NEET Previous Year Questions (2016-2024): Organisms & Populations | Biology Class 12 PDF Download
2024
Q1: Given below are two statements: (NEET 2024)
Statement I : Gause’s ‘Competitive Exclusion Principle’ states that two closely related species competing for the same resources cannot co-exist indefinitely and competitively inferior one will be eliminated eventually.
Statement II : In general, carnivores are more adversely affected by competition than herbivores.
In the light of the above statements, choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) Both Statement I and Statement II are true.
(b) Both Statement I and Statement II are false.
(c) Statement I is correct Statement II is false.
(d) Statement I is incorrect but Statement II is true.
Ans: (c)
Gause's 'Competitive Exclusion Principle' states that two closely related species competing for the same resources cannot co-exist indefinitely and the competitively inferior one will be eliminated eventaully. Thus, statement I is correct.
Statement II is incorrect as in general, herbivores and plants appear to be more adversely affected by competition than carnivores.
Q2: The equation of Verhulst-Pearl logistic growth is 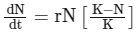 . From this equation, K indicates: (NEET 2024)
. From this equation, K indicates: (NEET 2024)
(a) Intrinsic rate of natural increase
(b) Biotic potential
(c) Carrying capacity
(d) Population density
Ans: (c)
Sol: The Verhulst-Pearl logistic growth equation you've presented is a fundamental model used to describe how populations grow under limited resource conditions. This model is sensitive to both the variables and coefficients it incorporates: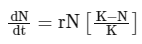 Here:
Here:
N represents the population size at time t.
r is the intrinsic rate of natural increase, indicating the rate at which the population grows per individual when resources are not limiting.
K represents the carrying capacity of the environment.
In the context of this equation:
The term 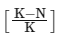 is a fraction that reduces the effective growth rate as the population size N approaches the carrying capacity K. This term essentially represents the remaining proportion of resources available as the population grows larger.
is a fraction that reduces the effective growth rate as the population size N approaches the carrying capacity K. This term essentially represents the remaining proportion of resources available as the population grows larger.
Based on this understanding:
Option A: "Intrinsic rate of natural increase" – Incorrect, this is represented by r in the equation.
Option B: "Biotic potential" – Incorrect, biotic potential generally refers to the maximum reproductive capacity of an organism under optimal conditions, often considered similar to r but not specifically the same as K.
Option C: "Carrying capacity" – Correct, as K in the equation is specifically describing the carrying capacity, which is the maximum population size that the environment can sustain indefinitely given the food, habitat, water, and other necessities available in the environment. Option D: "Population density" – Incorrect, while N relates directly to population density at any time, K is about the upper limit of that density sustainable by the environment. Therefore, Option C is the correct answer. The variable K in the Verhulst-Pearl logistic growth equation indeed stands for the carrying capacity.
2023
Q1: Match List I with List II. (NEET 2023)
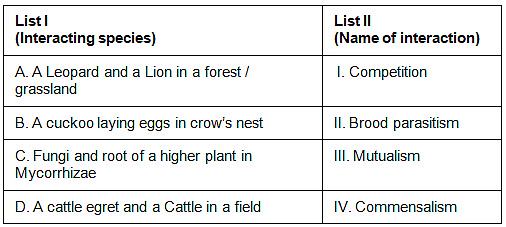
Choose the correct answer from the options given below.
(a) A-I, B-II, C-III, D-IV
(b) A-I, B-II, C-IV, D-III
(c) A-III, B-IV, C-I, D-II
(d) A-II, B-III, C-I, D-IV
Ans: (a)
- A leopard and a lion in a forest/grassland (A) : These two species are predators that hunt in the same environment and likely compete for the same prey. This is an example of competition (I).
- A cuckoo laying an egg in a crow's nest (B) : The cuckoo is known for laying its eggs in the nests of other birds, such as crows. The crow then raises the cuckoo's young, often at the expense of its own offspring. This is a form of brood parasitism (II).
