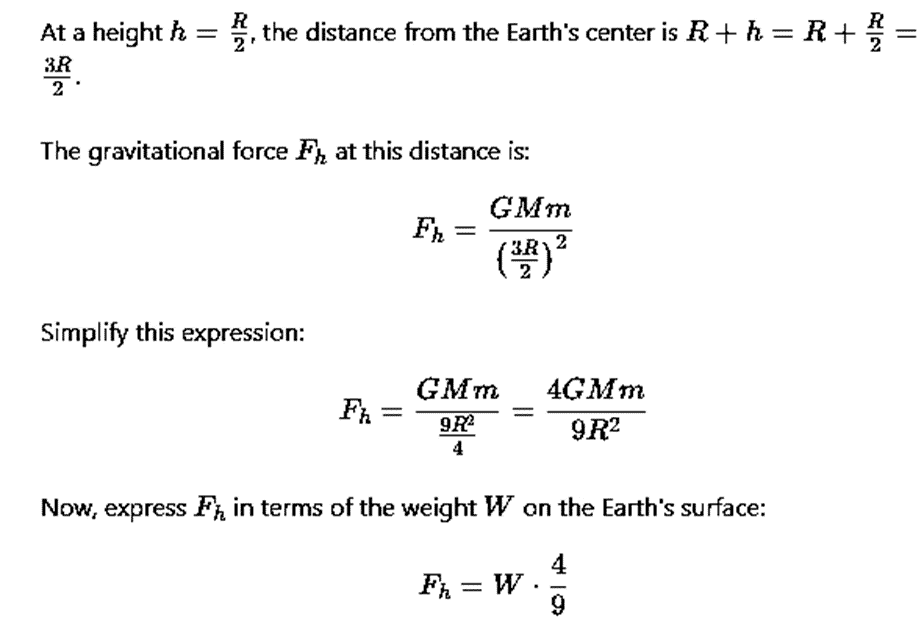
Since 72 N:
2019
Q1: A body weighs 200 N on the surface of the earth. How much will it weigh half way down to the centre of the earth? [2019]
(a) 150 N
(b) 200 N
(c) 250 N
(d) 100 N
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (d)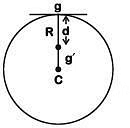 Acceleration due to gravity at a depth d from surface of earth
Acceleration due to gravity at a depth d from surface of earth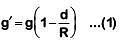 Where g = acceleration due to gravity at earth's surfaceMultiplying by mass 'm' on both sides of (1)
Where g = acceleration due to gravity at earth's surfaceMultiplying by mass 'm' on both sides of (1)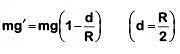
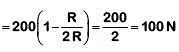
Q2: The work done to raise a mass m from the surface of the earth to a height h, which is equal to the radius of the earth, is :
(a) mgR
(b) 2mgR
(c) 1/2mgR
(d) 3/2mgR [2019]
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (c)
Initial potential energy at Earths surface is
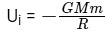
Final potential energy at height h = R :
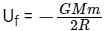
work done = change in PE
w = Uf- Ui
2018
Q1: If the mass of the Sun were ten times smaller and the universal gravitational constant were ten time larger in magnitude, which of the following is not correct ? [2018]
(a) Raindrops will fall faster
(b) Walking on the ground would become more difficult
(c) Time period of a simple pendulum on the Earth would decrease
(d) 'g' on the Earth will not change
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (d)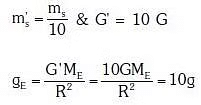 Raindrops will fall faster, Walking on the ground would become more difficult. Time period of a simple pendulum on the earth would decrease.
Raindrops will fall faster, Walking on the ground would become more difficult. Time period of a simple pendulum on the earth would decrease.
Q2: The kinetic energies of a planet in an elliptical orbit about the Sun, at positions A, B and C are KA, KBand KC, respectively. AC is the major axis and SB is perpendicular to AC at the position of the Sun S as shown in the figure. Then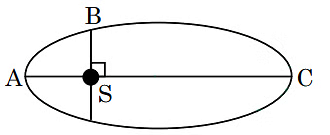
(a) KA< KB< KC
(b) KA> KB> KC
(c) KB< KA< KC
(d) KB> KA> KC [2018]
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (b)
Speed of the planet will be maximum when its distance from the sun is minimum as mvr = constant.
