NCERT Exemplar: Straight Lines | Mathematics (Maths) for JEE Main & Advanced PDF Download
Q.1. Find the equation of the straight line which passes through the point (1, – 2) and cuts off equal intercepts from axes.
Ans. Intercept form of straight line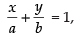 where a and b are the intercepts on the axis
where a and b are the intercepts on the axis
Given that a = b
∴ 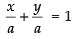 ...(i)
...(i)
If eq. (i) passes through the point (1, – 2), we get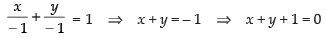
Hence, the required equation is x + y + 1 = 0.
Q.2. Find the equation of the line passing through the point (5, 2) and perpendicular to the line joining the points (2, 3) and (3, – 1).
Ans. Slope of the line joining the points (2, 3) and (3, – 1) is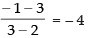
Slope of the required line which is perpendicular to it
Equation of the line passing through the point (5, 2) is
⇒ 4y – 8 = x – 5
⇒ x – 4y + 3 = 0
Hence, the required equation is x – 4y + 3 = 0.
Q.3. Find the angle between the lines y = (2 – √3) (x + 5) and y = (2 + √3 ) (x – 7).
Ans. The given equations are y = (2 - √3)(x + 5) ...(i)
and y = (2 + √3)(x - 7) ...(ii)
Slope of eq. (i) m1 (say) = (2 - √3)
and slope of eq. (ii) m2 (say) = (2 + √3)
Let θ be the angle between the two given lines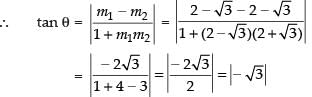
⇒ tan θ = √3 or - √3
∴ θ = 60° or 120°
Hence, the required angle is 60° or 120°.
Q.4. Find the equation of the lines which passes through the point (3, 4) and cuts off intercepts from the coordinate axes such that their sum is 14.
Ans. Equation of line having a and b intercepts on the axis is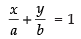 ...(i)
...(i)
Given that a + b = 14 ⇒ b = 14 – a
⇒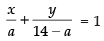 ...(ii)
...(ii)
If eq. (ii) passes through the point (3, 4) then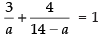
⇒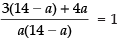
⇒ 42 + a = 14a – a2
⇒ a2 + a – 14a + 42 = 0
⇒ a2 – 13a + 42 = 0
⇒ a2 – 7a – 6a + 42 = 0
⇒ a(a – 7) – 6(a – 7) = 0
⇒ (a – 6)(a – 7) = 0
⇒ a = 6, 7
∴ b = 14 – 6 = 8, b = 14 – 7 = 7
Hence, the required equation of lines are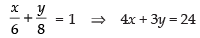
and 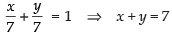
Q.5. Find the points on the line x + y = 4 which lie at a unit distance from the line 4x + 3y = 10.
Ans. Let (x1, y1) be any point lying in the equation x + y = 4
∴ x1 + y1 = 4 ...(i)
Distance of the point (x1, y1) from the equation 4x + 3y = 10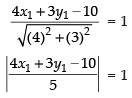
4x1 + 3y1 – 10 = ± 5
Taking (+) sign 4x1 + 3y1 – 10 = 5
⇒ 4x1 + 3y1 = 15 ...(ii)
From eq. (i) we get y1 = 4 – x1
Putting the value of y1 in eq. (ii) we get
4x1 + 3(4 – x1) = 15
⇒ 4x1 + 12 – 3x1 = 15
⇒ x1 + 12 = 15
⇒ x1 = 3 and y1 = 4 – 3 = 1
So, the required point is (3, 1)
Now taking (–) sign, we have
4x1 + 3y1 – 10 = – 5
⇒ 4x1 + 3y1 = 5 ...(iii)
From eq. (i) we get y1 = 4 – x1
⇒ 4x1 + 3(4 – x1) = 5
⇒ 4x1 + 12 – 3x1 = 5
⇒ x1 = 5 – 12 = – 7
and y1 = 4 – (– 7) = 11
So, the required point is (– 7, 11)
Hence, the required points on the given line are (3, 1) and (–7, 11).
Q.6. how that the tangent of an angle between the lines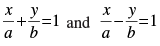 is
is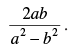
Ans.
Given that: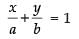 ...(i)
...(i)
and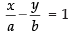 ...(ii)
...(ii)
Slope of eq. (i) m1 (say) =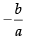
and slope of eq. (ii) m2 (say) =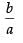
Let θ be the angle between the equation (i) and (ii)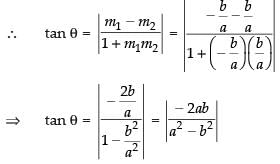
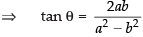
Hence proved.
Q.7. Find the equation of lines passing through (1, 2) and making angle 30° with y-axis.
Ans. Given that the line makes angle 30° with y-axis
∴ Angle made by the line with x-axis is 60°
∴ Slope of the line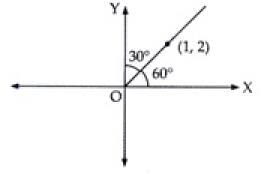
m = tan 60°
⇒ m = √3
So, the equation of the line passing through the point (1, 2) and slope √3 is
y – y1 = m(x – x1)
⇒ y – 2 = √3 (x - 1)
⇒ y – 2 = √3x - √3
⇒ y - √3x + √3 - 2 = 0
Hence, the required equation of line is y - √3x + √3 - 2 = 0.
Q.8. Find the equation of the line passing through the point of intersection of 2x + y = 5 and x + 3y + 8 = 0 and parallel to the line 3x + 4y = 7.
Ans. Given that: 2x + y = 5 ...(i)
x + 3y + 8 = 0 ...(ii)
3x + 4y = 7 ...(iii)
Equation of any line passing through the point of intersection of eq. (i) and eq. (ii) is
(2x + y – 5) + λ(x + 3y + 8) = 0 ...(iv) (λ = constant)
⇒ 2x + y – 5 + λx + 3λy + 8λ = 0
⇒ (2 + λ)x + (1 + 3λ)y – 5 + 8λ = 0
Slope of line m1 (say) =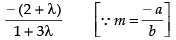
Now slope of line 3x + 4y = 7 is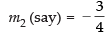
If eq. (iii) is parallel to eq. (iv) then
m1 = m2
⇒ 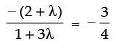
⇒ 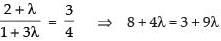
⇒ 9λ – 4λ = 5 ⇒ 5λ = 5 ⇒ l = 1
On putting the value of λ in eq. (iv) we get
(2x + y – 5) + 1(x + 3y + 8) = 0
⇒ 2x + y – 5 + x + 3y + 8 = 0
⇒ 3x + 4y + 3 = 0
Hence, the required equation is 3x + 4y + 3 = 0.
Q.9. For what values of a and b the intercepts cut off on the coordinate axes by the line ax + by + 8 = 0 are equal in length but opposite in signs to those cut off by the line 2x – 3y + 6 = 0 on the axes.
Ans. The given equation are ax + by + 8 = 0 ...(i)
and 2x – 3y + 6 = 0 ...(ii)
From eq. (i) we get,
ax + by + 8 = 0 ⇒ ax + by = – 8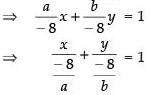
So, the intercepts on the axes are 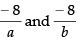
From eq. (ii), we get
2x – 3y + 6 = 0 ⇒ 2x – 3y = – 6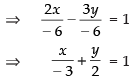
So, the intercepts are – 3 and 2.
