Class 10 Science - Previous Year Paper with Solutions- 2020
Section - A
Q.1. Name a cyclic unsaturated carbon compound. [1]
Ans. Benzene is a cyclic unsaturated carbon compound.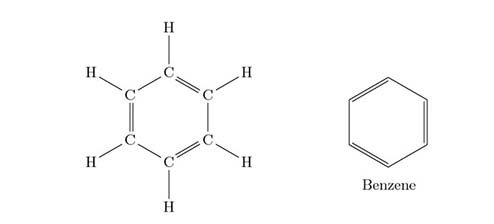 Q.2. State an important advantage of using alternating current (a.c.) over direct current (d.c.). [1]
Q.2. State an important advantage of using alternating current (a.c.) over direct current (d.c.). [1]
Ans. Alternating current gets transmitted over long distances without much loss of electricity. This is the main advantage of using alternating current over direct current.
Q.3. Answer the following questions on the bases of this paragraph
The growing size of the human population is a cause of concern for all people. The rates of birth and death in a given population will determine its size. Reproduction is the process by which organisms increase their population. The process of sexual maturation for reproduction is gradual and takes place while general body growth is still going on. Some degree of sexual maturation does not necessarily mean that the mind or body is ready for sexual acts or for having and bringing up children. Various contraceptive devices are being used by human beings to control the size of the population.
(a) List two common signs of sexual maturation in boys and girls. [1]
Ans. Two common signs of sexual maturation in boys and girls:
- Appearance of hair on different body parts such as arm pits, face and pubic area
- Development of mammary glands in girls and broadening of shoulders and chest in boys
(b) What is the result of reckless female foeticide? [1]
Ans. Due to reckless female foeticide, the ratio of the number of females to the number of males goes down and there is an imbalance in the overall sex ratio.
(c) Which contraceptive method changes the hormonal balance of the body? [1]
Ans. Chemical method of contraception, i.e. the use of oral pills changes the hormonal balance of the body.
(d) Write two factors which determine the size of a population. [1]
Ans. Birth rate and death rate are the factors which determine the size of a population.
Q.4. Answer the following questions on the bases of this paragraph
The human body is made up of five important components, of which water is the main component. Food, as well as potable water, is essential for every human being. Food is obtained from plants through agriculture. Pesticides are being used extensively for high yield in the fields. These pesticides are absorbed by the plants from the soil along with water and minerals and from the water bodies; these pesticides are taken up by the aquatic animals and plants. As these chemicals are non-biodegradable, they get accumulated progressively at each tropic level. The maximum concentration of these chemicals get accumulated in our bodies and greatly affects the health of our mind and body.
(a) Why is the maximum concentration of pesticides found in human beings? [1]
Ans. Maximum concentration of pesticides is found in human beings because man is a tertiary consumer and present at the top level of the food chain. As a result, the concentration of chemicals is the highest due to bio-magnification.
(b) Give one method which could be applied to reduce our intake of pesticides through food to some extent. [1]
Ans. Use of organic manures and bio-fertilisers instead of synthetic pesticides for crops might help to reduce our intake of pesticides through food to some extent.
(c) Various steps in a food chain represent
(a) Food web
(b) Trophic level
(c) Ecosystem
(d) Bio-magnification
Ans. (b) Trophic level
Solution. The various steps in a food chain represent the trophic levels.
(d) With regard to various food chains operating in an ecosystem, man is a [1]
(a) Consumer
(b) Producer
(c) Producer and consumer
(d) Producer and decomposer
Ans. (a) Consumer
Solution. Man is dependent on other organisms for his food requirements. Hence, man is a consumer.
Q.5. Which one of the following is responsible for the sustenance of underground water? [1]
(a) Loss of vegetation cover
(b) Diversion for high water-demanding crops
(c) Pollution from urban wastes
(d) Afforestation
Ans. (d) Afforestation
Solution. Afforestation helps to increase forest cover. The tree cover prevents water from immediately rushing into rivers. As a result, water can seep into the ground and replenish the groundwater levels.
Q.6. Incomplete combustion of coal and petroleum [1]
(A) Increases air pollution
(B) Increases efficiency of machines
(C) Reduces global warming
(D) Produces poisonous gases
The correct option is
(a) A and B
(b) A and D
(c) B and C
(d) C and D
Ans. (b) A and D
Solution. Incomplete combustion of fossil fuels such as coal and petroleum produces poisonous gases and increases air pollution.
