NEET Previous Year Questions (2014-2025): Amines | Chemistry Class 12 PDF Download
2025
Q1: The correct order of decreasing basic strength of the given amines is: (NEET 2025)
(a) N-ethylethanamine > ethanamine > N -methylaniline > benzenamine
(b) benzenamine > ethanamine > N -methylaniline >N-ethylethanamine
(c) N -methylaniline > benzenamine > ethanamine >N-ethylethanamine
(d) N-ethylethanamine > ethanamine > benzenamine >N-methylaniline
Ans: (a)
Lower is the value of pKb, higher is the basicity.
Also, aliphatic amines are stronger bases than aromatic amines.
pKb : Benzenamine > N-Methylaniline > Ethanamine > N-Ethylethanamine
Basic strength : N-Ethylethanamine > Ethanamine > N-Methylaniline > Benzenamine
- N-methylaniline: The nitrogen is part of an aromatic ring, and the lone pair of electrons on nitrogen is delocalized into the ring through resonance, reducing its availability for protonation. This makes it less basic.
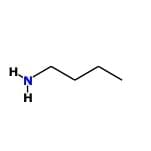
- Benzenamine: Similar to N-methylaniline, its lone pair is delocalized into the aromatic ring, making it less basic than aliphatic amines.
- Ethanamine: This is a simple aliphatic amine where the lone pair on nitrogen is readily available for protonation. It is more basic than aromatic amines.
- N-ethylethanamine: This is a secondary aliphatic amine, and the presence of two alkyl groups provides a stronger inductive effect, increasing the availability of the lone pair. It is the most basic among the given compounds.
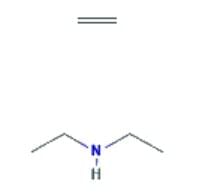
- The correct order of decreasing basic strength is N-ethylethanamine > ethanamine > N-methylaniline > benzenamine
Q2: Given below are two statements: (NEET 2025)
Statement I: Benzenediazonium salt is prepared by the reaction of aniline with nitrous acid at 273 - 278 K. It decomposes easily in the dry state
Statement II: Insertion of iodine into the benzene ring is difficult and hence iodobenzene is prepared through the reaction of benzenediazonium salt with KI.
In the light of the above statements, choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below:
(a) Statement I is correct; Statement II is incorrect
(b) Statement I is incorrect; Statement II is correct
(c) Both Statement I and Statement II are correct
(d) Both Statement I and Statement II are incorrect
Ans: (c)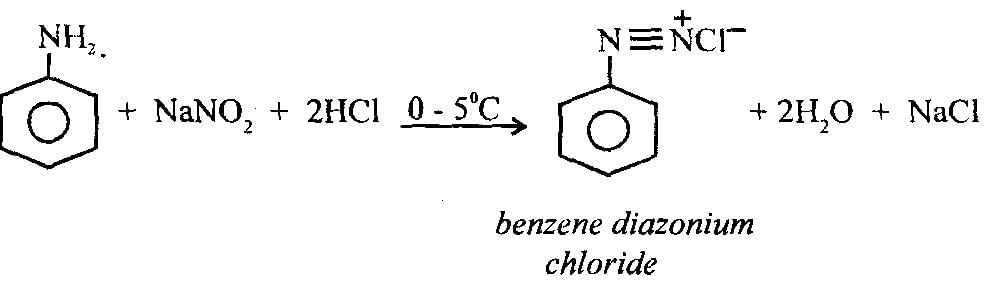
Statement I:
- Benzenediazonium salt is indeed prepared by the reaction of aniline with nitrous acid at 273–278 K.
- It is unstable in the dry state, decomposing readily due to the release of nitrogen gas.
- Hence, Statement I is correct.
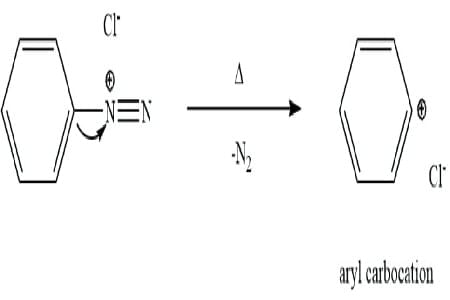
- Statement II:
- Iodine insertion directly into the benzene ring is challenging due to iodine's low reactivity.