According to the question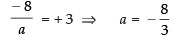
and 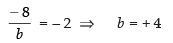
Hence, the required values of a and b are 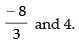
Q.10. If the intercept of a line between the coordinate axes is divided by the point (–5, 4) in the ratio 1 : 2, then find the equation of the line.
Ans. Let a and b be the intercepts on the given line.
∴ Coordinates of A and B are (a, 0) and (0, b) respectively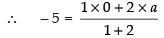
⇒ 2a = – 15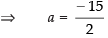
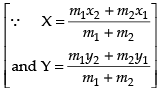
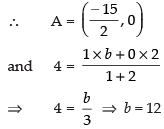
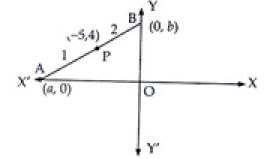
∴ B = (0, 12)
So, the equation of line AB is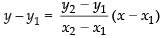
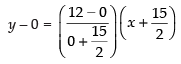
⇒ 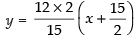
⇒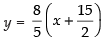
⇒ 5y = 8x + 60
⇒ 8x – 5y + 60 = 0
Hence, the required equation is 8x – 5y + 60 = 0.
Q.11. Find the equation of a straight line on which length of perpendicular from the origin is four units and the line makes an angle of 120° with the positive direction of x-axis.
[Hint: Use normal form, here ω =30°.]
Ans.
Given that:
OM = 4 units
∠BAX = 120°
∴ ∠BAO = 180° - 120°or ∠MAO = 60°
∠MOA + ∠MAO = 90° 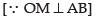
θ + 60° = 90°
∴ θ = 30°
So, equation of AB in its normal form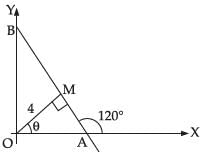
x cos θ + y sin θ = p
⇒ x cos 30° + y sin 30° = 4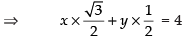
⇒ √3x + y = 8
Hence, the required equation is √3x + y = 8.
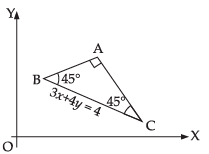
Q.12. Find the equation of one of the sides of an isosceles right angled triangle whose hypotenuse is given by 3x + 4y = 4 and the opposite vertex of the hypotenuse is (2, 2).
Ans. Given that equation of the hypotenuse is 3x + 4y = 4 and
opposite vertex is (2, 2)
Slope BC = -3/4
Let slope of AC be m
∴ 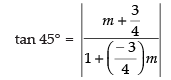
⇒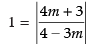
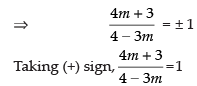
⇒ 4m + 3 = 4 – 3m
⇒ 7m = 1
⇒ m = 1/7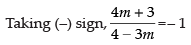
⇒ 4m + 3 = – 4 + 3m
⇒ 4m – 3m = – 3 – 4 ⇒ m = – 7
∴ Equation of AC with slope (1/7) is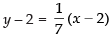
⇒ 7y – 14 = x – 2
⇒ x – 7y + 12 = 0
Equation of AC with slope (– 7) is
y – 2 = – 7(x – 2)
⇒ y – 2 = – 7x + 14
⇒ 7x + y – 16 = 0
Hence, the required equation are x – 7y + 12 = 0 and 7x + y – 16 = 0.
LONG ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
Q.13. If the equation of the base of an equilateral triangle is x + y = 2 and the vertex is (2, – 1), then find the length of the side of the triangle.
[Hint: Find length of perpendicular (p) from (2, – 1) to the line and use p = l sin 60°, where l is the length of side of the triangle].
Ans. Equation of the base AB of a ΔABC is x + y = 2
In ΔABD,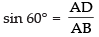
⇒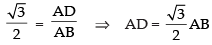
Length of perpendicular from A(2, – 1) to the line x + y = 2 is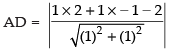
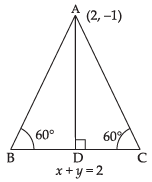
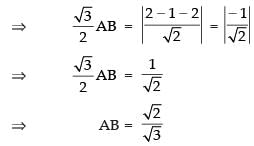
Hence, the required length of side =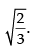
Q.14. A variable line passes through a fixed point P. The algebraic sum of the perpendiculars drawn from the points (2, 0), (0, 2) and (1, 1) on the line is zero. Find the coordinates of the point P.
[Hint: Let the slope of the line be m. Then the equation of the line passing through the fixed point P (x1, y1) is y – y1 = m (x – x1). Taking the algebraic sum of perpendicular distances equal to zero, we get y – 1 = m (x – 1). Thus (x1, y1) is (1, 1).]
Ans. Let (x1, y1) be the coordinates of the given point P and m be the slope of the line.
∴ Equation of the line is y – y1 = m(x – x1) ...(i)
Given points are A(2, 0), B(0, 2) and C(1, 1).
Perpendicular distance from A(2, 0) to the line (i) d1 (say)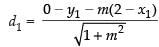
Perpendicular distance from B(0, 2) d2 (say)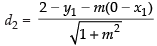
Similarly, perpendicular distance from C(1, 1) d3 (say)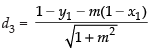
According to the question, we have
d1 + d2 + d3 = 0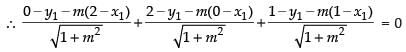
⇒ – y1 – 2m + mx1 + 2 – y1 + mx1 + 1 – y1 – m + mx1 = 0
⇒ 3mx1 – 3y1 – 3m + 3 = 0
⇒ mx1 – y1 – m + 1 = 0
Since the point (1, 1) satisfies the above equation.
Hence, the point (1, 1) lies on the line.
Q.15. In what direction should a line be drawn through the point (1, 2) so that its point of intersection with the line x + y = 4 is at a distance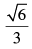 from the given point.
from the given point.
Ans.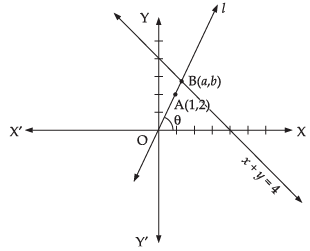
Let the given line x + y = 4 and required line ‘l’ intersect at B(a, b).
Slope of line ‘l’ is given by m =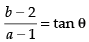 ...(i)
...(i)
Given that AB =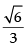
So, by distance formula for point A(1, 2) and B(a, b), we get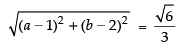
On squaring both the side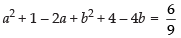
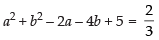 ...(ii)
...(ii)
Point B(a, b) also satisfies the eqn. x + y = 4
∴ a + b = 4 ...(iii)
On solving (ii) and (iii), we get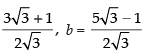
Putting values of a and b in eqn. (i), we have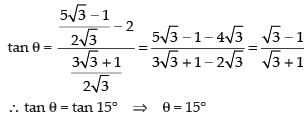
Q.16. A straight line moves so that the sum of the reciprocals of its intercepts made on axes is constant. Show that the line passes through a fixed point.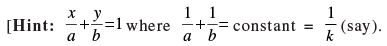 This implies that
This implies that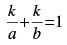
line passes through the fixed point (k, k).]
Ans. Intercepts form of a straight line is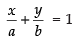
where a and b are the intercepts made by the line on the axes.
Given that: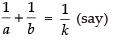
⇒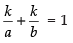
which shows that the line is passing through the fixed point (k, k).
Q.17. Find the equation of the line which passes through the point (– 4, 3) and the portion of the line intercepted between the axes is divided internally in the ratio 5 : 3 by this point.
