Important Formula & Tips: Averages | General Aptitude for GATE - Mechanical Engineering PDF Download
What are Averages?
Averages can be defined as the central value in a set of data.
- Average can be calculated simply by dividing the sum of all values in a set by the total number of values.
- In other words, an average value represents the middle value of a data set. The data set can be of anything like age, money, runs, etc.

Example:
What is the average of the first five consecutive odd numbers?
Solution:
The first five consecutive odd numbers are: 1, 3, 5, 7, 9.
Here, the number of data or observations is 5 and the sum of these 5 numbers is 25.
So, average = 25 / 5 = 5.
Basic Formulae to Remember
- Simple Average =
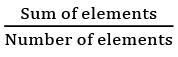
- Weighted Average =
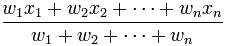
- Arithmetic Mean = (a1 + a2 + a3 ….an) / n
- Geometric Mean =

- Harmonic Mean =
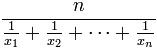
- For two numbers a and b:
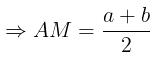
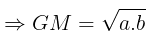
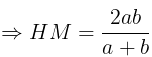
Median and Mode
- The median of a finite list of numbers can be found by arranging all the observations from lowest value to highest value and picking the middle one.
- The mode is the value that occurs most often: Mode = 3*Median - 2*Mean
Note:
Sum of 1st n consecutive natural numbers = [n(n+1)]/2
Average of 1st n consecutive natural numbers = (n+1)/2
Important Points
- When a person replaces another person then:
- If the average is increased, then
Age of new person= Age of person who left + (Increase in average * total number of persons) - If the average is decreased, then
Age of new person= Age of person who left - (Decrease in average * total number of persons)
- If the average is increased, then
- When a person joins the group:
- In case of an increase in average,
Age of new member= Previous average+ (Increase in average * Number of members including new member) - In case of a decrease in average,
Age of new member= Previous average- (Decrease in average * Number of members including new member)
- In case of an increase in average,
- In the Arithmetic Progression there are two cases:
- When the number of terms is odd - the average will be the middle term.
- When a number of terms are even - the average will be the average of two middle terms.
Averages: Important Formula
| Average of first n natural numbers | (n+1) / 2 |
| Average of squares of first n natural numbers | (n+1) (2n+1) / 6 |
| Average of cubes of first n natural numbers | n (n+1)2 / 4 |
| Average of first n even numbers | n + 1 |
| Average of squares of first n even numbers | 2 (n+1) (2n+1) / 3 |
| Average of cube of first n even numbers | 2n (n+1)2 |
| Average of first n odd numbers | n |
| Average of squares of first n odd numbers | (2n+1) (2n-1) / 3 |
| Average of cube of first n odd numbers | n(2n2 – 1) |
Shortcut Techniques
Questions based on averages can be easily solved using shortcuts. By using shortcuts, any question can be solved quickly and efficiently which can save a lot of time.
1. To find the average or change in average
Example 1:
The average of a batsman in 16 innings is 36. In the next innings, he is scoring 70 runs. What will be his new average?
- a) 44
- b) 38
- c) 40
- d) 48
Solution:
Conventionally solving:
New average = (old sum+ new score)/(total number of innings) = ((16 ×36)+70)/((16+1)) = 38
Shortcut technique:
- Step 1) Take the difference between the new score and the old average = 70 – 36= 34
- Step 2) This is 34 extra runs which are spread over 17 innings. So, the innings average will increase by 34/17 = 2
- Step 3) Hence, the average increases by => 36+2 = 38.Here are a few more average questions and their solutions using the same technique.
Example 2:
The average mark of 19 children in a particular school is 50. When a new student with marks 75 joins the class, what will be the new average of the class?
Solution:
Step 1) Take the difference between the old average and the new marks = 75-50=25
Step 2) This score of 25 is distributed over 20 students => 25/20 = 1.25
Step 3) Hence, the average increases by 1.25=> 50+1.25 = 51.25.
2. Another example where the average dips:
Example 3:
The average age of Mr. Mark’s 3 children is 8 years. A new baby is born. Find the average age of all his children?
Solution:
The new age will be 0 years. The difference between the old average and the new age = 0-8= -8
This age of 8 years is spread over 4 children => (-8/4= -2) Hence, the average reduces to 8-2= 6 years.
3. To find new value when the average is given:
Example 1:
The average age of 29 students is 18. If the age of the teacher is also included the average age of the class becomes 18.2. Find the age of the teacher?
- a) 28
- b) 32
- c) 22
- d) 24
Solution:
Conventionally solving:
Let the average age of the teacher = x(29 × 18 + x × 1)/30Solving for x, we get x = 24.
Shortcut Technique:
Using the shortcut, based on the same method used previously:
Step 1: Calculate the change in average = 18.2 – 18 = 0.2.This change in 0.2 is reflected over a sample size of 30.
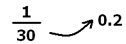
The new age is increased by 30 × 0.2 = 6 years above the average i.e. 18 + 6 = 24; which is the age of the teacher.
Method of Deviation to Find the Average
The concept of an assumed mean is not new. It is widely used to reduce the calculation in finding the average in statistics where the data is huge.
Here, We will demonstrate the application of the assumed mean to solve some aptitude questions based on averages and weighted averages.
Let us take an example to understand the concept
Example: In a class of 30 students, the average age is 12 years. If the age of the class teacher is included, the new average age of the class becomes 13 years. Find the age of the class teacher.
Solution:
Standard Approach
Applying the standard approach, the total age of the 30 students = 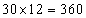 years. When the class teacher is included, the new total age of the class =
years. When the class teacher is included, the new total age of the class =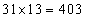 years. Note that the increase in the total age is because of the class teacher only. Hence the age of the class teacher = 403 – 360 = 43 years
years. Note that the increase in the total age is because of the class teacher only. Hence the age of the class teacher = 403 – 360 = 43 years
Deviation method
To understand the deviation method, let us simulate the problem. In the case of average age, assume that each student has 12 chocolates with them.