Q.7. When sodium hydrogen carbonate is added to ethanoic acid, a gas evolves. Consider the following statements about the gas evolved? [1]
(A) It turns lime water milky.
(B) It is evolved with a brisk effervescence.
(C) It has a smell of burning sulphur.
(D) It is also a by-product of respiration.
The correct statements are
(a) A and B only
(b) B and D only
(c) A, C and D
(d) A, B and D
Ans. (d) A, B and D
Solution. When sodium hydrogen carbonate is added to ethanoic acid, CO2 is evolved. It turns lime water milky. It is evolved with a brisk effervescence and is also a by-product of respiration.
Q.8. When a small amount of acid is added to water, the phenomena which occur are [1]
(A) Dilution
(B) Neutralisation
(C) Formation of H3O+ ions
(D) Salt formation
The correct statements are
(a) A and C
(b) B and D
(c) A and B
(d) C and D
Ans. (a) A and C
Solution. When a small amount of acid is added to water, the phenomena which occur are dilution and formation of H3O+ ions.
Q.9. A real image is formed by light rays after reflection or refraction when they [1]
(A) Actually meet or interest with each other
(B) Actually converge at a point
(C) Appear to meet when they are produced in the backward direction
(D) Appear to diverge from a point
Which of the above statements are correct?
(a) A and D
(b) B and D
(c) A and B
(d) B and C
OR
Consider the following properties of virtual images:
(A) Cannot be projected on the screen
(B) Are formed by both concave and convex lenses
(C) Are always erect
(D) Are always inverted
The correct properties are
(a) A and D
(b) A and B
(c) A, B and C
(d) A, B and D
Ans. (c) A and B
Solution. A real image is formed by light rays after reflection and refraction when they actually meet or intersect with each other and when they actually converge at a focal point.
OR
Ans. (c). A, B and C
Solution. Virtual images cannot be projected on the screen, are formed by both concave and convex lenses and are always erect.
Q.10. At the time of a short circuit, the electric current in the circuit [1]
(a) Varies continuously
(b) Does not change
(c) Reduces substantially
(d) Increases heavily
OR
Two bulbs of 100 W and 40 W are connected in series. The current through the 100-W bulb is 1 A. The current through the 40-W bulb will be
(a) 0.4 A
(b) 0.6 A
(c) 0.8 A
(d) 1 A
Ans. (d) Increases heavily
Solution. During a short circuit, when the two wires come in contact with each other, the resistance of the circuit so formed becomes very small, and thus, the current flowing in the circuit increases heavily.
OR
Ans. (d) 1 A
Solution. When appliances are connected in series, the current flowing in both appliances is the same. Thus, the current flowing through both bulbs will be 1 A.
Q.11. Calcium oxide reacts vigorously with water to produce slaked lime. [1]
CaO(s) + H2O(l) → Ca(OH)2(aq)
This reaction can be classified as
(A) Combination reaction
(B) Exothermic reaction
(C) Endothermic reaction
(D) Oxidation reaction
Which of the following is a correct option?
(a) A and C
(b) C and D
(c) A, C and D
(d) A and B
OR
When hydrogen sulphide gas is passed through a blue solution of copper sulphate, black precipitate of copper sulphide is obtained and the sulphuric acid so formed remains in the solution. The reaction is an example of a
(a) Combination reaction
(b) Displacement reaction
(c) Decomposition reaction
(d) Double displacement reaction
Ans. (d). A and B
Solution. Calcium oxide reacts vigorously with water to produce slaked lime.
CaO(s) + H2O(l) → Ca(OH)2(aq) is a combination reaction and is an exothermic reaction.
OR
Ans. (d) Double displacement reaction
Solution. When hydrogen sulphide gas is passed through a blue solution of copper sulphate, a black precipitate of copper sulphide is obtained, and the sulphuric acid so formed remains in the solution. The reaction is an example of a double displacement reaction.
Q.12. In a double displacement reaction such as the reaction between sodium sulphate solution and barium chloride solution, [1]
(A) The exchange of atoms takes place
(B) The exchange of ions takes place
(C) A precipitate is produced
(D) An insoluble salt is produced
The correct option is
(a) B and D
(b) A and C
(c) Only B
(d) B, C and D
Ans. (a) B and D
Solution. In a double displacement reaction such as the reaction between sodium sulphate solution and barium chloride solution, an exchange of ions takes place and an insoluble precipitate of barium sulphate is formed.
For questions 13 and 14, two statements are given—one labelled Assertion A) and the other labelled Reason (R). Select the correct answer to these questions from the codes (a), (b), (c) and (d) given below:
(a) Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of the Assertion.