Ans. Let AB be a line passing through a point (– 4, 3) and meets x-axis at A(a, 0) and y-axis at B(0, b).
∴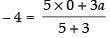
⇒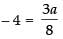
⇒ 3a = – 32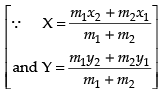
∴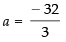
and 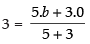
⇒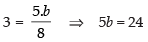
⇒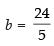
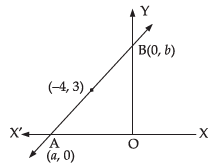
Intercept form of the line is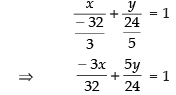
⇒– 9x + 20y = 96 ⇒ 9x - 20y + 96 = 0
Hence, the required equation is 9x - 20y + 96 = 0.
Q.18. Find the equations of the lines through the point of intersection of the lines x – y + 1 = 0 and 2x – 3y + 5 = 0 and whose distance from the point (3, 2) is 7/5.
Ans. Given equations are
x – y + 1 = 0 ...(i)
and 2x – 3y + 5 = 0 ...(ii)
Solving eq. (i) and eq. (ii) we get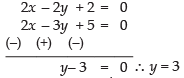
From eq. (i) we have x – 3 + 1 = 0 ⇒ x = 2
So, (2, 3) is the point of intersection of eq. (i) and eq. (ii).
Let m be the slope of the required line
∴ Equation of the line is
y – 3 = m(x – 2)
⇒ y – 3 = mx – 2m
⇒ mx – y + 3 – 2m = 0
Since, the perpendicular distance from (3, 2) to the line is 7/5 then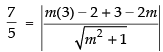
⇒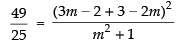
⇒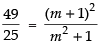
⇒ 49m2 + 49 = 25m2 + 50m + 25
⇒ 49m2 – 25m2 – 50m + 49 – 25 = 0
⇒ 24m2 – 50m + 24 = 0
⇒ 12m2 – 25m + 12 = 0
⇒ 12m2 – 16m – 9m + 12 = 0
⇒ 4m(3m – 4) – 3(3m – 4) = 0
⇒ (3m – 4)(4m – 3) = 0
⇒ 3m – 4 = 0 and 4m – 3 = 0
∴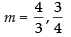
Equation of the line taking m = 4/3 is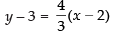
⇒ 3y – 9 = 4x – 8 ⇒ 4x - 3y + 1 = 0
Equation of the line taking m = 3/4 is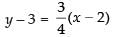
⇒ 4y – 12 = 3x – 6 ⇒ 3x - 4y + 6 = 0
Hence, the required equations are 4x - 3y + 1 = 0 and 3x - 4y + 6 = 0
Q.19. If the sum of the distances of a moving point in a plane from the axes is 1, then find the locus of the point.
[Hint: Given that 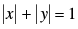 , which gives four sides of a square.]
, which gives four sides of a square.]
Ans. Let coordinates of a moving point P be (x, y).
Given that the sum of the distances from the axes to the point is always 1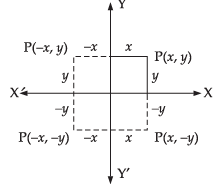
∴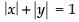
⇒ x + y = 1
⇒ – x – y = 1
⇒ – x + y = 1
⇒ x – y = 1
Hence, these equations gives us the locus of the point P which is a square.
Q.20. P1, P2 are points on either of the two lines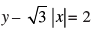 at a distance of 5 units from their point of intersection. Find the coordinates of the foot of perpendiculars drawn from P1, P2 on the bisector of the angle between the given lines.
at a distance of 5 units from their point of intersection. Find the coordinates of the foot of perpendiculars drawn from P1, P2 on the bisector of the angle between the given lines.
[Hint: Lines are y = √3 x + 2 and y = – √3 x + 2 according as x ≥ 0 or x < 0. y-axis is the bisector of the angles between the lines. P1, P2 are the points on these lines at a distance of 5 units from the point of intersection of these lines which have a point on y-axis as common foot of perpendiculars from these points. The y-coordinate of the foot of the perpendicular is given by 2 + 5 cos30°.]
Ans. Given lines are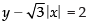
⇒ y - √3x = 2, if x ≥ 0 ...(i)
and y + √3x = 2, if x < 0 ...(ii)
Slope of eq. (i) is tan θ = √3 ∴ θ = 60°
Slope of eq. (ii) is tan θ = - √3 ∴ θ = 120°
Solving eq. (i) and eq. (ii) we get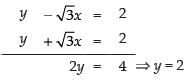
Putting the value of y is eq. (i) we get
x = 0
∴ Point of intersection of line (i) and (ii) is Q(0, 2)
∴ QO = 2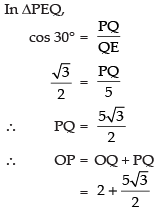
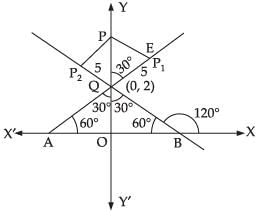
Hence, the coordinates of the foot of perpendicular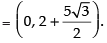
Q.21. If p is the length of perpendicular from the origin on the line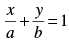 and a2, p2, b2 are in A.P, then show that a4 + b4 = 0.
and a2, p2, b2 are in A.P, then show that a4 + b4 = 0.
Ans. Given equation is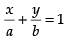
Since, p is the length of perpendicular drawn from the origin to the given line
∴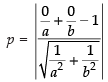
Squaring both sides, we have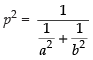
⇒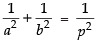 ...(i)
...(i)
Since a2, p2, b2 are in A.P.
∴ 2p2 = a2 + b2
⇒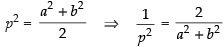
Putting the value of 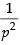 is eq. (i) we get,
is eq. (i) we get,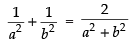
⇒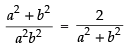
⇒ (a2 + b2)2 = 2a2b2
⇒ a4 + b4 + 2a2b2 = 2a2b2
⇒ a4 + b4 = 0.
Hence proved.
OBJECTIVE ANSWERS TYPE QUESTIONS
Q.22. A line cutting off intercept – 3 from the y-axis and the tengent at angle to the x-axis is 3/5, its equation is
(a) 5y – 3x + 15 = 0
(b) 3y – 5x + 15 = 0
(c) 5y – 3x – 15 = 0
(d) None of these
Ans. (a)
Solution.
Since the lines cut off intercepts – 3 on y-axis then the line is passing through the point (0, – 3).
Given that: tan θ = 3/5 ⇒ Slope of the line m = 3/5
So, the equation of the line is
y – y1 = m(x – x1)
⇒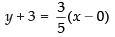
⇒ 5y + 15 = 3x
⇒ 3x – 5y – 15 = 0 ⇒ 5y - 3x + 15 = 0
Hence, the correct option is (a).
Q.23. Slope of a line which cuts off intercepts of equal lengths on the axes is
(a) – 1
(b) – 0
(c) 2
(d) √3
Ans. (a)
Solution.
Intercept form of a line is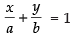
⇒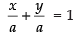 (∴ a = b)
(∴ a = b)
⇒ x + y = a
⇒ y = – x + a
∴ Slope is – 1
Hence, the correct option is (a).
Q.24. The equation of the straight line passing through the point (3, 2) and perpendicular to the line y = x is
(a) x – y = 5
(b) x + y = 5
(c) x + y = 1
(d) x – y = 1
Ans. (b)
Solution.