- The class teacher came up with a few number chocolates and redistribution of the chocolates in the class is done such that every person including the class teacher has the same number of chocolates; which results in 13 chocolates per person (the new average).
- Now, it is obvious that if the class teacher comes with only 12 chocolates, the average remains the same i.e. 12 only (Because he is carrying the number of chocolates which is equal to the average number of chocolates of the group).
- But here with the inclusion of class teachers, the average increases by 1. That means he came with the number of chocolates such that he gave 1 chocolate to each student so that every 30 students now has 13 chocolates.
- Also, in the end, he is left with 13 chocolates for himself so that including him, each member of the class is now carrying 13 chocolates.
Therefore, he came with 30 + 13 = 43 chocolates. Or the age of the class teacher is 43 years.
Important Facts About Averages
- If each number is increased/decreased by a certain quantity n, then the mean also increases or decreases by the same quantity.
- If each number is multiplied/ divided by a certain quantity n, then the mean also gets multiplied or divided by the same quantity.
- If the same value is added to half of the quantities and the same value is subtracted from the other half quantities then there will not be any change in the final value of the average.
Weighted Mean/Average
The weighted arithmetic mean, usually denoted by
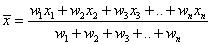 ,
,
where x1, x2, x3, …, xn are averages and w1, w2, w3, .., wn are their respective weight-ages
Example: In a class of 25 boys and 15 girls, the average heights of the two groups of boys and girls are 150 cm and 140 cm respectively. Find the average height of the class.
Solution:
Standard approach:
Total weight of the group of boys = 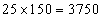 and for the group of girls, the total weight =
and for the group of girls, the total weight =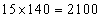 Therefore, the average height of the class =
Therefore, the average height of the class =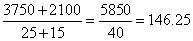
Deviation Approach:
Assume that each boy and each girl is carrying 150 and 140 chocolates respectively.
- We have to distribute the total chocolates such that each boy and girl must carry an equal number of chocolates.
- Since each boy carries 10 chocolates more than each girl, let us take away 10 chocolates from each boy so that now each boy and girl carries 140 chocolates. The excess chocolates we have is equal to
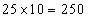 .
. - These excess chocolates are to be equally distributed among the boys and the girls. so, everyone will be getting
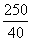 =6.25 more chocolates. Hence the average of the class = 140+6.25 = 146.25 cm.
=6.25 more chocolates. Hence the average of the class = 140+6.25 = 146.25 cm.
Tips and Tricks to Solve Questions Based on Averages
- Tip 1:
Average = Sum of the observations / Number of observations - Tip 2:
The average of any consecutive series is the middle term (median).
⇒ For example 8, 10, 12 in this series middle term is 10 which is also the average of the series.
Required percentage = [(12 – 8)/8] × 100 = 50%
Solved Examples
Q1: The average goal scored by 15 selected players in EPL is 16. The maximum number of goals scored by a player is 20 and the minimum is 12. The goals scored by players are between 12 and 20. What can be the maximum number of players who scored at least 18 goals?
a) 10
b) 5
c) 9
d) 6
e) None of these
Solution: Option (c)
To maximize the number of players who scored 18 and above number of goals, one should assume that only one person has scored 20. To counter him, there will be one person who will score 12 goals.
i.e. 15 – 2 = 13 players left.
Now to maximize the 18 and above goals for every two players who are scoring 18, there will be one player scoring 12. This is done, to arrive at an average of 16. We will have 8 players with a score of 18 and 4 players with a score of 12. The last player will have a score of 16 Thus, the maximum number of people with 18 and more goals = 9.
Q2: The average weight of a group of 8 girls is 50 kg. If 2 girls R and S replace P and Q, the new average weight becomes 48 kg. The weight of P= Weight of Q and the weight of R = Weight of another girl T is included in the group and the new average weight becomes 48 kg. Weight of T= Weight of R. Find the weight of P?
a) 48 kgs
b) 52 kgs
c) 46 kgs
d) 56 kgs
Solution: Option (d)
8 x 50 +R+S-P-Q= 48×8 R+S-P-Q=-16
P+Q-R-S= 16 R=S and P=Q
P-R=8
One more person is included and the weight = 48 kg
Let the weight be a = (48 × 8 + a)9/9 = 48
A = 48 kg= weight of R
=> Weight of P= 48+8= 56 kg.
Q3: The average number of goals scored by 15 selected players in EPL is 16. The maximum number of goals scored by a player is 20 and the minimum is 12. The goals scored by players is between 12 and 20. What can be the maximum number of players who scored at least 18 goals?
a) 10
b) 5
c) 9
d) 6
Solution: Option (c)
To maximize the number of players who scored 18 goals or more, one should assume that only one person has scored 20. To counter him, there will be one person who will score 12 goals.
i.e. 15 – 2 = 13 players left.
Now to maximize the 18 and above goals for every two players who are scoring 18, there will be one player scoring 12. This is done, to arrive at an average of 16. We will have 8 players with a score of 18 and 4 players with a score of 12. The last player will have a score of 16 Thus, the maximum number of people with 18 and more goals = 9.
|
193 videos|169 docs|152 tests
|
FAQs on Important Formula & Tips: Averages - General Aptitude for GATE - Mechanical Engineering
| 1. What are averages? |  |
| 2. What is the formula to find the average? |  |
| 3. What is the difference between median and mode? |  |
| 4. How can deviation be used to find the average? |  |
| 5. What is the concept of weighted mean/average? |  |

