- Iodobenzene can be efficiently prepared via the reaction of benzenediazonium salt with KI, as the diazonium group facilitates substitution with iodine.
- Hence, Statement II is correct.
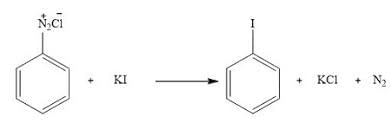
Therefore, both Statement I and Statement II are correct.
2024
Q1: Given below are two statements: (NEET 2024)Statement I : Aniline does not undergo Friedel-Crafts alkylation reaction.
Statement II : Aniline cannot be prepared through Gabriel synthesis.
In the light of the above statements, choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) Both statement I and Statement II are true
(b) Both Statement I and Statement II are false
(c) Statement I is correct but Statement II is false
(d) Statement I is incorrect but Statement II is true
Ans: (a)
- Aniline does not undergo Friedel-Crafts alkylation reaction due to salt formation with aluminium chloride, the Lewis acid, which is used as a catalyst.
- Aniline (aromatic primary amine) cannot be prepared by Gabriel phthalimide synthesis because aryl halides do not undergo nucleophilic substitution with anion formed by phthalimide.
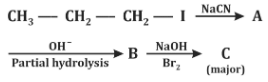
Q2: Identify the major product C formed in the following reaction sequence. (NEET 2024)
 (a) Butylamine
(a) Butylamine
(b) Butanamide
(c) α-Bromobutanoic acid
(d) Propylamine
Ans: (d)
Step 1:
CH₃–CH₂–CH₂–I + NaCN → CH₃–CH₂–CH₂–CN
- This is a nucleophilic substitution reaction (SN2).
- Product A = Butyl cyanide (Butanenitrile)
Step 2:
CH₃–CH₂–CH₂–CN → Partial hydrolysis → CH₃–CH₂–CH₂–CONH₂
- Nitrile undergoes partial hydrolysis (controlled conditions) to give amide.
- Product B = Butanamide
Step 3:
CH₃–CH₂–CH₂–CONH₂ + Br₂/NaOH → CH₃–CH₂–CH₂–NH₂
- This is the Hofmann bromamide reaction (converts amides to amines with loss of one carbon atom).
- Final product C = Propylamine
Final Answer: (d) Propylamine
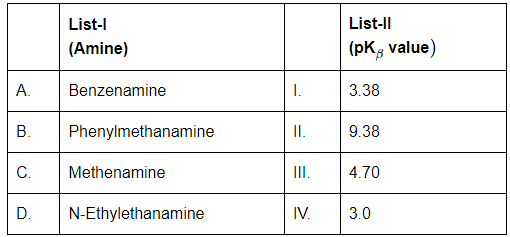
Q3: Match List-I with List-II (NEET 2024)
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A-II, B-III, C-I, D-IV
(b) A-III, B-II, C-I, D-IV
(c) A-II, B-I, C-III, D-IV
(d) A-I, B-III, C-II, D-IV
Ans: (b)
A. Benzenamine (Aniline)
- Aromatic amine; lone pair on nitrogen is delocalized into the benzene ring → less available for protonation.
- Therefore, it's a weak base.
- pK₍ᵦ₎ ≈ 4.70 → Matches with III
B. Phenylmethanamine (Benzylamine)
- The -NH₂ group is not directly attached to the benzene ring (it's on a CH₂ group), so the electron pair is not delocalized.
- Thus, it's a stronger base than aniline.
- pK₍ᵦ₎ ≈ 9.38 → Matches with II
C. Methenamine (Hexamethylenetetramine)
- It’s a weak base due to steric hindrance and resonance.
- pK₍ᵦ₎ ≈ 3.38 → Matches with I
D. N-Ethylethanamine (Diethylamine)
- Aliphatic amine with two ethyl groups; inductive effect increases basicity.
- But slightly lower than benzylamine.