Eqn of line ‘l’ is given by
y – y1 = m(x – x1).
Since l passing through the point P(3, 2).
∴ y – 2 = m(x – 3)
⇒ y = mx + 2 – 3m ...(i)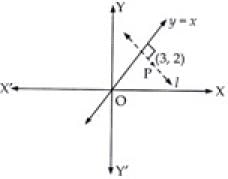
Since it is given that lines y = x and ‘l’ are perpendicular to each other,
∴ m × 1 = –1
[∴ m1 × m2 = –1]
m = –1
Put m = – 1 in eqn. (i), we get
y = –x + 2 – 3(–1)
y = –x + 5 x + y = 5
Hence, correct option is (b).
Q.25. The equation of the line passing through the point (1, 2) and perpendicular to the line x + y + 1 = 0 is
(a) y – x + 1 = 0
(b) y – x – 1 = 0
(c) y – x + 2 = 0
(d) y – x – 2 = 0
Ans. (b)
Solution.
Equation of any line perpendicular to the given
line x + y + 1 = 0 is x – y + k = 0 ...(i)
If eq. (i) passes through the point (1, 2) then
1 – 2 + k = 0 ⇒ k = 1
Putting the value of k is eq. (i) we have
x – y + 1 = 0 ⇒ y – x – 1 = 0
Hence, the correct option is (b).
Q.26. The tangent of angle between the lines whose intercepts on the axes are a, – b and b, – a, respectively, is
(a)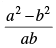
(b)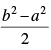
(c)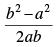
(d) None of these
Ans. (c)
Solution.
First equation of line having intercepts on the axes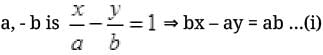
Second equation of line having intercepts on the axes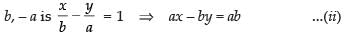
Slope of eq. (i) m1 = b/a
Slope of eq. (ii) m2 = a/b
∴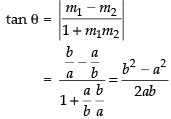
Hence, the correct option is (c).
Q.27. If the line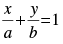 passes through the points (2, –3) and (4, –5), then (a, b) is
passes through the points (2, –3) and (4, –5), then (a, b) is
(a) (1, 1)
(b) (– 1, 1)
(c) (1, – 1)
(d) (– 1, –1)
Ans. (d)
Solution.
Equation of line passing through the points (2, – 3) and (4, – 5) is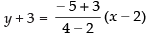
⇒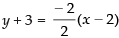
⇒ y + 3 = – (x – 2)
⇒ y + 3 = – x + 2
⇒ x + y = – 1
⇒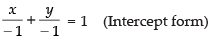
∴ a = – 1, b = – 1
Hence, the correct option is (d).
Q.28. The distance of the point of intersection of the lines 2x – 3y + 5 = 0 and 3x + 4y = 0 from the line 5x – 2y = 0 is
(a)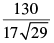
(b)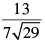
(c)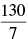
(d) None of these
Ans. (a)
Solution.
Given equations are:
2x – 3y + 5 = 0 ...(i)
3x + 4y = 0 ...(ii)
From eq. (ii) we get,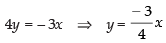 ...(iii)
...(iii)
Putting the value of y in eq. (i) we have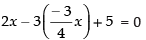
⇒ 8x + 9x + 20 = 0
⇒ 17x + 20 = 0
⇒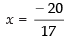
Putting the value of x in eq. (iii) we get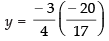
⇒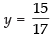
∴ Point of intersection is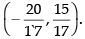
Now perpendicular distance from the point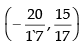 to the given line 5x – 2y = 0 is
to the given line 5x – 2y = 0 is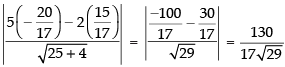
Hence, the correct option is (a).
Q.29. The equations of the lines which pass through the point (3, –2) and are inclined at 60° to the line √3x + y = 1 is
(a) y + 2 = 0, √3x – y – 2 – 3√3 = 0
(b) x – 2 = 0, √3x – y + 2 + 3√3 = 0
(c) √3x – y – 2 – 3 √3 = 0
(d) None of these
Ans. (a)
Solution.
Equation of line is given by
√3x + y + 1 = 0
⇒ y = - √3x - 1
∴ Slope of this line, m1 = - √3
Let m2 be the slope of the required line
∴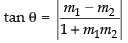
⇒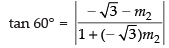
⇒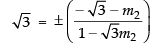
⇒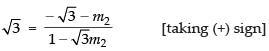
⇒ √3 - 3m2 = - √3 - m2
⇒ 2m2 = 2 √3 ⇒ m2 = √3
and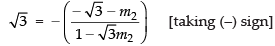
⇒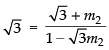
⇒ √3 - 3m2 = √3 + m2
⇒ 4m2 = 0 ⇒ m2 = 0
∴ Equation of line passing through (3, – 2) with slope √3 is
y + 2 = √3(x - 3)
⇒ y + 2 = √3x - 3 √3
⇒ √3x - y - 2 - 3 √3 = 0
and the equation of line passing through (3, -2) with slope 0 is
y + 2 = 0(x - 3)
⇒ y + 2 = 0
Hence, the correct option is (a).
Q.30. The equations of the lines passing through the point (1, 0) and at a distance 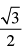 from the origin, are
from the origin, are
(a) √3x + y – √3 = 0, √3x – y – √3 = 0
(b) √3x + y + √3 = 0, √3x – y + √3 = 0
(c) x + √3y – √3 = 0, x – √3y – √3 = 0
(d) None of these.
Ans. (a)
Solution.
Equation of any line passing through (1, 0) is
y – 0 = m(x – 1) ⇒ mx – y – m = 0
Distance of the line from origin is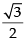
∴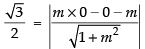
⇒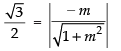
Squaring both sides, we get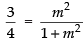
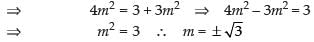
∴ Required equations are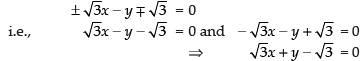
Hence, the correct option is (a).
Q.31. The distance between the lines y = mx + c1 and y = mx + c2 is
(a)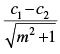
(b)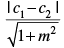
(c)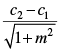
(d) 0
Ans. (b)
Solution.
Given equations are y = mx + c1 ...(i)
and y = mx + c2 ...(ii)
Slopes of eq. (i) and eq. (ii) are same i.e., m
So, they are parallel lines.
∴ Distance between the two lines = 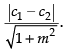
Hence, the correct option is (b).
Q.32. The coordinates of the foot of perpendiculars from the point (2, 3) on the line y = 3x + 4 is given by
(a)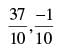
(b)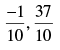
(c)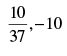
(d)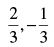
Ans. (b)
Solution.
Given equation is y = 3x + 4
⇒ 3x – y + 4 = 0 ...(i)
Slope = 3
Equation of any line passing through the point (2, 3) is
y – 3 = m(x – 2) ...(ii)
If eq. (i) is perpendicular to eq. (ii) then
m x 3 = - 1 [∴ m1 x m2 = - 1]
⇒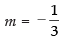
Putting the value of m in eq. (ii) we get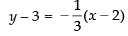
⇒ 3y – 9 = – x + 2
⇒ x + 3y = 11 ...(iii)
Solving eq. (i) and eq. (iii) we get
3x – y = – 4 ⇒ y = 3x + 4 ...(iv)
Putting the value of y in eq. (iii) we get
x + 3(3x + 4) = 11
⇒ x + 9x + 12 = 11
⇒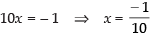
From eq. (iv) we get,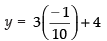
⇒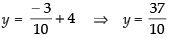
So the required coordinates are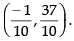
Hence, the correct option is (b).