(b) Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of the Assertion.
(c) A is true, but R is false.
(d) A is false, but R is true.
Q.13. Assertion (A): Esterification is a process in which a sweet-smelling substance is produced.
Reason (R): When esters react with sodium hydroxide, an alcohol and sodium salt of carboxylic acid are obtained.
(a) Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of the Assertion.
(b) Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of the Assertion.
(c) A is true, but R is false.
(d) A is false, but R is true.
Ans. (b) Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of the Assertion.
Solution. Ethanoic acid reacts with ethanol in the presence of an acid catalyst to give a sweet-smelling compound called ester, and the process is known as esterification.
Q.14. Assertion (A): A solar cooker cooks the metal due to the greenhouse effect.
Reason (R): The plane mirror is responsible for producing the greenhouse effect.
(a) Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of the Assertion.
(b) Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of the Assertion.
(c) A is true, but R is false.
(d) A is false, but R is true.
Ans. (c) A is true, but R is false.
Solution. The solar cooker consists of a concave mirror which acts as a reflector. Sun rays striking the glass lid get trapped inside the cooker. Thus, the inside of the box is heated as sunlight enters through the glass top and heats the cooking pot. Thermal energy is then radiated inside the box but cannot get out of the glass lid and the box gets hotter, producing the greenhouse effect.
Section - B
Q.15. (a) Write the mathematical expression for Joule’s law of heating.
(b) Compute the heat generated while transferring 96000 coulomb of charge in two hours through a potential difference of 40 V. [3]
Ans. (a) Mathematical expression of Joule’s law of heating is:
H = I2Rt,
where
H – Amount of heat generated
I – Current
R – Resistance
t – Time
(b) Q = 96000 C
t = 2 h = 2 × 60 = 120 s
V = 40 V
We know
I = Q/t
I = 96000/120 = 800 A
By Joule’s law of heating,
H = VIt
H = 40 × 800 × 120 = 3,840,000 J = 3840 kJ
Q.16. Draw a labelled diagram to show [3]
(i) the reddish appearance of the sun at sunrise or sunset and
(ii) the white appearance of the sun at noon when it is overhead.
Ans. (i)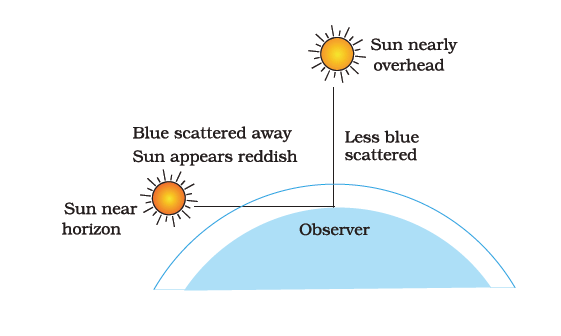
(ii) 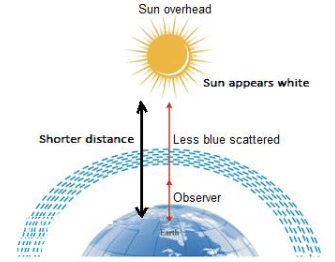
Q.17. (a) Draw the structures for (i) ethanol (ii) ethanoic acid.
(b) Why is the conversion of ethanol to ethanoic acid considered an oxidation reaction?