- pK₍ᵦ₎ ≈ 3.0 → Matches with IV
Hence Finale Answer is (b) A-III, B-II, C-I, D-IV
Q4: Match List-I with List-II (NEET 2024)
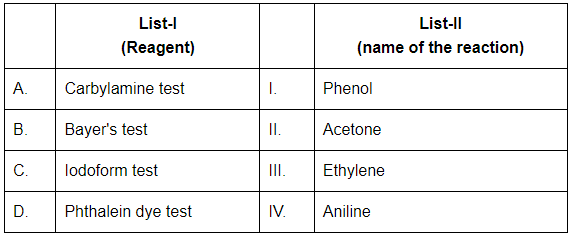
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A-IV, B-III, C-II, D-I
(b) A-IV, B-II, C-III, D-I
(c) A-IV, B-II, C-I, D-III
(d) A-II, B-III, C-I, D-IV
Ans: (a)
A. Carbylamine test → IV. Aniline
- The Carbylamine test is used to detect primary amines like aniline (C₆H₅NH₂).
- When treated with chloroform and alcoholic KOH, it produces an offensive-smelling isocyanide.
B. Bayer's test → III. Ethylene
- Bayer's test uses alkaline potassium permanganate to detect unsaturation (double/triple bonds) like in ethylene (C₂H₄).
- A purple KMnO₄ solution gets decolorized in the presence of an alkene.
C. Iodoform test → II. Acetone
- The Iodoform test detects compounds with the structure CH₃CO– or CH₃CH(OH)–, like acetone (CH₃COCH₃).
- It gives a yellow precipitate of iodoform (CHI₃).
D. Phthalein dye test → I. Phenol
- The Phthalein dye test is used for phenols.
- Phenol reacts with phthalic anhydride in acidic medium to form phenolphthalein, which is a pH indicator.
So, the correct match is: A–IV, B–III, C–II, D–I → Option (a)
Q5: Given below are two statements: (NEET 2024)
Statement I: Benzenediazonium chloride is a colourless crystalline solid. It is insoluble in water but reacts with water when warmed.
Statement II: Benzenediazonium chloride on reacting with HCl in presence of copper powder gives chlorobenzene as the product. This is an example of Gattermann reaction.
In the light of the above statements, choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) Both Statement I and Statement II are true
(b) Both Statement I and Statement II are false
(c) Statement I is true but Statement II is false
(d) Statement I is false but Statement II is true
Ans: (c)
Statement I: "Benzenediazonium chloride is a colourless crystalline solid. It is insoluble in water but reacts with water when warmed." This statement is true. Benzenediazonium chloride is indeed a colourless solid and is known to be insoluble in cold water but can hydrolyze upon warming, leading to the formation of phenol and nitrogen gas.
Statement II: "Benzenediazonium chloride on reacting with HCl in presence of copper powder gives chlorobenzene as the product. This is an example of Gattermann reaction." This statement is false. The reaction of benzenediazonium chloride with HCl and copper powder produces chlorobenzene, but it is not a Gattermann reaction. The Gattermann reaction typically involves the formylation of aromatic compounds, not the formation of chlorobenzene from diazonium salts.
Since Statement I is true and Statement II is false, the correct answer is (d): "Statement I is true but Statement II is false."
Q6: The compound that does not undergo Friedel-Crafts alkylation reaction but gives a positive carbylamine test is: (NEET 2024)
(a) Aniline
(b) Pyridine
(c) N-Methylaniline
(d) Triethylamine
Ans: (a)
Friedel-Crafts Alkylation Reaction is an electrophilic substitution reaction. It requires a Lewis acid catalyst (like AlCl₃) and an electron-rich aromatic ring.
Aniline (C₆H₅NH₂) has an amino group (-NH₂) that is strongly electron-donating through resonance, making the ring electron-rich, but:
- The lone pair on nitrogen of aniline reacts with AlCl₃, forming a complex.
- This deactivates the aromatic ring, preventing the Friedel-Crafts reaction from occurring.
Aniline does give a positive carbylamine test:
- Carbylamine test is used to detect primary amines.
