Class 10 Exam > Class 10 Notes > Notes of Heredity and Evolution with Mind map..
Notes of Heredity and Evolution with Mind map.. - Class 10 PDF Download
Most of the students would think that "This chapter is lengthy, so how can I remember some important points?" And other Students may thought that "If I learn all the important points of this chapter, then I would forget some points. So what should I do?". Please, don't be get worry, I'll explain it really well friends...
SO WHY LATE, LET US START THE CHAPTER...
-:HEREDITY AND EVOLUTION:-
INTRODUCTION:- You have already learned the Chapter "How do Organism reproduce". In that chapter you have learnt how the organisms reproduce by asexually and sexually In that, you have noticed that variations occurs from Unicellular organisms to Multicellular organisms like Birds, Mammals etc.., Now, you are going to learn about how the organism gets variation in environmental condition, and can know how the species will be evolved from the primitive organisms, and also you can know how plant's characteristics are expressed as a dominant or recessive, and also same in the individuals. We can learn how the Evolution occurs stage - by - stage... So, these are all the concepts, I'm gonna explaining you friends..
Reproduction is the process in which organism give rise to new individual of own kind with subtle differences.
In asexually reproducing organisms, there would be only minor difference because of small inaccuracies in DNA copying.
In sexually reproducing organisms, both parents would have quiet different patterns of accumulated variations (XY, XX) thus the next generation is inherited (passed) by common basis body design and subtle changes in them and successive generations (future generation organisms) will have differences when compared to the first generation organisms as well as newly created differences.
Variations have equal chance of surviving but not for all the variations. It depends on nature of variation. Selection of Variation for survival is not done by us. It is done by the environmental factors (like wind, rainy, sunny etc..,) Variation occurs as the environmental condition changes.
What is the month now? It's October, Animals and Humans know how to take care of their health whether it may be sunny day, rainy day, winter season, autumn season etc.., etc..,. So, if they don't care how to take care of their health. Do they (Animals and Humans) survive?. No, as the season and time changes, we should change our lifestyle for the betterment of our life. This makes you to promote survival...
So, now the question is,
1) If trait 'A' exist in 10% of a population of an Asexually reproducing species (remember the point it is asexually reproducing species) and a trait 'B' exist in 60% of the same population. So, which trait is likely to have arisen earlier?.
In this question they asked, which trait has arisen earlier. 60% or 10%? You know 10% is lesser than 60%. So, 60% is the answer.
Answer:- Trait 'B'. Because, it must have arisen earlier and has now spread to 60%.
Next question,
2) How does the creation of variations in a species promote survival?
Means, how the creation (rise) of variation helps the species to get survival?
Answer:- Reproductive process especially in Sexual reproduction give rise to the new individual (organisms) that are similar (looks like same) but slightly (lightly) difference, thus new variants (organisms) emerge in Species (group of organisms like plants and animals).The variants which are suitable to prevailing (most common) environment survive by natural selection, as environment goes on changes, (winter, summer, rainy, cloudy etc..,) the variants also changes their characteristics (behavior or quality) to adopt it in a changed environment for the survival.
We know the word Variation, but what is the definition of it?. Let us see the definition of Variation as well as Genetics.
(a) Variation:- Difference in characteristics between parents and offsprings.
(b) Genetics:- Deals with the study of Heredity and Variation.
So now, we had come to the concept of Heredity. So, what is Heredity?.
3) Define Heredity?
Answer:- The process by which traits and characteristics are inherited (passed) from parents to the offsprings (children).
(OR)
Heredity can be defined as "Similarity between parents and offsprings".
During sexual reproduction, child get same trait (like height, dwarf, colour, hair, eye) which is influenced by both maternal (mother) and paternal (father) DNA material. Thus, for each trait, there will be two versions in each child. So, What will be? , Then? , The trait seen in child? , This is explained by 'Gregor Johann Mendel' (Father of modern genetics).
Mendel observed the traits first in plants by doing experiment. So, which plant he used in his experiment? Let us see the plant he used in his experiment.