Write the oxidising agent used in the reaction involved. [3]
Ans. (a) (i) Structure of Ethanol:
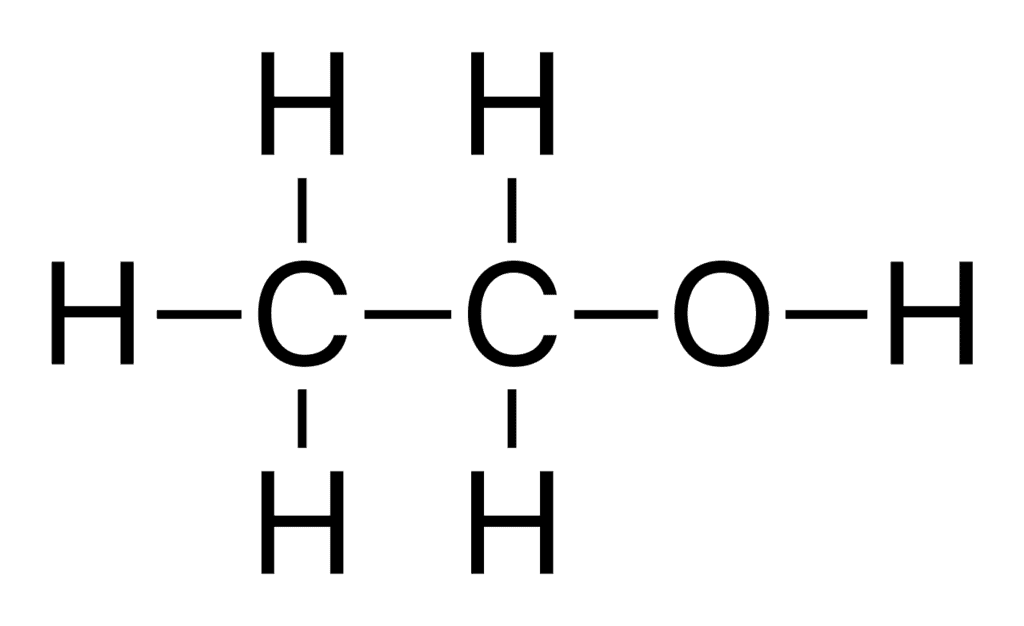
(ii) Structure of Ethanoic Acid: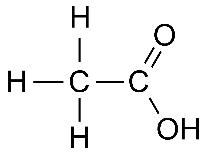
(b) Conversion of ethanol to ethanoic acid is considered an oxidation reaction as oxygen is added to ethanol to form ethanoic acid in the presence of alkaline KMnO4. Alkaline potassium permanganate (KMnO4) is used as an oxidising agent in the reaction.
Q.18. Name the parts (a) to (e) in the following diagram. [3]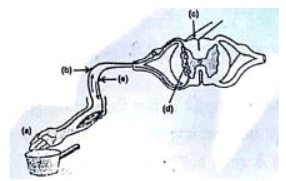
What is the term given to the sequence of events occurring in the diagram?
OR
(a) What is tropism?
(b) How do auxins promote the growth of a tendril around a support? [3]
Ans. 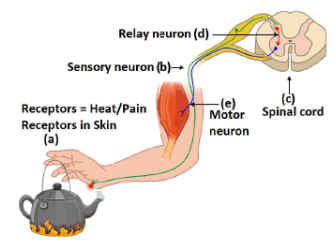
The sequence of events or the pathway of nerve impulses during reflex actions constitutes a reflex arc.
OR
(a)
- Tropism is the growth movement of a plant in response to the external stimulus in which the direction of the response depends on the direction of the stimulus.
Auxin is a plant hormone which is synthesised at the tips of roots and shoots. - It helps in the elongation of cells. When a tendril comes in contact with a support, the auxins stimulate the elongation of the cells on the opposite side of the stimulus, which results in the coiling of the tendrils around the support.
Q.19. Why is the Tyndall effect shown by colloidal particles? State four instances of observing the Tyndall effect. [3]
OR
Differentiate between a glass slab and a glass prism. What happens when a narrow beam of (i) monochromatic light and (ii) white light pass through (a) a glass slab and (b) a glass prism? [3]
Ans.
- The scattering of light by particles in its path is called the Tyndall effect. The colloidal particles like molecules of air and other fine particles in the atmosphere have a size smaller than the wavelength of visible light.
- When a beam of light is incident on these colloidal particles, they are more effective in scattering light of shorter wavelengths. Hence, colloidal particles show the Tyndall effect.
- Four instances of observing the Tyndall effect:
(i) The sky appears blue due to the Tyndall effect.
(ii) Scattering of light passing through the canopy of a dense forest.
(iii) The beam of a headlight visible in fog.
(iv) The blue colour of smoke coming out from a 2-stroke engine.
OR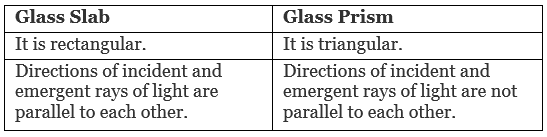
(i) When monochromatic light passes through a
(a) Glass slab: Light gets refracted and the incident and emergent rays are parallel to each other.
(b) Glass prism: Light gets deviated but does not get dispersed as the light is of the same wavelength.
(ii) When white light passes through a
(a) Glass slab: Light gets refracted and the incident and emergent rays of light are parallel to each other.
(b) Glass prism: Light gets dispersed into seven constituent colours.
Q.20. Define the term pollination. Differentiate between self-pollination and cross-pollination. What is the significance of pollination? [3]
Ans. Pollination: The process of the transfer of pollen grains from the anther to the stigma of a flower is called pollination.