Q.33. If the coordinates of the middle point of the portion of a line intercepted between the coordinate axes is (3, 2), then the equation of the line will be
(a) 2x + 3y = 12
(b) 3x + 2y = 12
(c) 4x – 3y = 6
(d) 5x – 2y = 10
Ans. (a)
Solution.
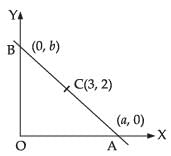
Let the given line meets the axes at A(a, 0) and B(0, b).
Given that C(3, 2) is the mid-point of AB
∴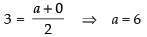
and 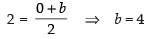
Intercept form of the line AB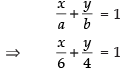
⇒ 2x + 3y = 12
Hence, the correct option is (a).
Q.34. Equation of the line passing through (1, 2) and parallel to the line y = 3x – 1 is
(a) y + 2 = x + 1
(b) y + 2 = 3 (x + 1)
(c) y – 2 = 3 (x – 1)
(d) y – 2 = x – 1
Ans. (c)
Solution.
Given equation is y = 3x – 1
Slope = 3
Slope of the line passing through the given point (1, 2) and parallel to the given line = 3
So, the equation of the required line is
y – 2 = 3(x – 1)
Hence, the correct option is (c).
Q.35. Equations of diagonals of the square formed by the lines x = 0, y = 0, x = 1 and y = 1 are
(a) y = x, y + x = 1
(b) y = x, x + y = 2
(c) 2y = x, y + x = 1/3
(d) y = 2x, y + 2x = 1
Ans. (a)
Solution.
Given equation x = 0, y = 0, x = 1 and y = 1 form a square of side 1 unit
From figure, we get that OABC is square having corners O(0, 0), A(1, 0), B(1, 1) and C(0, 1)
Equation of diagonal AC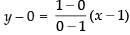
⇒ y = – (x – 1)
⇒ y = – x + 1
⇒ y + x = 1
Equation of diagonal OB is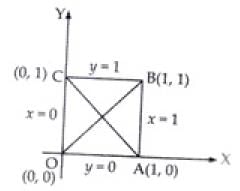
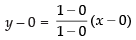
⇒ y = x
Hence, the correct option is (a).
Q.36. For specifying a straight line, how many geometrical parameters should be known?
(a) 1
(b) 2
(c) 4
(d) 3
Ans. (b)
Solution.
Different form of equation of straight lines are
Slope intercept form, y = mx + c, Parameter = 2
Intercept form,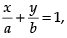 Parameter = 2
Parameter = 2
One-point form, y – y1 = m(x – x1), Parameter = 2
Normal form, x cos w + y sin w = P, Parameter = 2
Hence, the correct option is (b).
Q.37. The point (4, 1) undergoes the following two successive transformations :
(i) Reflection about the line y = x
(ii) Translation through a distance 2 units along the positive x-axis
Then the final coordinates of the point are
(a) (4, 3)
(b) (3, 4)
(c) (1, 4)
(d)
Ans. (b)
Solution.
Let the reflection of A(4, 1) in y = x be B(a, b) mid-point of AB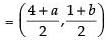 which lies on y = x
which lies on y = x
⇒ 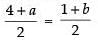 .....(i)
.....(i)
⇒ 4 + a = 1 + b
⇒ a - b = -3 ....(i)
The slope of the line y = x is 1 and slope of AB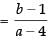
∴ 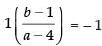
⇒ b - 1 = -a + 4
⇒ a + b = 5 .....(ii)
Solving eq. (i) and eq. (ii) we get
a = 1 and b = 4
∴ The point after translation is (1 + 2, 4) or (3, 4).
Hence, the correct option is (b).
Q.38. A point equidistant from the lines 4x + 3y + 10 = 0, 5x – 12y + 26 = 0 and 7x + 24y – 50 = 0 is
(a) (1, –1)
(b) (1, 1)
(c) (0, 0)
(d) (0, 1)
Ans.
Solution.
Given equations are
4x + 3y + 10 = 0 ...(i)
5x – 12y + 26 = 0 ...(ii)
and 7x + 24y – 50 = 0 ...(iii)
Let (x1, y1) be any point equidistant from eq. (i), eq. (ii) and eq. (iii).
Distance of (x1, y1) from eq. (i)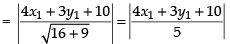
Distance of (x1, y1) from eq. (ii)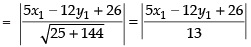
Distance of (x1, y1) from eq. (iii)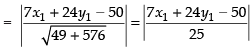
If the point (x1, y1) is equidistant from the given lines, then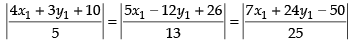
We see that putting x1 = 0 and y1 = 0, the above relation is satisfied i.e.,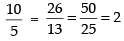
Hence, the correct option is (c).
Q.39. A line passes through (2, 2) and is perpendicular to the line 3x + y = 3. Its y-intercept is
(a) 1/3
(b) 2/3
(c) 1
(d) 4/3
Ans.
Solution.
Any line perpendicular to 3x + y = 3
x – 3y = λ (λ = constant)
If it passes through the point (2, 2) then
2 – 3(2) = λ ⇒ λ = – 4
∴ Required equation is x – 3y = – 4
⇒ – 3y = – x – 4
⇒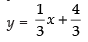 [∴ y = mx + c]
[∴ y = mx + c]
So, the y-intercept is 4/3.
Hence, the correct option is (d).
Q.40. The ratio in which the line 3x + 4y + 2 = 0 divides the distance between the lines 3x + 4y + 5 = 0 and 3x + 4y – 5 = 0 is
(a) 1 : 2
(b) 3 : 7
(c) 2 : 3
(d) 2 : 5
Ans. (b)
Solution.
The given equations are
3x + 4y + 5 = 0 ...(i)
3x + 4y – 5 = 0 ...(ii)
and 3x + 4y + 2 = 0 ...(iii)
Clearly, eq. (i), (ii) and (iii) are parallel to each other as the
coefficients of x and y are same.
Distance between parallel lines (i) and (iii) we get
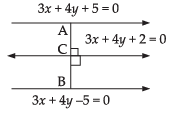
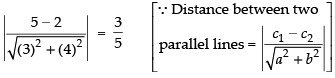
Distance between parallel lines (ii) and (iii) we get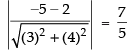
∴ Ratio between the distances =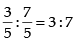
Hence, the correct option is (b).
Q.41. One vertex of the equilateral triangle with centroid at the origin and one side as x + y – 2 = 0 is
(a) (–1, –1)
(b) (2, 2)
(c) (–2, –2)
(d) (2, –2)
[Hint: Let ABC be the equilateral triangle with vertex A (h, k) and let D (α, β) be the point on BC. Then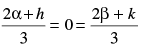 . Also α + β – 2 = 0 and
. Also α + β – 2 = 0 and
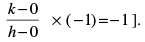
Ans. (c)
Solution.
Let ABC be an equilateral triangle with vertex (x1, y1).
AD ⊥ BC and let (a, b) be the coordinates of D.