- Aniline is a primary aromatic amine and reacts with chloroform (CHCl₃) and alc. KOH to produce foul-smelling isocyanide, confirming a positive test.
So, Aniline fails Friedel-Crafts alkylation but passes the carbylamine test, making option (a) the correct answer.
2023
Q1: Which of the following reactions will NOT give primary amine as the product? (NEET 2023)(a)
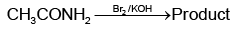
(b)
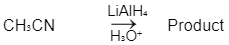
(c)
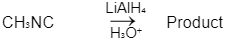
(d)
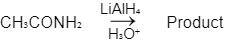
Ans: C
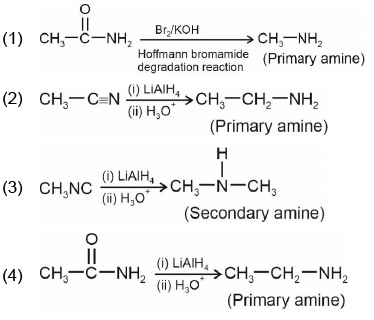
Q2: Identify the product in the following reaction: (NEET 2023)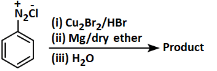
(a) 
(b) 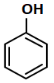
(c) 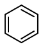
(d) 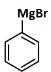
Ans: (c)
Reagents:
- Cu₂Br₂/HBr — This is used in Sandmeyer reaction to replace –N₂⁺ with Br, forming bromobenzene.
- Mg/dry ether — Converts bromobenzene to phenyl magnesium bromide (Grignard reagent).
- H₂O — On hydrolysis, the Grignard reagent gives benzene.
Step-by-step:
- Aniline → diazonium salt → bromobenzene (via Sandmeyer)
- Bromobenzene → phenyl MgBr (via Mg)
- Phenyl MgBr + H₂O → benzene
Q3: The least basic compounds/species among the following is: (NEET 2023)
(a) 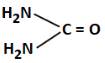
(b) 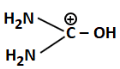
(c) 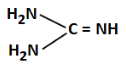
(d) 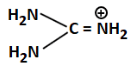
Ans: (b)
We are comparing basicity among different compounds with amino groups.
(a) Guanidine derivative with a carbonyl (=O) — moderately basic
(b) Has a positive charge on carbon and –OH; very unstable and least likely to donate lone pair, hence least basic
(c) Iminoguanidine — contains imine (=NH), relatively more basic
(d) A guanidinium ion — stabilized by resonance, still more basic than (b)
Correct Answer: (b) — least basic due to positive charge on C and low electron availability
Q4: Which of the following is the correct sequence of reagents for converting 4-nitrotoluene to 2-bromotoluene? (NEET 2023)
(a) NaNO₂/HCl; Sn/HCl; Br₂; H₂O/H₃PO₂
(b) Sn/HCl; NaNO₂/HCl; Br₂; H₂O/H₃PO₂
(c) Br₂; Sn/HCl; NaNO₂/HCl; H₂O/H₃PO₂
(d) Sn/HCl; Br₂; NaNO₂/HCl; H₂O/H₃PO₂
Ans: (c)
Step-by-step reasoning:
Bromination first (Br₂):
- Bromination of 4-nitrotoluene occurs electrophilically.
- Due to the deactivating, meta-directing nature of the –NO₂ group, Br goes to the position ortho to –CH₃, i.e., 2-position.
Reduction (Sn/HCl):
Now reduce –NO₂ to –NH₂, converting nitro group to amine.
Diazotization (NaNO₂/HCl):
Convert –NH₂ to diazonium salt.
Hydro-de-diazoniation (H₂O/H₃PO₂):
Use H₃PO₂ to remove the diazonium group, forming 2-bromotoluene.
Therefore, correct sequence is: Br₂ → Sn/HCl → NaNO₂/HCl → H₂O/H₃PO₂
2022
Q1: Given below are two statements
Statement I: Primary aliphatic amines react with HNO2 to give unstable diazonium salts.
Statement II: Primary aromatic amines react with HNO2 to form diazonium salts which are stable even above 300 K. In the light of the above statements, choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below (NEET 2022)
(a) Statement I is correct but Statement II is incorrect.