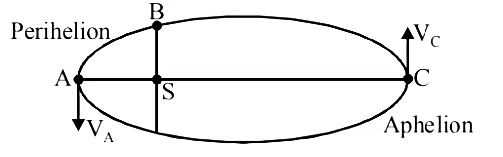 Point A is perihelion and C is aphelion.
Point A is perihelion and C is aphelion.
Clearly, VA> VB> VC
So, KA> KB> KC
2017
Q1: The acceleration due to gravity at a height 1 km above the earth is the same as at a depth d below the surface of earth. Then: - [2017]
(a) d = 1 km
(b) 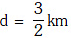 (c) d = 2 km(d)
(c) d = 2 km(d) 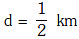
 View Answer
View Answer 
The gravitational acceleration gh at a height h above the Earth's surface is given by:
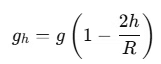
where:
- g is the gravitational acceleration on the Earth's surface,
- R is the radius of the Earth.
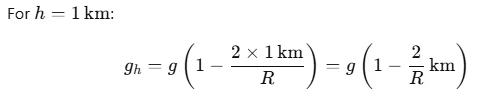
The gravitational acceleration gd at a depth d below the Earth's surface is given by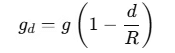
Q2: Two astronauts are floating in gravitational free space after having lost contact with their spaceship. The two will : - [2017]
(a) Move towards each other.
(b) Move away from each other.
(c) Will become stationary
(d) Keep floating at the same distance between them.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a)
Astronauts move towards each other under mutual gravitational force.
2016
(a) 2000 km
(b) 2600 km
(c) 1600 km
(d) 1400 km
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (b)
-GM/r = 5.4 x 10-7
-GM/r2 = 6.0
dividing both the equations, r = 9000 km.
so height from the surface = 9000 - 6400 = 2600 km
Q2: The ratio of escape velocity at earth (ve) to the escape velocity at a planet (vp) whose radius and mean density are twice as that of earth is : [2016]
(a) 1: √2
(b) 1: 2
(c) 1: 2√2
(d) 1: 4
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (c)
The mass M of a planet can be written in terms of its density ρ and volume V: 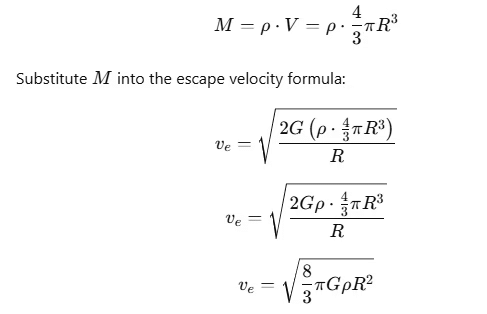
Thus, we can see that escape velocity depends on both the radius R and the mean density ρ as: 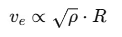

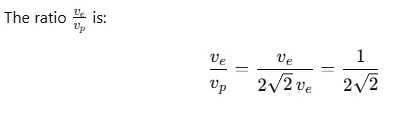
(a) 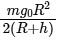
(b) 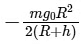
(c) 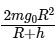
(d) 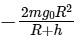
 View Answer
View Answer 
The gravitational potential energy U of a satellite of mass m at a distance R+h from the Earth's center is given by: 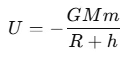
where G is the gravitational constant, and M is the mass of the Earth.