Differences between self-pollination and cross-pollination:
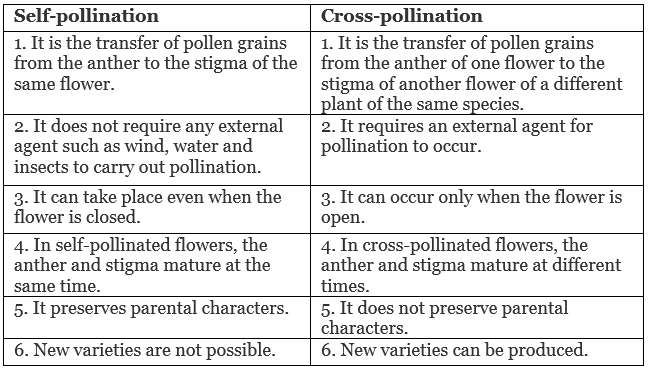
Significance of pollination:
- It is essential for the process of fertilisation.
- Fertilisation results in the formation of fruits and seeds.
- In the absence of pollination, fruit and seed formation will not occur.
Q.21. List the important products of the chlor-alkali process. Write one important use of each. [3]
OR
How is washing soda prepared from sodium carbonate? Give its chemical equation. State the type of this salt. Name the type of hardness of water which can be removed by it. [3]
Ans. When electricity is passed through an aqueous solution of sodium chloride (brine), it decomposes to form sodium hydroxide and chlorine and hydrogen gas is liberated.
Sodium hydroxide is used
- For de-greasing metals, soaps and detergents
- For making paper and artificial fibres
Chlorine is used
- In the production of bleaching powder
- In the preparation of chloroform, carbon tetrachloride and plastics
Hydrogen is used
- In the hydrogenation of oils to obtain vegetable ghee
- As fuel for rockets
OR
Washing soda is prepared from sodium carbonate by recrystallisation.
Na2CO3 + 10 H2O → Na2CO3.10 H2O
Washing soda is a basic salt. It is used to remove the permanent hardness of water.
Q.22. 1 g of copper powder was taken in a China dish and heated. What change takes place on heating? When hydrogen gas is passed over this heated substance, a visible change is seen in it. Give the chemical equations of the reactions, the name and the colour of the products formed in each case. [3]
Ans.
- When copper powder taken in a China dish is heated, it reacts with oxygen in the air and forms copper oxide which forms a black layer on the surface.
- When hydrogen gas is passed over the copper oxide layer on the surface, it reacts with hydrogen to form elemental copper and water is formed.
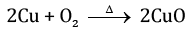
(black colour)
CuO+ H2 → Cu + H2O
Q.23. The near point of the eye of a person is 50 cm. Find the nature and power of the corrective lens required by the person to enable him to see clearly the objects placed at 25 cm from the eye. [3]
Ans. Near point of eye (v) = –50 cm
This means the person is unable to see nearby objects and is suffering from hypermetropia.
Object distance (u) = –25 cm
1/f = 1/v - 1/u
1/f = 1/(-50) - 1/(-25)
1/f = 1/-50 + 1/25
f = + 50 cm
f = + 0.5 m
Positive sign indicates that the corrective lens is a convex lens. Power of lens,
P = 1/f
P = 1/0.5 = +2.D
Q.24. What are homologous structures? Give an example. Is it necessary that homologous structures always have a common ancestor? Justify your answer. [3]
Ans. Homologous structures are organs which have the same structure and origin but different functions.
Example: Forelimbs of man and bird have the same structure, but they have different functions of handling and flying, respectively. Yes, homology indicates common ancestry. Homologous organs have the same basic plan of body organisation during development, but in the adult condition, these organs are modified to perform different functions as an adaptation to different environments.
Section - C
Q.25. Draw a ray diagram in each of the following cases to show the formation of the image when the object is placed
(i) Between the optical centre and the principal focus of a convex lens
(ii) Anywhere in front of a concave lens
(iii) At 2F of a convex lens State the signs and values of magnifications in the above mentioned cases i and ii. [5]
OR
An object 4.0 cm in size is placed 25.0 cm in front of a concave mirror of focal length 15.0 cm.
(i) At what distance from the mirror should a screen be placed in order to obtain a sharp image?
(ii) Find the size of the image.