- Fungi and the root of a higher plant in mycorrhizae (C) : Mycorrhizae are symbiotic relationships between fungi and plant roots, in which the fungi help the plant absorb water and nutrients from the soil, while the plant provides the fungi with carbohydrates. This is an example of mutualism (III).
- A cattle egret and a cattle in a field (D) : Cattle egrets are often seen near cattle, feeding on the insects that the cattle stir up as they move and graze. The egret benefits from this interaction (by getting easy access to food), while the cattle are unaffected. This is an example of commensalism (IV).
Given this information, the correct match is :
Option D : A-I, B-II, C-III, D-IV
Q2: Match List I with List II. (NEET 2023)
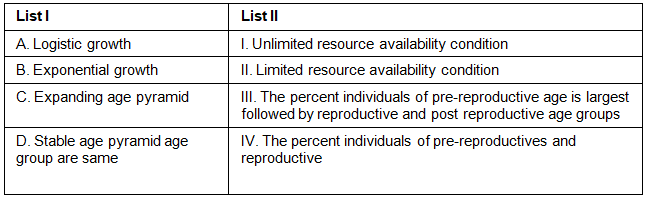
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
- (a) A-II, B-I, C-III, D-IV
(b) A-II, B-III, C-I, D-IV
(c) A-II, B-IV, C-I, D-III
(d) A-II, B-IV, C-III, D-I
Ans: (a)
Logistic growth (A) is a type of population growth that occurs under conditions of limited resources (II). - Exponential growth (B) is a type of population growth that occurs under conditions of unlimited resources (I).
- An expanding age pyramid (C) represents a population where the percentage of individuals in the pre-reproductive age group is the largest, followed by the reproductive and post-reproductive age groups (III).
- A stable age pyramid (D) represents a population where the percentage of individuals in the pre-reproductive and reproductive age groups are approximately equal (IV).
So, the correct match is : A-II, B-I, C-III, D-IV.
2022
Q1: Which one of the following statements cannot be connected to Predation? (NEET 2022)
(a) It might lead to extinction of a species
(b) Both the interacting species are negatively impacted
(c) It is necessitated by nature to maintain the ecological balance
(d) It helps in maintaining species diversity in a community
Ans: (b)
One of the species in predation gains benefit on the expense of the other. Predators help in maintaining species diversity in a community, by reducing the intensity of competition among competing prey species. If a predator is too efficient and overexploits its prey, then the prey might become extinct.
Q2: While explaining interspecific interaction of population, (+) sign is assigned for beneficial interaction, (−) sign is assigned for detrimental interaction and (0) for neutral interaction. Which of the following interactions can be assigned (+) for one species and (−) for another species involved in the interaction? (NEET 2022)
(a) Amensalism
(b) Commensalism
(c) Competition
(d) Predation
Ans: (d)
In predation, one species is benefited where as the other is harmed. It is (+ −) type of population interaction.
Q3: If '8' Drosophila in a laboratory population of '80' died during a week, the death rate in the population is ____ individuals per Drosophila per week. (NEET 2022)
(a) 10
(b) 1.0
(c) zero
(d) 0.1
Ans: (d)
If 8 Drosophila in a laboratory population of 80 died during a week, the death rate in the population is 8/80 = 0.1 individuals per Drosophila per week.
2021
Q1: Inspite of interspecific competition in nature, which mechanism the competing species might have evolved for their survival? (NEET 2021)
(a) Mutualism
(b) Predation
(c) Resource partitioning
(d) Competitive release
Ans: (c)
- Inspite of interspecific competition the competing species may co-exist by doing resource partitioning.
- In mutualism two organisms are equally benefitted.
- In predation one organism (Predator) eats the another one (Prey).
- In competition release there occurs dramatical increase in population of a less distributed species when its superior competitor is removed.