Mendel choose the Pea plants (Scientific name - "Pisum sativum"). Now the question is,
4) Why Mendel choose Pea plants for his experiment?
Means, why he choose only pea plants itself for his experiment, but not other plants is used in his experiment. What are the qualties do Pea plants have? Let us see, what are the qualties do Pea plants have.
Answer:-
[•] Pea plants can be grow easily.
[•] They produces large number of seeds.
[•] They have a short lifespan.
[•] They have 7 contrasting characters.
[•] They subjected to both self and cross pollination.
You observe all the qualities of Pea plants, but you may thought that what are those 7 contrasting characters?. Let us see..
5) Mention the contrasting characters of Pea plants?
Answer:-
a) Stem length (tall/dwarf).
b) Colour of Seed (Yellow/Green).
c) Colour of Seed coat (Grey/White).
d) Shape of seed (Round/Wrinkled).
e) Colour of pod. (Pod means covering layer of seed which helps to protect seeds from unfavorable condition).
f) Shape of pod.
g) Position of flower.
Mendel asusually cross the plants, to observe the traits, which will be expressed as a dominant or recessive. So let it be.. We shouldn't disturb him. He do whatever he want. As he is crossing the plants to observe the traits which have been expressed, let us know how many types are there in crossing the plants.
There are mainly two types, they are:-
[•] Monohybrid cross.
[•] Dihybrid cross.
We can know the two types, but it's look like incomplete, let us know the details of Monohybrid and Dihybrid cross.
6) Define Monohybrid cross?
Answer:- A cross between two pea plants which differ in one specific character.
Now, we should tell about the Mendel, because, he is so busy in crossing the Pea plants for his experiment. See, how much hard work he is doing. So, we should discuss what he is going to write it in his notebook regarding to his observation.
Mendel choose tall (TT) and short (tt) Pea plants for Monohybrid cross.
Offsprings resulting (showing it's trait) immediately from cross of the first set of parents (plants T × t) is called F1 generation (progeny).
In F1 generation, all of them are tall (Tt).
Offsprings resulting (showing it's trait) from cross (self pollination) among the members of F1 generation are called F2 generation.

Here, in this above picture, you can see the Checker board or Punnet square of Monohybrid cross. Please, observe it.. Now, let us define Homozygous and Heterozygous.
Homozygous:- Similar type of trait present in Zygote ( Zygote forms after the fusion of male and female gamete) of chromosomes.
Example :- TT.
Heterozygous:- Different type of trait present in Zygote of chromosomes.
Example :- Tt.
For any character (traits), these are the two forms (Homozygous - TT and Heterozygous - Tt) of factors in sexually reproducing organisms which may be identical or different forms, normally one express itself called Dominant trait and another does not express itself even though it is present is called Recessive trait.
Example:- Monohybrid cross tall (T) is Dominant trait and dwarf (t) is Recessive trait.
7) Define Dihybrid cross?
Answer:- A cross between two pea plants with two pairs and contrasting characters.
Round Green (Ry) × Wrinkled Yellow (ry).
Note:- F1 generation plants are Round Green only (RrYy).
Note:- F2 generation have four kind of plants.
Dominant trait:- The trait which express it's character.
Recessive trait:- The trait which doesn't express it's character even though present.