Given that the centroid G lies at the origin i.e., (0, 0)
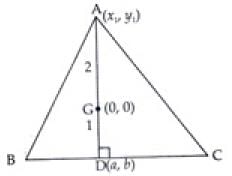
Since, the centroid of a triangle,divides the median in the ratio 1 : 2
So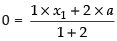
⇒ x1 + 2a = 0 ...(i)
and 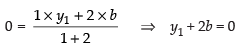 ...(ii)
...(ii)
Equations of BC is given by x + y – 2 = 0 ...(iii)
Point D(a, b) lies on the line x + y – 2 = 0
So a + b – 2 = 0 ...(iv)
Slope of eq. (iii) is = – 1
and the slope of AG =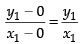
Since, they are perpendicular to each other
∴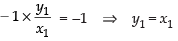
From eq. (i) and (ii) we get
x1 + 2a = 0 ⇒ 2a = - x1
y1 + 2b = 0 ⇒ 2b = - y1
∴ a = b
From eq. (iv) we get
a + b – 2 = 0
⇒ a + a – 2 = 0
⇒ 2a – 2 = 0 ⇒ a = 1 and b = 1 [∴ a = b]
∴ x1 = – 2 x 1 = - 2
and y1 = – 2 x 1 = - 2
Hence, the correct option is (c).
FILL IN THE BLANK
Q.42. If a, b, c are in A.P., then the straight lines ax + by + c = 0 will always pass through ____.
Ans. Given equation is ax + by + c = 0 ...(i)
Since a, b and c are in A.P.
∴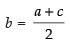
⇒ a + c = 2b
⇒ a – 2b + c = 0 ...(ii)
Comparing eq. (i) with eq. (ii) we get,
x = 1, y = – 2
So, the line will pass through (1, – 2)
Hence, the value of the filler is (1, – 2).
Q.43. The line which cuts off equal intercept from the axes and pass through the point (1, –2) is ____.
Ans. Intercept form of the line is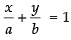 ...(i)
...(i)
Given that a = b
∴ 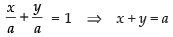 ...(ii)
...(ii)
If the line (i) passes through (1, – 2) we get
1 – 2 = a ⇒ a = – 1
So, the required equation is x + y = – 1 ⇒ x + y + 1 = 0.
Hence, the value of the filler is x + y + 1 = 0.
Q.44. Equations of the lines through the point (3, 2) and making an angle of 45° with the line x – 2y = 3 are ____.
Ans. Given line is x – 2y = 3 and the point is (3, 2)
Equation of a line passing through the point (3, 2) is
y – 2 = m(x – 3) ...(i)
Angle between eq. (i) and the given line x – 2y = 3 whose slope is 1/2
∴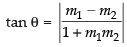
⇒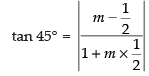
⇒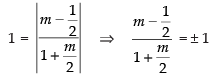
Taking (+) sign,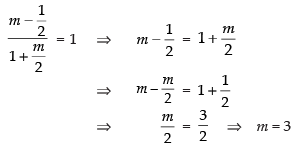
Taking (–) sign,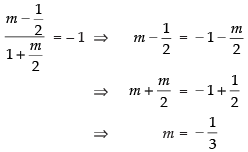
So, the required equations are,
When m = 3,
y – 2 = 3(x – 3)
⇒ y – 2 = 3x – 9
⇒ 3x – y – 7 = 0
When m =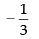
y - 2 = 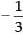 (x-3)
(x-3)
⇒ 3y – 6 = – x + 3
⇒ x + 3y – 9 = 0
Hence, the value of the filler is 3x – y – 7 = 0 and x + 3y – 9 = 0.
Q.45. The points (3, 4) and (2, – 6) are situated on the ____ of the line 3x – 4y – 8 = 0.
Ans. Given line is 3x – 4y – 8 = 0 ...(i)
and the given points are (3, 4) and (2, – 6).
For point (3, 4), line becomes = 3(3) – 4(4) – 8
= 9 – 16 – 8
= 9 – 24 = – 15 < 0
For the point (2, – 6), line becomes
= 3(2) – 4(– 6) – 8 = 6 + 24 – 8 = 30 – 8
= 22 > 0
So, the points (3, 4) and (2, – 6) are situated on the opposite sides of 3x – 4y – 8 = 0.
Hence, the value of the filler is opposite.
Q.46. A point moves so that square of its distance from the point (3, –2) is numerically equal to its distance from the line 5x – 12y = 3. The equation of its locus is ____.
Ans. The given equation of line is 5x – 12y = 3 and the given point is (3, – 2).
Let (a, b) be any moving point
∴ Distance between (a, b) and the point (3, – 2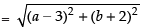
and the distance of (a, b) from the line 5x – 12y = 3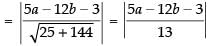
According to the question, we have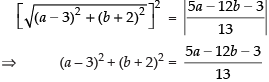
Taking numerical values only, we have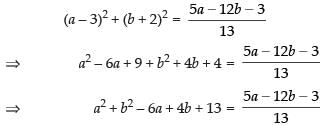
⇒ 13a2 + 13b2 – 78a + 52b + 169 = 5a – 12b – 3
⇒ 13a2 + 13b2 – 83 + 64b + 172 = 0
So, the locus of the point is 13x2 + 13y2 – 83x + 64y + 172 = 0.
Hence, the value of the filler is 13x2 + 13y2 – 83x + 64y + 172 = 0.
Q.47. Locus of the mid-points of the portion of the line x sin θ + y cos θ = p intercepted between the axes is ____.
Ans. Given equation of the line is
x cos θ + y sin θ = p ...(i)
Let C(h, k) be the mid-point of the given line AB where it meets the two axis at A(a, 0) and B(0, b).
Since (a, 0) lies on eq. (i) then
a cos θ+ 0 = p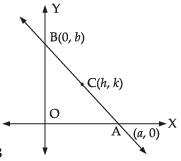
⇒ 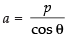 ...(ii)
...(ii)
B(0, b) also lies on the eq. (i) then 0 + b sin θ = p
⇒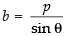 ...(iii)
...(iii)
Since C(h, k) is the mid-point of AB
∴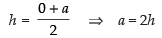
and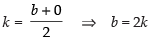
Putting the values of a and b is eq. (ii) and (iii) we get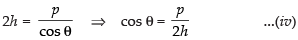
and 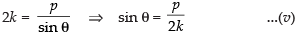
Squaring and adding eq. (iv) and (v) we get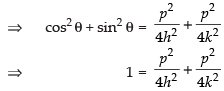
So, the locus of the mid-point is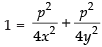
⇒ 4x2y2 = p2(x2 + y2)
Hence, the value of the filler is 4x2y2 = p2(x2 + y2).
STATE TRUE OR FALSE
Q.48. If the vertices of a triangle have integral coordinates, then the triangle can not be equilateral.
Ans. We know that if the vertices of triangle has integral coordinates, then the triangle can not be equilateral.
So, the given statement is True.
Q.49. The points A (– 2, 1), B (0, 5), C (– 1, 2) are collinear.
Ans. Given points are A(– 2, 1), B(0, 5), C(– 1, 2)
Area of ΔABC =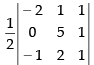
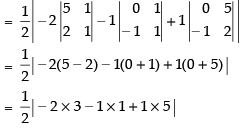
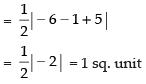
So, the given points are not collinear.
Hence, the given statement is False.
Q.50. Equation of the line passing through the point (a cos3θ, a sin3θ) and perpendicular to the line x sec θ + y cosec θ = a is x cos θ – y sin θ = a sin 2θ.