Q2: Amensalism can be represented as: (NEET 2021)
(a) Species A (-) : Species B (-)
(b) Species A (+) : Species B (0)
(c) Species A (-) : Species B (0)
(d) Species A (+) : Species B (+)
Ans: (c)
Amensalism is an interaction between two organisms of different species in which one species inhibits the growth of other species by secreting certain chemicals. The first species is neither get benefited nor harmed.
(+) : (0) interaction is observed in commensalism.
(+) : (+) interaction is observed in mutualism.
(−) : (−) interaction is seen in competition.
Q3: In the exponential growth equation Nt =N0ert, e represents : (NEET 2021)
(a) The base of natural logarithms
(b) The base of geometric logarithms
(c) The base of number logarithms
(d) The base of exponential logarithms
Ans: (a)
In the exponential growth equation
Nt = N0ert, e represents the base of natural logarithms
Nt = Population density after time t
N0 = Population density at time zero
r = Intrinsic rate of natural increase called biotic potential.
2020
Q1: Which of the following is not an attribute of a population? (NEET 2020)
(a) Mortality
(b) Species interaction
(c) Sex ratio
(d) Natality
Ans: (b)
Natality refers to the number of births during a given period in the population that are added to the initial density. Mortality is the number of deaths in the population during a given period. Population interaction is the interaction between different populations. It refers to the effects that the organisms in a community have on one another. The sex ratio is the ratio of males to females in a population.
Q2: The process of growth is maximum during (NEET 2020)
(a) Log phase
(b) Lag phase
(c) Dormancy
(d) Senescence
Ans: (a)
In exponential growth, the initial growth is slow (lag phase) and it increases rapidly thereafter at an exponential rate in log or exponential phase.
2019
Q1: Match Column-I with Column –II. (NEET 2019)
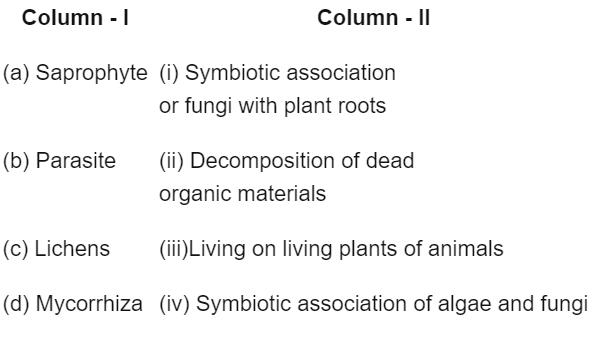
Choose the correct answer from the options given below :
(a) 
(b) 
(c) 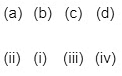
(d) 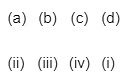
Ans: (d)
- A saprophyte is an organism that survives on dead and decaying organisms like fungi and decomposition bacteria.
- A parasite is an organism that survives on living plants and animals.
- A lichen is symbiotic association of algae & fungi.
- Mycorrhiza is a symbiotic association of fungi and roots of higher plants like pinus
2018
Q1: Which one of the following population interactions is widely used in medical science for the production of antibiotics? (NEET 2018)
(a) Commensalism
(b) Mutualism
(c) Parasitism
(d) Amensalism
Ans: (d)
In amensalism, one species is harmed whereas the other is unaffected. Antibiosis also shows this feature where the antibiotics released by the microbial group (Penicillium) Has affect on other microbes (such as Staphylococcus.
Q2: Natality refers to (NEET 2018)
(a) Death rate
(b) Birth rate
(c) Number of individuals leaving the habitat
(d) Number of individuals entering a habitat
Ans: (b)
Natality refers to the number of births during a given period in the population that are added to the initial density.
Q3: In a growing population of a country, (NEET 2018)
(a) Pre-reproductive individuals are more than the reproductive individuals
(b) Reproductive individuals are less than the post-reproductive individuals
(c) Reproductive and pre-reproductive individuals are equal in number
(d) Pre-reproductive individuals are less than the reproductive individuals
Ans: (a)
In a population where the number of pre-reproductive individuals or the younger individual is larger than the reproductive individuals, the population will increase.