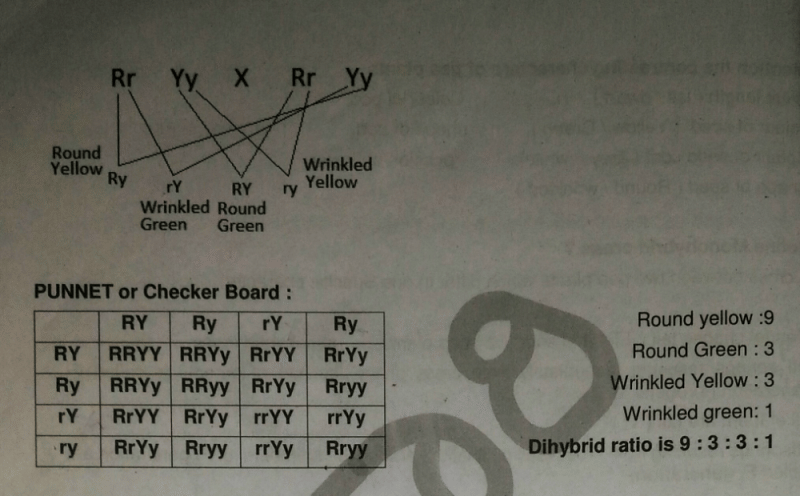
Here in the above picture, you can observe the Checker board or Punnet square of Dihybrid cross. You can see the Dihybrid cross ratio. This Punnet square is mentioned wrong. So, please look at out your NCERT textbook..
I have told you that the traits get express. So, let us know how the traits get express.
8) How do these traits get expressed?
Answer:- Gene in DNA stimulates (actives) the rate of enzymes function which produces particular protein or hormones. If enzymes work more efficiently, produces more hormone, so plants grow taller. If enzymes work less efficiently, produces less hormone which results the plant to grow short. Thus gene control characteristics. In a Heterozygous plant (Tt), only the gene 'T' will be able to make hormone as it is dominant over the 't' gene. So plant grow tall as trait 'T' expressed as dominant.
Now, you cleared that how the traits get expressed. Let us know how the traits get expressed in Dihybrid cross..
9) How do trait get expressed in Dihybrid cross?
Answer:- Gene set or chromosomes (XX,XY) controls separate character, normally move independently each other during gamete formation (XY and XX). So combination of characteristics which are not present in the parental forms are produced in F2 generation along with the parental form.
Let us know how the chromosome number is restored in future generation (successive generation) during Sexual reproduction..
10) How does chromosomes number is restored in successive generation during sexual reproduction?
Answer:- For any character, there are two forms of Gene set or chromosomes (XX,XY) in sexually reproducing organisms, but their germ cell or gamete consist only one form of Gene or chromosome (X and Y). When gamete fuse to form progeny, [offsprings (XX - boy) and (XY - girl] the pair of chromosomes are restored.
After so many while, Finally, Mendel's experiment is came to an end.. I'm totally hats off for his contribute. He wrote a note of his last observation in his experiment. I'm totally tired of talking about him.. Okay, let us make an end of his experiment faster.. let us know that what his experiment proved in his experiment..
11) How do Mendel experiment show that traits may be dominant or recessive?
Answer:- When Mendel cross pollinated pure tall pea plants with dwarf pea plants, he got tall plants in F1 generation. He got both tall and dwarf pea plants in the ratio of 3:1 in F2 generation. This shows that dwarf character was present in F1 tall plants. But, it was not expressed. Only, trait of tallness was expressed. From this, we may conclude, traits may be dominant or recessive.
Next question,
12) How do Mendel's experiment show that traits are inherited independently? (Most important question).
Answer:- In Dihybrid cross, chromosomes control separate character, normally move independent of each other during gamete formation. So, combination of characteristics which are not present in the parental form are produced in next F2 generation. From this, we can show that traits are inherited independently.
Mendel's experiment is finally completed and he contributed to the biological scientists. He has been appreciated by the scientists who have been very well in Botanical research as well as in plant research institutions. He has been awarded.. But sorry, I don't know those awards. Because, it is out of the book.
Now, there is no more to explain regarding to the Mendel's experiment... That's all about him..
I haven't explained some important points, because, in this mind map, I have already mentioned, so please look at out..
