Class 9 Exam > Class 9 Notes > Tissue Notes....
Tissue Notes.... - Class 9 PDF Download
DEFINITION
Tissue
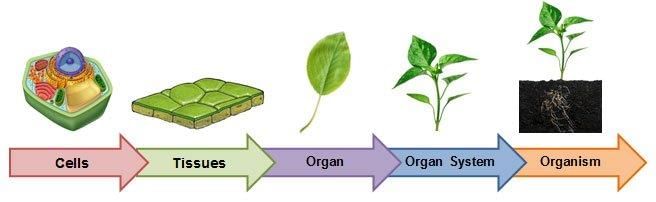
- Tissue is a group of cells that are similar in structure and are organised together to perform vital functions.
- Different types of tissues work together and form an organ.
- Organs are arranged into a system to form an organ system. For example, reproductive system etc.
- An organism consists of such organ system working together.
- Study of tissues is called as histology.
DEFINITION
Plant tissue and animal tissue
| Plant tissue | Animal tissue |
| Cells of plant tissue have cell wall. | Cells of animal tissue do not have cell wall. |
| Some tissues are living and some are dead. | All tissues are living. |
| Growth is restricted to the tips of stem and roots. | Growth is uniform all over the body. |
| They are mainly of two types permanent tissue and meristematic tissue. | They are of four types muscle tissue, epithelial tissue, nervous tissue and connective tissue. |
| These tissues require less energy and maintenance as plants do not require movement. | Due to entensive body mobility these tissues require more energy and maintenance. |
| They provide strength and support to the plant. | They control all functions. |
DEFINITION
Types of meristematic tissue
Classification based on origin and development.
- Promeristem or primordial meristem
- Primary meristem
- Secondary meristem
- Apical meristem
- Intercalary meristem
- Lateral Meristem
- Protoderm meristem
- Procambium meristem
- Ground Meristem
- Mass meristem
- Rib or file meristem
- Plate meristem
DEFINITION
Growth of roots in onion bulbs
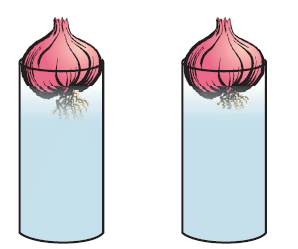
- From the activity of growth of roots in onion bulbs, it can be found that growth of plants occurs only in certain regions.
- Meristematic tissues are located in these regions, which are responsible for growth.
DEFINITION
Difference between meristematic and permanent tissue
| Meristematic tissue | Permanent tissue |
| These tissues have the capacity to divide. | These tissues have lost the capacity of division. |
| They have thin cell wall. | They have thick cell wall. |
| They produce permanent tissues. | They are produced by meristematic tissue. |
| They contain many small vacuoles in their cytoplasm. | They contain only a single large vacuole in their cytoplasm. |
| Intercellular space is absent. | Intercellular spaces is present. |
| They contain dense cytoplasm with prominent nucleus. | They contain thin cytoplasm with normal nucleus. |
| It is a simple tissue. | It can be simple or complex. |
DEFINITION
Simple permanent tissue (supportive tissue) - Sclerenchyma
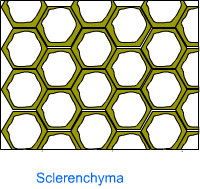
- These are long, thick, narrow, dead cells with a deposit of lignin in their cell wall.
- They have no intercellular spaces.
- Sclerenchyma occur around the vascular tissues in stems, in the veins of leaves, and in the covering of seeds and nuts.
- They provide strength to the plant.
DEFINITION
Epidermal cells
- The epidermis cells is a single-layered group of cells that covers plants' leaves, flowers, roots and stems.
- It forms a boundary between the plant and the external environment.
- The epidermis serves several functions, it protects against water loss, regulates gas exchange, secretes metabolic compounds, and (especially in roots) absorbs water and mineral nutrients.
DEFINITION
Epithelial tissue
- Epithelial tissues act like a barrier to keep the different body systems separate.