For a satellite in orbit, the gravitational force provides the necessary centripetal force. Thus, the orbital speed v of the satellite is given by:
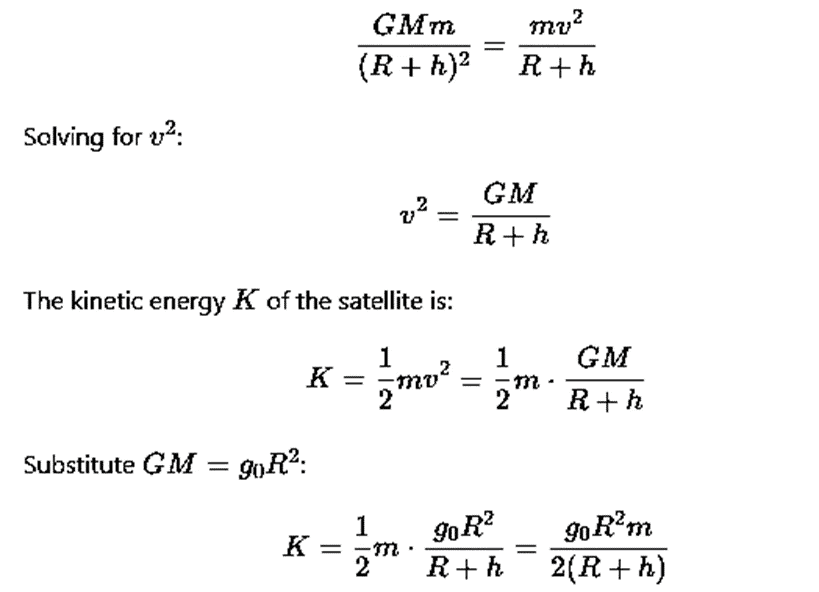
The total energy E of the satellite is the sum of its kinetic and potential energies: 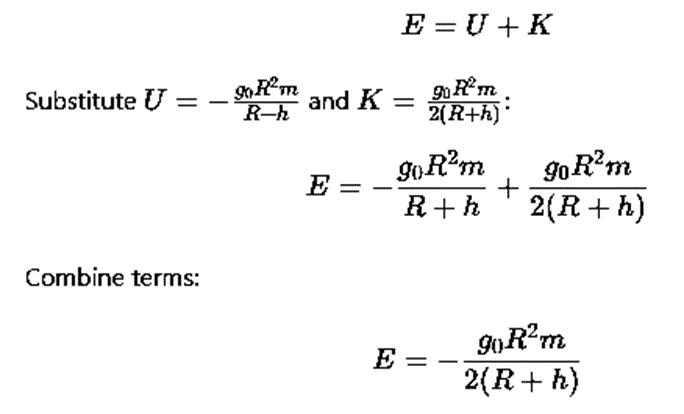
Q4: Starting from the centre of the earth having radius R, the variation of g (acceleration due to gravity) is shown by
(a) 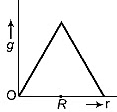
(b) 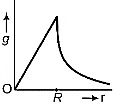
(c) 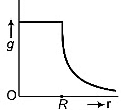
(d) 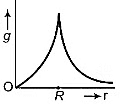 [2016]
[2016]
 View Answer
View Answer 
Since, acceleration due to gravity is given as
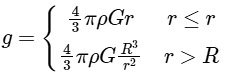
2015
Q1: Kepler's third law states that square of period of revolution (T) of a planet around the sun, is proportional to third power of average distance r between sun and planet i.e. T2 = Kr3. here K is constant.
If the masses of sun and planet are M and m respectively then as per Newton?s law of gravitation force of attraction between them isF= GMm/r2 , here G is gravitational constant. The relation between G and K is described as : [2015]
(a) K=1/G
(b) GK4π2
(c) GMK=4π2
(d) K=G
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (c)
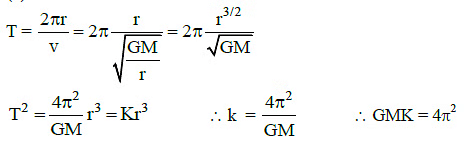
Q2: Two spherical bodies of mass M and 5 M and radii R and 2 R are released in free space with initial separation between their centres equal to 12 R. If they attract each other due to gravitational force only, then the distance covered by the smaller body before collision is : [2015]
(a) 1.5 R
(b) 2.5 R
(c) 4.5 R
(d) 7.5 R
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (d)
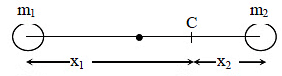
Let centre of mass C at a distance x1 from m1 and x2 from m2
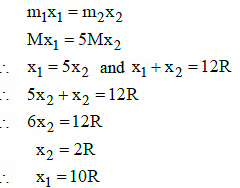
Since the masses are moving under mutual attraction the position of centre of mass remains constant.
When the masses are in contact, let x'1 and x'2 be the distance of their centres from the centre of mass.