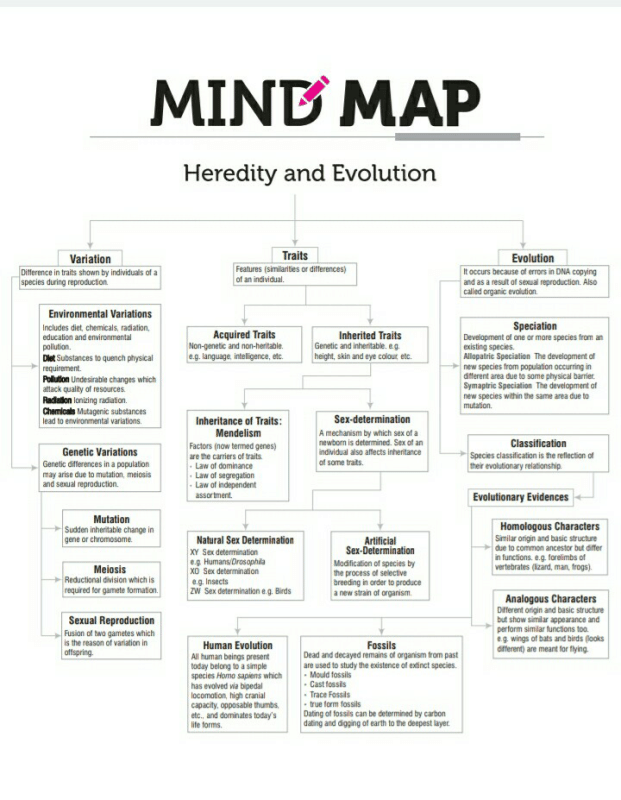
Mind map of "Heredity and Evolution"..
Let us discuss the new concept "Autosomes and Sex chromosomes".
13) What are Autosomes and Sex chromosomes?
Answer:- In human, there are 23 pairs of chromosomes. Only 22 pairs (non-reproductive) determine character other than Sex is called Autosomes. The one pair, which determine sex of child is called Sex chromosomes.
Now the concept of Heredity is end. Let us start the new concept "Evolution".
"EVOLUTION", how this words makes you to like a very proud feel when you are going to medical field.. But you may thought that why I am saying like this. Those who are fond to study in Medical field, they would like science more than their life and they learn so many things in Medical field. It never ends even if we get buried..
Let us know the details of Evolution with it's definition...
14) What is Evolution?
Answer:- Changes inherited during biological population over successive generation.
(OR)
Gradual change in species and genetic makeup that allows it to adopt to it's surrounding better than others.
(OR)
Study of how complex organisms of today are evolved from simple form of past.
Note:- Evolution is continuous process.
The frequency of inherited trait (genes or chromosomes) changes over generatios is the essence (existence) of idea of Evolution.
Let us discuss how the individual with particular trait leads to increase in population.
15) What are the different ways in which individual with particular trait increase in population?
Answer:-
(I'll take Cockroach, Sparrow and Elephant name for this answer. Because, Beetle, Crow and Elephant is mentioned in the textbook. So, it should be different. You can take any of the insects name.. it's your choice).
Event 1:- All Red Cockroaches on green bush are eaten by the Sparrow. But Green Cockroaches among them were survived.
It is an example of Natural selection in which change in the frequency of trait like Green, results in adaptation of cockroach population to their environment better and give survival advantage.
Event 2:- Among Red and Blue cockroaches, Red Cockroaches disappear due to the accident event (Elephant is stepped on the Cockroaches) and Blue Cockroaches are survived.
It is an example for Genetic drift in which change in the frequency of the trait like Blue is due to accidental event, even though that does not give any survival advantage.
Note:- Sometimes, evolution may happens due to Mutation (Sudden change in DNA sequence).
Note:
Genetic drift:- The random change in general frequency and gene number by chance only, irrespective of its being advantageous or not in population.
Let us know the traits which are been acquired and inherited.. There are mainly two types of traits, namely,
[•] Acquired traits.
[•] Inherited traits.
[•] Acquired traits:- Traits are acquired by organism during their lifetime, these traits are not passed from one generation to another.
Examples:- Swimming, Drawing, Muscle building.
[•] Inherited traits:- Traits are controlled by genes, can be passed from one generation to another.
Examples:- Colour of Cockroach, Colour of eye, skin and hair.
Let us learn the details of Speciation and the factors which leads to the rise of new species.
Speciation:- Origin (rise) of a new species from existing one.