Ans. Equation of any line perpendicular to x sec θ + y cosec θ = a is
x cosec θ – y sec θ = k ...(i)
If eq. (i) passes through (a cos3 θ, a sin3 θ) then
a cos3 θ.cosec θ – a sin3 θ.sec θ = k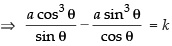
∴ Required equation is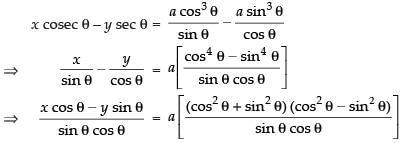
⇒ x cos θ – y sin θ = a(cos2 θ – sin2 θ)
⇒ x cos θ – y sin θ = a cos 2θ.
Hence, the given statement is False.
Q.51. The straight line 5x + 4y = 0 passes through the point of intersection of the straight lines x + 2y – 10 = 0 and 2x + y + 5 = 0.
Ans. Given equations are x + 2y – 10 = 0 ...(i)
and 2x + y + 5 = 0 ...(ii)
From eq. (i) x = 10 – 2y ...(iii)
Putting the value of x in eq. (ii) we get
2(10 – 2y) + y + 5 = 0
⇒ 20 – 4y + y + 5 = 0
⇒ – 3y + 25 = 0
⇒ y = 25/3
Putting the value of y in eq. (iii) we get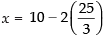
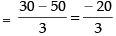
∴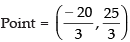
If the given line 5x + 4y = 0 passes through the point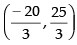
then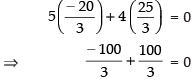
⇒ 0 = 0 satisfied.
So, the given line passes through the point of intersection of the given lines.
Hence, the given statement is True.
Q.52. The vertex of an equilateral triangle is (2, 3) and the equation of the opposite side is x + y = 2. Then the other two sides are y – 3 = (2 ± √3 ) (x – 2).
Ans. Let ABC be an equilateral triangle with vertex (2, 3) and the opposite side is x + y = 2 with slope –1.
Suppose slope of line AB is m.
Since each angle of equilateral triangle is 60°.
∴ Angle between AB and BC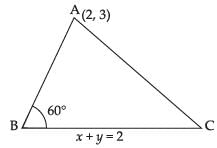
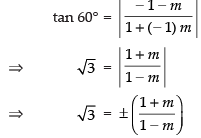
Taking (+) sign,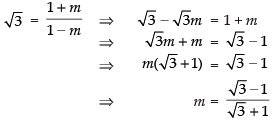
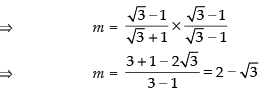
Taking (–) sign, m = 2 + √3
So, the equations of other two lines are
y - 3 = (2 ± √3 )( x- 2)
Hence, the statement is True.
Q.53. The equation of the line joining the point (3, 5) to the point of intersection of the lines 4x + y – 1 = 0 and 7x – 3y – 35 = 0 is equidistant from the points (0, 0) and (8, 34).
Ans. Given equations are
4x + y – 1 = 0 ...(i)
and 7x – 3y – 35 = 0 ...(ii)
From eq. (i) y = 1 – 4x ...(iii)
Putting the value of y in eq. (ii) we get
7x – 3(1 – 4x) – 35 = 0
⇒ 7x – 3 + 12x – 35 = 0
⇒ 19x – 38 = 0
⇒ x = 2 From eq. (iii) we get, y = 1 – 4 x 2 ⇒ y = − 7
The point of intersection is (2, - 7).
Equation of line joining the point (3, 5) to the point (2, – 7) is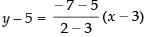
⇒ y – 5 = 12(x – 3)
⇒ y – 5 = 12x – 36
⇒ 12x – y – 31 = 0 ...(iv)
Distance of eq. (iv) from the point (0, 0)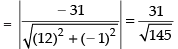
Distance of eq. (iv) from the point (8, 34) is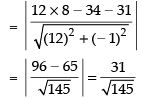
Hence, the given statement is True.
Q.54. The line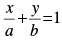 moves in such a way that
moves in such a way that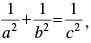 where c is a constant.
where c is a constant.
The locus of the foot of the perpendicular from the origin on the given line is x2 + y2 = c2.
Ans. The given equation is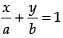 ...(i)
...(i)
Equation of the line passing through (0, 0) and perpendicular to eq. (i) is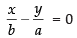 ..(ii)
..(ii)
Squaring and adding eq. (i) and (ii) we get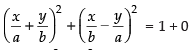
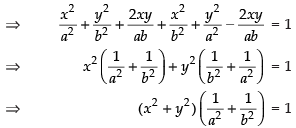
⇒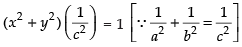
⇒x2 + y2 = c2
Hence, the given statement is True.
Q.55. The lines ax + 2y + 1 = 0, bx + 3y + 1 = 0 and cx + 4y + 1 = 0 are concurrent if a, b, c are in G.P.
Ans. Given equations are
ax + 2y + 1 = 0 ...(i)
bx + 3y + 1 = 0 ...(ii)
cx + 4y + 1 = 0 ...(iii)
Solving eq. (i) and (ii) we get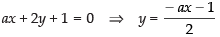
Putting the value of y in eq. (ii) we have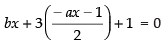
⇒ 2bx – 3ax – 3 + 2 = 0
⇒ (2b – 3a)x = 1
⇒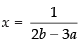
∴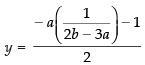
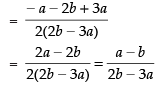
So, the point of intersection of eq. (i) and (ii) is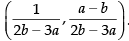
If eq. (i), (ii) and (iii) are concurrent, then the above point must lie on eq. (iii)
cx + 4y + 1 = 0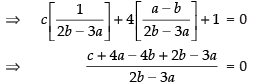
⇒ c + a – 2b = 0
⇒ 2b = a + c
So, a, b and c are in A.P. and not in G.P.
Hence, the given statement is False.
Q.56. Line joining the points (3, – 4) and (– 2, 6) is perpendicular to the line joining the points (–3, 6) and (9, –18).
Ans. The given points are (3, – 4) and (– 2, 6), (– 3, 6) and (9, – 18).
Slope of the line joining the points (3, – 4) and (– 2, 6)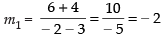
Slope of the line joining the points (– 3, 6) and (9, – 18)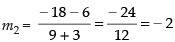
Since m1 = m2 = – 2
So, the lines are parallel and not perpendicular.
Hence, the given statement is False.
Match the questions given under Column C1 with their appropriate answers given under the Column C2
Q.57. 
Ans.
(a) Let P(x1, y1)be any point on the given line
x + 5y = 13 ∴ x1 + 5y1 = 13
Distance of line 12x – 5y + 26 = 0 from the point P(x1, y1)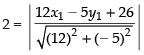
⇒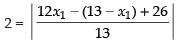
⇒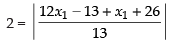
⇒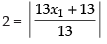
⇒ 2 = ± (x1 + 1)
⇒ 2 = x1 + 1 ⇒ x1 = 1 (Taking (+) sign)
and 2 = – x1 – 1 ⇒ x1 = – 3 (Taking (–) sign)
Putting the values of x1 in eq. x1 + 5y1 = 13.
We get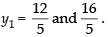
So, the required points are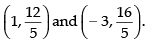
Hence, (a) ↔ (iii).