(iii) Draw a ray diagram to show the formation of the image in this case. [5]
Ans. Ray diagrams:
(i) Between the optical centre and the principal focus of a convex lens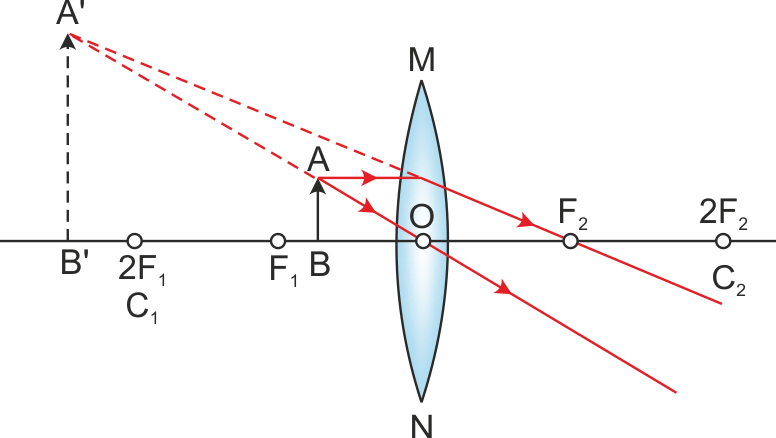 (ii) Anywhere in front of a concave lens
(ii) Anywhere in front of a concave lens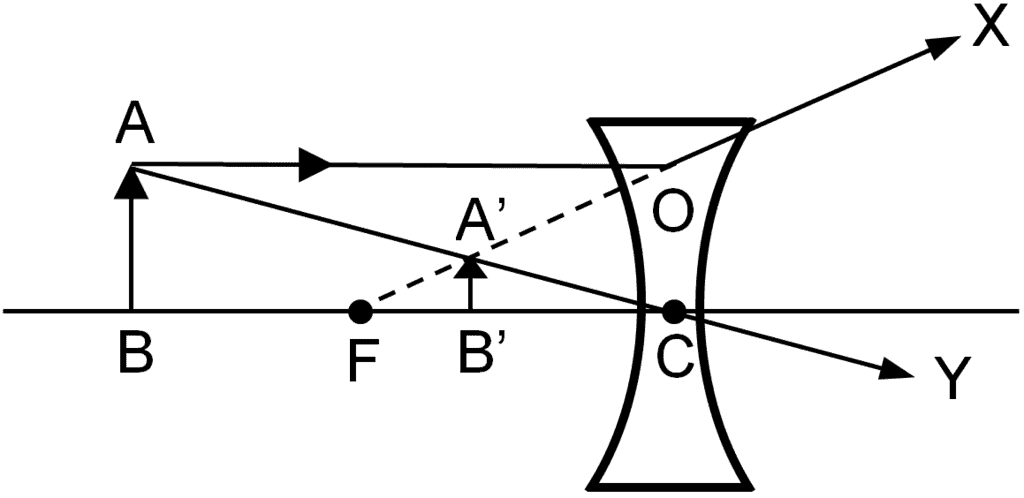 (iii) At 2F of a convex lens
(iii) At 2F of a convex lens
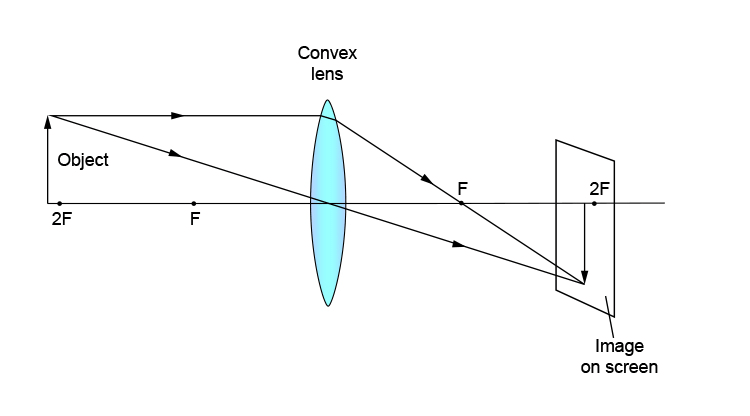
Signs and values of magnification
(i) The image formed in the first case is virtual and erect. Thus, magnification is positive. An image formed is magnified; thus, the magnification of the image will be greater than one.
(ii) The image formed in the second case is virtual, erect and diminished. Thus, the magnification of the image will be negative and less than one.
(iii) The image formed in the third case is real, inverted and of the same size as that of the object. Thus, the magnification of the image is equal to one.
OR
(i) ho = 4 cm
u = –25 cm
f = –15 cm (focal length of a concave mirror)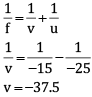
negative sign indicate that image is formed at the same side as that of an object.