(OR)
It is evolutionary process by which reproductively isolated (separated) biological population evolve to become distinct species.
16) What are the factors could lead to rise in new species?
Answer:- The factors could lead to rise in new species are:-
[•] Genetic drift.
[•] Natural selection.
[•] Mutation.
[•] Geographical isolation and species.
16) Define Natural selection, Mutation and Geographical isolation and species?
Answer:-
Natural selection:- Change in the frequency of trait that doesn't give any survival advantage.
Mutation:- Sudden change in DNA sequence.
Geographical isolation and species:- The separation of two population of the same species by physical barrier (environmental condition like wind, water) and niche (place).
Note: Types of Speciation are:-
(a) Allopatric.
(b) Paripatric.
(c) Parapatric.
(d) Sympatric.
Note:- Speciation is very quick in sexually reproducing organisms as they get accumulated (over a period of time) variations from both parents. But, it is slow in asexually reproducing animals and self pollinating plants as they get less variation from their parents. Geographical isolation does not impact (effect) much on asexual reproducing organisms and self pollinating plants.
17) Will Geographical isolation be a major factor in speciation of self pollinating plant species, why or why not?
Answer:- No, as the population is self pollination, it would be less prone (suffer) to factors which result from Geographical location.
Note:- On cross pollinating species, Geographical isolation would be major factor as it could result in faster accumulation of variation in the two geographically separated populations.
Next question,
18) Will Geographical isolation be a major factor in the speciation of an organism that reproduce asexually, why or why not?
Answer:- No, little variation in asexual organisms due to the Geographical isolation may not be passed to next generation, as the change in DNA is not enough to rise new species.
Now, let us discuss Evolution and Classification.
Evolution and Classification
Similarity and difference among organisms is used to classify organisms, which can be done on the basis used of 'characteristics'.
What is the meaning of word 'characteristics'? Let us know.
Characteristics are details of appearance or behavior.
Examples:- Humans supposed to walk or ride a bike, plants prepare their own food is their characteristics. You can observe, they (plants and Humans) showing their behavior.
Let us see how the Evolutionary relationship can be detected and what are those Evolutionary relationship with complete explanation of each and every point..
Evolutionary relationship can be detected on the basis of followings.
(OR)
The evidences to find out the Evolutionary relationship are:-
[1] Structural evidence (Anatomy).
[2] Fossil evidence.
[3] Embryological evidence.
[4] DNA comparison.
Structural evidence can be detected by using two types, namely,
(a) Homologous organs.
(b) Analogous organs.
(a) Homologous organs:- Organs having common body structures but perform different function.
Examples:- Forelimbs of Amphibians, Reptiles, Birds and Mammals.
(b) Analogous organs:- Organs having different body structures but perform similar function.
Examples:- Wings of Bat, Birds, Insects.
Let us learn regarding to the fossils..
Fossils:- Preserve remains of living organisms from remote past.
We can know what is Fossils? But we don't know how the formation of fossil occurs layer by layer.. so why not, let it check the answer of it...
19) How do Fossils form layer by layer?
Answer:- About 100 million years ago, some invertebrate (organisms without backbone) on sea bed (land) die, buried in sand and sand stone formed under pressure as the Fossil formation takes place in deep of Earth's crust.
I'm taking an example of Dinosaur and Horse..
Million years later, Dinosaurs living in that area will die, it is buried in mud which is compressed (tightly joined) into rock. Again, million of years later, Horse like creature dying in the same area fossilized in rocks above these earlier rocks.
You can know that how the formation of Fossil takes place. Do you just want the information of the formation of Fossils? No, it's not enough.. We should know how the fossil's age is estimated.. So, let us see..
Age estimation of Fossils
1. Deeper the layer where the fossil is found, older it is.
It means, how much fossil is deposited deeper in the Earth crust than other fossils, it indicates that it is older than other fossils. Deeper the fossil is found, then it is very older than any other fossils. Of the fossil is founded in a very deeper layer of the earth's crust, then it indicates that this fossil is so older than any other fossils.