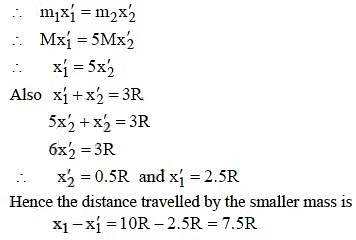
Q3: A remote-sensing satellite of earth revolves in a circular orbit at a height of 0.25 × 106 m above the surface of earth. If earth's radius is 6.38 × 106 m and g = 9.8 ms−2, then the orbital speed of the satellite is [2015]
(a) 9.13 km s−1
(b) 6.67 km s−1
(c) 7.76 km s−1
(d) 8.56 km s−1
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (c)
The orbital speed of the satellite is
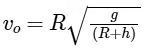
where R is the earth’s radius, g is the acceleration due to gravity on earth’s surface and h is the height above the surface of earth.
Here, R = 6.38 × 106m, g = 9.8 m s–2and h = 0.25 × 106m
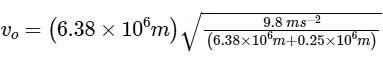
= 7.76 × 103 m s–1 = 7.76 km s–1
Q4: A satellite S is moving in an elliptical orbit around the earth. The mass of the satellite is very small compared to the mass of the earth. Then,
(a) the linear momentum of S remains constant in magnitude.
(b) the acceleration of S is always directed towards the centre of the earth.
(c) the angular momentum of S about the centre of the earth changes in direction, but its magnitude remains constant.
(d) the total mechanical energy of S varies periodically with time. [2015]
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (b)
The gravitational force on the satellite will be aiming towards the centre of the earth so acceleration of the satellite will also be aiming towards the centre of the earth.
2014
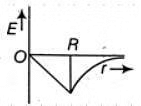
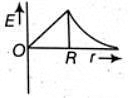
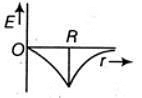
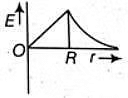
Q1: Dependence of intensity of gravitational field (E) of earth with distance (r) from centre of earth is correctly represented by: [2014]
(a)
 (b)
(b)
 (c)
(c)
 (d)
(d)
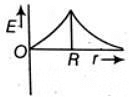
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (b)
For a point inside the earth i.e. r < R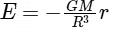 where M and R be mass and radius of the earth respectively. At the centre, r = 0
where M and R be mass and radius of the earth respectively. At the centre, r = 0
For a point outside the earth i.e. r > R,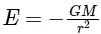 On the surface of the earth i.e, r = R
On the surface of the earth i.e, r = R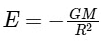 The variation of E with distance r from the centre is as shown in the figure.
The variation of E with distance r from the centre is as shown in the figure.
Q2: A block hole is an object whose gravitational field is so strong that even light cannot escape from it. To what approximate radius would earth (mass = 5.98 × 1024 kg) have to be compressed to be a black hole ? [2014]
(a) 10−2 m
(b) 100 m
(c) 10-9 m
(d) 10-6m
 View Answer
View Answer 
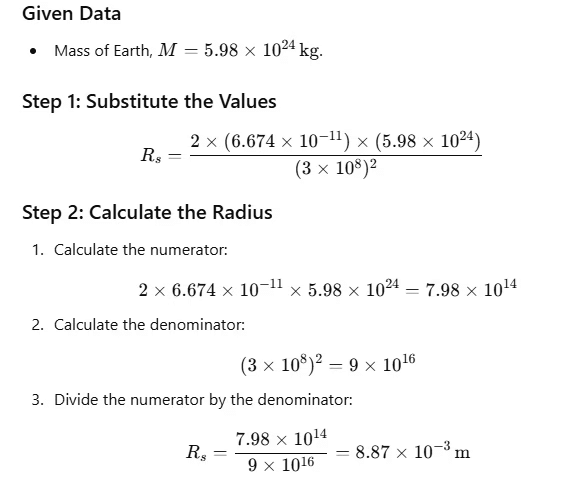
|
119 videos|494 docs|98 tests
|
FAQs on NEET Previous Year Questions (2014-2025): Gravitation - Physics Class 11
| 1. What is the universal law of gravitation and how does it apply to celestial bodies? |  |
| 2. How do gravitational forces affect the motion of planets in our solar system? |  |
| 3. What is the difference between mass and weight in the context of gravitation? |  |
| 4. How does gravity affect the shape of celestial bodies, such as planets and stars? |  |
| 5. What is gravitational potential energy and how is it related to height? |  |

