(b) Let P(x1, y1) be any point on the given line
x + y = 4 ∴ x1 + y1 = 4 ...(i)
Distance of the line 4x + 3y – 10 = 0 from the point P(x1, y1)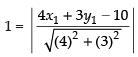
⇒ 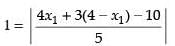
⇒ 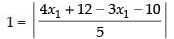
⇒ 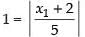
⇒ 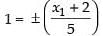
⇒ 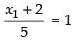 (Taking (+) sign)
(Taking (+) sign)
⇒ x1 + 2 = 5 ⇒ x1 = 3
and 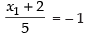 (Taking (–) sign)
(Taking (–) sign)
⇒ x1 + 2 = – 5 ⇒ x1 = – 7
Putting the values of x1 in eq. (i) we get
x1 + y1 = 4
at x1 = 3, y1 = 1
at x1 = – 7, y1 = 11
So, the required points are (3, 1) and (– 7, 11).
Hence, (b) ↔ (i).
(c) Given that AP = PQ = QB
Equation of line joining A(– 2, 5) and B(3, 1) is
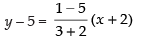
⇒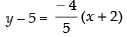
⇒ 5y – 25 = – 4x – 8
⇒ 4x + 5y – 17 = 0
Let P(x1, y1) and Q(x2, y2) be any two points on the line AB P(x1, y1) divides the line AB in the ratio 1 : 2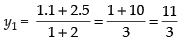
So, the coordinates of P(x1, y1) =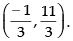
Now point Q(x2, y2) is the mid-point of PB
∴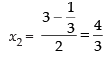
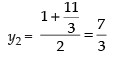
Hence, the coordinates of Q(x2, y2) =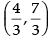
Hence, (c) ↔ (ii).
Q.58. The value of the λ, if the lines (2x + 3y + 4) + λ (6x – y + 12) = 0 are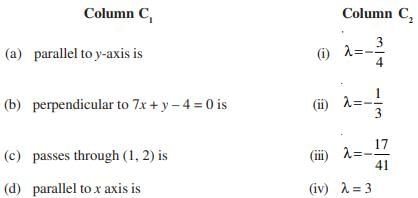
Ans.
(a) Given equation is (2x + 3y + 4) + λ(6x – y + 12) = 0
⇒ (2 + 6λ)x + (3 – λ)y + 4 + 12λ = 0 ...(i)
If eq. (i) is parallel to y-axis, then
3 – λ = 0 ⇒ λ = 3
Hence, (a) ↔ (iv)
(b) Given lines are
(2x + 3y + 4) + λ(6x - y + 12) = 0 ...(i)
⇒ (2 + 6λ)x + (3 - λ)y + 4 + 12λ = 0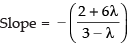
Second equation is 7x + y – 4 = 0 ...(ii)
Slope = – 7
If eq. (i) and eq. (ii) are perpendicular to each other
∴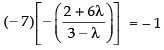
⇒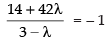
⇒ 14 + 42λ = – 3 + λ
⇒ 42λ – λ =– 17
⇒ 41λ = – 17
⇒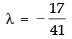
Hence, (b) ↔ (iii).
(c) Given equation is (2x + 3y + 4) + λ(6x - y + 12) = 0 ...(i)
If eq. (i) passes through the given point (1, 2) then
(2 x 1 + 3 x 2 + 4) + λ(6 x 1 - 2 + 12) = 0
⇒ (2 + 6 + 4) + λ(6 - 2 + 12) = 0
⇒ 12 + 16λ = 0
⇒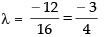
Hence, (c) ↔ (i).
(d) The given equation is (2x + 3y + 4) + λ(6x - y + 12) = 0
⇒ (2 + 6λ)x + (3 - λ)y + 4 + 12λ = 0 ...(i)
If eq. (i) is parallel to x-axis, then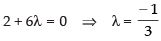
Hence, (d) ↔ (ii).
Q.59. The equation of the line through the intersection of the lines 2x – 3y = 0 and 4x – 5y = 2 and
Ans.
(a) Given equations are 2x – 3y = 0 ...(i)
and 4x – 5y = 2 ...(ii)
Equations of line passing through eq. (i) and (ii) we get
(2x – 3y) + k(4x – 5y – 2) = 0 ...(iii)
If eq. (iii) passes through (2, 1), we get
(2 x 2 - 3 x 1) + k(4 x 2 - 5 x 1 - 2) = 0
⇒ (4 - 3) + k(8 - 5 - 2) = 0
⇒ 1 + k(8 – 7) = 0
⇒ k = – 1
So, the required equation is
(2x – 3y) – 1(4x – 5y – 2) = 0
⇒ 2x – 3y – 4x + 5y + 2 = 0
⇒ – 2x + 2y + 2 = 0
⇒ x – y – 1 = 0
Hence, (a) ↔ (iii).
(b) Equation of any line passing through the point of intersection of the line 2x - 3y = 0 and 4x - 5y = 2 is
(2x - 3y) + k(4x - 5y - 2) = 0 ...(i)
⇒ (2 + 4k)x + (- 3 - 5k)y - 2k = 0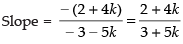
Slope of the given line x + 2y + 1 = 0 is - 1/2.
If they are perpendicular to each other then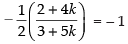
⇒ 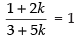
⇒ 1 + 2k = 3 + 5k
⇒ 3k = – 2 ⇒ k = - 2/3
Putting the value of k is eq. (i) we get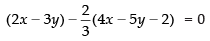
⇒ 6x – 9y – 8x + 10y + 4 = 0
⇒ – 2x + y + 4 = 0
⇒ 2x – y = 4
Hence, (b) ↔ (i)
(c) Given equations are
2x - 3y = 0 ...(i)
4x - 5y = 2 ...(ii)
Equation of line passing through eq. (i) and (ii) we get
(2x - 3y) + k(4x - 5y - 2) = 0
⇒ (2 + 4k)x + (– 3 – 5k)y – 2k = 0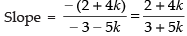
Slope of the given line 3x – 4y + 5 = 0 is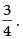
If the two equations are parallel, then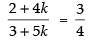
⇒ 8 + 16k = 9 + 15k
⇒ 16k – 15k = 9 – 8
⇒ k = 1
So, the equation of the required line is
(2x – 3y) + 1(4x – 5y – 2) = 0
2x – 3y + 4x – 5y – 2 = 0
⇒ 6x – 8y – 2 = 0
⇒ 3x – 4y – 1 = 0
Hence, (c) ↔ (iv)
(d) Given equations are
2x - 3y = 0 ...(i)
4x - 5y - 2 = 0 ...(ii)
Equation of line passing through the intersection of eq. (i) and (ii) we get
(2x - 3y) + k(4x - 5y - 2) = 0
⇒ (2 + 4k)x + (- 3 - 5k)y - 2k = 0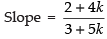
Since the equation is equally inclined with axes
∴ Slope = tan 135° = tan (180° – 45°) = – tan 45° = – 1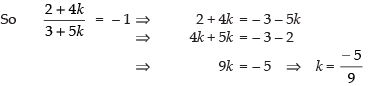
Required equation is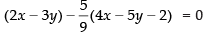
⇒ 18x – 27y – 20x + 25y + 10 = 0
⇒ – 2x – 2y + 10 = 0
⇒ x + y – 5 = 0
Hence, (d) ↔ (ii)
|
172 videos|503 docs|154 tests
|
FAQs on NCERT Exemplar: Straight Lines - Mathematics (Maths) for JEE Main & Advanced
| 1. What is the equation of a straight line in the slope-intercept form? |  |
| 2. How can we find the slope of a straight line given two points on it? |  |
| 3. What is the significance of the y-intercept in a straight line equation? |  |
| 4. Can a straight line have a slope of zero? |  |
| 5. How can we determine if two straight lines are parallel or perpendicular to each other? |  |





