2. Age estimation by detecting ratios of isotopes of different elements.
It means, Age estimation of the fossils is detected by the Isotopes of different elements. You haven't know that how the age estimation of Fossils is detected... I'll explain..
The Palentologists (those who study regarding to the Fossils) detect the age of the fossils by using the radioactivity of isotopes of different elements. Different isotopes of elements helps to show how much the fossil is older. Isotopes of element like carbon is installed in the machine which can be hold it in hand. If we place the machine near the fossil, it helps to scatter the light to fossil and the year how much older it is, will be calculated and the number of years how much older it is, will be displayed in the machine. Different colour indicates whether the fossil is very older or newer.
You may think that I have told already that the Fossils give evidence for the Evolution. So, how it give evidence for the Evolution? Let us discuss..
20) How do Fossils give evidence for evolution?
Answer:-
[•] Fossils at upper layers are more complex than that of older layers.
It means, upper layer of will be more stronger (complex) than the older fossil which is deposited in the deeper layer of the earth's crust.
[•] Fossil records shows that there is link between Birds and Reptiles.
It means, fossil collection shows that there is something link between Reptiles and Birds. So let us see the example..
Example:- Fossilized feathered like dinosaur like ARCHAEOPTERYX had tail like reptiles and feather like birds. It also have beak like a bird and it's teeth like a reptiles. So, it is considered as link between Birds and Reptiles.
Next question,
21) How does DNA comparison can be taken as evidence for evolution?
Answer:- Changes in DNA during reproduction is basic event in evolution. So, comparing the DNA of different species gives us direct estimation of how much DNA has changed during evolution of species.
It means, changes of DNA during reproduction will be the basic event of evolution. Because, Change in DNA occurs only during reproduction of organism itself as most of the variations occurs during the reproduction itself. Change in DNA makes evolution of species. We can check the estimation (calculation) of DNA of different species like birds, animals, plants, etc.., This helps to know us that how much species DNA has changed to check the evolution.
Let us discuss Evolution by Stages.
Evolution by Stages
Complete variation in organisms did not come or appeared at once, it is the gradual change as one variation appeared as advantage to primitive (older) Artificial selection organisms gradually developed into sophisticated (more experienced) organs in next (future) generation.
Here, some evolutions of important organs and methods are discussed.
(1) Evolution of eyes.
(2) Evolution of feathers.
(3) Artificial selection.
Let us discuss about Evolution of eyes, Evolution of feathers and also Artificial selection.
EVOLUTION OF EYES
In primitive (older) organism, there were no eyes. But, in Euglena, there was eye spot which could recognize (identify) light. And in Planaria, eye like structure appeared. Because, it is advantage for the Planaria as the eye is slightly well developed. Evolution of complete eye will be occurs or takes place in higher animals.
EVOLUTION OF FEATHERS
In some dinosaurs, feather like structure was used to provide insulation (protection from the foreign beings like weather conditions, attacking species etc..,) but later, they(feathers) were used for flight (fly in the sky). Because of Evolution of feathers.
ARTIFICIAL SELECTION
It is the process of selecting desired (more wanted) trait to breed (to cross) other plants / animals to get desired traits.
Examples:- Obtaining of Dogs from Wolves, Obtaining of Sheep's from Crows, Obtaining of Kohlrabi, Cauliflower, Broccoli, Cabbage, Red cabbage, Kale from Wild cabbage.
Let us discuss regarding to Molecular Phylogeny.
Molecular Phylogeny:- It is a branch of Biology, which analysis (study the details of) genetic hereditary, molecular differences in DNA sequence (happens) to gain information of an organisms evolutionary relationship.
Note:- This is based on idea of organisms, which is more distantly related will accumulate (over a long period of time) a greater number of differences in DNA.
Let us discuss regarding to the Evolution and Progress.
Evolution and Progress
Evolution is not the progress. It is simply generation of diversity and shaping of diversity by environmental selection. The only progression thing in evolution is, formation of complex organisms over the time. Thus, all organisms which have a exist body design and better, then it is suitable to their environment.
