Revision Notes: Gaseous State | Physical Chemistry PDF Download
Points to be Remembered
1. Gaseous Laws:
A. Boyle's Law : At constant temperature for a definite mass of a gas the volume is inversely proportional to the pressure of the gas.
Mathematically, V ∝ 1/P at constant T and M
B. Graphical Representation of Boyle's Law :
- P vs. V :
The mathematical form of Boyle's law is : V ∝ 1/P or, V = K/P or, PV = K (constant)
Hence, a plot of P vs. V will be a rectangular hyperbolic in nature.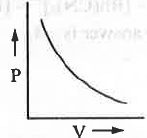
- V vs. 1/P or, P vs. 1/V :
The mathematical form of Boyle's law is : V ∝ 1/P or, V = K/P .......... (1)
Also, V ∝ 1/P or, P ∝ 1/V or, P = K/V .......... (2)
Hence, a plot of V vs. 1/P or, P vs. 1/V will be a straight line passing through the origin with slope K in each cases.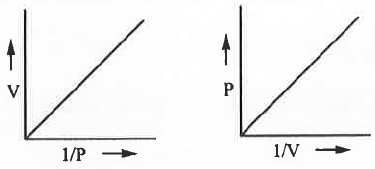
- logP vs. logV :
The mathematical form of Boyle's law is : V ∝ 1/P or, P ∝ 1/V or, P = K/V
Taking log on both sides, logP = logK - logV
Hence, a plot of logP vs. logV will be a straight line with slope = -1 and intercept = logK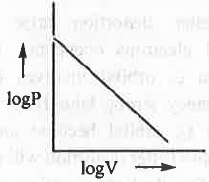
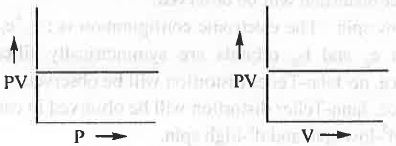
- PV vs. P or, PV vs. V : The mathematical form of Boyle's law is : V ∝ 1/P or, P ∝ 1/V or, P = K/V or, PV = K Hence, a plot of PV vs. P will be a straight line parallel to P-axis with intercept K. Similarly, a plot of PV vs. V will also be a straight line parallel to V-axis with intercept K.
B. Charles' Law : At constant pressure due to increase or, decrease of temperature by 1°C, the volume of a definite mass of a gas will be 1/273 times more or, less than the volume of the gas at 0°C.
Mathematically, Vt = V0(1+t/273)
C. Dalton's Law of Partial Pressure : If two or, more non-interacting gases are enclosed into a vessel of definite volume, the total pressure of the gas mixture will be the sum of the partial pressure of the individual gases.
Mathematically, P = p1 + p2 + p3 + .......
where, P, p1, p2, P3,.... are the total pressure of the gas mixture and partial pressures of gases 1, 2, 3, ......respectively.
D. Graham's Law of Diffusion : At constant temperature and pressure, the rate of diffusion of a gases is inversely proportional to the square root of their densities.
Mathematically, rd ∝ 1/√d at constant T and P
where, rd and d are rate of diffusion and density of the gas respectively.
2. Kinetic Theory of Gases :
It is based on some assumptions. These are given below :
- All the molecules of a gas are of same size, shape and masses and these are considered as hard perfectly elastic spheres.
- When considered volume occupied by gas molecules, these are assumed to be point masses i.e. gas molecules practically does not occupy any volume.
- No attractive or, repulsive force is present between the gas molecules.
- The collisions among the gas molecules and the collisions between the gas molecules and wall of the container are perfectly elastic.
The kinetic gas equation is : P = (1/3)mnC2r.m.s/V = (1/3)pC2r.m.s.
where, m, n, V, Cr.m.s. are mass, no. of molecules, volume of vessel and root mean square velocity of the gas molecule.