(ii)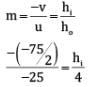
∴ = - 6 cm
Negative sign indicates that the image formed is inverted and real.
(iii)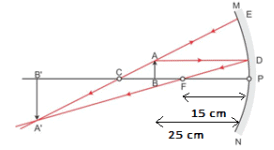
Q.26. (a) What is the law of dominance of traits? Explain with an example.
(b) Why are traits acquired during the lifetime of an individual not inherited? Explain? [5]
Ans.
(a) Law of Dominance: According to this law, characters are controlled by discrete units called factors which occur in pairs, with one member of the pair dominating over the other in a dissimilar pair. This law explains the expression of only one of the parental characters in the F1 generation and the expression of both parental characters in the F2 generation.
For example: a tall pea plant can be crossed with a dwarf pea plant in the following manner.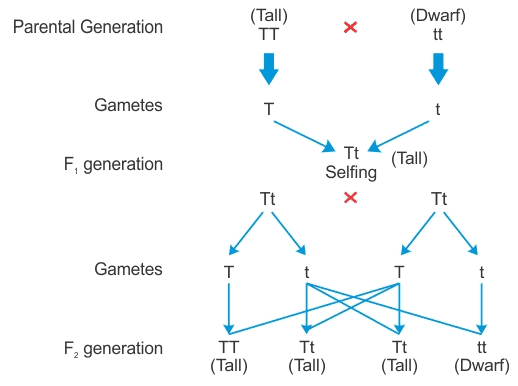 (b) Traits or characteristics which develop in response to the environment and cannot be inherited are called acquired traits. These traits cannot be inherited because there is no change in genes or DNA involved. Only those variations are inherited which come into the germ cell of the organism.
(b) Traits or characteristics which develop in response to the environment and cannot be inherited are called acquired traits. These traits cannot be inherited because there is no change in genes or DNA involved. Only those variations are inherited which come into the germ cell of the organism.
Q.27. (a) A gas is released during photosynthesis. Name the gas and also state the way by which the gas is evolved.
(b) What are stomata? What governs the opening and closing of stomata? [5]
OR
(a) Draw a diagram of the human alimentary canal and label the gall bladder, pancreas, liver and small intestine on it.
(b) Give two reasons to explain why absorption of digested food occurs mainly in the small intestine. [5]
Ans. (a) Oxygen gas (O2) is released during photosynthesis.
During photosynthesis, plants absorb carbon dioxide and sunlight to produce carbohydrates. Solar energy trapped by chlorophyll breaks down the water molecule by the process of photolysis during which oxygen is released. This released oxygen is emitted in the atmosphere.
(b) Stomata are tiny pores present on the surface of leaves which help in gaseous exchange and transpiration.
- The opening and closing of the stomata is controlled by the guard cells.
- When water flows into the guard cells, they swell up and the curved surface causes the stomata to open.
- When the guard cells lose water, they shrink and become flaccid and straight, thus closing the stomata.
OR
(a) Human alimentary canal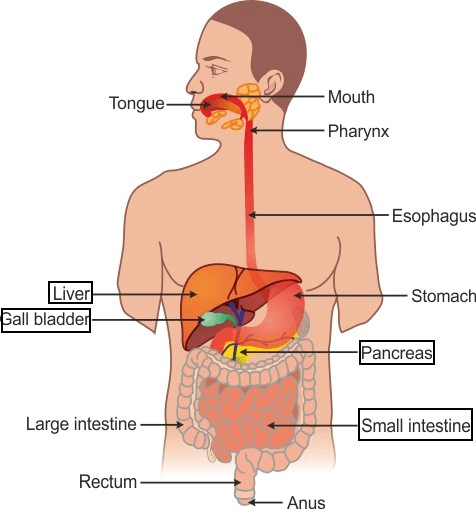
(b)
- The inner surface of the small intestine has millions of tiny, finger-like projections called villi.
- The presence of villi gives the inner walls of the small intestine a very large surface area.
- The large inner surface area of the small intestine helps in the rapid absorption of digested food.
- Also, the wall of the small intestine is richly supplied with blood vessels which help to carry the absorbed food to each and every cell of the body.
Hence, absorption of digested food occurs mainly in the small intestine.
Q.28. Carbon cannot reduce the oxides of sodium, magnesium and aluminium to their respective metals. Why? Where in the reactivity series are these metals placed? How are these metals obtained from their ores? Take an example to explain the process of extraction along with chemical equations. [5]
Ans.