2017
Q1: Asymptote in a logistic growth curve is obtained when (NEET 2017)
(a) K = N
(b) K > N
(c) K < N
(d) the value of 'r' approaches zero.
Ans: (a)
Solution.
Asymptote in a logistic growth curve is obtained when population density (N) reaches the carrying capacity (K), i.e., N = K.
Q2: Mycorrhizae are the example of (NEET 2017)
(a) Amensalism
(b) Antibiosis
(c) Mutualism
(d) Fungistasis.
Ans: (c)
Mycorrhiza is a mutualistic interaction between a fungus and roots of higher plants.
2016
Q1: If '+' sign is assigned to beneficial interaction, '-' sign to detrimental and 'O'sign to neutral interaction, then the population interaction requesented by '+' '-' refers to (NEET 2016 Phase 2)
(a) Mutualism
(b) Amensalism
(c) Commensalism
(d) Parasitism
Ans: (d)
Parasitism is an association in which one organism (the parasite) lives on (ectoparasitism) or in (endoparasitism) the body of another organism (host), from which it obtains its nutrients. This association is beneficial for the parasites as they get continuous supply of nutrients from their host and are able to rapidly multiply their numbers. But it is detrimental for the host organism as parasitic infection leads to various complications and diseases in the host body may also be fatal to the host under certain circumstances.
Q2: The principle of competitive exclusion was stated by (NEET 2016 Phase 2)
(a) C. Darwin
(b) G.f. Gause
(c) Mae Arthur
(d) Verhulst and Pearl
Ans: (b)
Two or more species with closely similar niche requirements cannot exist indefinitely in the same area as sooner or later they come into competition for possession of it. This is called as Cause’s competitive exclusion principle, which states that an ecological niche cannot be simultaneously and completely occupied by established populations of more than one species. Two species can live in same habitat but not in the same niche. More similar the two niches are, severe the competition is.
Q3: Gause's principle of competitive exclusion states that (NEET 2016 Phase 1)
(a) No two species can occupy the same niche indefinitely for the same limiting resources
(b) Larger organisms exclude smaller ones through competition
(c) More abundant species will exclude the less abundant species through competition
(d) Competition for the same resources exclude species having different food preferences
Ans: (a)
Gause’s principle of competitive exclusion can be restated to say that no two species can occupy the same niche indefinitely when resources are limiting. Certainly species can and do coexist while competing for some of the same resources. Nevertheless, Gause’s theory predicts that when two species coexist on a long-term basis, either resources must not be limited or their niches will always differ in one or more features; otherwise, one species will outcompete the other and the extinction of the second species will inevitably result, a process referred to as competitive exclusion.
Q4: When does the growth rate of a population following the logistic model equal zero? The logistic model is given as dN/dt = rN(1-N/K) (NEET 2016 Phase 1)
(a) When N/K equals zero
(b) When death rate is greater than birth rate
(c) When N/K is exactly one
(d) When N nears the carrying capacity of habitat.
Ans: (c)
In logistic growth model population growth equation is described as
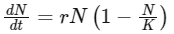
N = population density at time t;
r = Intrinsic rate of natural increase;
K = carrying capacity
When N/K = 1; 1 - N/K = 0
Therefore, dN/dt = 0
|
78 videos|277 docs|174 tests
|
FAQs on NEET Previous Year Questions (2016-2024): Organisms & Populations - Biology Class 12
| 1. What is the significance of studying organisms and populations in biology? |  |
| 2. How do biotic and abiotic factors influence populations? |  |
| 3. What are some common population dynamics models used in ecology? |  |
| 4. How do human activities impact organisms and their populations? |  |
| 5. What role does natural selection play in shaping populations? |  |

|
Explore Courses for NEET exam
|

|