(b) Statement I is incorrect but Statement II is correct.
(c) Both Statement I and Statement II are correct.
(d) Both Statement I and Statement II are incorrect.
Ans: (a)
Statement II is incorrect. The aromatic diazonium salts are unstable above 300 K.
Q2: The product formed from the following reaction sequence is (NEET 2022)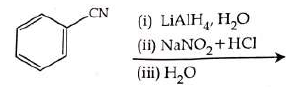
(a) 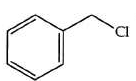
(b) 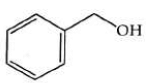
(c) 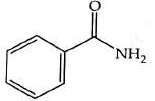
(d) 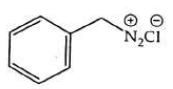
Ans: (b)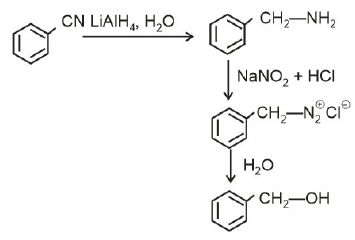
2021
Q1: Identify the compound that will react with Hinsberg's reagent to give a solid which dissolves in alkali. (NEET 2021)
(a)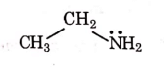
(b)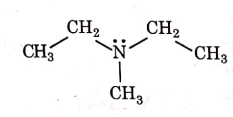
(c)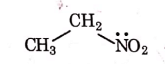
(d)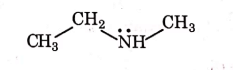
Ans: (a)
1° amines react with Hingsberg's reagent to give a solid, which dissolve in alkali.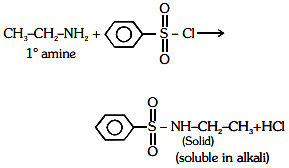
Q2: The reagent 'R' in the given sequence of a chemical reaction is : (NEET 2021)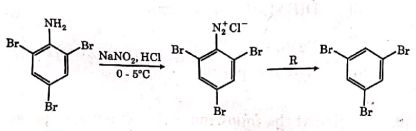
(a) HI
(b) CuCN/KCN
(c) H2O
(d) CH3CH2OH
Ans: (d)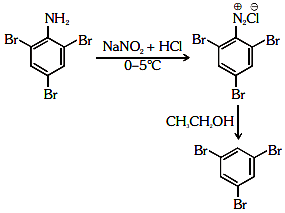
R : CH3CH2OH
Certain mild reducing agents like hypophosphorus acid or ethanol reduce diazonium salts to arene and themselves get oxidised to phosphorous acid and ethanal respectively.
2020
Q1: Which of the following amine will give the carbylamine test? (NEET 2020)
(a)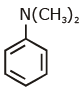
(b)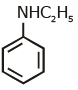
(c)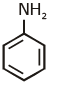
(d)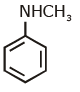
Ans: (c)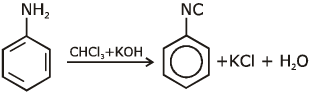 Carbylamine reaction is give by 1° amine & aniline.
Carbylamine reaction is give by 1° amine & aniline.
2019
Q1: The correct order of the basic strength of methyl substituted amines in aqueous solution is: (NEET 2019)
(a) (CH3)2NH > CH3NH2 > (CH3)3N
(b) (CH3)3N > CH3NH2 > (CH3)2NH
(c) (CH3)3N > (CH3)2NH > CH3NH2
(d) CH3NH2 > (CH3)2NH > (CH3)3N
Ans: (a)
In aqueous solution, electron donating inductive effect, solvation effect (H-bonding) and steric hindrance all together affect basic strength of substituted amines
Basic character: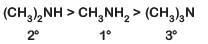
2018
Q1: Nitration of aniline in strong acidic medium also gives m-nitroaniline because (NEET 2018)
(a) In spite of substituents nitro group always goes to only m-position.
(b) In electrophilic substitution reactions amino group is meta directive.