Now, it is the last concept we are going to discuss. It is Human evolution.
Human evolution
Human evolution is a part of biological evolution as distinct species. Here, we study how the changes and development of Human beings is occurred, this involves mainly physical anthropology (physical study of humans), linguistics (study of languages), and genetics.
Note: The tools used to study Human evolution are:-
(a) Excavating, time-dating, study of fossils.
(b) Determining DNA sequence.
Now the question is,
22) What are the tools used to study the Human evolution?
Answer:- The tools used to study Human evolution are:-
(a) Excavating, time-dating, study of fossils.
(b) Determining DNA sequence.
Note: On the basis of colour, size, look, there are 5 races (aganist) But, it is not on biological basis. All they have similar DNA composition. So, all races belongs to same species and can breed among themselves.
Next question is,
23) A man with blood group 'A' married a woman with blood group 'O' and their daughter has blood group'O' is the information enough to tell you, which of the following traits - blood group 'A' or 'O' is dominant? Why or why not?
Answer:- No, this information is not sufficient to determine which of the traits blood group 'A' or 'O' is dominant, this is because, we don't know about the blood group of all the progeny (offsprings), blood group 'A' can be genetically AA or AO. Hence, this information is incomplete to draw any such conclusion.
Next question,
24) How the sex of the child is determined in Human beings?
Answer:-
[•] Women have perfect pair of sex chromosomes called XX.
[•] Men have a mismatched pair of sex chromosomes called XY.
[•] If father release X chromosome and fuses an egg of mother's X chromosome, then the born baby will be Girl (XX).
[•] If father release Y chromosome and fuses an egg of mother's X chromosome, then the born baby will be Boy (XY).
Next question,
25) What are traits acquired during lifetime of an individual, but not inherited?
Answer:- Traits acquired during their lifetime are the changes in the non-reproductive cell (somatic cells) of the organism are not capable of being transferred to the next generation. Changes that occurs in DNA of germ cell are only inherited.
It means, as the traits which are acquired during lifetime will be stored in non-reproductive cell (means, somatic cells). The traits can be pass if these traits are stored in reproductive cell (non-somatic cells). Traits will be inherited when the changes that occurs in DNA of germ cell.
Now, the last question is,
26) What are the small number of surviving tigers, a cause of worry from the point of view of genetics?
Answer:- The tigers have very less variation in genetic characteristics among each other, and if nature (environmental condition) would change drastically (very strong effect), no tigers may survive.
Example:- Diseases by microbes.
Decrease in population of tigers also indicates tigers variants are not adopted to the existing environment.
Thank you one and all...
Hope this document may helps a lot for you...
FAQs on Notes of Heredity and Evolution with Mind map.. - Class 10
| 1. What is heredity? |  |
Ans. Heredity refers to the passing on of traits or characteristics from parents to offspring through their genes. It is the process by which genetic information is transmitted from one generation to the next.
| 2. What is evolution? |  |
Ans. Evolution is the process of gradual change in the inherited traits of a population over successive generations. It involves the accumulation of small genetic variations through natural selection, genetic mutation, and genetic recombination.
| 3. How do genes determine heredity? |  |
Ans. Genes are segments of DNA that contain instructions for the formation of specific traits or characteristics. The genes inherited from parents determine the traits an individual will possess. They are passed on from parents to offspring through gametes (sperm and egg cells).
| 4. What is the role of natural selection in evolution? |  |
Ans. Natural selection is a key mechanism of evolution. It refers to the process by which certain traits become more or less common in a population over time due to their impact on survival and reproduction. Individuals with advantageous traits are more likely to survive and pass on their genes, leading to the evolution of a population.
| 5. How does genetic variation contribute to evolution? |  |
Ans. Genetic variation is the presence of differences in the genetic makeup of individuals within a population. It is the raw material for evolution. Genetic variation allows for the occurrence of different traits, and through natural selection, certain variations may become more prevalent in a population, leading to evolutionary changes.
Related Searches



