- Metals like sodium, magnesium and aluminium are very reactive and form strong oxides.
- They have greater affinity for oxygen than for carbon. Carbon is not a strong reducing agent; therefore, carbon cannot reduce the oxides of sodium, magnesium and aluminium.
- These metals are placed at the top of the reactivity series.
- The metals placed at the top of the reactivity series are very reactive and are obtained by electrolytic reduction.
Example: Sodium and magnesium are obtained by the electrolysis of their molten chlorides. The metals are deposited at the cathode, whereas chlorine is liberated at the anode. Sodium metal is extracted by the electrolytic reduction of molten sodium chloride.
The reactions are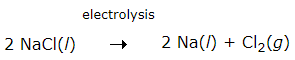
At the cathode: Na+ + e- → Na
At the anode: 2 Cl- → Cl2 + 2e-
Q.29. The position of certain elements in the modern periodic table are shown below.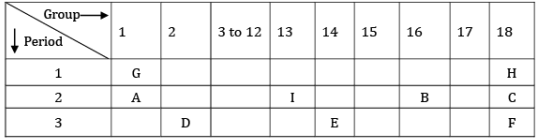
Using the above table, answer the following questions giving reasons in each case:
(i) Which element will form only covalent compounds?
(ii) Which element is a non-metal with valency 2?
(iii) Which element is a metal with valency 2?
(iv) Out of H, C and F, which has the largest atomic size?
(v) To which family does H, C and F belong? [5]
OR
Define atomic size. Give its unit of measurement. In the modern periodic table, what trend is observed in the atomic radius in a group and a period, and why is it so? [5]
Ans.
(i) Element E will form only a covalent compound.
(ii) Element B is a non-metal with valency 2.
(iii) Element D is a metal with valency 2.
(iv) Out of H, C and F, element F has the largest atomic size.
(v) Elements H, C and F belong to the family of noble gases.
OR
- Atomic size is the distance between the centre of the nucleus and the outermost shell.
It is measured in Angstrom (Å). - In the modern periodic table, the atomic radius increases down the group.
- This is due to the new shells being added as we go down the group. This increases the distance between the outermost shell and the nucleus.
- Atomic size decreases on moving from left to right along the period. This is due to an increase in nuclear charge which tends to pull the electrons closer to the nucleus and reduces the size of the atom.
Q.30. (a) Explain with the help of the pattern of magnetic field lines, the distribution of the magnetic field due to a current-carrying circular loop.
(b) Why is it that the magnetic field of a current-carrying coil having n turns is ‘n’ times as large as that produced by a single turn (loop)? [5]
Ans.
(a)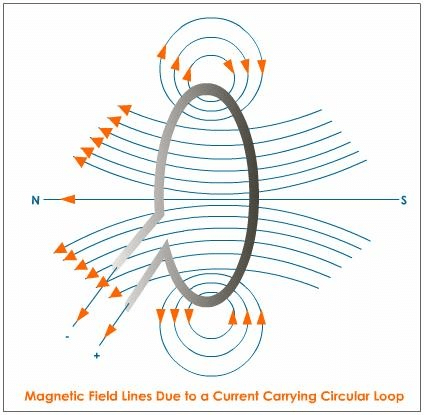
- Magnetic field lines near the coil are nearly circular or concentric. The magnetic field at the centre of the coil is maximum and almost uniform.
- Looking at a face of the coil, if the current around it is in the clockwise direction, then the face is the south pole. If the current around it is in the anticlockwise direction, then the face is the north pole. This is called the clock rule.
(b)
- The magnitude of a magnetic field at the centre of the coil is directly proportional to the number of turns of the coil and current flowing through the loop. Thus, if the number of turns is increased by ‘n’ turns, the current increases and thus with this, the magnetic field also increases. Thus, the strength of the magnetic field also increases.
Hence, the magnetic field of a current-carrying coil having n turns is ‘n’ times as large as that produced by a single turn.
FAQs on Class 10 Science - Previous Year Paper with Solutions- 2020
| 1. What is the format of the Science Past Year Paper for Class 10 in 2020? |  |
| 2. How many sections are there in the Science Past Year Paper for Class 10 in 2020? |  |
| 3. What is the content covered in Section A of the Science Past Year Paper for Class 10 in 2020? |  |
| 4. How many meaningful Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) should be provided for the Science Past Year Paper for Class 10 in 2020? |  |
| 5. What should be the complexity level of the questions and answers in the Science Past Year Paper for Class 10 in 2020? |  |






