3. Different Types of Velocities of Gas Molecules :
- Average Velocity : It is expressed by the equation : Cav = √[8RT/πM]
- Root Mean Square Velocity : It is expressed by the equation : Cπns = √[3RT/M]
- Most Probable Velocity : It is expressed by the equation : Cmp = √[2RT/M]
The RMS speed of He(g) at 0°C is 1300 ms-1. The most probable speed of He will be The expression of root mean square speed is :
Cπns = √[3RT/M] ..... (1)
and the expression of most probable speed is :
Cmp = √(2RT/M) ..... (2)
This equation can be rearranged as :
Cmp = √(2RT/M) = √(3RT/M) X V(2/3) = 1300 X 0.816 = 1061.4 ms-1.
4. Effect of Temperature on the Speed Distribution :
Maxwell's speed distribution law for 3-D is : (1/n).dne/dc = 47t(m/2πkT)3/2 .c2.e-(mc2/2kT) In the equation, two T terms are present - 1/T3/2 and e-(me2/2kT)
- Lower Speed Region : At the lower speed region 1/T3/2 term will dominate. Hence, with the increase in temperature, the speed distribution will decrease i.e. the curve at higher temperature will run below the curve at lower temperature.
- Higher Speed Region : At higher speed region, the exponential term will dominate. Hence, with increase in T, the speed distribution will increase i.e. the curve at higher temperature will run above the curve at lower temperature.
5. Effect of Molecular Mass on the Speed Distribution :
Maxwell's speed distribution law for 3-D is : (1/n).dne/dc = 4π(m/2πkT)3/2 .c2.e-(mc2/kT).
In the equation, two m terms are present - (m/2πkT)3/2 and e-(mc2πkT).
- Lower Speed Region : At the lower speed region m3/2 term will dominate. Hence, with the increase in mass, the speed distribution will decrease i.e. the curve for higher mass will run above the curve for lower mass.
- Higher Speed Region : At higher speed region, the exponential term will dominate. Hence, with increase in m, the speed distribution will decrease i.e. the curve for higher mass will run below the curve for lower mass.
6. Frequency of Binary Collision :
The frequency of binary collision is expressed by : ZAA = (1/√2).7t.σ2.cav.n2
where, σ = diameter, cav = average velocity and n = no. of molecules/c.c. = P/kT.
7. Mean Free Path :
The mean free path is defined as the ratio of the average speed of a molecule to the no. of collision suffered by a molecule per sec.
Mathematically, λ = 1/[√2.π.σ2.n]
8. van der Waals' Equation :
- Volume Correction : Let V be the volume of the contained. Also, n be the no, of moles of the gas present in the volume V. If b the volume occupied by one mole of gas, for n mole the volume occupation will be nb. Hence, the free volume available for the movement of the gas molecule : (V-nb).
- Pressure Correction: The attractive force (f) is proportional to the square pf the density i.e. f ∝ d2 Also, density is proportional to the no. of molecules present per unit volume i.e. d = (n/V) Hence, f ∝ (n/V)2 or, Pa ⇌ an2/v2
Hence, the van der Waals' equation is : (P + an2/V2).(V = nb) = nRT.
9. Units of a and b:
- Unit of a : van der Waals' equation is : (P + an2/V2).(V - nb) = nRT.
As an2/V2 quantity is added to P, an2/V2 should have same unit 10 that of P.
Hence, unit of P -5 Unit of (an2/V2) or. Unit of a = Unit of(PV2/n2) - atm.lit2,mol-2
Hence, the unit of a is atm.lit2.mol-2 - Unit of b : van der Waals' equation is : (P + an2/V2).(V - nb) = nRT.
As nb quantity is subtracted from V, nb should have similar unit to that of V.
Hence, unit of V = Unit of nb or, Unit of b = Unit of (V/n) = Lit.mol-1.
Hence, the unit of b is Lit.mol-1.
10. Critical Constants :
The values of critical constants are given below :
Vc =3b, Pc = a/27b2 and Tc = 8a/27Rb
|
84 videos|142 docs|67 tests
|
FAQs on Revision Notes: Gaseous State - Physical Chemistry
| 1. What are the properties of gaseous state? |  |
| 2. How does temperature affect the behavior of gases? |  |
| 3. What is Boyle's law and how is it related to the gaseous state? |  |
| 4. What is the ideal gas law and how is it used in the gaseous state? |  |
| 5. What is the concept of partial pressure in the gaseous state? |  |
