- It forms a lining all over the body of the organism and protects the inner lying parts.
DEFINITION
Simple squamous epithelium
- Flat, thin and scale like cells with no intercellular spaces.
- Provides mechanical support and transportation of substances through selectively permeable membrane.
- It is found in the outer layer of the skin, lining of blood vessels, lungs, alveoli, oesophagus, lining of mouth.
DEFINITION
Stratified squamous epithelium
- The cells are arranged in a pattern of layers.
- They are found in the outer layer of skin and cornea.
- The major function of this tissue type is protection, as it is found in areas that undergo wear-and-tear.
DEFINITION
Columnar epithelium
- Consists of tall, rectangular or column shaped cells (cylindrical cells).
- It is found in the lining of the stomach and intestines.
- It facilitates the movement of nutrients across the epithelial barrier.
DEFINITION
Ciliated columnar epithelium
- Consists of columnar cells with thread like projections called as cilia.
- These cilia push the mucus forward into the nasal tract to clear it.
DEFINITION
Cuboidal epithelium
- Consists of cubical (cube-shaped) cells.
- It is found in the lining of the kidney tubules, salivary glands and thyroid glands, where it provides mechanical support.
- It plays an important role in absorption of useful material and secretion of saliva.
DEFINITION
Connective tissue
- The cells of a connective tissue are loosely scattered in a matrix.
- The matrix can be a fluid, jelly like, dense or rigid. The nature of matrix depends on the function a connective tissue serves.
- The role of connective tissue is to protect, support, and bind together parts of the body.
DEFINITION
Blood
- Blood is composed of blood cells (RBC, WBC), platelets and plasma.
- RBC is most abundant cell in blood. It carries oxygen and carbon dioxide by forming complex with haemoglobin.
- WBC helps in providing immunity to the body.
- Platelets help in blood clotting.
- Blood plays an important role in transportation of various substances in the body.
- It also helps in osmoregulation and temperature control.
DEFINITION
Characteristics of blood
Characteristic | Circulating, never stationary |
Taste | Salty |
Colour | Bright red |
Volume of blood in average human body | 5- 6 litre |
DEFINITION
Lymph
- It is the fluid surrounding the body cells.
- It contains WBCs.
- Its main function is transporation and protection against diseases.
DEFINITION
Tendons, ligaments, adipose tissue
Tendons
- Tendons are tough and non-elastic and provide great strength and limited flexibility.
- It is fibrous connective tissue that usually connects muscle to bone.
- Ligament is the fibrous connective tissue that connects bones to other bones.
- They are tough, elastic and provide strength and flexibility.
- Adipose tissue is composed of fat globules.
- This tissue is found below the skin and beneath the organs.
- It provides insulation and works as a cushion.
DEFINITION
Bone
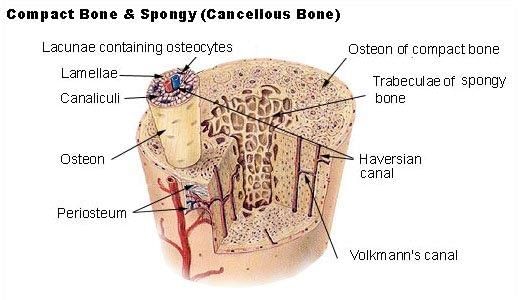
- Bone is mainly composed of osteoblasts.
- Bone makes the skeletal system.
- Skeletal system is responsible for providing structural framework to the body.
- It provides protection to important organs and facilitates movements.
- Bone cells are embedded in a hard matrix composed of calcium and phosphorus compounds.
- Bones anchor the muscles.
DEFINITION
Cartilage
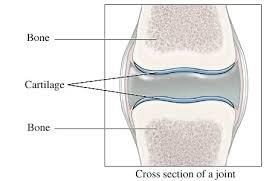
- Cartilage is semi-transparent, elastic, non-porous tissue.
- It is found in the nose, ears, rings of trachea, larynx etc.