(c) In absence of substituents nitro group always goes to m-position
(d) In acidic (strong) medium aniline is present as anilinium ion.
Ans: (b)
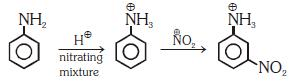 In acidic medium aniline is protonated to form anilinium ion which is meta directing.
In acidic medium aniline is protonated to form anilinium ion which is meta directing.
2017
Q1: Which of the following reactions is appropriate for converting acetamide to methanamine? (NEET 2017)
(a) Hoffmann bromamide reaction
(b) Stephens reaction
(c) Gabriel phthalimide synthesis
(d) Carbylamine reaction
Ans: (a)
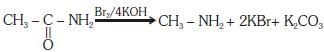
This reaction is known as hoffmann bromamide reaction.
2016
Q1:The correct statement regarding the basicity of arylamines is : (NEET 2016)
(a) Arylamines are generally more basic than alkylamines, because the nitrogen atom in arylamines is sp-hybridized.
(b) Arylamines are generally less basic than alkylamines because the nitrogen lone pair electrons are delocalized by interaction with the aromatic ring π electrons system.
(c) Arylamines are generally more basic than alkylamines because the nitrogen lone pair electrons are not delocalized by interaction with the aromatic ring π electron system.
(d) Arylamines are generally more basic than alkylamines because of aryl group
Ans: (b)
In arylamines, lone pair of electrons on nitrogen atom is delocalised over the benzene ring, thus, not available for donation. So, arylamines are less basic than alkylamines.
2015
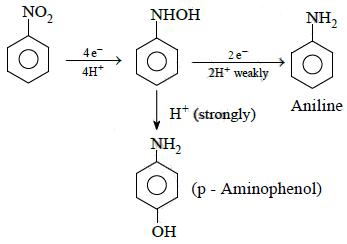
Q1: The electrolytic reduction of nitrobenzene in strongly acidic medium produces: (NEET 2015)
(a) Aniline
(b) p-Aminophenol
(c) Azoxybenzene
(d) Azobenzene
Ans: (b)
Electrolytic reduction of nitrobenzene in weakly acidic medium gives aniline but in strongly acidic medium, it gives para-amino phenol obviously through the acid catalysed rearrangement of initially formed phenyl hydroxyl amine.
2014
Q1: In the following reaction, the product (A) (NEET 2014)
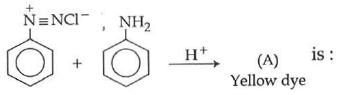
(a)
(b)
(c)
(d)
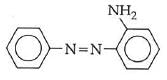
Ans: (b)
The above reaction is a coupling reaction of aniline with diazonium salt to give azo benzene compound. This coupling reaction takes place at the para-position to - NH2 group of benzene. This reaction act as electrophilic substitution reaction of aniline.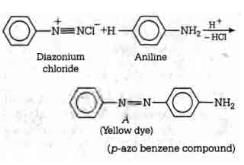
Q2: Which of the following will be most stable diazonium salt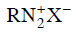 ? (NEET 2014)
? (NEET 2014)
(a)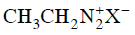
(b)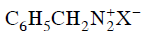
(c)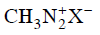
(d)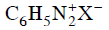
Ans: (d)
Diazonium salt containing aryl group directly linked to the nitrogen atom is most stable due to resonance stabilization between the benzene nucleus and N-atom.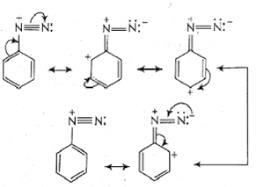 [Resonance structure of benzene diazonium ion]
[Resonance structure of benzene diazonium ion]
|
75 videos|278 docs|78 tests
|
FAQs on NEET Previous Year Questions (2014-2025): Amines - Chemistry Class 12
| 1. What are the different types of amines? |  |
| 2. How do you identify amines in organic compounds? |  |
| 3. What is the basicity of amines and how does it compare to ammonia? |  |
| 4. What are the common uses of amines in everyday products? |  |
| 5. How do amines react with acids? |  |






