DEFINITION
Muscular tissue
- Muscular tissue is composed of muscle cells.
- Muscle cells are specialized cells which have the capability to contract and expand and have tensile strength.
- Due to contraction and expansion, muscles facilitate various kinds of movements in the body.
- Muscular tissues are of three types striated muscle, smooth muscle and cardiac muscle.
DEFINITION
Difference between smooth, striated and cardiac muscle
| Characters | Smooth muscle | Striated muscle | Cardiac muscle |
| Common names | Unstriped/nonstriated /involuntary / visceral | Striped/voluntary /skeletal | Heart muscle |
| Arrangement | In the form of thin sheets | In the form of fascicles | In the form of network |
| Shape of the muscle fibres | Elongated, spindle shaped | Elongated cylindrical and unbranched | Elongated cylindrical and branched |
| Sarcolemma | Absent | Absent | Thin and indistinct |
| Sarcoplasm | Scanty | Abundant | Abundant |
| Nucleus | Single in each fibre; situated in the broadest region | Many in each fibre; situated towards sarcolemma | Many in each fibre; situated away from sarcolemma |
| Intercalary discs | Absent | Absent | Present separating the nuclei |
| Myofibrils | Do not form striations | Form distinct striations | Form faint striations |
| Blood supply | Poor | Rich | Very rich |
| Nerve supply | Sensory nerves from CNS | Motor nerves from CNS | Sysmpathetic, Parasympathetic nerves from ANS |
| Contractions | Slow, rhythmic and sustained | Slow, or rapid arhythmic and not sustained | Slow highly rhythmic and not sustained |
| Fatigability | Does not easily experience fatigue | Very easily experiences fatigue | Never Experiences fatigue |
| Mode of action | Involuntary | Voluntary | Involuntary |
| Occurrence | Almost all visceral organs except the heart | Associated with bones in limbs, also in diaphragm and tongue | Only in the heart and aorta |
DEFINITION
Neural tissue
- Neural tissue is specialized for the conduction of electrical impulses that convey information or instructions from one region of the body to another.
- Parts of neural tissue are neuron, synapse, neurotransmitters, neuroglia, Schwann cells.
- Neurons are classified on the basis of their structure (nonpolar, unipolar, pseudounipolar, bipolar and multipolar) and function (sensory, motor and interneurons).
- Neuroglia are cells of the central nervous system (CNS) and peripheral nervous system (PNS) that support and protect the neurons. They are divided into two categories macroglia and microglia.
FAQs on Tissue Notes.... - Class 9
| 1. What are tissue notes? |  |
Ans. Tissue notes are small-sized pieces of paper or thin sheets that are used to jot down important information or key points. They are often used by students to summarize and revise their class notes in a concise and organized manner.
| 2. How can tissue notes help in studying? |  |
Ans. Tissue notes can be very helpful in studying as they provide a condensed version of the subject matter. They allow students to quickly review important concepts, facts, and formulas. Tissue notes can also serve as a handy reference during exams or when preparing for class discussions.
| 3. What should be included in tissue notes? |  |
Ans. Tissue notes should include the most essential information from the original notes or study material. This may include key definitions, formulas, diagrams, examples, and important facts or concepts. It is important to keep the notes concise and organized for easy reference.
| 4. Are tissue notes effective for exam preparation? |  |
Ans. Yes, tissue notes can be highly effective for exam preparation. By condensing the study material into concise points, tissue notes help in improving retention and understanding of the subject matter. They also save time during revision as students can quickly review the key points instead of going through lengthy notes or textbooks.
| 5. How can I create effective tissue notes? |  |
Ans. To create effective tissue notes, start by reviewing your class notes or study material thoroughly. Identify the most important points and organize them in a logical manner. Use bullet points or headings to make the notes more readable. Additionally, use colors or symbols to highlight key information. Regularly review and update your tissue notes to ensure they are accurate and comprehensive.
Related Searches



















